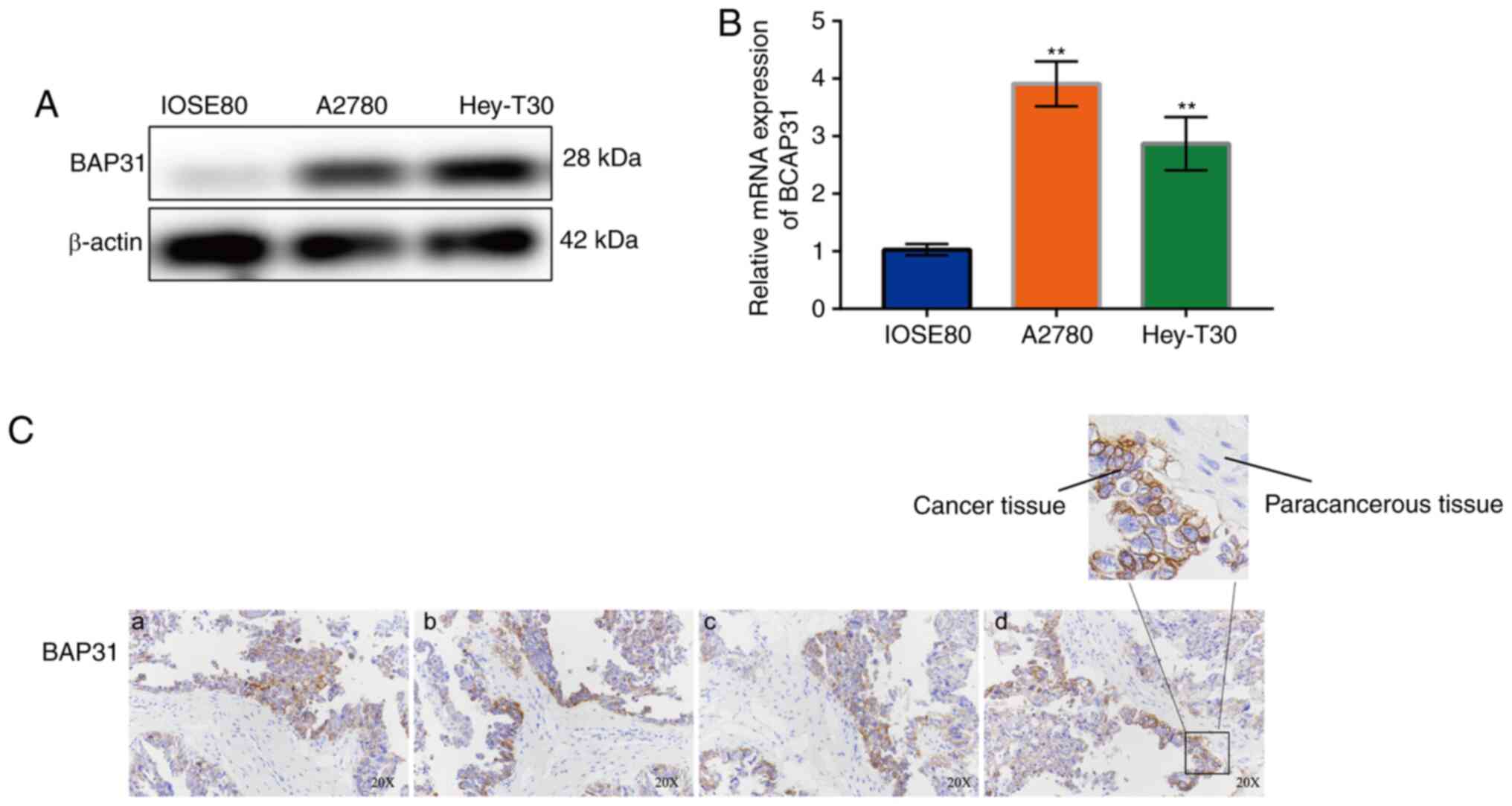
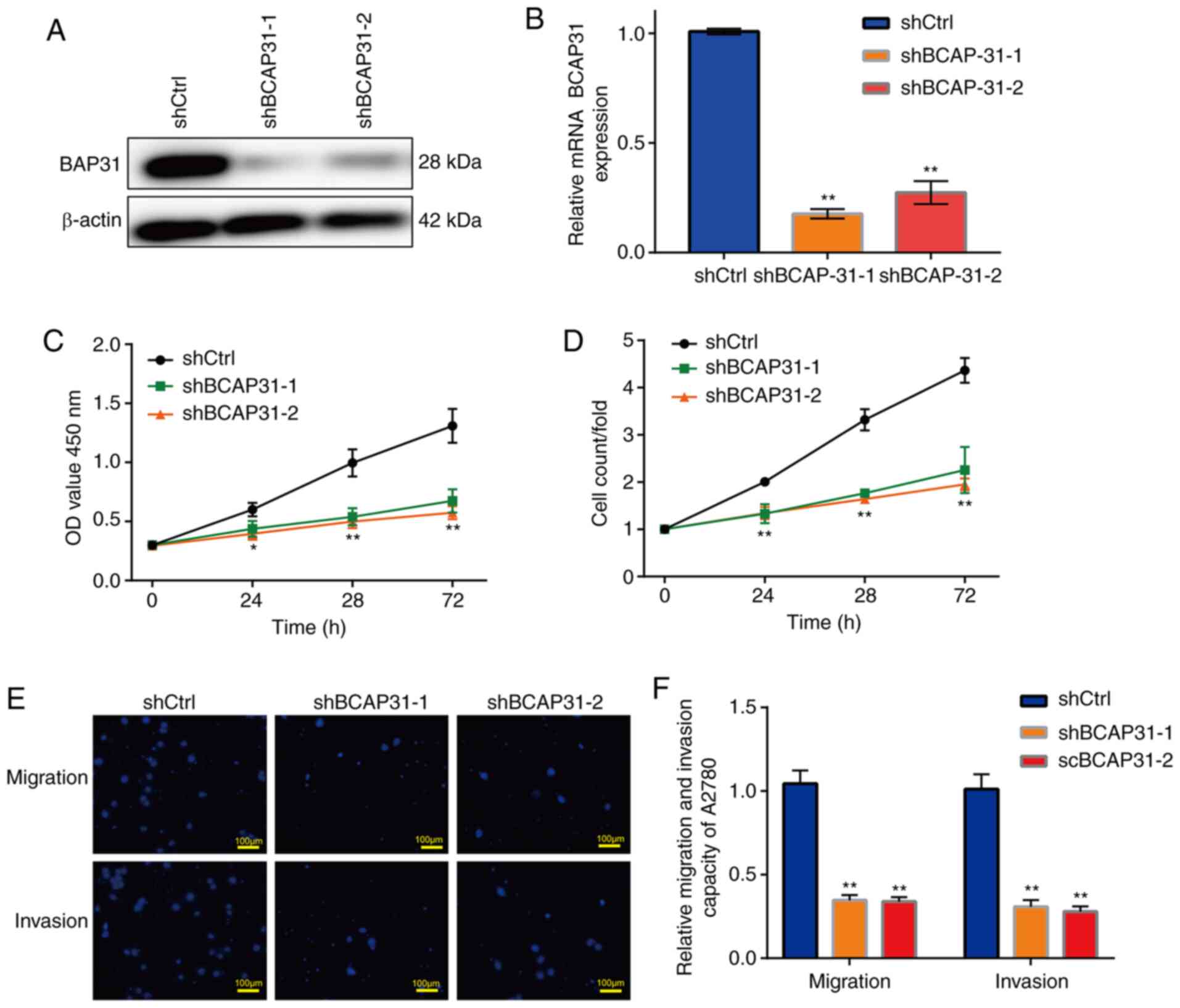
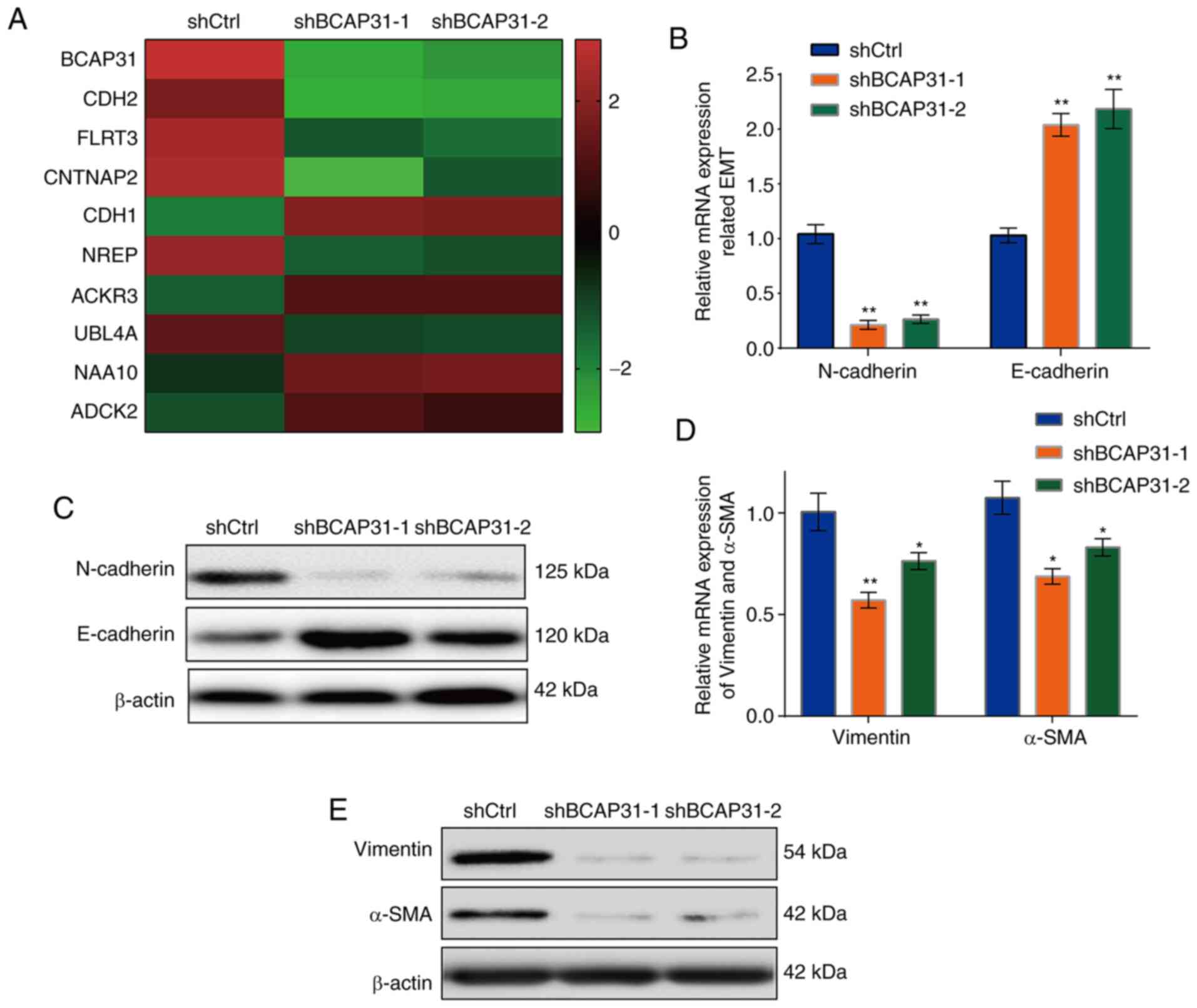
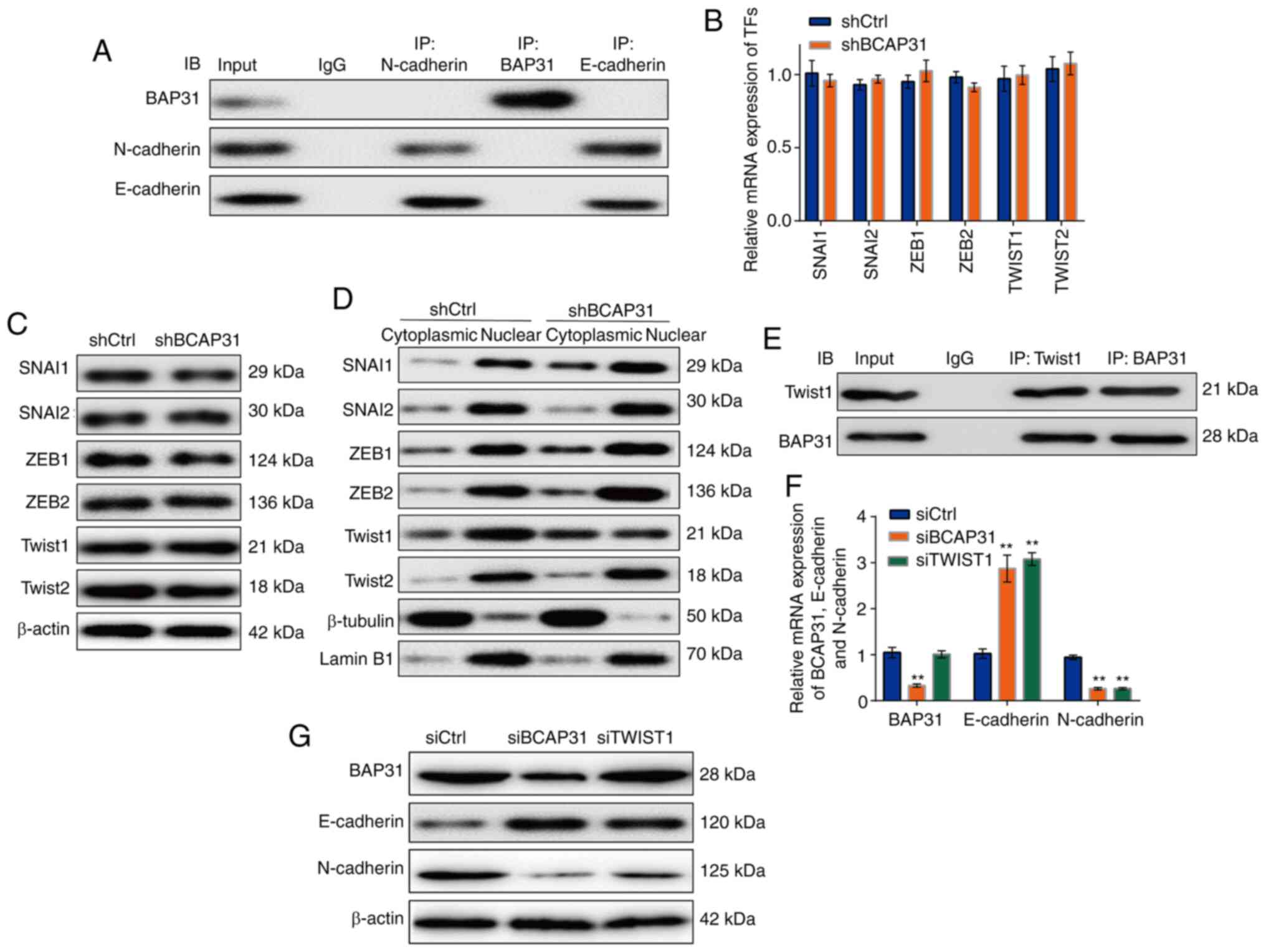
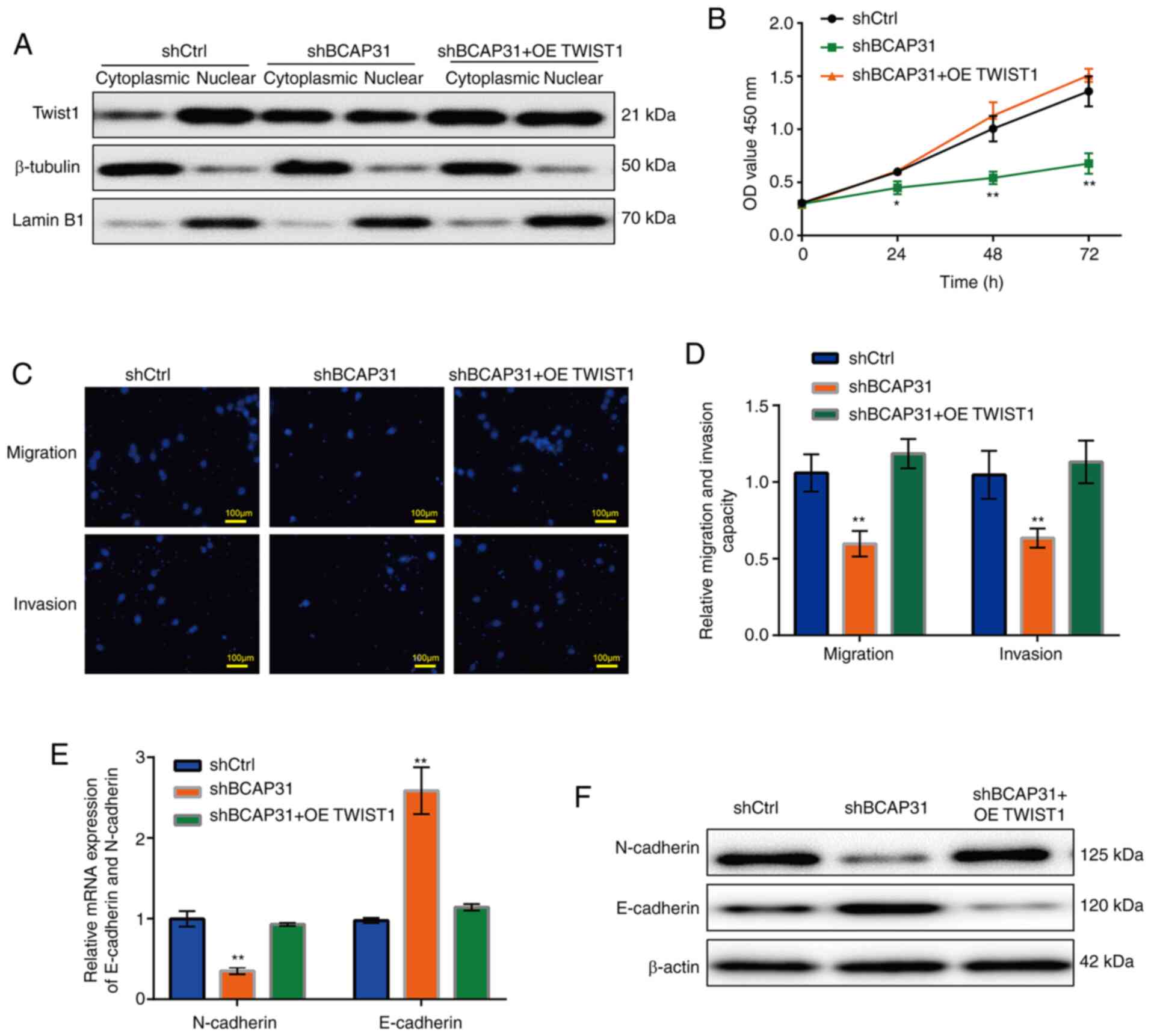
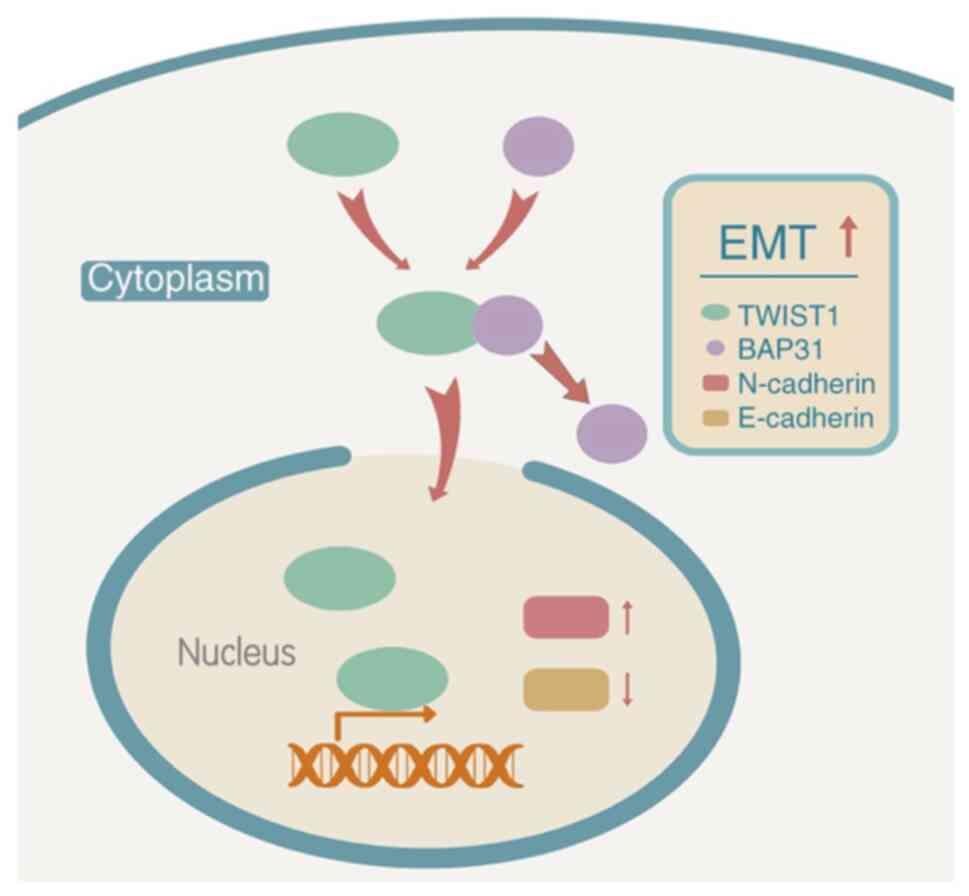
|
1
|
Siegel RL, Miller KD and Jemal A: Cancer
statistics, 2020. CA Cancer J Clin. 70:7–30. 2020.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
