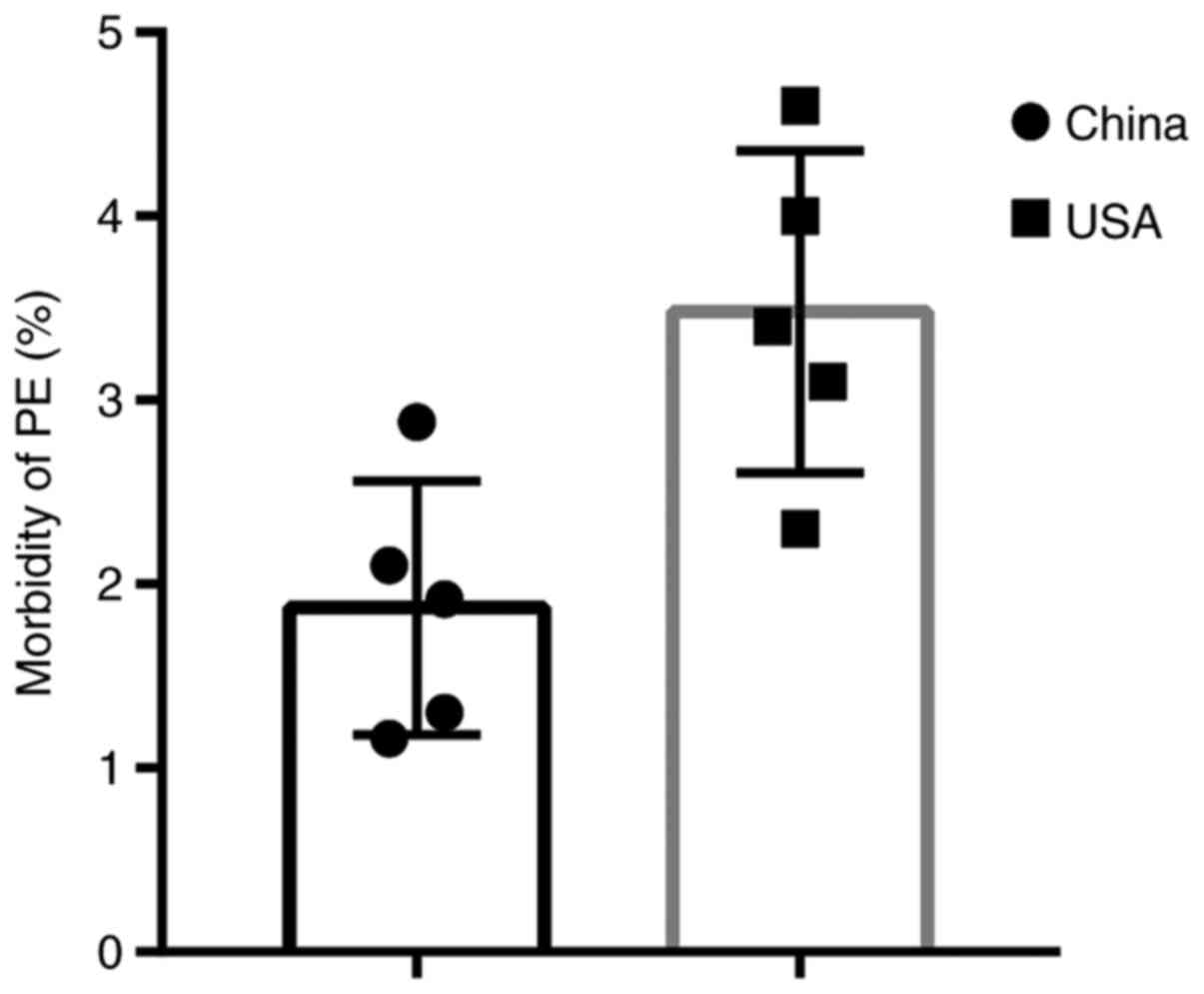
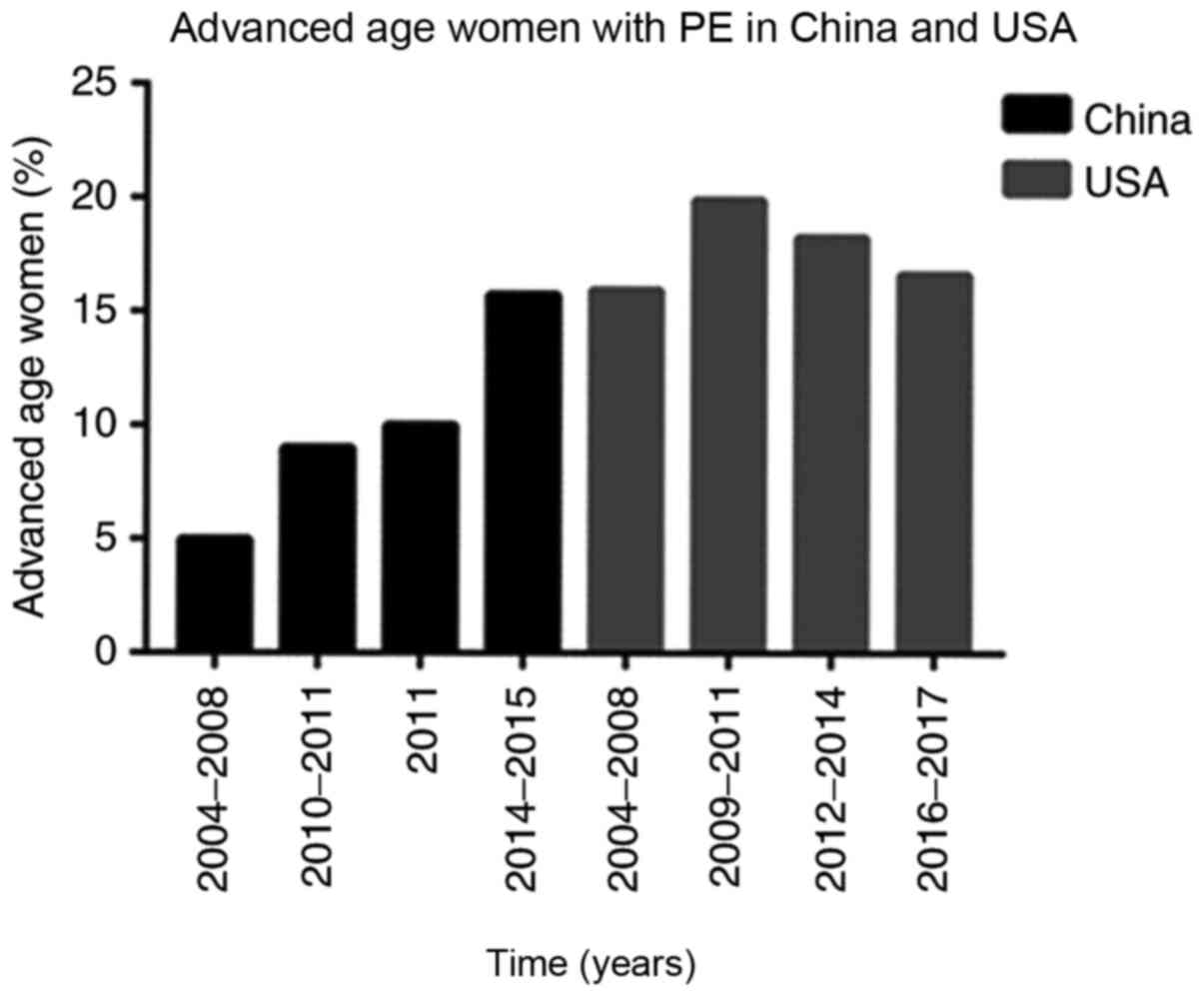
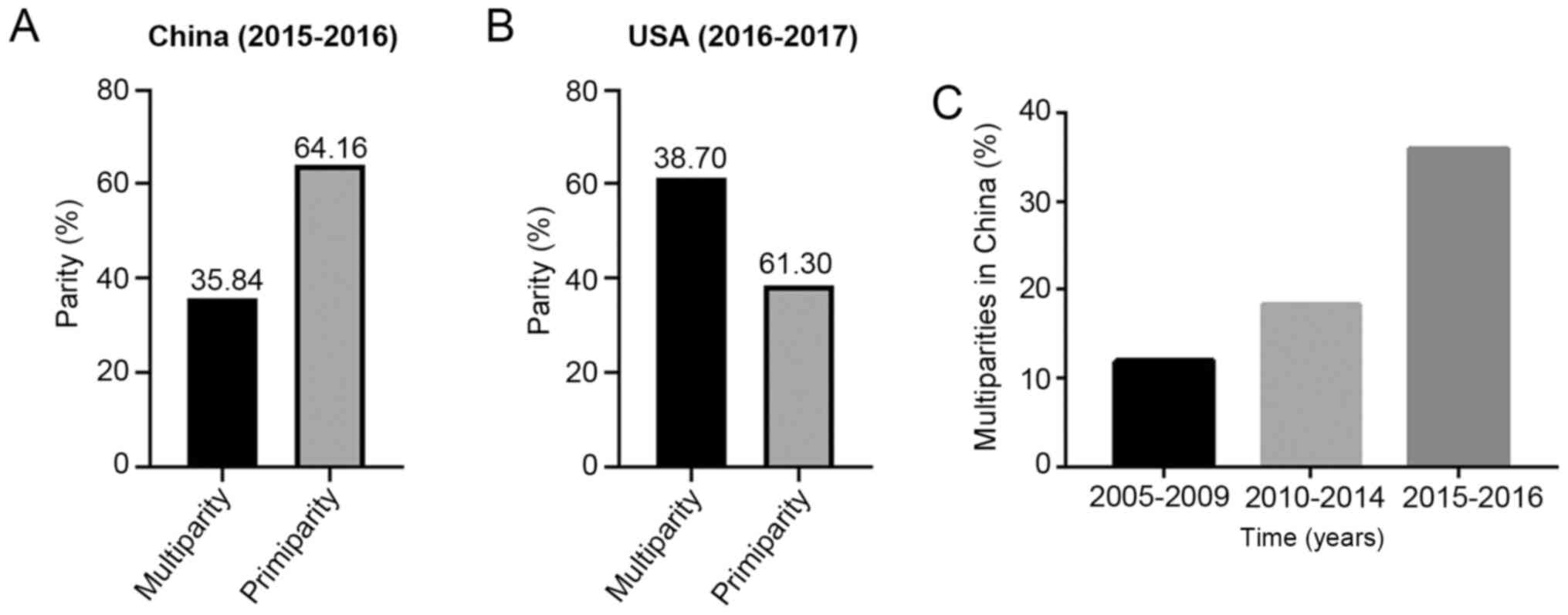
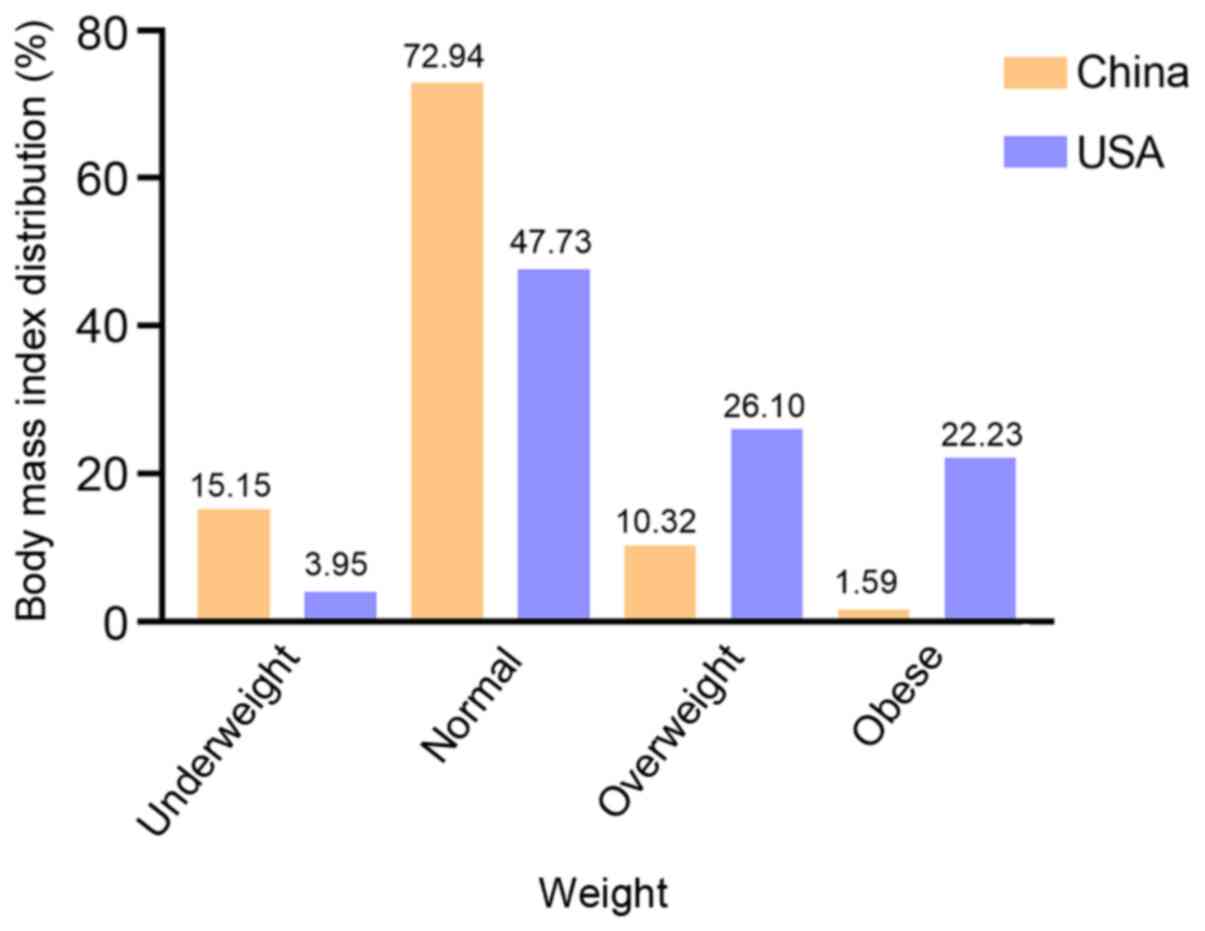
|
1
|
Rana S, Lemoine E, Granger JP and
Karumanchi SA: Preeclampsia: Pathophysiology, challenges, and
perspectives. Circ Res. 124:1094–1112. 2019.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
2
|
Jackson SP, Darbousset R and Schoenwaelder
SM: Thromboinflammation: Challenges of therapeutically targeting
coagulation and other host defense mechanisms. Blood. 133:906–918.
