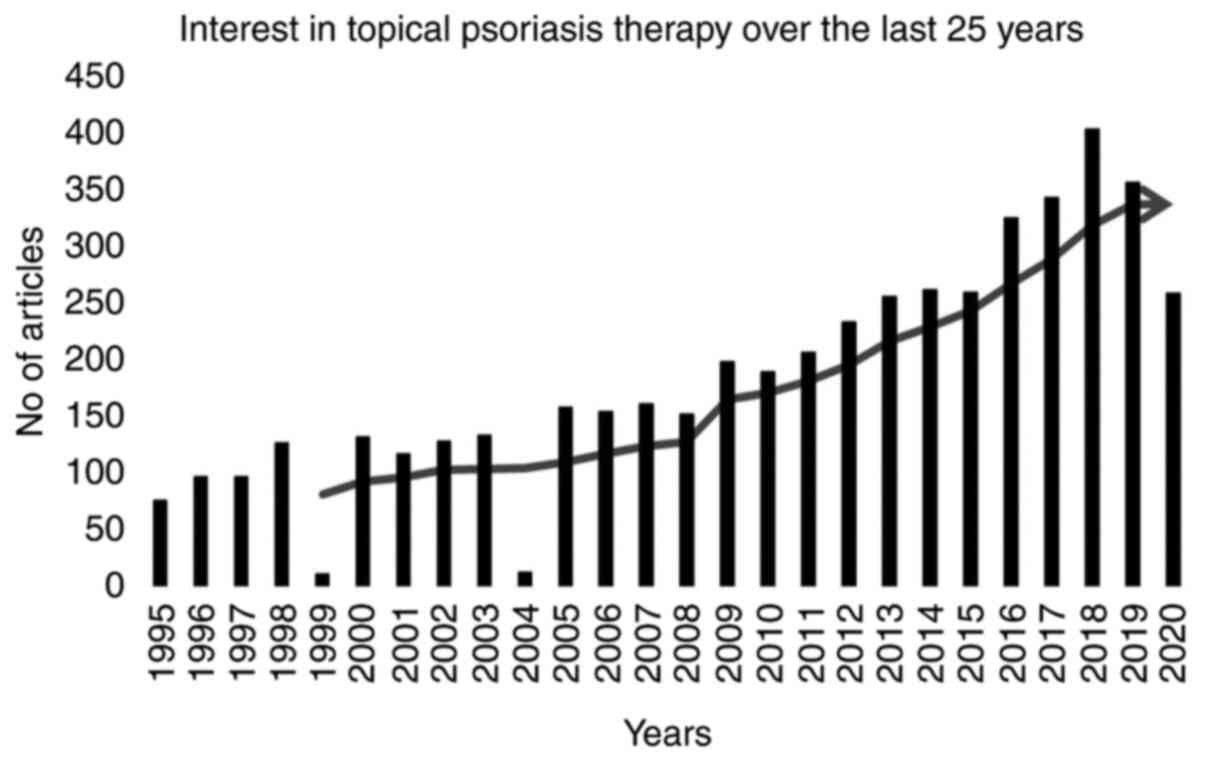
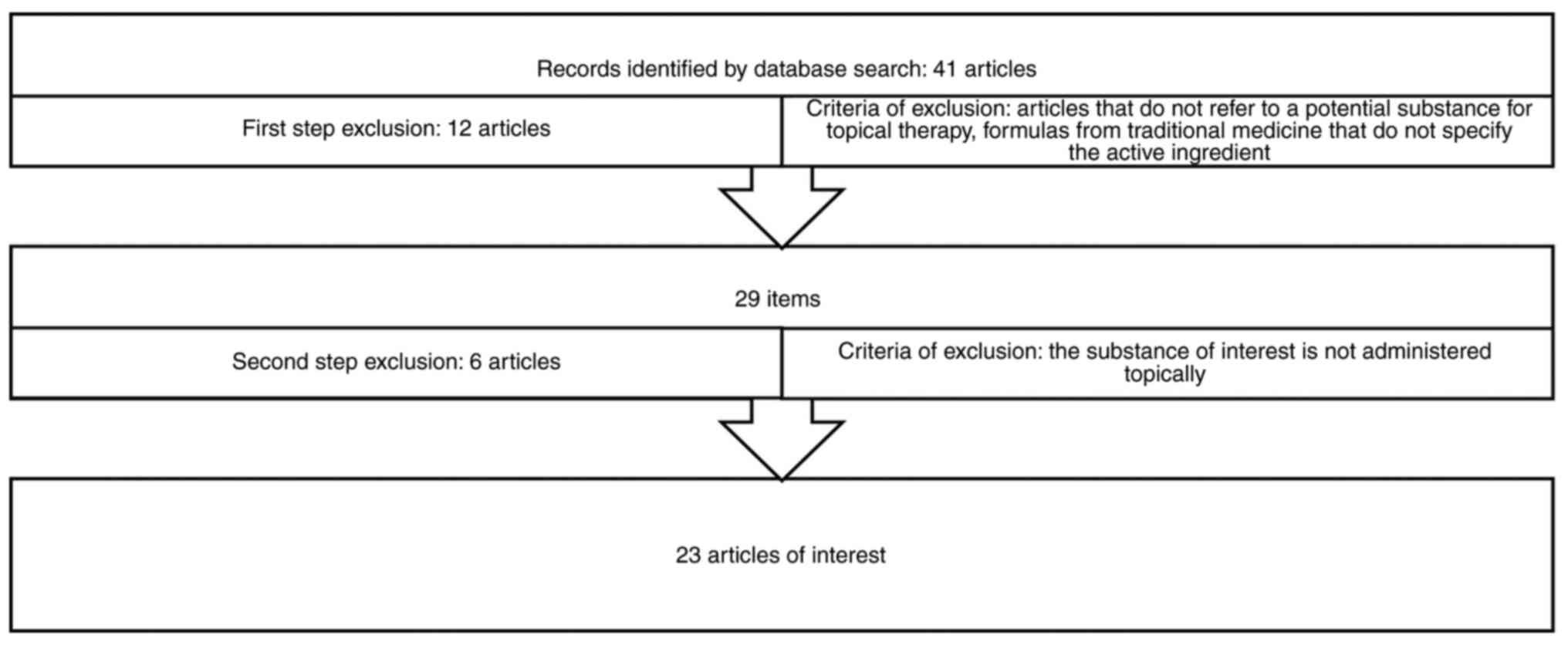
|
1
|
Bologna JL, Schaffer JV and Cerroni L:
Dermatology. 4th edition. Elsevier, Amsterdam, pp138-159, 2018.
|
|
2
|
Caruntu C, Boda D, Dumitrascu G,
Constantin C and Neagu M: Proteomics focusing on immune markers in
psoriatic arthritis. Biomark Med. 9:513–528. 2015.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
3
|
Rendon A and Schäkel K: Psoriasis
pathogenesis and treatment. Int J Mol Sci. 20(1475)2019.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
4
|
Alecu M, Coman G, Mușetescu Cojoacă ME and
Coman OA: Dermatology facing autoinflammatory syndrome. Rom J
Morphol Embryol. 56:7–14. 2015.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
5
|
Costescu M, Coman OA, Tampa M, Tudose I,
Coman L and Georgescu SR: Axillary basal cell carcinoma-a rare form
of a frequent kind of carcinoma. Rom J Morphol Embryol. 54 (Suppl
3):S851–S856. 2013.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
6
|
Nicolae I, Nicolae CD, Coman OA,
Stefanescu M, Coman L and Ardeleanu C: Serum total gangliosides
level: Clinical prognostic implication. Rom J Morphol Embryol.