2
|
Su Z, Graybill WS and Zhu Y: Detection and
monitoring of ovarian cancer. Clin Chim Acta. 415:341–345.
2013.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
3
|
Torre LA, Trabert B, DeSantis CE, Miller
KD, Samimi G, Runowicz CD, Gaudet MM, Jemal A and Siegel RL:
Ovarian cancer statistics, 2018. CA Cancer J Clin. 68:284–296.
2018.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
4
|
Narod S: Can advanced-stage ovarian cancer
be cured. Nat Rev Clin Oncol. 13:255–261. 2016.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
5
|
Lim D and Oliva E: Precursors and
pathogenesis of ovarian carcinoma. Pathology. 45:229–242.
2013.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
6
|
Vang R, Shih IeM and Kurman RJ: Ovarian
low-grade and high-grade serous carcinoma: Pathogenesis,
clinicopathologic and molecular biologic features, and diagnostic
problems. Adv Anat Pathol. 16:267–282. 2009.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
7
|
Nelson BH: The impact of T-cell immunity
on ovarian cancer outcomes. Immunol Rev. 222:101–116.
2008.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
8
|
Kim KM, Adachi T, Nielsen PJ, Terashima M,
Lamers MC, Köhler G and Reth M: Two new proteins preferentially
associated with membrane immunoglobulin D. EMBO J. 13:3793–3800.
1994.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
9
|
Adachi T, Schamel WW, Kim KM, Watanabe T,
Becker B, Nielsen PJ and Reth M: The specificity of association of
the IgD molecule with the accessory proteins BAP31/BAP29 lies in
the IgD transmembrane sequence. EMBO J. 15:1534–1541.
