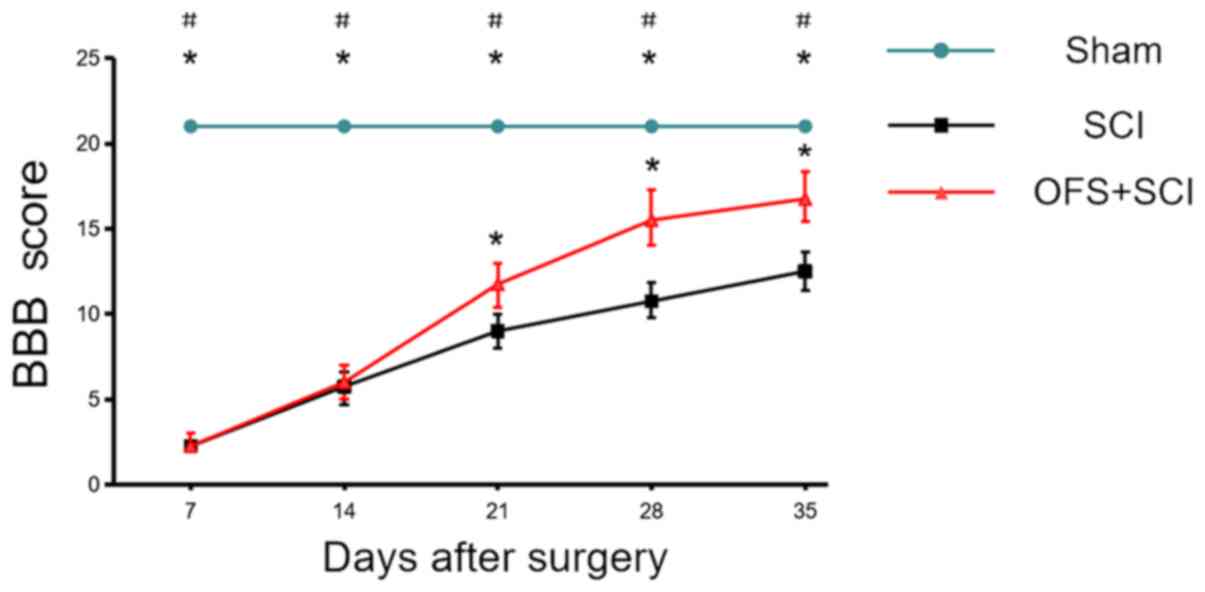
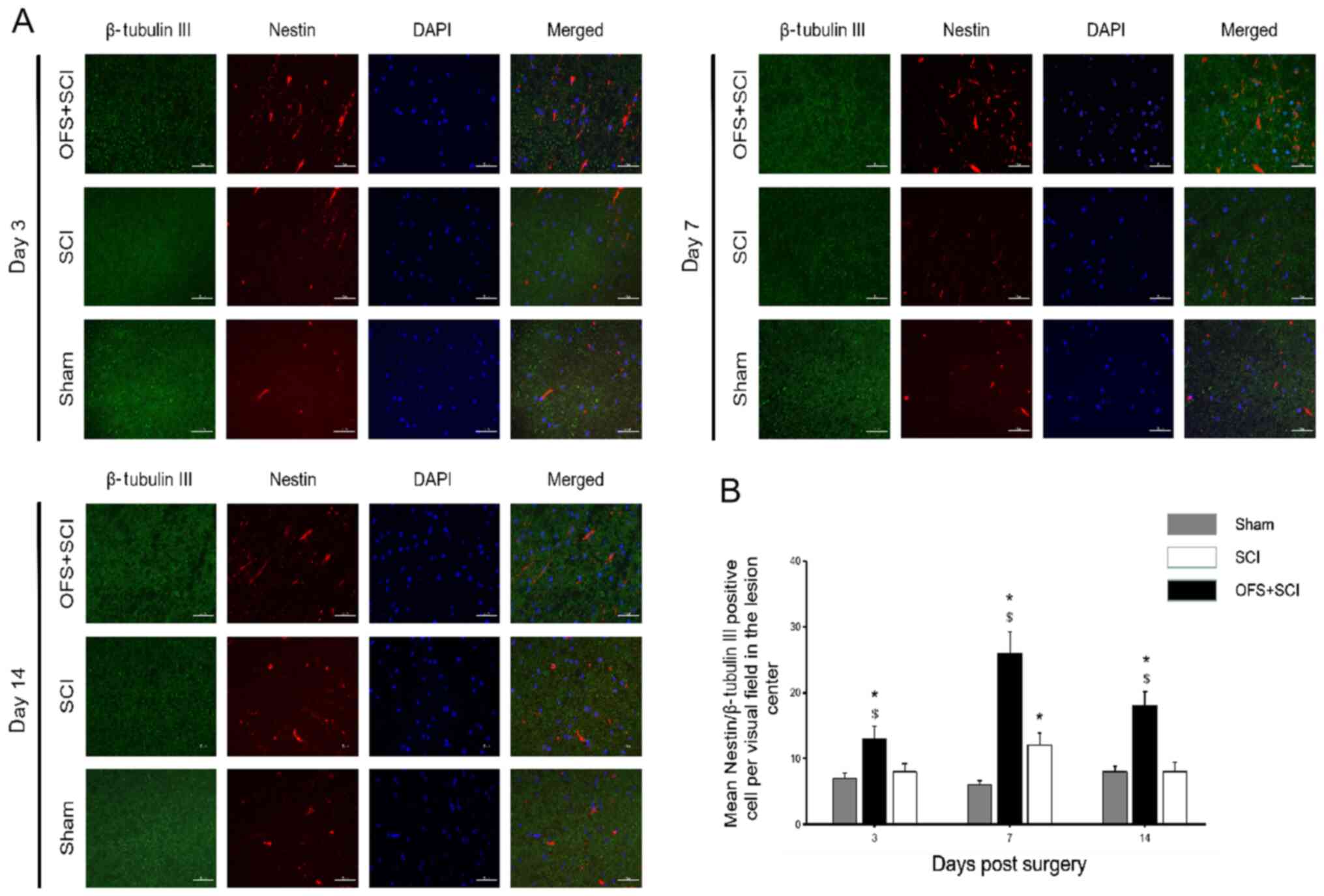
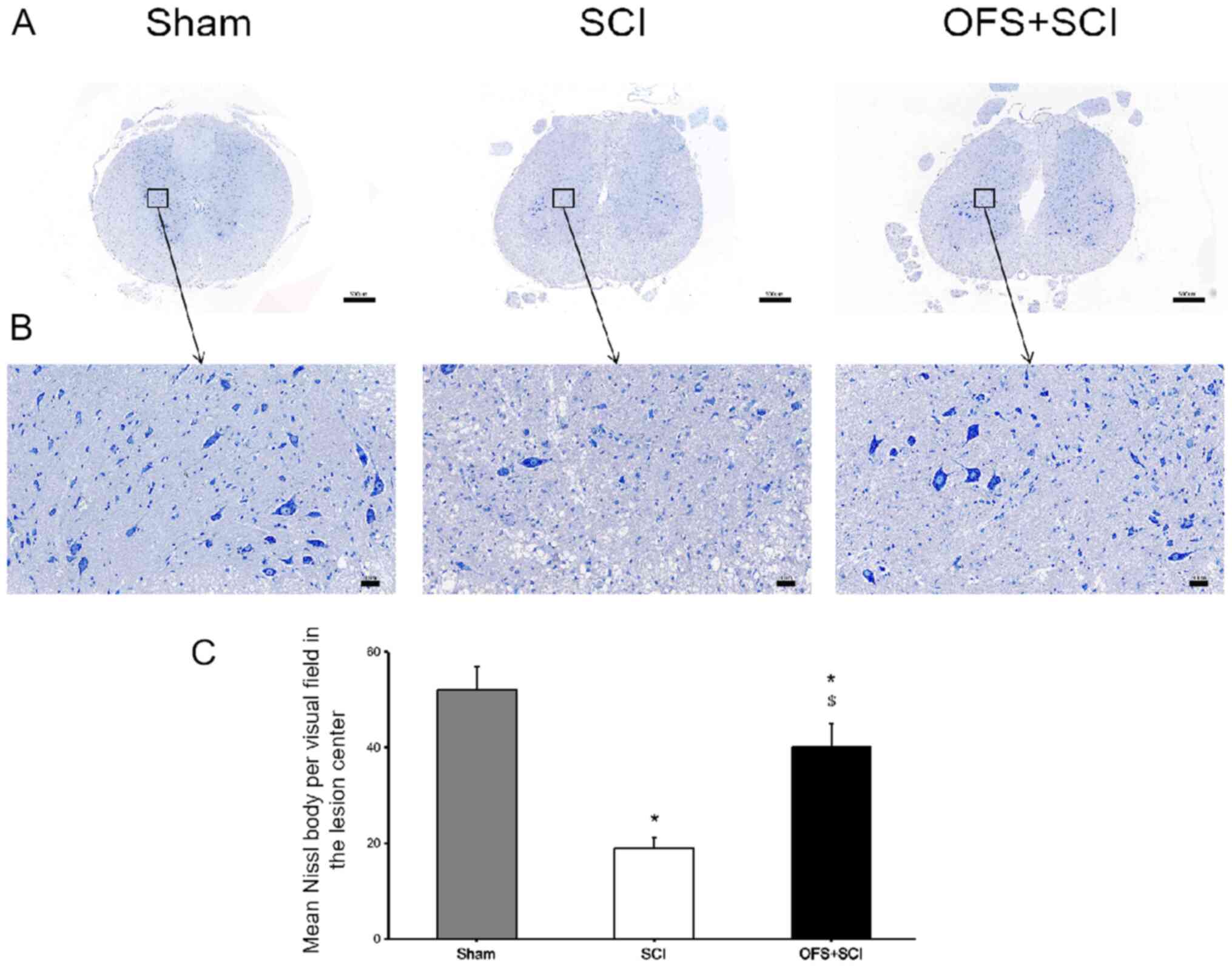