52:1277–1281. 2011.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
7
|
Algahtani M, Ahmad M, Nourein I and Ahmad
J: Co-delivery of imiquimod and curcumin by nanoemugel for improved
topical delivery and reduced psoriasis-like skin lesions.
Biomolecules. 10(968)2020.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
8
|
Evans EA, Sayers SR, Kodji X, Xia Y,
Shaikh M, Rizvi A, Frame J, Brain SD, Philpott MP, Hannen RF and
Caton PW: Psoriatic skin inflammation induces a pre-diabetic
phenotype via the endocrine actions of skin secretome. Mol Metab.
41(101047)2020.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
9
|
Xu Z, Qin Z, Zhang J and Wang Y:
Microglia-mediated chronic psoriatic itch induced by imiquimod. Mol
Pain: Jun 24, 2020 (Epub ahead of print). doi:
10.1177/1744806920934998.
|
|
10
|
Bai X, Yu C, Yang L, Luo Y, Zhi D, Wang G
and Dang E: Anti-psoriatic properties of paeoniflorin: Suppression
of the NF-kappaB pathway and Keratin 17. Eur J Dermatol.
30:243–250. 2020.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
11
|
Ren F, Zhang M, Zhang C and Sang H:
Psoriasis-like inflammation induced renal dysfunction through the
TLR/NF-κB signal pathway. Biomed Res Int.
2020(3535264)2020.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
12
|
Duan X, Liu X, Liu N, Huang Y, Jin Z,
Zhang S, Ming Z and Chen H: Inhibition of keratinocyte necroptosis
mediated by RIPK1/RIPK3/MLKL provides a protective effect against
psoriatic inflammation. Cell Death Dis. 11(134)2020.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
13
|
Yu S, Wu X, Shi Z, Huynh M, Jena PK, Sheng
L, Zhou Y, Han D, Wan YY and Hwang ST: Diet-induced obesity
exacerbates imiquimod-mediated psoriasiform dermatitis in anti-PD-1
antibody-treated mice: Implications for patients being treated with
checkpoint inhibitors for cancer. J Dermatol Sci. 97:194–200.
2020.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
14
|
Man MQ and Elias PM: Could inflammaging
and its sequelae be prevented or mitigated? Clin Interv Aging.
14:2301–2304. 2019.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
15
|
Shankar GM, Alex VV, Nisthul AA, Bava SV,
Sundaram S, Retnakumari AP, Chittalakkottu S and Anto RJ:
Pre-clinical evidences for the efficacy of tryptanthrin as a potent
suppressor of skin cancer. Cell Prolif. 53(e12710)2020.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
16
|
Chiang CC, Cheng WJ, Lin CY, Lai KH, Ju
SC, Lee C, Yang SH and Hwang TL: Kan-Lu-Hsiao-Tu-Tan, a traditional
Chinese medicine formula, inhibits human neutrophil activation and
ameliorates imiquimod-induced psoriasis-like skin inflammation. J
Ethnopharmacol. 246(112246)2020.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
17
|
Rapalli VK, Singhvi G, Gorantla S, Waghule
T, Dubey SK, Saha RN, Hasnain MS and Nayak AK: Stability indicating
liquid chromatographic method for simultaneous quantification of
betamethasone valerate and tazarotene in in vitro and ex vivo
studies of complex nanoformulation. J Sep Sci. 42:3413–3420.