1996.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
10
|
Namba T, Tian F, Chu K, Hwang SY, Yoon KW,
Byun S, Hiraki M, Mandinova A and Lee SW: CDIP1-BAP31 complex
transduces apoptotic signals from endoplasmic reticulum to
mitochondria under endoplasmic reticulum stress. Cell Rep.
5:331–339. 2013.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
11
|
Breckenridge DG, Stojanovic M, Marcellus
RC and Shore GC: Caspase cleavage product of BAP31 induces
mitochondrial fission through endoplasmic reticulum calcium
signals, enhancing cytochrome c release to the cytosol. J
Cell Biol. 160:1115–1127. 2003.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
12
|
Wakana Y, Takai S, Nakajima K, Tani K,
Yamamoto A, Watson P, Stephens DJ, Hauri HP and Tagaya M: Bap31 is
an itinerant protein that moves between the peripheral endoplasmic
reticulum (ER) and a juxtanuclear compartment related to
ER-associated Degradation. Mol Biol Cell. 19:1825–1836.
2008.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
13
|
Matroule JY, Carthy CM, Granville DJ,
Jolois O, Hunt DW and Piette J: Mechanism of colon cancer cell
apoptosis mediated by pyropheophorbide-a methylester
photosensitization. Oncogene. 20:4070–4084. 2001.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
14
|
Yu S, Wang F, Fan L, Wei Y, Li H, Sun Y,
Yang A, Jin B, Song C and Yang K: BAP31, a promising target for the
immunotherapy of malignant melanomas. J Exp Clin Cancer Res.
34(36)2015.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
15
|
Tan N, Liu Q, Liu X, Gong Z, Zeng Y, Pan
G, Xu Q and He S: Low expression of B-cell-associated protein 31 in
human primary hepatocellular carcinoma correlates with poor
prognosis. Histopathology. 68:221–229. 2016.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
16
|
Wang A, Zhang Y and Cao P: Inhibition of
BAP31 expression inhibits cervical cancer progression by
suppressing metastasis and inducing intrinsic and extrinsic
apoptosis. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 508:499–506. 2019.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
17
|
Ma C, Jin RM, Chen KJ, Hao T, Li BS, Zhao
DH and Jiang H: Low expression of B-Cell-Associated protein 31 is
associated with unfavorable prognosis in human colorectal cancer.
Pathol Res Pract. 214:661–666. 2018.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
18
|
Dang E, Yang S, Song C, Jiang D, Li Z, Fan
W, Sun Y, Tao L, Wang J, Liu T, et al: BAP31, a newly defined
cancer/testis antigen, regulates proliferation, migration, and
invasion to promote cervical cancer progression. Cell Death Dis.
9(791)2018.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
19
|
Nieto MA, Huang RY, Jackson RA and Thiery
JP: EMT: 2016. Cell. 166:21–45. 2016.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
20
|
Thiery JP, Acloque H, Huang RY and Nieto
MA: Epithelial-mesenchymal transitions in development and disease.
Cell. 139:871–890. 2009.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
21
|
Loh CY, Chai JY, Tang TF, Wong WF, Sethi
G, Shanmugam MK, Chong PP and Looi CY: The E-cadherin and
N-cadherin switch in epithelial-to-mesenchymal transition:
Signaling, therapeutic implications, and challenges. Cells.
8(1118)2019.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
22
|
Ling ZQ, Li P, Ge MH, Zhao X, Hu FJ, Fang
XH, Dong ZM and Mao WM: Hypermethylation-modulated down-regulation
of CDH1 expression contributes to the progression of esophageal
cancer. Int J Mol Med. 27:625–635. 2011.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
23
|
Umbas R, Schalken JA, Aalders TW, Carter
BS, Karthaus HF, Schaafsma HE, Debruyne FM and Isaacs WB:
Expression of the cellular adhesion molecule E-cadherin is reduced
or absent in high-grade prostate cancer. Cancer Res. 52:5104–5109.
1992.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
24
|
Petrova YI, Schecterson L and Gumbiner BM:
Roles for E-cadherin cell surface regulation in cancer. Mol Biol
Cell. 27:3233–3244. 2016.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
25
|
Fransvea E, Angelotti U, Antonaci S and
Giannelli G: Blocking transforming growth factor-beta up-regulates
E-cadherin and reduces migration and invasion of hepatocellular
carcinoma cells. Hepatology. 47:1557–1566. 2008.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
26
|
Tang G, Du R, Tang Z and Kuang Y:
MiRNALet-7a mediates prostate cancer PC-3 cell invasion, migration
by inducing epithelial-mesenchymal transition through CCR7/MAPK
pathway. J Cell Biochem. 119:3725–3731. 2018.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
27
|
del Valle I, Rudloff S, Carles A, Li Y,
Liszewska E, Vogt R and Kemler R: E-cadherin is required for the
proper activation of the Lifr/Gp130 signaling pathway in mouse
embryonic stem cells. Development. 140:1684–1692. 2013.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
28
|
Hazan RB, Qiao R, Keren R, Badano I and
Suyama K: Cadherin switch in tumor progression. Ann N Y Acad Sci.
