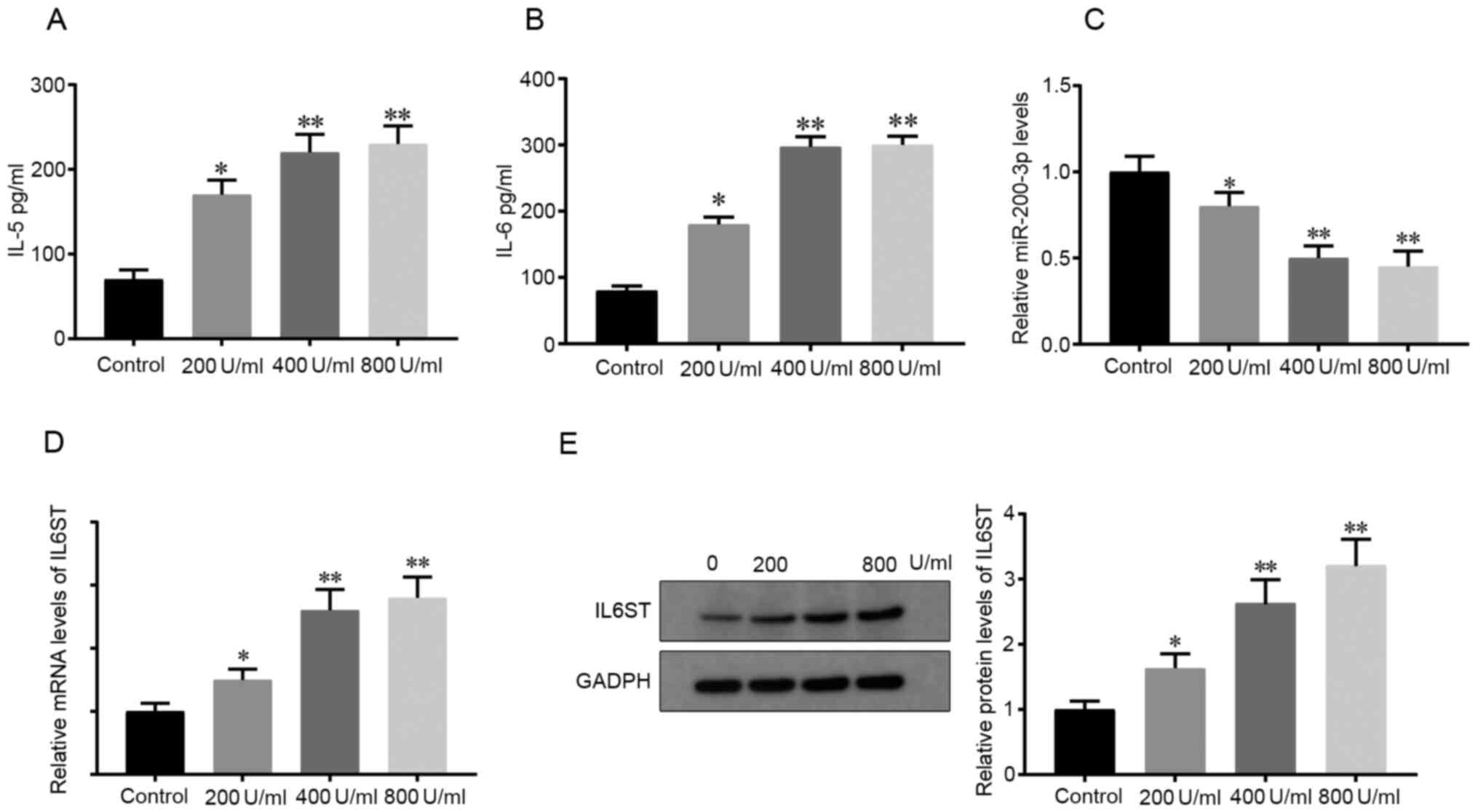
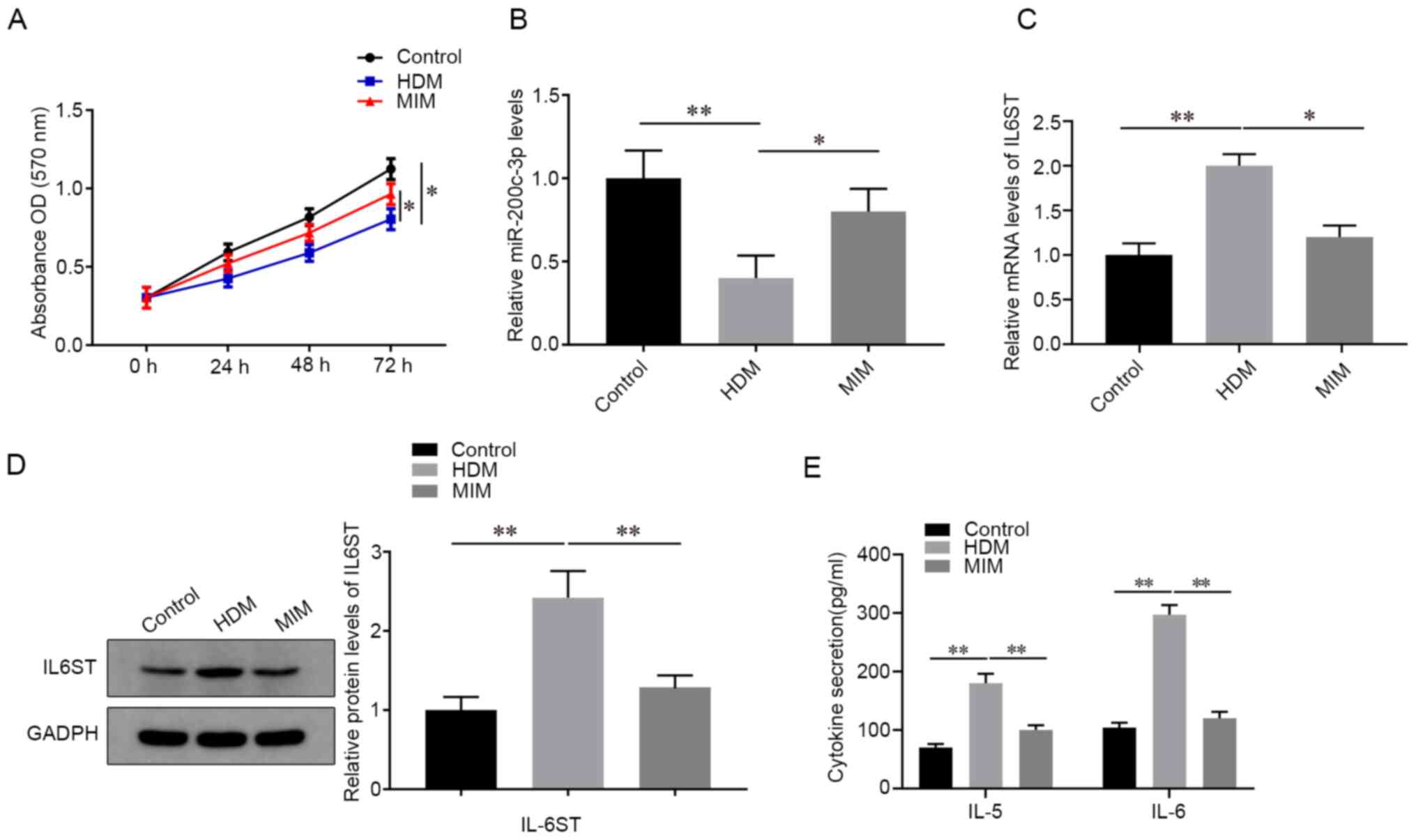
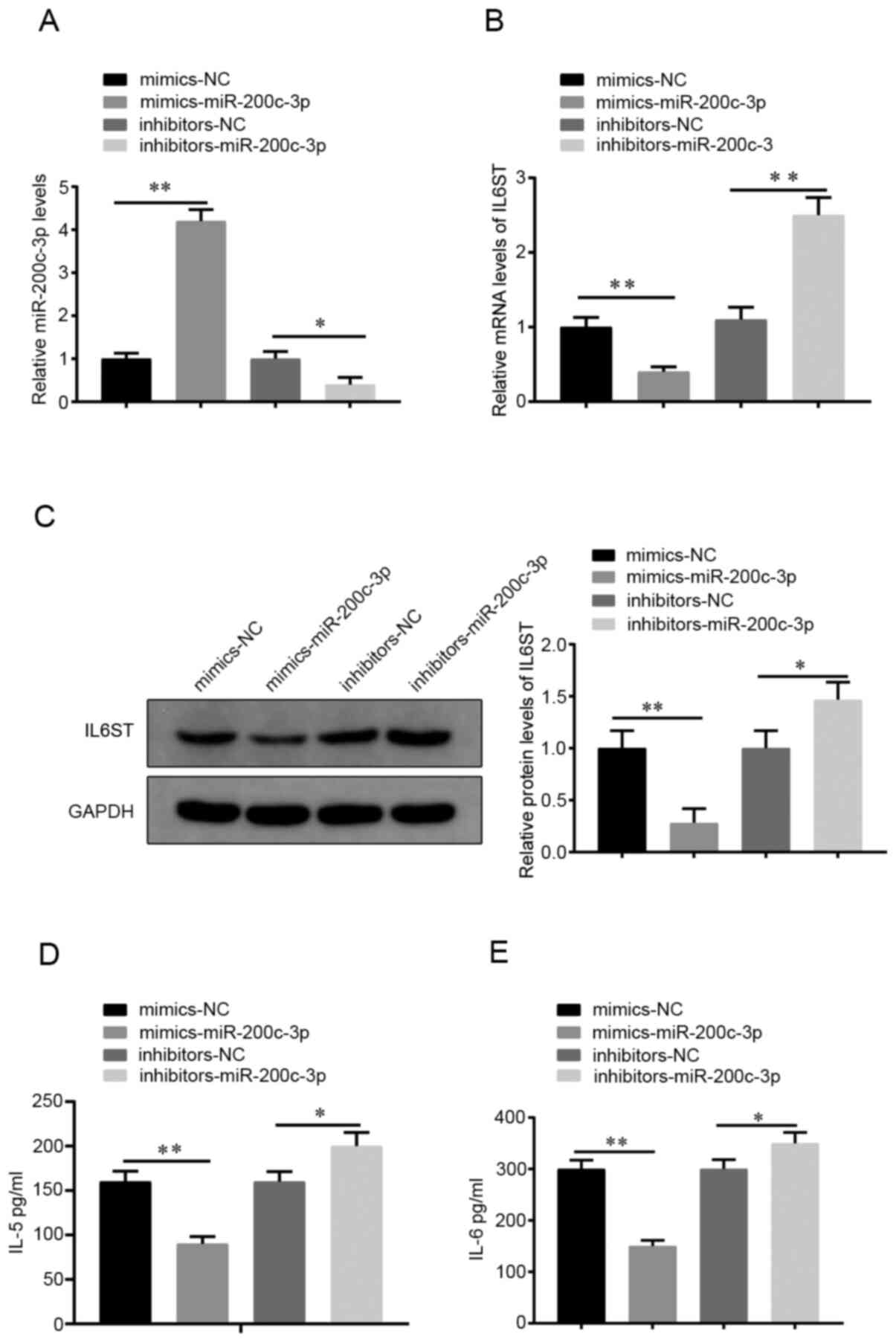
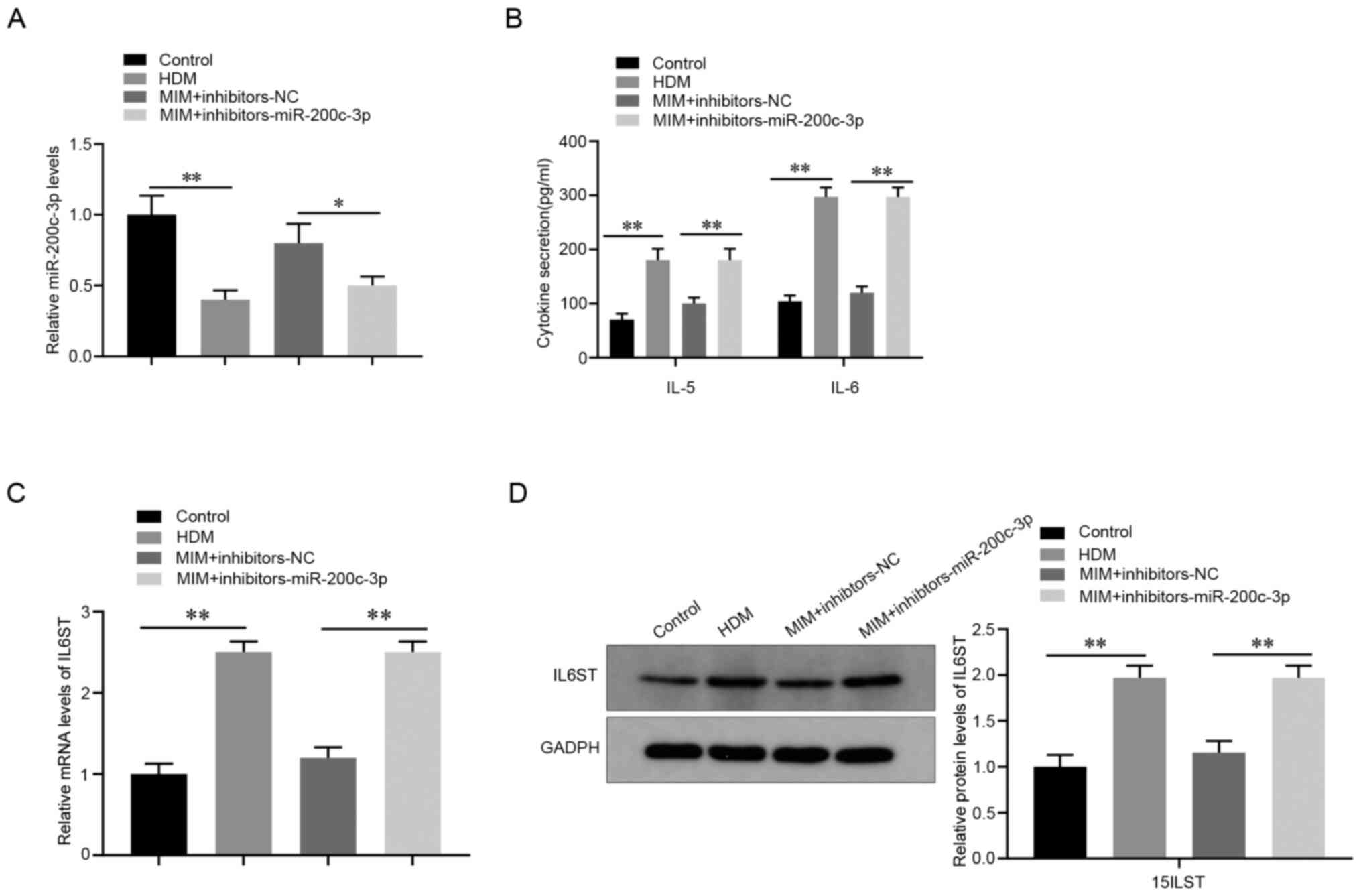