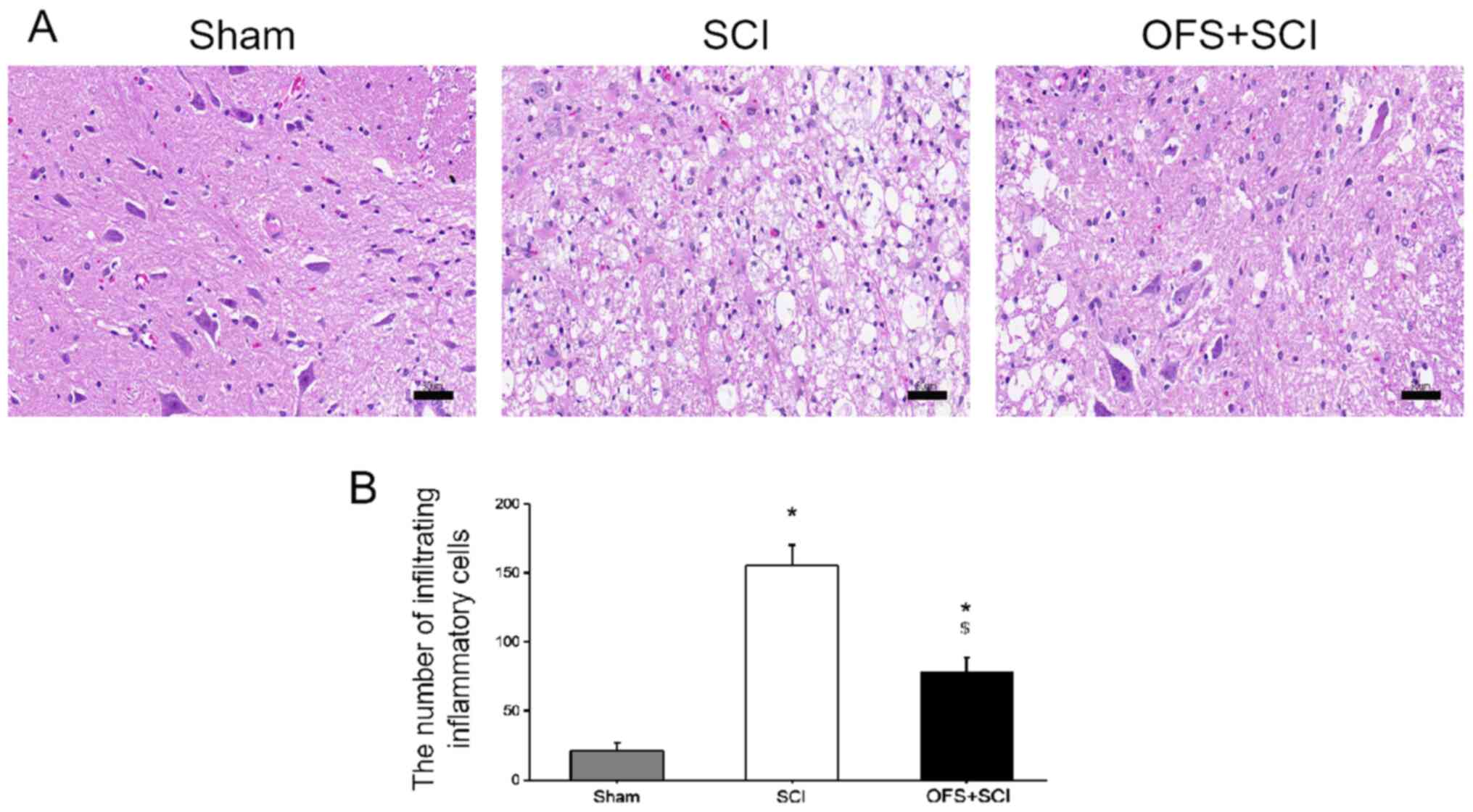
|
1
|
Wyndaele M and Wyndaele JJ: Incidence,
prevalence and epidemiology of spinal cord injury: What learns a
worldwide literature survey? Spinal Cord. 44:523–529.