2019.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
3
|
Coutinho T, Lamai O and Nerenberg K:
Hypertensive disorders of pregnancy and cardiovascular diseases:
Current knowledge and future directions. Curr Treat Options
Cardiovasc Med. 20(56)2018.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
4
|
Poon LC, Shennan A, Hyett JA, Kapur A,
Hadar E, Divakar H, McAuliffe F, da Silva Costa F, von Dadelszen P,
McIntyre HD, et al: The international federation of gynecology and
obstetrics (FIGO) initiative on pre-eclampsia: A pragmatic guide
for first-trimester screening and prevention. Int J Gynaecol
Obstet. 145 (Suppl 1):S1–S33. 2019.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
5
|
Dymara-Konopka W, Laskowska M and
Oleszczuk J: Preeclampsia-current management and future approach.
Curr Pharm Biotechnol. 19:786–796. 2018.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
6
|
Osungbade KO and Ige OK: Public health
perspectives of preeclampsia in developing countries: Implication
for health system strengthening. J Pregnancy.
2011(481095)2011.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
7
|
American College of Obstetricians and Gy
ETM_16253_261205_Shi necologists. Gestational hypertension and
preeclampsia: ACOG Practice Bulletin, number 222. Obstet Gynecol.
135:e237–e260. 2020.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
8
|
Fasanya HO, Hsiao CJ, Armstrong-Sylvester
KR and Beal SG: A critical review on the use of race in
understanding racial disparities in preeclampsia. J Appl Lab Med.
6:247–256. 2021.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
9
|
ACOG Practice Bulletin No. 202 Summary.
Gestational Hypertension and Preeclampsia. Obstet Gynecol.
133(1)2019.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
10
|
Umesawa M and Kobashi G: Epidemiology of
hypertensive disorders in pregnancy: Prevalence, risk factors,
predictors and prognosis. Hypertens Res. 40:213–220.
2017.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
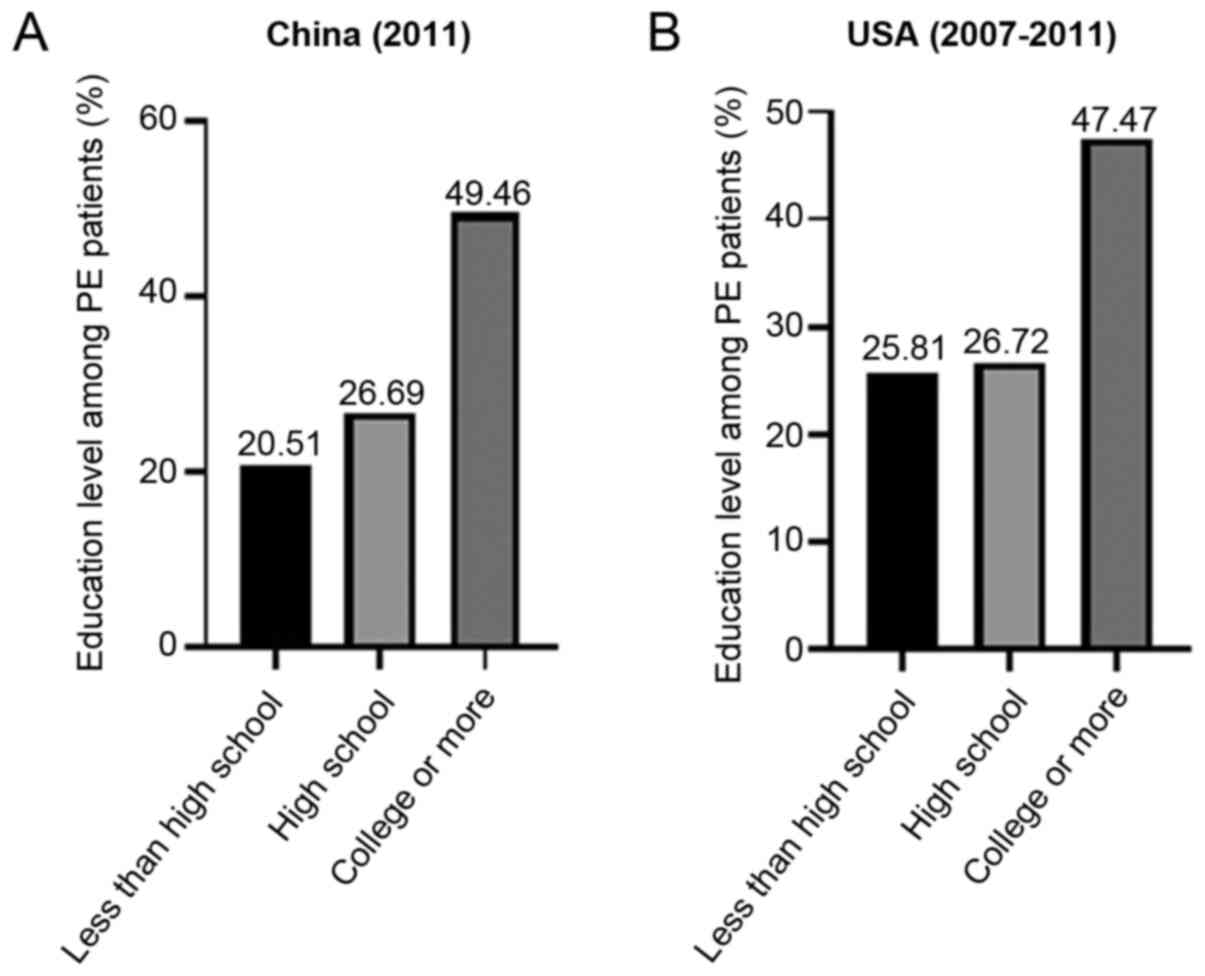
|
|
11
|
Xiao J, Shen F, Xue Q, Chen G, Zeng K,
Stone P, Zhao M and Chen Q: Is ethnicity a risk factor for
developing preeclampsia? An analysis of the prevalence of
preeclampsia in China. J Hum Hypertens. 28:694–698. 2014.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
12
|
Ye C, Ruan Y, Zou L, Li G, Li C, Chen Y,
Jia C, Megson IL, Wei J and Zhang W: The 2011 survey on
hypertensive disorders of pregnancy (HDP) in China: Prevalence,
risk factors, complications, pregnancy and perinatal outcomes. PLoS
One. 9(e100180)2014.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
13
|
Wang Q, Zhang H, Liang Q, Knibbs LD, Ren
M, Li C, Bao J, Wang S, He Y, Zhu L, et al: Effects of prenatal
exposure to air pollution on preeclampsia in Shenzhen, China.