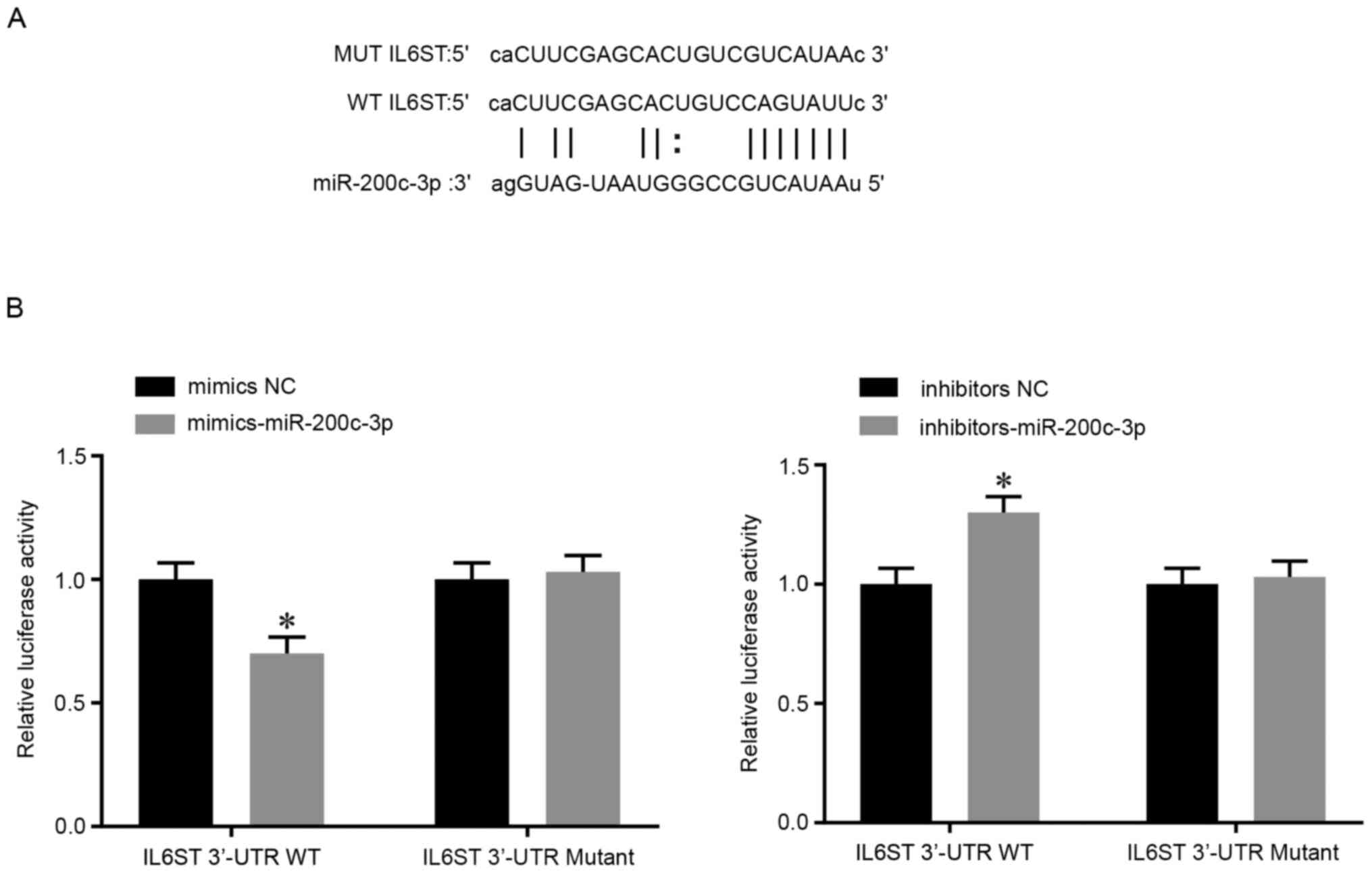
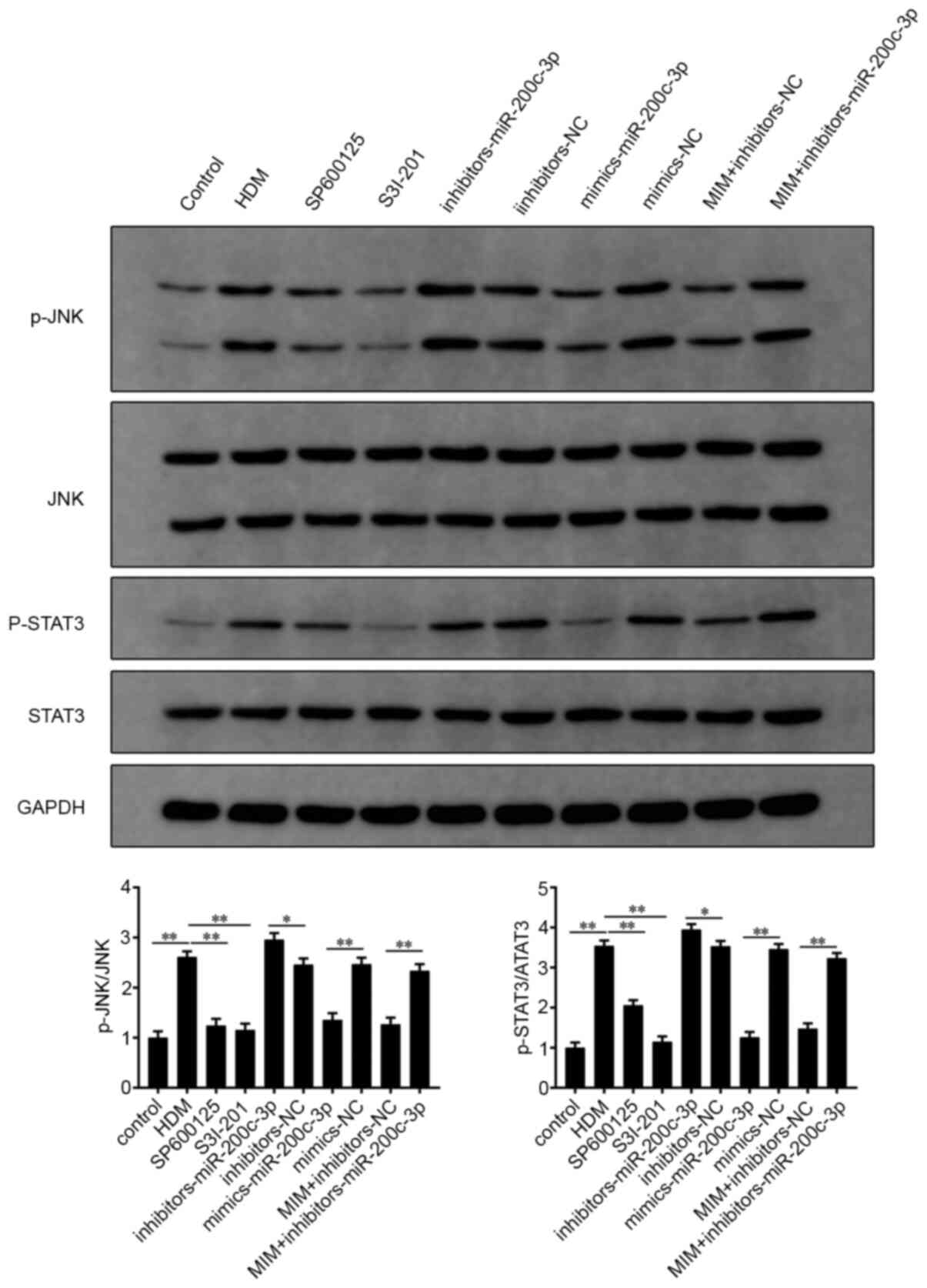
|
1
|
Lambrecht BN and Hammad H: The immunology
of asthma. Nat Immunol. 16:45–56. 2015.PubMed/NCBI View
Article : Google Scholar
|
|
2
|
Papi A, Brightling C, Pedersen SE and
Reddel HK: Asthma. Lancet. 391:783–800. 2018.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
3
|
Gon Y and Hashimoto S: Role of airway
epithelial barrier dysfunction in pathogenesis of asthma. Allergol
Int. 67:12–17. 2018.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
4
|
Mertens TCJ, Karmouty-Quintana H, Taube C
and Hiemstra PS: Use of airway epithelial cell culture to unravel
the pathogenesis and study treatment in obstructive airway
diseases. Pulm Pharmacol Ther. 45:101–113. 2017.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
5
|
Mitchell PD and O'Byrne PM:
Epithelial-derived cytokines in asthma. Chest. 151:1338–1344.