2019.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
18
|
Shih CM, Hsieh CK, Huang CY, Huang CY,
Wang KH, Fong TH, Trang NT, Liu KT and Lee AW: Lycopene inhibit
IMQ-induced psoriasis-like inflammation by inhibiting ICAM-1
production in mice. Polymers (Basel). 12(1521)2020.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
19
|
Li Q, Li F, Qi X, Wei F, Chen H and Wang
T: Pluronic® F127 stabilized reduced graphene oxide
hydrogel for the treatment of psoriasis: In vitro and in vivo
studies. Colloids Surf B Biointerfaces. 195(111246)2020.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
20
|
Shinde G, Desai P, Shelke S, Patel R,
Bangale G and Kulkarni D: Mometasone furoate-loaded aspasomal gel
for topical treatment of psoriasis: Formulation, optimization, in
vitro and in vivo performance. J Dermatolog Treat: Jul 8, 2020
(Epub ahead of print). doi: 10.1080/09546634.2020.1789043.
|
|
21
|
Schwarz A, Philippsen R and Schwarz T:
Induction of regulatory T cells and correction of cytokine
dysbalance by short-chain fatty acids: Implications for psoriasis
therapy. J Invest Dermatol. 141:95–104.e2. 2021.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
22
|
Guo JW, Cheng YP, Liu CY, Thong HY, Huang
CJ, Lo Y, Wu CY and Jee SH: Salvianolic acid B in microemulsion
formulation provided sufficient hydration for dry skin and
ameliorated the severity of imiquimod-induced psoriasis-like
dermatitis in mice. Pharmaceutics. 12(457)2020.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
23
|
Dharamdasani V, Mandal A, Qi QM, Suzuki I,
Bentley MV and Mitragotri S: Topical delivery of siRNA into skin
using ionic liquids. J Control Release. 323:475–482.
2020.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
24
|
Li H, Li J, Zhang X, Feng C, Fan C, Yang
X, Zhang R, Zhu F, Zhou Y, Xu Y, et al: DC591017, a
phosphodiesterase-4 (PDE4) inhibitor with robust anti-inflammation
through regulating PKA-CREB signaling. Biochem Pharmacol.
177(113958)2020.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
25
|
Di Fusco D, Stolfi C, Di Grazia A, Dinallo
V, Laudisi F, Marafini I, Colantoni A, Monteleone I and Monteleone
G: Albendazole negatively regulates keratinocyte proliferation.
Clin Sci (Lond). 134:907–920. 2020.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
26
|
Song B, Song R, Cheng M, Chu H, Yan F and
Wang Y: Preparation of calcipotriol emulsion using bacterial
exopolysaccharides as emulsifier for percutaneous treatment of
psoriasis vulgaris. Int J Mol Sci. 21(77)2020.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
27
|
Lee WR, Lin YK, Alalaiwe A, Wang PW, Liu
PY and Fang JY: Fractional laser-mediated siRNA delivery for
mitigating psoriasis-like lesions via IL-6 silencing. Mol Ther
Nucleic Acid. 19:240–251. 2020.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
28
|
Feng H, Wu R, Zhang S, Kong Y, Liu Z, Wu
H, Wang H, Su Y, Zhao M and Lu Q: Topical administration of
nanocarrier miRNA-210 antisense ameliorates imiquimod-induced
psoriasis-like dermatitis in mice. J Dermatol. 47:147–154.
2020.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
29
|
Negi P, Sharma I, Hemrajani C, Rathore C,
Bisht A, Raza K and Katare OP: Thymoquinone-loaded lipid vesicles:
A promising nanomedicine for psoriasis. BMC Complement Altern Med.
19(334)2019.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
30
|
Balkrishna A, Sakat SS, Joshi K, Joshi K,
Sharma V, Ranjan R, Bhattacharya K and Varshney A: Cytokines driven
anti-inflammatory and anti-psoriasis like efficacies of
nutraceutical sea buckthorn (Hippophae rhamnoides) oil.
Front Pharmacol. 10(1186)2019.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
31
|
Zhai H, Hu S, Liu T, Wang F, Wang X, Wu G,
Zhang Y, Sui M, Liu H and Jiang L: Nitidine chloride inhibits
proliferation and induces apoptosis in colorectal cancer cells by
suppressing the ERK signaling pathway. Mol Med Rep. 13:2536–2542.