Environ Pollut. 237:18–27. 2018.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
14
|
Wang C, Lin L, Su R, Zhu W, Wei Y, Yan J,
Feng H, Li B, Li S and Yang H: Hemoglobin levels during the first
trimester of pregnancy are associated with the risk of gestational
diabetes mellitus, pre-eclampsia and preterm birth in Chinese
women: A retrospective study. BMC Pregnancy Childbirth.
18(263)2018.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
15
|
Ananth CV, Keyes KM and Wapner RJ:
Pre-eclampsia rates in the United States, 1980-2010:
Age-period-cohort analysis. BMJ. 347(f6564)2013.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
16
|
Abalos E, Cuesta C, Grosso AL, Chou D and
Say L: Global and regional estimates of preeclampsia and eclampsia:
A systematic review. Eur J Obstet Gynecol Reprod Biol. 170:1–7.
2013.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
17
|
Marić I, Mayo JA, Druzin ML, Wong RJ, Winn
VD, Stevenson DK and Shaw GM: Maternal height and risk of
preeclampsia among race/ethnic groups. Am J Perinatol. 36:864–871.
2019.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
18
|
Khandwala YS, Baker VL, Shaw GM, Stevenson
DK, Lu Y and Eisenberg ML: Association of paternal age with
perinatal outcomes between 2007 and 2016 in the United States:
Population based cohort study. BMJ. 363(k4372)2018.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
19
|
Armaly Z, Jadaon JE, Jabbour A and Abassi
ZA: Preeclampsia: Novel mechanisms and potential therapeutic
approaches. Front Physiol. 9(973)2018.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
20
|
Lou WZ, Jiang F, Hu J, Chen XX, Song YN,
Zhou XY, Liu JT, Bian XM and Gao JS: Maternal serum angiogenic
factor sFlt-1 to PlGF ratio in preeclampsia: A useful marker for
differential diagnosis and prognosis evaluation in chinese women.
Dis Markers. 2019(6270187)2019.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
21
|
Leon LJ, McCarthy FP, Direk K,
Gonzalez-Izquierdo A, Prieto-Merino D, Casas JP and Chappell L:
Preeclampsia and cardiovascular disease in a large UK pregnancy
cohort of linked electronic health records: A CALIBER Study.
Circulation. 140:1050–1060. 2019.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
22
|
Khalil A, Rezende J, Akolekar R, Syngelaki
A and Nicolaides KH: Maternal racial origin and adverse pregnancy
outcome: A cohort study. Ultrasound Obstet Gynecol. 41:278–285.
2013.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
23
|
Kang Q, Li W, Xiao J, Yu N, Fan L, Sha M,
Ma S, Wu J and Chen S: Integrated analysis of multiple microarray
studies to identify novel gene signatures in preeclampsia.
Placenta. 105:104–118. 2021.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
24
|
English FA, Kenny LC and McCarthy FP: Risk
factors and effective management of preeclampsia. Integr Blood
Press Control. 8:7–12. 2015.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
25
|
Steegers EA, Von DP, Duvekot JJ and
Pijnenborg R: Pre-eclampsia. Lancet. 376:631–644. 2010.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
26
|
Rana S, Karumanchi SA and Lindheimer MD:
Angiogenic factors in diagnosis, management, and research in
preeclampsia. Hypertension. 63:198–202. 2014.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
27
|
Jebbink J, Wolters A, Fernando F, Afink G,
van der Post J and Ris-Stalpers C: Molecular genetics of
preeclampsia and HELLP syndrome-A review. Biochim Biophys Acta.
1822:1960–1969. 2012.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
28
|
Liu B, Li Y, Yao Y, Li H, Liang H, Xin M,
Wang L, Zhao L, Lin J and Liu S: Polymorphisms of the IL27 gene in
a Chinese Han population complicated with pre-eclampsia. Sci Rep.
