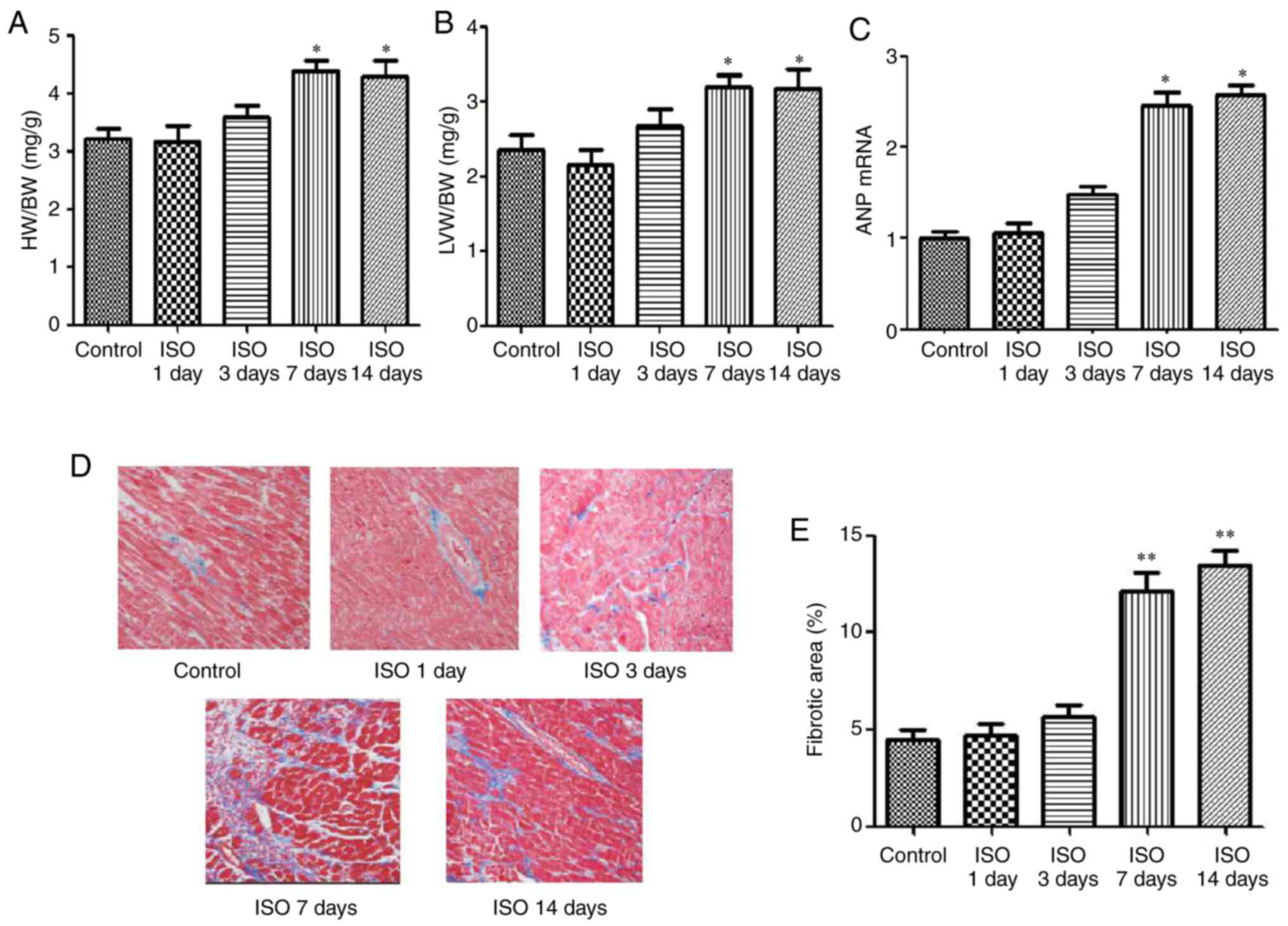
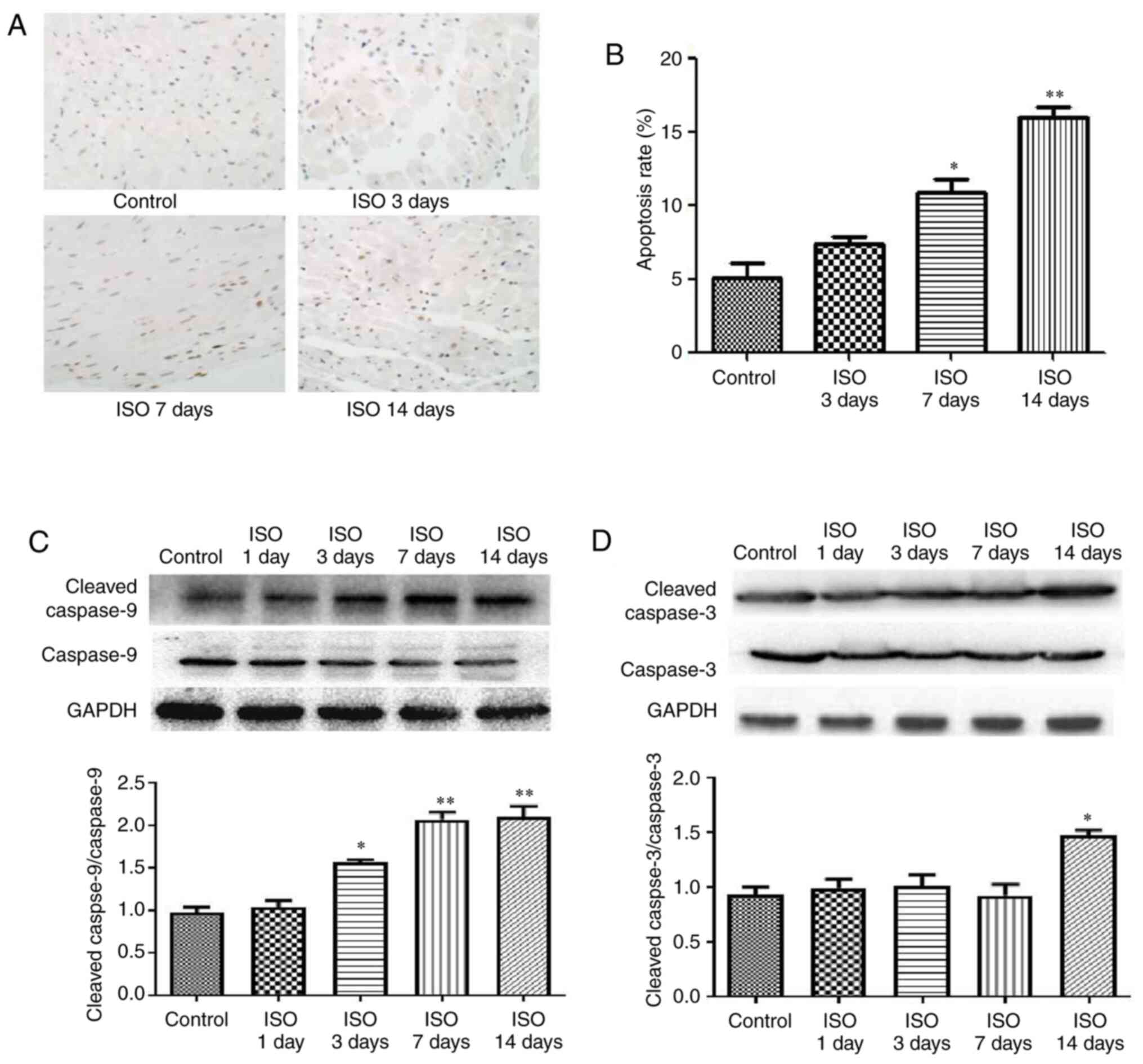
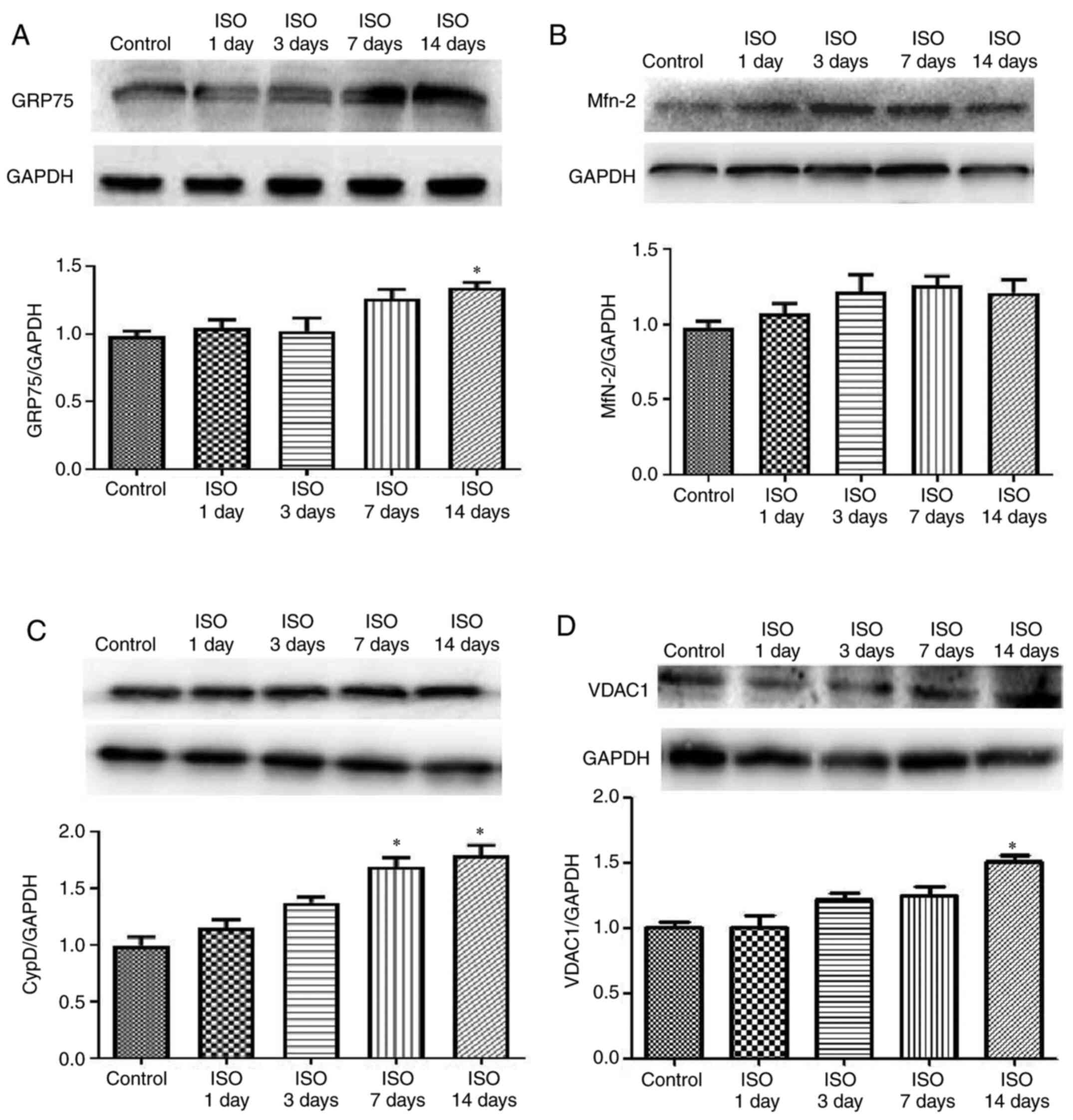
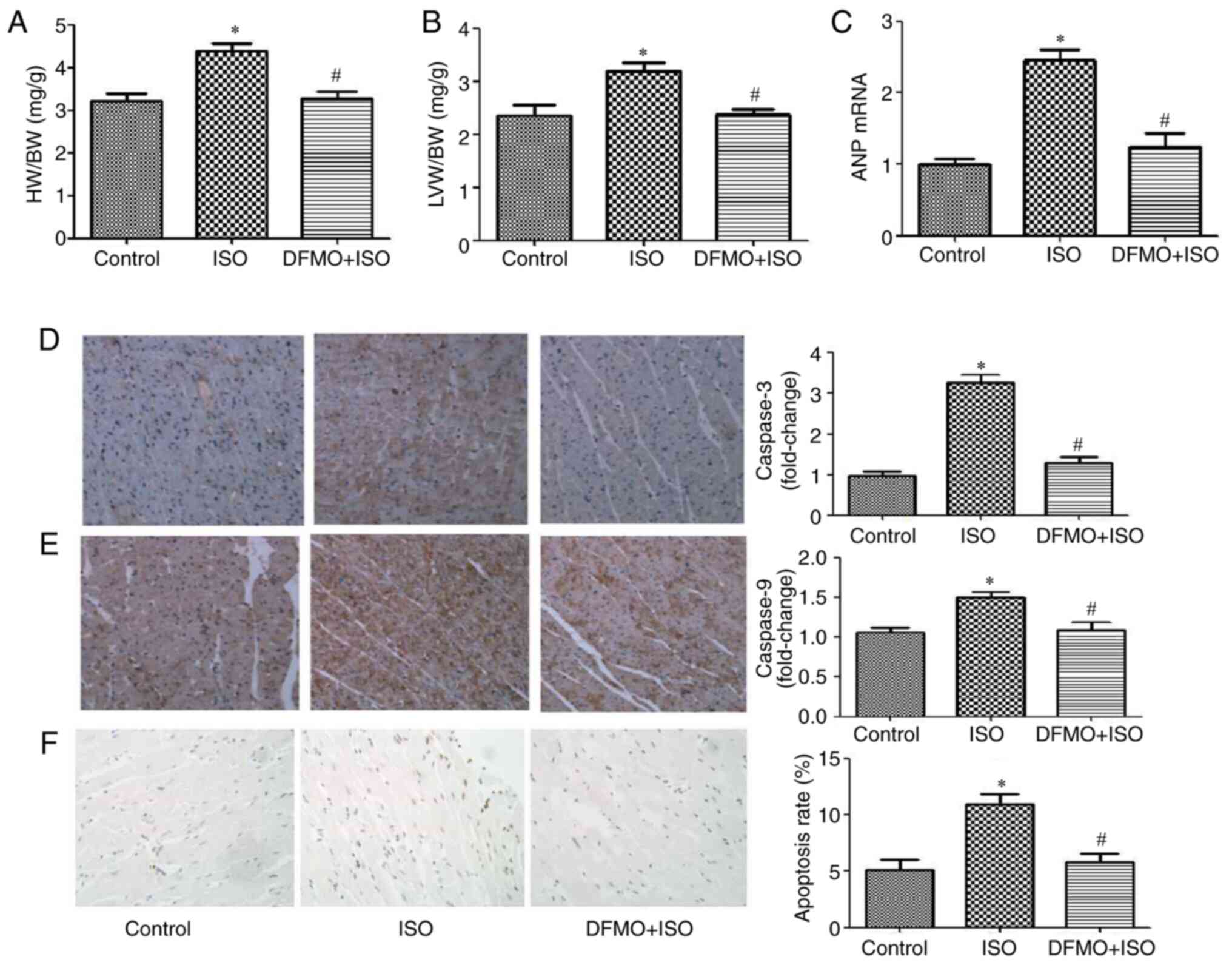
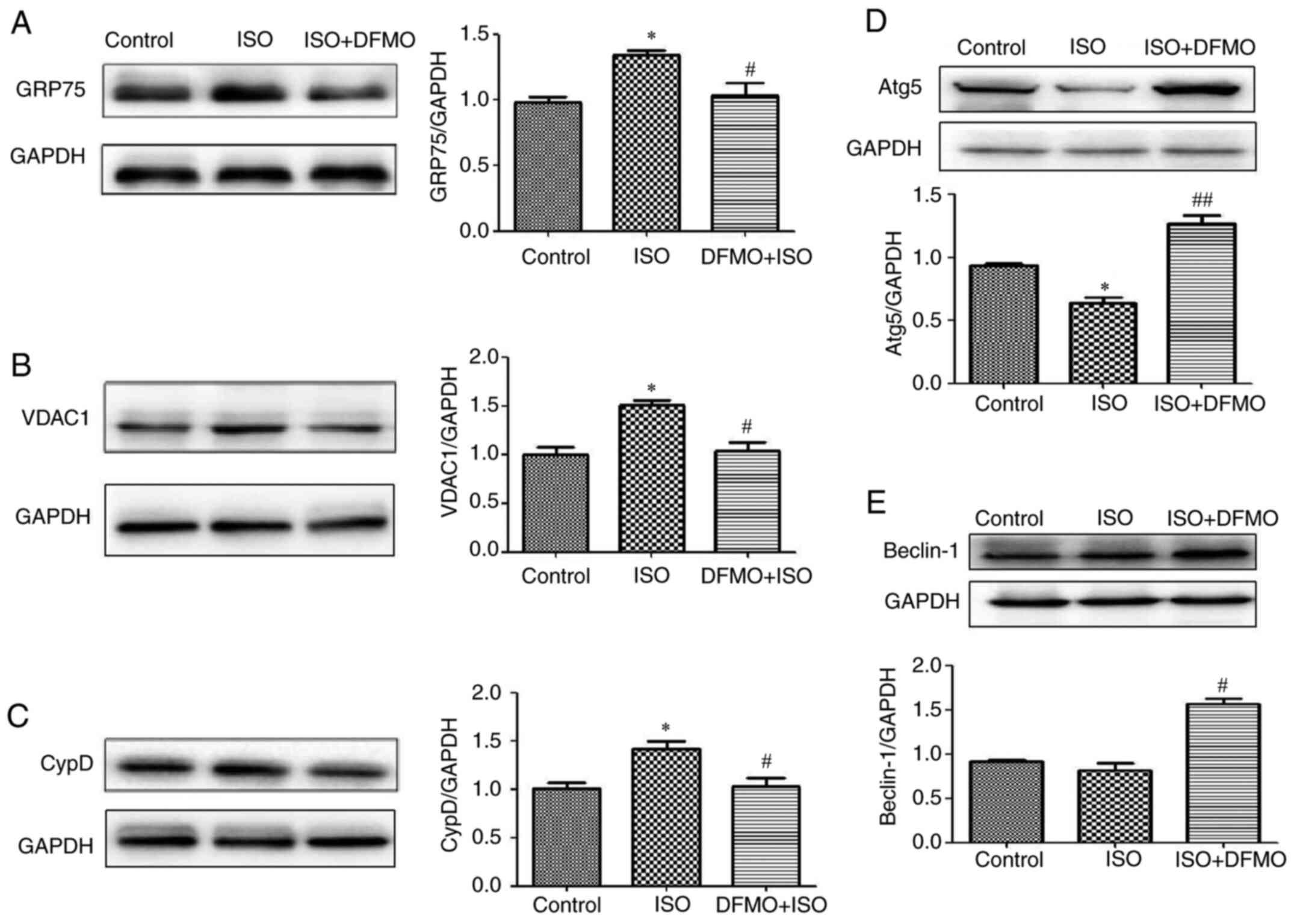
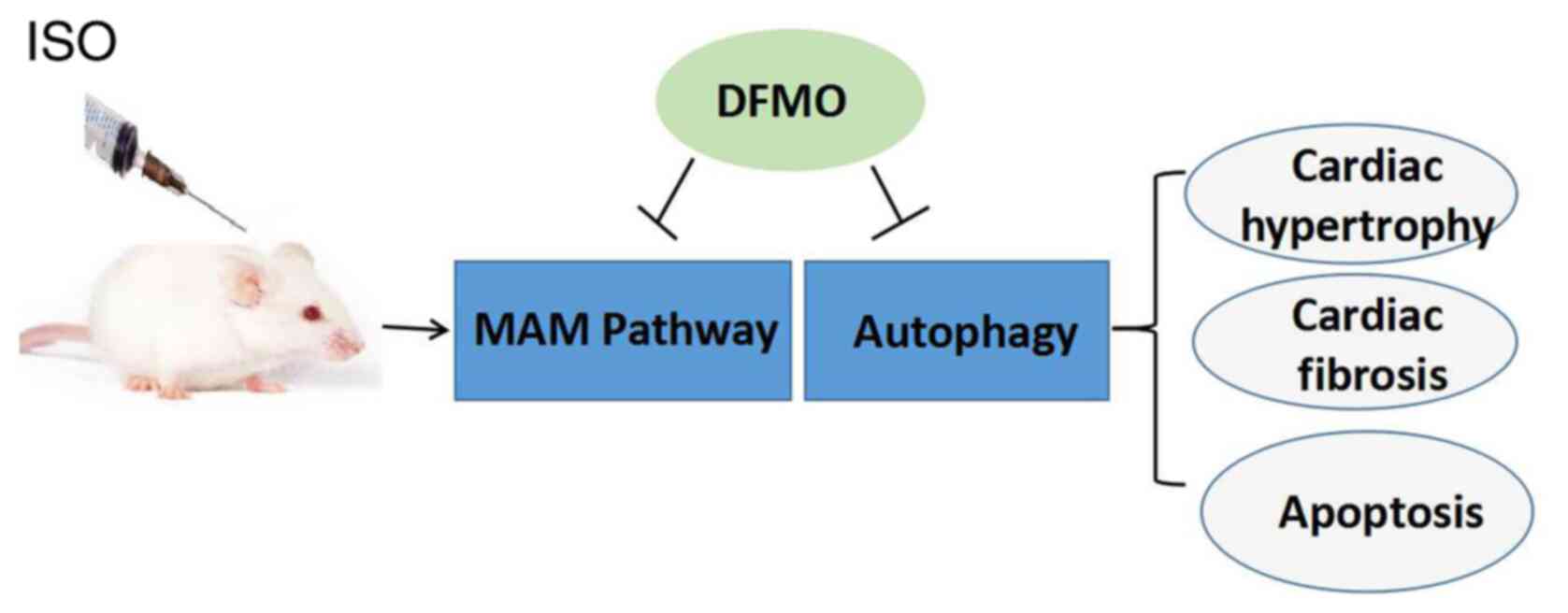
|
1
|
Branco AF, Sampaio SF, Wieckowski MR,
Sardão VA and Oliveira PJ: Mitochondrial disruption occurs
downstream from - adrenergic overactivation by isoproterenol in
differentiated, but not undifferentiated H9c2 cardiomyoblasts:
Differential activation of stress and survival pathways. Int J