2016.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
32
|
Yang XG, Jiang BW, Jing QQ, Li WJ, Tan LP,
Bao YL, Song ZB, Yu CL, Liu L, Liu YC and Li YX: Nitidine chloride
induces S phase cell cycle arrest and mitochondria-dependent
apoptosis in HaCaT cells and ameliorates skin lesions in
psoriasis-like mouse models. Eur J Pharmacol.
863(172680)2019.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
33
|
Weng JR, Huang TH, Lin ZC, Alalaiwe A and
Fang JY: Cutaneous delivery of
[1-(4-chloro-3-nitrobenzenesulfonyl)-1H-indol-3-yl]-methanol, an
indole-3-carbinol derivative, mitigates psoriasiform lesion by
blocking MAPK/NF-κB/AP-1 activation. Biomed Pharmacother.
119(109398)2019.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
34
|
Chandra A, Aggarwal G, Manchanda S and
Narula A: Development of topical gel of methotrexate incorporated
ethosomes and salicylic acid for the treatment of psoriasis. Pharm
Nanotechnol. 7:362–374. 2019.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
35
|
Dimitris D, Ekaterina-Michaela T,
Christina K, Ioannis S, Ioanna SK, Aggeliki L, Sophia H, Michael R
and Helen S: Melissa officinalis ssp. altissima extracts: A
therapeutic approach targeting psoriasis in mice. J Ethnopharmacol.
246(112208)2020.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
36
|
Bahramizadeh M, Bahramizadeh M, Kiafar B,
Jafarian AH, Nikpoor AR, Hatamipour M, Esmaily H, Rezaeemehr Z,
Golmohammadzadeh S, Moosavian SA and Jafari MR: Development,
characterization and evaluation of topical methotrexate-entrapped
deformable liposome on imiquimod-induced psoriasis in a mouse
model. Int J Pharm. 569(118623)2019.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
37
|
Negrei C, Ginghină O, Caruntu C, Burcea
Dragomiroiu G, Jinescu G and Boda D: Investigation relevance of
methotrexate polyglutamates in biological systems by high
performance liquid chromatography. Rev Chim Bucharest. 66:766–768.
2015.
|
|
38
|
Negrei C, Caruntu C, Ginghina O,
Dragomiroiu GT, Toderescu CD and Boda D: Qualitative and
quantitative determination of methotrexate polyglutamates in
erythrocytes by high performance liquid chromatography. Rev
Chim-Bucharest. 66:607–610. 2015.
|
|
39
|
Boda D, Negrei C, Nicolescu F and Badalau
C: Assessment of some oxidative stress parameters in methotrexate
treated psoriasis patients. Farmacia. 62:704–710. 2014.
|
|
40
|
Sakurai K, Dainichi T, Garcet S, Tsuchiya
S, Yamamoto Y, Kitoh A, Honda T, Nomura T, Egawa G, Otsuka A, et
al: Cutaneous p38 mitogen-activated protein kinase activation
triggers psoriatic dermatitis. J Allergy Clin Immunol.
144:1036–1049. 2019.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
41
|
Elmowafy E, El-Gogary RI, Ragai MH and
Nasr M: Novel antipsoriatic fluidized spanlastic nanovesicles: In
vitro physicochemical characterization, ex vivo cutaneous retention
and exploratory clinical therapeutic efficacy. Int J Pharm.
568(118556)2019.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
42
|
Gad SC, Sullivan DW Jr, Mujer CV,
Spainhour CB and Crapo JD: Nonclinical safety and toxicokinetics of
MnTE-2-PyP (BMX-010), a topical agent in phase 2 trials for
psoriasis and atopic dermatitis. Int J Toxicol. 38:291–302.
2019.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
43
|
Meng S, Sun L, Wang L, Lin Z, Liu Z, Xi L,
Wang Z and Zheng Y: Loading of water-insoluble celastrol into
niosome hydrogels for improved topical permeation and
anti-psoriasis activity. Colloids Surf B Biointerfaces.