6(23029)2016.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
29
|
Ren R, Gao M, Fan P, Liu X, Liu R, Ma L,
Chen Y, Liu Y and Bai H: Association study between-765G>C and
-1195G>A functional polymorphisms in the cyclooxygenase 2 gene
and risk of preeclampsia. Zhonghua Yi Xue Yi Chuan Xue Za Zhi.
32:245–249. 2015.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar : (In Chinese).
|
|
30
|
Rivers ER, Horton AJ, Hawk AF, Favre EG,
Senf KM, Nietert PJ, Chang EY, Foley AC, Robinson CJ and Lee KH:
Placental Nkx2-5 and target gene expression in early-onset and
severe preeclampsia. Hypertens Pregnancy. 33:412–426.
2014.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
31
|
Best LG, Saxena R, Anderson CM, Barnes MR,
Hakonarson H, Falcon G, Martin C, Castillo BA, Karumanchi A, Keplin
K, et al: Two variants of the C-reactive protein gene are
associated with risk of pre-eclampsia in an American Indian
population. PLoS One. 8(e71231)2013.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
32
|
Best LG, Balakrishnan P, Cole SA, Haack K,
Kocarnik JM, Pankratz N, Anderson MZ, Franceschini N, Howard BV,
Lee ET, et al: Genetic analysis of hsCRP in American Indians: The
strong heart family study. PLoS One. 14(e0223574)2019.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
33
|
Dior UP, Laufer N, Chill HH,
Granovsky-Grisaru S, Yagel S, Yaffe H and Gielchinsky Y: Increased
incidence of preeclampsia in mothers of advanced age conceiving by
oocyte donation. Arch Gynecol Obstet. 297:1293–1299.
2018.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
34
|
Fikadu K, F GM, Getahun F, Chufamo N and
Misiker D: Determinants of pre-eclampsia among pregnant women
attending perinatal care in hospitals of the Omo district, Southern
Ethiopia. J Clin Hypertens (Greenwich). 23:153–162. 2020.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
35
|
Lagerweij GR, Brouwers L, De Wit GA, Moons
K, Benschop L, Maas A, Franx A, Wermer M, Roeters van Lennep JE,
van Rijn BB and Koffijberg H: Impact of preventive screening and
lifestyle interventions in women with a history of preeclampsia: A
micro-simulation study. Eur J Prev Cardiol. 27:1389–1399.
2020.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
36
|
Delnord M, Mortensen L, Hindori-Mohangoo
AD, Blondel B, Gissler M, Kramer MR, Richards JL, Deb-Rinker P,
Rouleau J, Morisaki N, et al: International variations in the
gestational age distribution of births: An ecological study in 34
high-income countries. Eur J Public Health. 28:303–309.
2018.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
37
|
Best LG, Saxena R, Anderson CM, Barnes MR,
Hakonarson H, Falcon G, Martin C, Castillo BA, Karumanchi A, Keplin
K, et al: Correction: Two Variants of the C-Reactive Protein Gene
Are Associated with Risk of Pre-Eclampsia in an American Indian
Population. PLOS One. 8(e71231)2013.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
38
|
Marozio L, Picardo E, Filippini C,
Mainolfi E, Berchialla P, Cavallo F, Tancredi A and Benedetto C:
Maternal age over 40 years and pregnancy outcome: A hospital-based
survey. J Matern Fetal Neonatal Med. 32:1602–1608. 2019.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
39
|
Ogawa K, Urayama KY, Tanigaki S, Sago H,
Sato S, Saito S and Morisaki N: Association between very advanced
maternal age and adverse pregnancy outcomes: A cross sectional
Japanese study. BMC Pregnancy Childbirth. 17(349)2017.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
40
|
Khalil A, Syngelaki A, Maiz N, Zinevich Y
and Nicolaides KH: Maternal age and adverse pregnancy outcome: A
cohort study. Ultrasound Obstet Gynecol. 42:634–643.
2013.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
41
|
Bréart G, Barros H, Wagener Y and Prati S:
Characteristics of the childbearing population in Europe. Eur J
Obstet Gynecol Reprod Biol. 111 (Suppl 1):S45–S52. 2003.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
42
|
Mathews TJ and Hamilton BE: Mean age of
mothers is on the rise: United States, 2000-2014. NCHS Data Brief.
232:1–8. 2016.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
43
|
Lu L, Qu Y, Tang J, Chen D, Chen D and Mu
D: Risk factors associated with late preterm births in the
underdeveloped region of China: A cohort study and systematic
review. Taiwan J Obstet Gynecol. 54:647–653. 2015.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
44
|
Laopaiboon M, Lumbiganon P, Intarut N,
Mori R, Ganchimeg T, Vogel JP, Souza JP and Gülmezoglu AM: WHO
Multicountry Survey on Maternal Newborn Health Research Network.