Biochem Cell Biol. 45:2379–2391. 2013.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
2
|
Berenji K, Drazner MH, Rothermel BA and
Hill JA: Does load-induced ventricular hypertrophy progress to
systolic heart failure? Am J Physiol Heart Circ Physiol.
289:H8–H16. 2005.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
3
|
Forte M, Schirone L, Ameri P, Basso C,
Catalucci D, Modica J, Chimenti C, Crotti L, Frati G, Rubattu S, et
al: The role of mitochondrial dynamics in cardiovascular diseases.
Br J Pharmacol. 15:1–17. 2020.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
4
|
Wyss RK, Méndez-Carmona N, Sanz MN, Arnold
M, Segiser A, Fiedler GM, Carrel TP, Djafarzadeh S, Tevaearai
Stahel HT and Longnus SL: Mitochondrial integrity during early
reperfusion in an isolated rat heart model of donation after
circulatory death-consequences of ischemic duration. J Heart Lung
Transplant. 38:647–657. 2019.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
5
|
Dudek J, Hartmann M and Rehling P: The
role of mitochondrial cardiolipin in heart function and its
implication in cardiac disease. Biochim Biophys Acta Mol Basis Dis.
1865:810–821. 2019.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
6
|
Raut GK, Manchineela S, Chakrabarti M,
Bhukya CK, Naini R, Venkateshwari A, Reddy VD, Mendonza JJ, Suresh
Y, Nallari P, et al: Imine stilbene analog ameliorate
isoproterenol-induced cardiac hypertrophy and hydrogen
peroxide-induced apoptosis. Free Radic Biol Med. 153:80–88.
2020.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
7
|
Wang S, Binder P, Fang Q, Wang Z, Xiao W,
Liu W and Wang X: Endoplasmic reticulum stress in the heart:
Insights into mechanisms and drug targets. Br J Pharmacol.
175:1293–1304. 2018.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
8
|
Rieusset J: Mitochondria and endoplasmic
reticulum: Mitochondria-endoplasmic reticulum interplay in type 2
diabetes pathophysiology. Int J Biochem Cell Biol. 43:1257–1262.
2011.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
9
|
Monteiro JP, Oliveira PJ and Jurado AS:
Mitochondrial membrane lipid remodeling in pathophysiology: A new
target for diet and therapeutic interventions. Prog Lipid Res.
52:513–528. 2013.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
10
|
Tang LL, Wang JD, Xu TT, Zhao Z, Zheng JJ,
Ge RS and Zhu DY: Mitochondrial toxicity of perfluorooctane
sulfonate in mouse embryonic stem cell-derived cardiomyocytes.
Toxicology. 382:108–116. 2017.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
11
|
Sironi L, Restelli LM, Tolnay M, Neutzner
A and Frank S: Dysregulated interorganellar crosstalk of
mitochondria in the pathogenesis of Parkinson's disease. Cells.