2017.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
6
|
Zhang H, Sun Y, Rong W, Fan L, Cai Y, Qu
Q, Gao Y and Zhao H: miR-221 participates in the airway epithelial
cells injury in asthma via targeting SIRT1. Exp Lung Res.
44:272–279. 2018.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
7
|
Kho AT, McGeachie MJ, Moore KG, Sylvia JM,
Weiss ST and Tantisira KG: Circulating microRNAs and prediction of
asthma exacerbation in childhood asthma. Respir Res.
19(128)2018.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
8
|
Lam JK, Chow MY, Zhang Y and Leung SW:
siRNA versus miRNA as therapeutics for gene silencing. Mol Ther
Nucleic Acids. 4(e252)2015.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
9
|
Ong J, Timens W, Rajendran V, Algra A,
Spira A, Lenburg ME, Campbell JD, van den Berge M, Postma DS, van
den Berg A, et al: Identification of transforming growth
factor-beta-regulated microRNAs and the microRNA-targetomes in
primary lung fibroblasts. PLoS One. 12(e0183815)2017.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
10
|
Kivihall A, Aab A, Soja J, Sładek K, Sanak
M, Altraja A, Jakiela B, Bochenek G and Rebane A: Reduced
expression of miR-146a in human bronchial epithelial cells alters
neutrophil migration. Clin Transl Allergy. 9(62)2019.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
11
|
Liu Z, Zhang XH, Callejas-Diaz B and
Mullol J: MicroRNA in United airway diseases. Int J Mol Sci.
17(716)2016.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
12
|
Svitich OA, Sobolev VV, Gankovskaya LV,
Zhigalkina PV and Zverev VV: The role of regulatory RNAs (miRNAs)
in asthma. Allergol Immunopathol (Madr). 46:201–205.
2018.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
13
|
Taka S, Tzani-Tzanopoulou P, Wanstall H
and Papadopoulos NG: MicroRNAs in asthma and respiratory
infections: Identifying common pathways. Allergy Asthma Immunol
Res. 12:4–23. 2020.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
14
|
Tang X, Wu F, Fan J, Jin Y, Wang J and
Yang G: Posttranscriptional regulation of interleukin-33 expression
by MicroRNA-200 in bronchial asthma. Mol Ther. 26:1808–1817.
2018.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
15
|
Lustri BC, Sperandio V and Moreira CG:
Bacterial chat: Intestinal metabolites and signals in
host-microbiota-pathogen interactions. Infect Immun. 85:e00476–17.
2017.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
16
|
Tuddenham S and Sears CL: The intestinal
microbiome and health. Curr Opin Infect Dis. 28:464–470.
2015.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
17
|
Wang G, Huang S, Wang Y, Cai S, Yu H, Liu
H, Zeng X, Zhang G and Qiao S: Bridging intestinal immunity and gut
microbiota by metabolites. Cell Mol Life Sci. 76:3917–3937.