1014:155–163. 2004.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
29
|
Muramaki M, Miyake H, Terakawa T, Kumano
M, Sakai I and Fujisawa M: Expression profile of E-cadherin and
N-cadherin in non-muscle-invasive bladder cancer as a novel
predictor of intravesical recurrence following transurethral
resection. Urol Oncol. 30:161–166. 2012.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
30
|
Shintani Y, Hollingsworth MA, Wheelock MJ
and Johnson KR: Collagen I promotes metastasis in pancreatic cancer
by activating c-Jun NH(2)-terminal kinase 1 and up-regulating
N-cadherin expression. Cancer Res. 66:11745–11753. 2006.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
31
|
Puisieux A, Brabletz T and Caramel J:
Oncogenic roles of EMT-inducing transcription factors. Nat Cell
Biol. 16:488–494. 2014.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
32
|
Hamamori Y, Wu HY, Sartorelli V and Kedes
L: The basic domain of myogenic basic helix-loop-helix (bHLH)
proteins is the novel target for direct inhibition by another bHLH
protein, Twist. Mol Cell Biol. 17:6563–6573. 1997.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
33
|
Lee MS, Lowe GN, Strong DD, Wergedal JE
and Glackin CA: TWIST, a basic helix-loop-helix transcription
factor, can regulate the human osteogenic lineage. J Cell Biochem.
75:566–577. 1999.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
34
|
Verzi MP, Anderson JP, Dodou E, Kelly KK,
Greene SB, North BJ, Cripps RM and Black BL: N-twist, an
evolutionarily conserved bHLH protein expressed in the developing
CNS, functions as a transcriptional inhibitor. Dev Biol.
249:174–190. 2002.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
35
|
Mironchik Y, Winnard PT Jr, Vesuna F, Kato
Y, Wildes F, Pathak AP, Kominsky S, Artemov D, Bhujwalla Z, Van
Diest P, et al: Twist overexpression induces in vivo angiogenesis
and correlates with chromosomal instability in breast cancer.
Cancer Res. 65:10801–10809. 2005.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
36
|
Ansieau S, Bastid J, Doreau A, Morel AP,
Bouchet BP, Thomas C, Fauvet F, Puisieux I, Doglioni C, Piccinin S,
et al: Induction of EMT by twist proteins as a collateral effect of
tumor-promoting inactivation of premature senescence. Cancer Cell.
14:79–89. 2008.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
37
|
Rodriguez Y, Gonzalez-Mendez RR and
Cadilla CL: Evolution of the twist subfamily vertebrate proteins:
Discovery of a signature motif and origin of the twist1
glycine-rich motifs in the amino-terminus disordered domain. PLoS
One. 11(e0161029)2016.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
38
|
Ansieau S, Morel AP, Hinkal G, Bastid J
and Puisieux A: TWISTing an embryonic transcription factor into an
oncoprotein. Oncogene. 29:3173–3184. 2010.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
39
|
Satoh K, Hamada S, Kimura K, Kanno A,
Hirota M, Umino J, Fujibuchi W, Masamune A, Tanaka N, Miura K, et
al: Up-regulation of MSX2 enhances the malignant phenotype and is
associated with twist 1 expression in human pancreatic cancer
cells. Am J Pathol. 172:926–939. 2008.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
40
|
Ru GQ, Wang HJ, Xu WJ and Zhao ZS:
Upregulation of Twist in gastric carcinoma associated with tumor
invasion and poor prognosis. Pathol Oncol Res. 17:341–347.
2011.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
41
|
Ranganathan S, Krishnan A and
Sivasithambaram ND: Significance of twist and iNOS expression in
human breast carcinoma. Mol Cell Biochem. 412:41–47.
2016.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
42
|
Khan MA, Chen HC, Zhang D and Fu J: Twist:
A molecular target in cancer therapeutics. Tumour Biol.
34:2497–2506. 2013.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
43
|
Lu Z and Chen J: Introduction of WHO
classification of tumours of female reproductive organs, fourth
edition. Zhonghua Bing Li Xue Za Zhi. 43:649–650. 2014.PubMed/NCBI(In Chinese).
|
|
44
|
Livak KJ and Schmittgen TD: Analysis of
relative gene expression data using real-time quantitative PCR and
the 2(-Delta Delta C(T)) method. Methods. 25:402–408.
2001.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
45
|
Wang L, Feng Z, Wang X, Wang X and Zhang
X: DEGseq: An R package for identifying differentially expressed
genes from RNA-seq data. Bioinformatics. 26:136–138.