9(233)2020.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
12
|
Murata D, Arai K, Iijima M and Sesaki H:
Mitochondrial division, fusion and degradation. J Biochem.
167:233–241. 2020.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
13
|
Ou Y, Wang SJ, Li D, Chu B and Gu W:
Activation of SAT1 engages polyamine metabolism with p53-mediated
ferroptotic responses. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA. 113:E6806–E6812.
2016.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
14
|
Pegg AE: Functions of polyamines in
mammals. J Biol Chem. 291:14904–14912. 2016.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
15
|
Murray Stewart T, Dunston TT, Woster PM
and Casero RA Jr: Polyamine catabolism and oxidative damage. J Biol
Chem. 293:18736–18745. 2018.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
16
|
Chen M, Xin J, Liu B, Luo L, Li J, Yin W
and Li M: Mitogen-activated protein kinase and intracellular
polyamine signaling is involved in TRPV1 activation-induced cardiac
hypertrophy. J Am Heart Assoc. 5(e003718)2016.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
17
|
Lin Y, Zhang X, Wang L, Zhao Y, Li H, Xiao
W, Xu C and Liu J: Polyamine depletion attenuates
isoproterenol-induced hypertrophy and endoplasmic reticulum stress
in cardiomyocytes. Cell Physiol Biochem. 34:1455–1465.
2014.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
18
|
Casero RA Jr, Murray Stewart T and Pegg
AE: Polyamine metabolism and cancer: Treatments, challenges and
opportunities. Nat Rev Cancer. 18:681–695. 2018.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
19
|
Lin Y, Liu JC, Zhang XJ, Li GW, Wang LN,
Xi YH, Li HZ, Zhao YJ and Xu CQ: Downregulation of the ornithine
decarboxylase/polyamine system inhibits angiotensin-induced
hypertrophy of cardiomyocytes through the NO/cGMP-dependent protein
kinase type-I pathway. Cell Physiol Biochem. 25:443–450.
2010.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
20
|
Pegg AE: Regulation of ornithine
decarboxylase. J Biol Chem. 281:14529–14532. 2006.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
21
|
Lin Y, Zhang X, Xiao W, Li B, Wang J, Jin
L, Lian J, Zhou L and Liu J: Endoplasmic reticulum stress is
involved in DFMO attenuating isoproterenol-induced cardiac
hypertrophy in rats. Cell Physiol Biochem. 38:1553–1562.
2016.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
22
|
Jiang G, Gong H, Niu Y, Yang C, Wang S,
Chen Z, Ye Y, Zhou N, Zhang G, Ge J, et al: Identification of amino
acid residues in angiotensin ii type 1 receptor sensing mechanical
stretch and function in cardiomyocyte hypertrophy. Cell Physiol
Biochem. 37:105–116. 2015.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
23
|
Wang W, Zhang H, Xue G, Zhang L, Zhang W,
Wang L, Lu F, Li H, Bai S, Lin Y, et al: Exercise training
preserves ischemic preconditioning in aged rat hearts by restoring
the myocardial polyamine pool. Oxid Med Cell Longev.
2014(457429)2014.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
24
|
Braunwald E: Heart failure. JACC Heart
Fail. 1:1–20. 2013.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
25
|
Perrone M, Caroccia N, Genovese I,
Missiroli S, Modesti L, Pedriali G, Vezzani B, Vitto VAM, Antenori
M, Lebiedzinska-Arciszewska M, et al: The role of
mitochondria-associated membranes in cellular homeostasis and
diseases. Int Rev Cell Mol Biol. 350:119–196. 2020.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
26
|
Imaeda A, Tanaka S, Tonegawa K, Fuchigami
S, Obana M, Maeda M, Kihara M, Kiyonari H, Conway SJ, Fujio Y, et
al: Myofibroblast β2 adrenergic signaling amplifies cardiac
hypertrophy in mice. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 510:149–155.
2019.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
27
|
de Lucia C, Eguchi A and Koch WJ: New
insights in cardiac β-adrenergic signaling during heart failure and
aging. Front Pharmacol. 9(904)2018.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
28
|
Ferrara N, Komici K, Corbi G, Pagano G,
Furgi G, Rengo C, Femminella GD, Leosco D and Bonaduce D:
β-adrenergic receptor responsiveness in aging heart and clinical
implications. Front Physiol. 4(396)2014.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
29
|
Ramani D, De Bandt JP and Cynober L:
Aliphatic polyamines in physiology and diseases. Clin Nutr.