2019.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
18
|
Ver Heul A, Planer J and Kau AL: The human
microbiota and asthma. Clin Rev Allergy Immunol. 57:350–363.
2019.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
19
|
Xu Z, Tao J, Chen P, Chen L, Sharma S,
Wang G and Dong Q: Sodium butyrate inhibits colorectal cancer cell
migration by downregulating Bmi-1 through enhanced miR-200c
expression. Mol Nutr Food Res. 62(e1700844)2018.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
20
|
Livak KJ and Schmittgen TD: Analysis of
relative gene expression data using real-time quantitative PCR and
the 2(-Delta Delta C(T)) method. Methods. 25:402–408.
2001.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
21
|
Choi JY, Lee HY, Hur J, Kim KH, Kang JY,
Rhee CK and Lee SY: TRPV1 blocking alleviates airway inflammation
and remodeling in a chronic asthma murine model. Allergy Asthma
Immunol Res. 10:216–224. 2018.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
22
|
Jie Z, Xia H, Zhong SL, Feng Q, Li S,
Liang S, Zhong H, Liu Z, Gao Y, Zhao H, et al: The gut microbiome
in atherosclerotic cardiovascular disease. Nat Commun.
8(845)2017.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
23
|
Mangiola F, Ianiro G, Franceschi F,
Fagiuoli S, Gasbarrini G and Gasbarrini A: Gut microbiota in autism
and mood disorders. World J Gastroenterol. 22:361–368.
2016.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
24
|
Dong J, Tai JW and Lu LF: miRNA-microbiota
interaction in gut homeostasis and colorectal cancer. Trends
Cancer. 5:666–669. 2019.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
25
|
Liu S, da Cunha AP, Rezende RM, Cialic R,
Wei Z, Bry L, Comstock LE, Gandhi R and Weiner HL: The host shapes
the gut microbiota via fecal MicroRNA. Cell Host Microbe. 19:32–43.
2016.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
26
|
Teng Y, Ren Y, Sayed M, Hu X, Lei C, Kumar
A, Hutchins E, Mu J, Deng Z, Luo C, et al: Plant-derived exosomal
MicroRNAs shape the gut microbiota. Cell Host Microbe.
24:637–652.e8. 2018.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
27
|
Chang CS and Kao CY: Current understanding
of the gut microbiota shaping mechanisms. J Biomed Sci.
26(59)2019.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
28
|
Bartel S, Schulz N, Alessandrini F,
Schamberger AC, Pagel P, Theis FJ, Milger K, Noessner E, Stick SM,
Kicic A, et al: Pulmonary microRNA profiles identify involvement of
Creb1 and Sec14l3 in bronchial epithelial changes in allergic
asthma. Sci Rep. 7(46026)2017.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
29
|
Martinez-Nunez RT, Rupani H, Platé M,
Niranjan M, Chambers RC, Howarth PH and Sanchez-Elsner T:
Genome-wide posttranscriptional dysregulation by MicroRNAs in human
asthma as revealed by frac-seq. J Immunol. 201:251–263.
2018.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
30
|
Danarto R, Astuti I, Umbas R and Haryana
SM: Urine miR-21-5p and miR-200c-3p as potential non-invasive
biomarkers in patients with prostate cancer. Turk J Urol. 46:26–30.
2019.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
31
|
Maolakuerban N, Azhati B, Tusong H, Abula
A, Yasheng A and Xireyazidan A: MiR-200c-3p inhibits cell migration
and invasion of clear cell renal cell carcinoma via regulating
SLC6A1. Cancer Biol Ther. 19:282–291. 2018.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
32
|
Bowman B: FADD and its phosphorylation
mediate mitogenic signaling in mutant Kras tumors, 2015.
|
|
33
|
Fan S, Sun JB, Li R, Song X and Li J:
Lycopene protects myocardial ischemia injury through anti-apoptosis
and anti-oxidative stress. Eur Rev Med Pharmacol Sci. 23:3096–3104.
2019.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|