2010.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
46
|
Scanlon CS, Van Tubergen EA, Inglehart RC
and D'Silva NJ: Biomarkers of epithelial-mesenchymal transition in
squamous cell carcinoma. J Dent Res. 92:114–121. 2013.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
47
|
Malgulwar PB, Nambirajan A, Pathak P,
Rajeshwari M, Suri V, Sarkar C, Singh M and Sharma MC:
Epithelial-to-mesenchymal transition-related transcription factors
are up-regulated in ependymomas and correlate with a poor
prognosis. Hum Pathol. 82:149–157. 2018.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
48
|
Namba T: BAP31 regulates mitochondrial
function via interaction with Tom40 within ER-mitochondria contact
sites. Sci Adv. 5(eaaw1386)2019.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
49
|
Machihara K and Namba T: BAP31 inhibits
cell adaptation to ER stress conditions, negatively regulating
autophagy induction by interaction with STX17. Cells.
8(1350)2019.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
50
|
Quistgaard EM: BAP31: Physiological
functions and roles in disease. Biochimie. 186:105–129.
2021.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
51
|
Wilson JD and Barlowe C: Yet1p and Yet3p,
the yeast homologs of BAP29 and BAP31, interact with the
endoplasmic reticulum translocation apparatus and are required for
inositol prototrophy. J Biol Chem. 285:18252–18261. 2010.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
52
|
Fu W, Sun H, Zhao Y, Chen M, Yang X, Liu Y
and Jin W: BCAP31 drives TNBC development by modulating
ligand-independent EGFR trafficking and spontaneous EGFR
phosphorylation. Theranostics. 9:6468–6484. 2019.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
53
|
Xu K, Han B, Bai Y, Ma XY, Ji ZN, Xiong Y,
Miao SK, Zhang YY and Zhou LM: MiR-451a suppressing BAP31 can
inhibit proliferation and increase apoptosis through inducing ER
stress in colorectal cancer. Cell Death Dis. 10(152)2019.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
54
|
Thiery JP: Epithelial-mesenchymal
transitions in tumour progression. Nat Rev Cancer. 2:442–454.
2002.PubMed/NCBI View
Article : Google Scholar
|
|
55
|
Shook D and Keller R: Mechanisms,
mechanics and function of epithelial-mesenchymal transitions in
early development. Mech Dev. 120:1351–1383. 2003.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
56
|
Yun SJ and Kim WJ: Role of the
epithelial-mesenchymal transition in bladder cancer: From prognosis
to therapeutic target. Korean J Urol. 54:645–650. 2013.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
57
|
Franco-Chuaire ML, Magda Carolina SC and
Chuaire-Noack L: Epithelial-mesenchymal transition (EMT):
Principles and clinical impact in cancer therapy. Invest Clin.
54:186–205. 2013.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
58
|
Rosso M, Majem B, Devis L, Lapyckyj L,
Besso MJ, Llauradó M, Abascal MF, Matos ML, Lanau L, Castellví J,
et al: E-cadherin: A determinant molecule associated with ovarian
cancer progression, dissemination and aggressiveness. PLoS One.
12(e0184439)2017.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
59
|
Wang M, Ren D, Guo W, Huang S, Wang Z, Li
Q, Du H, Song L and Peng X: N-cadherin promotes
epithelial-mesenchymal transition and cancer stem cell-like traits
via ErbB signaling in prostate cancer cells. Int J Oncol.
48:595–606. 2016.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
60
|
Hui L, Zhang S, Dong X, Tian D, Cui Z and
Qiu X: Prognostic significance of twist and N-cadherin expression
in NSCLC. PLoS One. 8(e62171)2013.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
61
|
Araki K, Shimura T, Suzuki H, Tsutsumi S,
Wada W, Yajima T, Kobayahi T, Kubo N and Kuwano H: E/N-cadherin
switch mediates cancer progression via TGF-β-induced
epithelial-to-mesenchymal transition in extrahepatic
cholangiocarcinoma. Br J Cancer. 105:1885–1893. 2011.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
62
|
Yang J, Mani SA, Donaher JL, Ramaswamy S,
Itzykson RA, Come C, Savagner P, Gitelman I, Richardson A and
Weinberg RA: Twist, a master regulator of morphogenesis, plays an
essential role in tumor metastasis. Cell. 117:927–939.
2004.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
63
|
Rosivatz E, Becker I, Specht K, Fricke E,
Luber B, Busch R, Höfler H and Becker KF: Differential expression
of the epithelial-mesenchymal transition regulators snail, SIP1,
and twist in gastric cancer. Am J Pathol. 161:1881–1891.
2002.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
64
|
Kwok WK, Ling MT, Lee TW, Lau TC, Zhou C,
Zhang X, Chua CW, Chan KW, Chan FL, Glackin C, et al: Up-regulation
of TWIST in prostate cancer and its implication as a therapeutic
target. Cancer Res. 65:5153–5162. 2005.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|