2006.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
2
|
Singh A, Tetreault L, Kalsi-Ryan S, Nouri
A and Fehlings MG: Global prevalence and incidence of traumatic
spinal cord injury. Clin Epidemiol. 6:309–331. 2014.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
3
|
Middleton JW, Dayton A, Walsh J, Rutkowski
SB, Leong G and Duong S: Life expectancy after spinal cord injury:
A 50-year study. Spinal Cord. 50:803–811. 2012.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
4
|
Devivo MJ: Epidemiology of traumatic
spinal cord injury: Trends and future implications. Spinal Cord.
50:365–372. 2012.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
5
|
Dyck SM and Karimi-Abdolrezaee S:
Chondroitin sulfate proteoglycans: Key modulators in the developing
and pathologic central nervous system. Exp Neurol. 269:169–187.
2015.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
6
|
Sabelström H, Stenudd M and Frisén J:
Neural stem cells in the adult spinal cord. Exp Neurol. 260:44–49.
2014.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
7
|
Grégoire CA, Goldenstein BL, Floriddia EM,
Barnabé-Heider F and Fernandes KJ: Endogenous neural stem cell
responses to stroke and spinal cord injury. Glia. 63:1469–1482.
2015.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
8
|
Stenudd M, Sabelström H and Frisén J: Role
of endogenous neural stem cells in spinal cord injury and repair.
JAMA Neurol. 72:235–237. 2015.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
9
|
Taveggia C, Feltri ML and Wrabetz L:
Signals to promote myelin formation and repair. Nat Rev Neurol.
6:276–287. 2010.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
10
|
Shapiro S, Borgens R, Pascuzzi R, Roos K,
Groff M, Purvines S, Rodgers RB, Hagy S and Nelson P: Oscillating
field stimulation for complete spinal cord injury in humans: A
phase 1 trial. J Neurosurg Spine. 2:3–10. 2005.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
11
|
Wu Y, Collier L, Qin W, Creasey G, Bauman
WA, Jarvis J and Cardozo C: Electrical stimulation modulates Wnt
signaling and regulates genes for the motor endplate and calcium
binding in muscle of rats with spinal cord transection. BMC
Neurosci. 14(81)2013.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
12
|
Piccin D and Morshead CM: Wnt signaling
regulates symmetry of division of neural stem cells in the adult
brain and in response to injury. Stem Cells. 29:528–538.
2011.PubMed/NCBI View
Article : Google Scholar
|
|
13
|
Li Z, Yao F, Cheng L, Cheng W, Qi L, Yu S,
Zhang L, Zha X and Jing J: Low frequency pulsed electromagnetic
field promotes the recovery of neurological function after spinal
cord injury in rats. J Orthop Res. 37:449–456. 2019.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
14
|
Jing JH, Qian J, Zhu N, Chou WB and Huang
XJ: Improved differentiation of oligodendrocyte precursor cells and
neurological function after spinal cord injury in rats by
oscillating field stimulation. Neuroscience. 303:346–351.
2015.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
15
|
Cho SR, Kim YR, Kang HS, Yim SH, Park CI,
Min YH, Lee BH, Shin JC and Lim JB: Functional recovery after the
transplantation of neurally differentiated mesenchymal stem cells
derived from bone marrow in a rat model of spinal cord injury. Cell
Transplant. 25(1423)2016.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
16
|
Basso DM, Beattie MS, Bresnahan JC,
Anderson DK, Faden AI, Gruner JA, Holford TR, Hsu CY, Noble LJ,
Nockels R, et al: MASCIS evaluation of open field locomotor scores:
Effects of experience and teamwork on reliability. Multicenter
Animal Spinal Cord Injury Study. J Neurotrauma. 13:343–359.