Advanced maternal age and pregnancy outcomes: A multicountry
assessment. BJOG. 121 (Suppl 1):S49–S56. 2014.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
45
|
Liu X, Ruan Y, Liu Y and Zhang W:
Relationship between maternal age and hypertensive disorders in
pregnancy. Zhonghua Yi Xue Za Zhi. 95:19–22. 2015.PubMed/NCBI(In Chinese).
|
|
46
|
Zhao RF, Zhou L and Zhang WY: Identifying
appropriate pre-pregnancy body mass index classification to improve
pregnancy outcomes in women of childbearing age in Beijing, China:
A retrospective cohort study. Asia Pac J Clin Nutr. 28:567–576.
2019.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
47
|
Sheen JJ, Huang Y, Andrikopoulou M, Wright
JD, Goffman D, D'Alton ME and Friedman AM: Maternal age and
preeclampsia outcomes during delivery hospitalizations. Am J
Perinatol. 37:44–52. 2019.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
48
|
deJongh BE, Paul DA, Hoffman M and Locke
R: Effects of pre-pregnancy obesity, race/ethnicity and
prematurity. Matern Child Health J. 18:511–517. 2014.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
49
|
Liu B, Xu G, Sun Y, Du Y, Gao R,
Snetselaar LG, Santillan MK and Bao W: Association between maternal
pre-pregnancy obesity and preterm birth according to maternal age
and race or ethnicity: A population-based study. Lancet Diabetes
Endocrinol. 7:707–714. 2019.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
50
|
Luo ZC, An N, Xu HR, Larante A, Audibert F
and Fraser WD: The effects and mechanisms of primiparity on the
risk of pre-eclampsia: A systematic review. Paediatr Perinat
Epidemiol. 21 (Suppl 1):S36–S45. 2007.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
51
|
Hernandez-Diaz S, Toh S and Cnattingius S:
Risk of pre-eclampsia in first and subsequent pregnancies:
Prospective cohort study. BMJ. 338(b2255)2009.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
52
|
Zheng Y, Ma C, Liu X, Wu S, Zhang W and
Zhao S: Association between HLA-A gene polymorphism and early-onset
preeclampsia in Chinese pregnant women early-onset. BMC Preg
Childbirth. 20(656)2020.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
53
|
Kenny LC and Kell DB: Immunological
tolerance, pregnancy, and preeclampsia: The roles of semen microbes
and the father. Front Med. 4(239)2017.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
54
|
Tran PL, Robillard PY, Dumont C, Schweizer
C, Omarjee A, Iacobelli S and Boukerrou M: Recurrent or first
preeclampsia in multiparae: A case-control study of singleton
pregnancies in Reunion Island. Eur J Obstet Gynecol Reprod Biol.
240:80–86. 2019.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
55
|
Xie M, Lao TT, Du M, Sun Q, Qu Z, Ma J,
Song X, Wang M, Xu D and Ma R: Risk for Cesarean section in women
of advanced maternal age under the changed reproductive policy in
China: A cohort study in a tertiary hospital in southwestern China.
J Obstet Gynaecol Res. 45:1866–1875. 2019.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
56
|
Kenny LC and Kell DB: Immunological
tolerance, pregnancy and pre-eclampsia: The roles of semen microbes
and the father. Front Med (Lausanne). 4(239)2017.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
57
|
Broughton Pipkin F: Risk factors for
preeclampsia. N Engl J Med. 344:925–926. 2001.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
58
|
Weir CB and Jan A: BMI Classification
Percentile And Cut Off Points. In: Stat Pearls Publishing
Copyright© 2020. Stat Pearls Publishing LLC, Treasure
Island, FL, 2020.
|
|
59
|
Lopez-Jaramillo P, Barajas J,
Rueda-Quijano SM, Lopez-Lopez C and Felix C: Obesity and
Preeclampsia: Common pathophysiological mechanisms. Front Physiol.
9(1838)2018.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
60
|
He XJ, Dai RX and Hu CL: Maternal
prepregnancy overweight and obesity and the risk of preeclampsia: A
meta-analysis of cohort studies. Obesity Res Clin Pract. 14:27–33.
2020.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
61
|
Ives CW, Sinkey R, Rajapreyar I, Tita ATN
and Oparil S: Preeclampsia-pathophysiology and clinical
presentations: JACC state-of-the-art review. J Am Coll Cardiol.
76:1690–1702. 2020.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
62
|
Ratnasiri AWG, Lee HC, Lakshminrusimha S,
Parry SS, Arief VN, DeLacy IH, Yang JS, DiLibero RJ, Logan J and
Basford KE: Trends in maternal prepregnancy body mass index (BMI)
and its association with birth and maternal outcomes in California,
2007-2016: A retrospective cohort study. PLoS One.
14(e0222458)2019.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
63
|
Cao Y, Liu Y, Zhao X, Duan D, Dou W, Fu W,
Chen H, Bo Y, Qiu Y, Chen G and Lyu Q: Adherence to a dietary
approaches to stop hypertension (DASH)-style diet in relation to
preeclampsia: A case-control study. Sci Rep.