33:14–22. 2014.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
30
|
Li Y and Liu X: The inhibitory role of
Chinese materia medica in cardiomyocyte apoptosis and underlying
molecular mechanism. Biomed Pharmacother.
118(109372)2019.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
31
|
Huang P, Fu J, Chen L, Ju C, Wu K, Liu H,
Liu Y, Qi B, Qi B and Liu L: Redd1 protects against post infarction
cardiac dysfunction by targeting apoptosis and autophagy. Int J Mol
Med. 44:2065–2076. 2019.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
32
|
Takeshima H, Venturi E and Sitsapesan R:
Takeshima1 H, Venturi E and Sitsapesan R: New and notable
ion-channels in the sarcoplasmic/endoplasmic reticulum: Do they
support the process of intracellular Ca2+ release? J
Physiol. 593:3241–3251. 2015.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
33
|
Sun D, Chen X, Gu G, Wang J and Zhang J:
Potential roles of mitochondria-associated ER membranes (MAMs) in
traumatic brain injury. Cell Mol Neurobiol. 37:1349–1357.
2017.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
34
|
Dingreville F, Panthu B, Thivolet C,
Ducreux S, Gouriou Y, Pesenti S, Chauvin MA, Chikh K,
Errazuriz-Cerda E, Van Coppenolle F, et al: Differential effect of
glucose on ER-mitochondria Ca2+ exchange participates in
insulin secretion and glucotoxicity-mediated dysfunction of
β-cells. Diabetes. 68:1778–1794. 2019.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
35
|
Betz C, Stracka D, Prescianotto-Baschong
C, Frieden M, Demaurex N and Hall MN: mTOR complex 2-Akt signaling
at mitochondria-associated endoplasmic reticulum membranes (MAM)
regulates mitochondrial physiology. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA.
110:12526–12534. 2013.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
36
|
Roman B, Kaur P, Ashok D, Kohr M, Biswas
R, O'Rourke B, Steenbergen C and Das sS: Nuclear-mitochondrial
communication involving miR-181c plays an important role in cardiac
dysfunction during obesity. J Mol Cell Cardiol. 144:87–96.
2020.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
37
|
Szabadkai G, Bianchi K, Várnai P, De
Stefani D, Wieckowski MR, Cavagna D, Nagy AI, Balla T and Rizzuto
R: Chaperone-mediated coupling of endoplasmic reticulum and
mitochondrial Ca2+ channels. J Cell Biol. 175:901–911.
2006.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
38
|
Mitra A, Basak T, Datta K, Naskar S,
Sengupta S and Sarkar S: Role of α-crystallin B as a regulatory
switch in modulating cardiomyocyte apoptosis by mitochondria or
endoplasmic reticulum during cardiac hypertrophy and myocardial
infarction. Cell Death Dis. 4(e582)2013.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
39
|
Javadov S, Rajapurohitam V, Kilić A,
Zeidan A, Choi A and Karmazyn M: Anti-hypertrophic effect of NHE-1
inhibition involves GSK-3beta-dependent attenuation of
mitochondrial dysfunction. J Mol Cell Cardiol. 46:998–1007.
2009.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
40
|
Li X, Lu J, Xu Y, Wang J, Qiu X, Fan L, Li
B, Liu W, Mao F, Zhu J, et al: Discovery of nitazoxanide-based
derivatives as autophagy activators for the treatment of
Alzheimer's disease. Acta Pharm Sin B. 10:646–666. 2020.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
41
|
Cheon SY, Kim H, Rubinsztein DC and Lee
JE: Autophagy, cellular aging and age-related human diseases. Exp
Neurobiol. 28:643–657. 2019.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
42
|
Mizushima N, Yoshimori T and Ohsumi Y: The
role of Atg proteins in autophagosome formation. Annu Rev Cell Dev
Biol. 27:107–132. 2011.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
43
|
Gelmetti V, De Rosa P, Torosantucci L,
Marini ES, Romagnoli A, Di Rienzo M, Arena G, Vignone D, Fimia GM
and Valente EM: PINK1 and BECN1 relocalize at
mitochondria-associated membranes during mitophagy and promote
ER-mitochondria tethering and autophagosome formation. Autophagy.
13:654–669. 2017.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|