1996.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
17
|
Cofano F, Boido M, Monticelli M, Zenga F,
Ducati A, Vercelli A and Garbossa D: Mesenchymal stem cells for
spinal cord injury: current options, limitations, and future of
cell therapy. Int J Mol Sci. 20(2698)2019.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
18
|
Galderisi U, Peluso G, Di Bernardo G,
Calarco A, D'Apolito M, Petillo O, Cipollaro M, Fusco FR and Melone
MA: Efficient cultivation of neural stem cells with controlled
delivery of FGF-2. Stem Cell Res (Amst). 10:85–94. 2013.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
19
|
Hernández J, Torres-Espín A and Navarro X:
Adult stem cell transplants for spinal cord injury repair: Current
state in preclinical research. Curr Stem Cell Res Ther. 6:273–287.
2011.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
20
|
Liu S and Chen Z: Employing Endogenous
NSCs to Promote Recovery of Spinal Cord Injury. Stem Cells Int.
2019(1958631)2019.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
21
|
Yu JH, Seo J-H, Lee JY, Lee M-Y and Cho
S-R: Induction of neurorestoration from endogenous stem cells. Cell
Transplant. 25:863–882. 2016.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
22
|
Sandner B, Prang P, Rivera FJ, Aigner L,
Blesch A and Weidner N: Neural stem cells for spinal cord repair.
Cell Tissue Res. 349:349–362. 2012.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
23
|
Schwab ME: Repairing the injured spinal
cord. Science. 295:1029–1031. 2002.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
24
|
Willert K, Brown JD, Danenberg E, Duncan
AW, Weissman IL, Reya T, Yates JR III and Nusse R: Wnt proteins are
lipid-modified and can act as stem cell growth factors. Nature.
423:448–452. 2003.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
25
|
David MD, Cantí C and Herreros J: Wnt-3a
and Wnt-3 differently stimulate proliferation and neurogenesis of
spinal neural precursors and promote neurite outgrowth by canonical
signaling. J Neurosci Res. 88:3011–3023. 2010.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
26
|
Sousa KM, Villaescusa JC, Cajanek L, Ondr
JK, Castelo-Branco G, Hofstra W, Bryja V, Palmberg C, Bergman T,
Wainwright B, et al: Wnt2 regulates progenitor proliferation in the
developing ventral midbrain. J Biol Chem. 285:7246–7253.
2010.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
27
|
Megason SG and McMahon AP: A mitogen
gradient of dorsal midline Wnts organizes growth in the CNS.
Development. 129:2087–2098. 2002.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
28
|
Murashov AK, Pak ES, Hendricks WA, Owensby
JP, Sierpinski PL, Tatko LM and Fletcher PL: Directed
differentiation of embryonic stem cells into dorsal interneurons.
FASEB J. 19:252–254. 2005.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
29
|
Hirabayashi Y, Itoh Y, Tabata H, Nakajima
K, Akiyama T, Masuyama N and Gotoh Y: The Wnt/beta-catenin pathway
directs neuronal differentiation of cortical neural precursor
cells. Development. 131:2791–2801. 2004.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
30
|
Binarová P and Tuszynski J: Tubulin:
structure, functions and roles in disease. Cells.
8(1294)2019.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
31
|
Lu P, Wang Y, Graham L, McHale K, Gao M,
Wu D, Brock J, Blesch A, Rosenzweig ES, Havton LA, et al:
Long-distance growth and connectivity of neural stem cells after
severe spinal cord injury. Cell. 150:1264–1273. 2012.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
32
|
Hesp ZC, Goldstein EZ, Miranda CJ, Kaspar
BK and McTigue DM: Chronic oligodendrogenesis and remyelination
after spinal cord injury in mice and rats. J Neurosci.
35:1274–1290. 2015.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
33
|
Kang SH, Fukaya M, Yang JK, Rothstein JD
and Bergles DE: NG2+ CNS glial progenitors remain
committed to the oligodendrocyte lineage in postnatal life and
following neurodegeneration. Neuron. 68:668–681. 2010.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
34
|
Guo YE, Suo N, Cui X, Yuan Q and Xie X:
Vitamin C promotes oligodendrocytes generation and remyelination.
Glia. 66:1302–1316. 2018.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
35
|
Skaper SD: Oligodendrocyte precursor cells
as a therapeutic target for demyelinating diseases. Prog Brain Res.
245:119–144. 2019.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|