10(9078)2020.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
64
|
Dasinger JH, Abais-Battad JM and Mattson
DL: Influences of environmental factors during preeclampsia. Am J
Physiol. 319:R26–R32. 2020.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
65
|
Mi B, Wen X, Li S, Liu D, Lei F, Liu R,
Shen Y, Chen Y, Zeng L, Liu X, et al: Vegetable dietary pattern
associated with low risk of preeclampsia possibly through reducing
proteinuria. Preg Hypertens. 16:131–138. 2019.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
66
|
Hofmeyr GJ, Betrán AP, Singata-Madliki M,
Cormick G, Munjanja SP, Fawcus S, Mose S, Hall D, Ciganda A, Seuc
AH, et al: Prepregnancy and early pregnancy calcium supplementation
among women at high risk of pre-eclampsia: A multicentre,
double-blind, randomised, placebo-controlled trial. Lancet.
393:330–339. 2019.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
67
|
Dekker GA: Risk factors for preeclampsia.
Clin Obstet Gynecol. 42:422–435. 1999.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
68
|
Ikem E, Halldorsson TI, Birgisdóttir BE,
Rasmussen MA, Olsen SF and Maslova E: Dietary patterns and the risk
of pregnancy-associated hypertension in the Danish National Birth
Cohort: A prospective longitudinal study. BJOG. 126:663–667.
2019.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
69
|
Syngelaki A, Sequeira Campos M, Roberge S,
Andrade W and Nicolaides KH: Diet and exercise for preeclampsia
prevention in overweight and obese pregnant women: Systematic
review and meta-analysis. J Matern Fetal Neonatal Med.
32:3495–3501. 2019.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
70
|
Ersbøll AS, Bojer AS, Hauge MG, Johansen
M, Damm P, Gustafsson F and Vejlstrup NG: Long-term cardiac
function after peripartum cardiomyopathy and preeclampsia: A danish
nationwide, clinical follow-up study using maximal exercise testing
and cardiac magnetic resonance imaging. J Am Heart Assoc.
7(e008991)2018.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
71
|
Cordero C, Windham GC, Schieve LA, Fallin
MD, Croen LA, Siega-Riz AM, Engel SM, Herring AH, Stuebe AM,
Vladutiu CJ and Daniels JL: Maternal diabetes and hypertensive
disorders in association with autism spectrum disorder. Autism Res.
12:967–975. 2019.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
72
|
Bahmanpour S: Guideline: Calcium
Supplementation in Pregnant Women. Geneva Switzerland Who. 6:61–92.
2013.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
73
|
Awad MA, Hasanin ME, Taha MM and Gabr AA:
Effect of stretching exercises versus autogenic training on
preeclampsia. J Exerc Rehabil. 15:109–113. 2019.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
74
|
Skow RJ, King EC, Steinback CD and
Davenport MH: The influence of prenatal exercise and pre-eclampsia
on maternal vascular function. Clin Sci. 131:2223–2240.
2017.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
75
|
Genest DS, Falcao S, Gutkowska J and
Lavoie JL: Impact of exercise training on preeclampsia potential
preventive mechanisms. Hypertension. 60:1104–1109. 2012.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
76
|
Qi HB: Diagnosis and management of
preeclampsia: Need for standardization. Chin J Perinatal Med.
18:411–413. 2015.(In Chinese).
|
|
77
|
Gu WR and Li XT: Intervention and
management of preeclampsia. Chin J Appl Gynecol Obstet. 36:29–32.
2020.(In Chinese).
|
|
78
|
Karlsen S, Say L, Souza JP, Hogue CJ,
Calles DL, Gülmezoglu AM and Raine R: The relationship between
maternal education and mortality among women giving birth in health
care institutions: Analysis of the cross sectional WHO Global
Survey on Maternal and Perinatal Health. BMC Public Health.
11(606)2011.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
79
|
Jim B and Karumanchi SA: Preeclampsia:
Pathogenesis, prevention, and long-term complications. Semin
Nephrol. 37:386–397. 2017.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
80
|
Atallah A, Lecarpentier E, Goffinet F,
Doret-Dion M, Gaucherand P and Tsatsaris V: Aspirin for prevention
of preeclampsia. Drugs. 77:1819–1831. 2017.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
81
|
Poon LC, Wright D, Rolnik DL, Syngelaki A,
Delgado JL, Tsokaki T, Leipold G, Akolekar R, Shearing S, De
Stefani L, et al: Aspirin for Evidence-Based Preeclampsia
Prevention trial: Effect of aspirin in prevention of preterm
preeclampsia in subgroups of women according to their
characteristics and medical and obstetrical history. Am J Obstet
Gynecol. 217:585.e1–585.e5. 2017.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
82
|
Zhang S, Ding Z, Liu H, Chen Z, Wu J,
Zhang Y and Yu Y: Association between mental stress and gestational
hypertension/preeclampsia: A meta-analysis. Obstet Gynecol Surv.
68:825–834. 2013.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
83
|
Korish AA: Magnesium sulfate therapy of
preeclampsia: An old tool with new mechanism of action and prospect
in management and prophylaxis. Hypertens Res. 35:1005–1011.
2012.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
84
|
Marić I, Mayo JA, Druzin ML, Druzin M,
Wong RJ, Winn VD, Stevenson DK and Shaw GM: Maternal height and
risk of preeclampsia among race/ethnic groups. Am J Perinatol.
36:864–871. 2019.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|