182(110352)2019.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
44
|
Ho TC, Yeh SI, Chen SL and Tsao YP: The
psoriasis therapeutic potential of a novel short laminin peptide
C16. Int J Mol Sci. 20(3144)2019.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
45
|
Căruntu C, Boda D, Caruntu A, Rotaru M,
Baderca F and Zurac S: In vivo imaging techniques for psoriatic
lesions. Rom J Morphol Embryol. 55 (Suppl 3):S1191–S1196.
2014.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
46
|
Batani A, Branisteanu DE, Ilie MA, Boda D,
Ianosi S, Ianosi G and Caruntu C: Assessment of dermal papillary
and microvascular parameters in psoriasis vulgaris using in vivo
reflectance confocal microscopy. Exp Ther Med. 15:1241–1246.
2018.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
47
|
Swindell WR, Michaels KA, Sutter AJ,
Diaconu D, Fritz Y, Xing X, Sarkar MK, Liang Y, Tsoi A, Gudjonsson
JE and Ward NL: Imiquimod has strain-dependent effects in mice and
does not uniquely model human psoriasis. Genome Med.
9(24)2017.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
48
|
Akbarzadeh A, Rezaei-Sadabad R, Davaran S,
Joo SW, Zargami N, Hanifehpour Y, Samiei M, Kouhi M and
Nejati-Koshki K: Liposome: Classification, preparation, and
applications. Nanoscale Ress Lett. 8(102)2013.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
49
|
Verma P and Pathak K: Therapeutic and
cosmeceutical potential of ethosomes: An overview. J Adv Pharm
Technol Res. 1:274–282. 2010.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
50
|
Kazi KM, Mandal AS, Biswas N, Guha A,
Chatterjee S, Behera M and Kuotsu K: Niosome: A future of targeted
drug delivery systems. J Adv Pharm Technol Res. 1:374–380.
2010.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
51
|
Wang Y, Li P, Zhang L, Fu J, Di T, Li N,
Meng Y, Guo J and Zhao J: Stress aggravates and prolongs
imiquimod-induced psoriasis-like epidermal hyperplasia and
IL-1β/IL-23p40 production. J Leukoc Biol. 108:267–281.
2020.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
52
|
Iwano R, Iwashita N, Takagi Y and Fukuyama
T: Estrogen receptor α activation aggravates imiquimod-induced
psoriasis-like dermatitis in mice by enhancing dendritic cell
interleukin-23 secretion. J Appl Toxicol. 40:1353–1361.
2020.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
53
|
Pu J, Wang R, Zhang G and Wang J: FGF-7
facilitates the process of psoriasis by inducing TNF-α expression
in HaCaT cells. Acta Biochim Biophys Sin (Shanghai). 51:1056–1063.
2019.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
54
|
Borek I, Köffel R, Feichtinger J, Spies M,
Glitzner-Zeis E, Hochgerner M, Sconocchia T, Krump C,
Tam-Amersdorfer C, Passegger C, et al: BMP7 aberrantly induced in
the psoriatic epidermis instructs inflammation-associated
langerhans cells. J Allergy Clin Immunol. 145:1194–1207.e11.
2020.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
55
|
Ju N, Shimamura M, Hayashi H, Ikeda Y,
Yoshida S, Nakamura A, Morishita R, Rakugi H and Nakagami H:
Preventative effects of the partial RANKL peptide MHP1-AcN in a
mouse model of imiquimod-induced psoriasis. Scic Rep.
9(15434)2019.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
56
|
Liu C, Liu H, Lu C, Deng J, Yan Y, Chen H,
Wang Y, Liang C, Wei J, Han L and Dai Z: Kaempferol attenuates
imiquimod-induced psoriatic skin inflammation in a mouse model.
Clin Exp Immunol. 198:403–415. 2019.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|