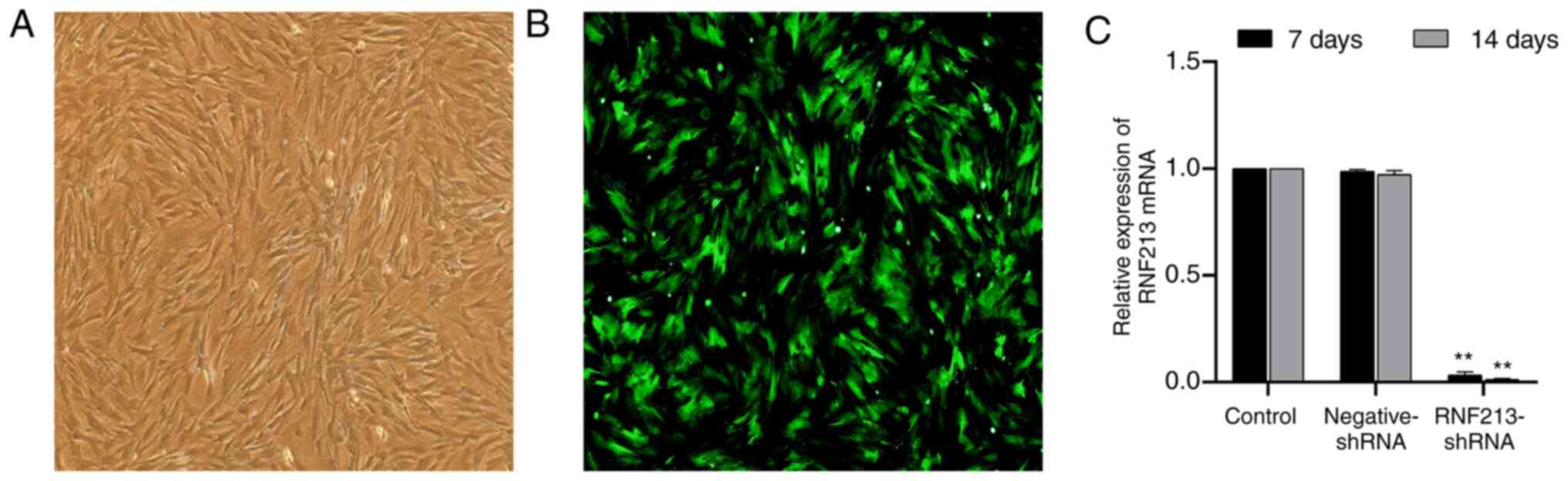
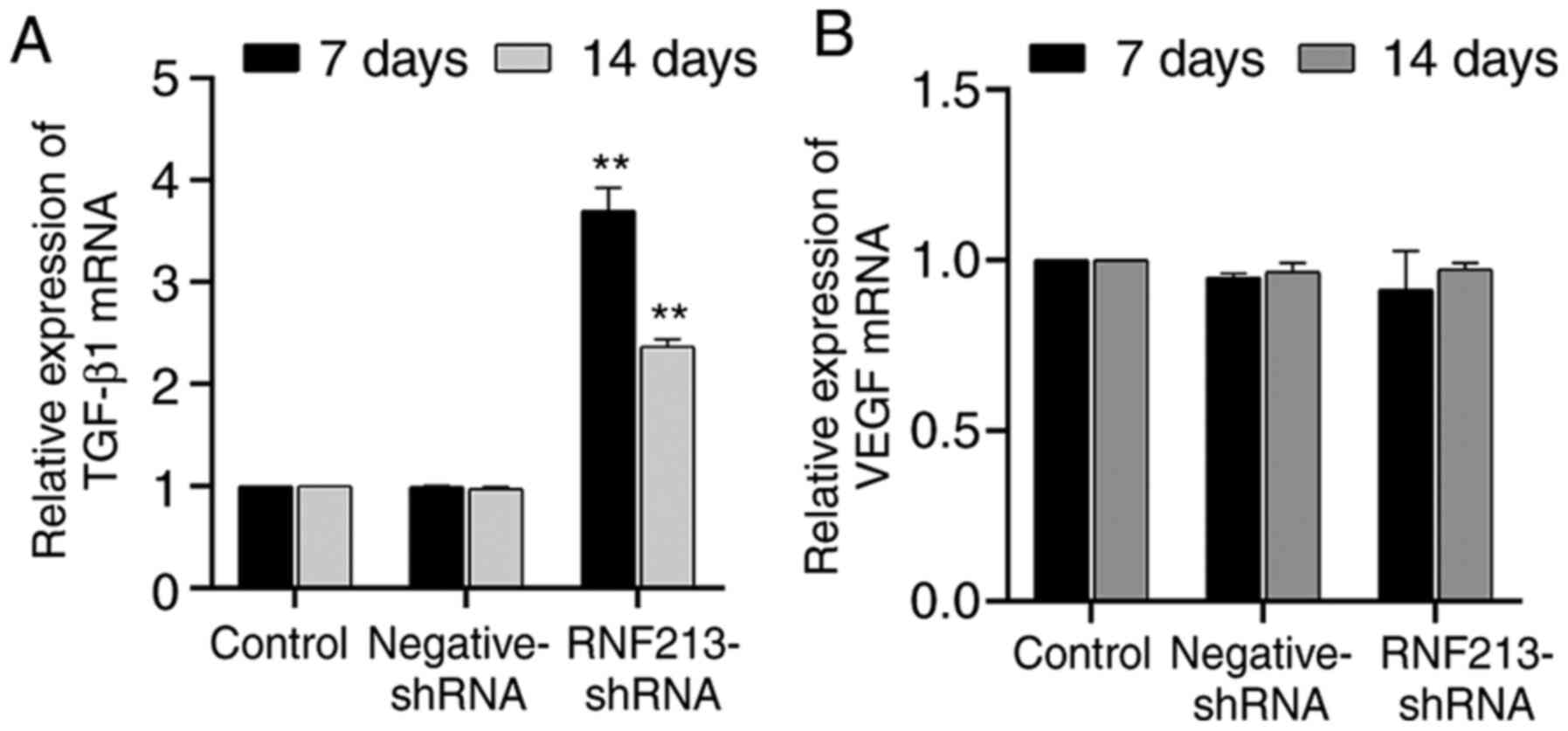
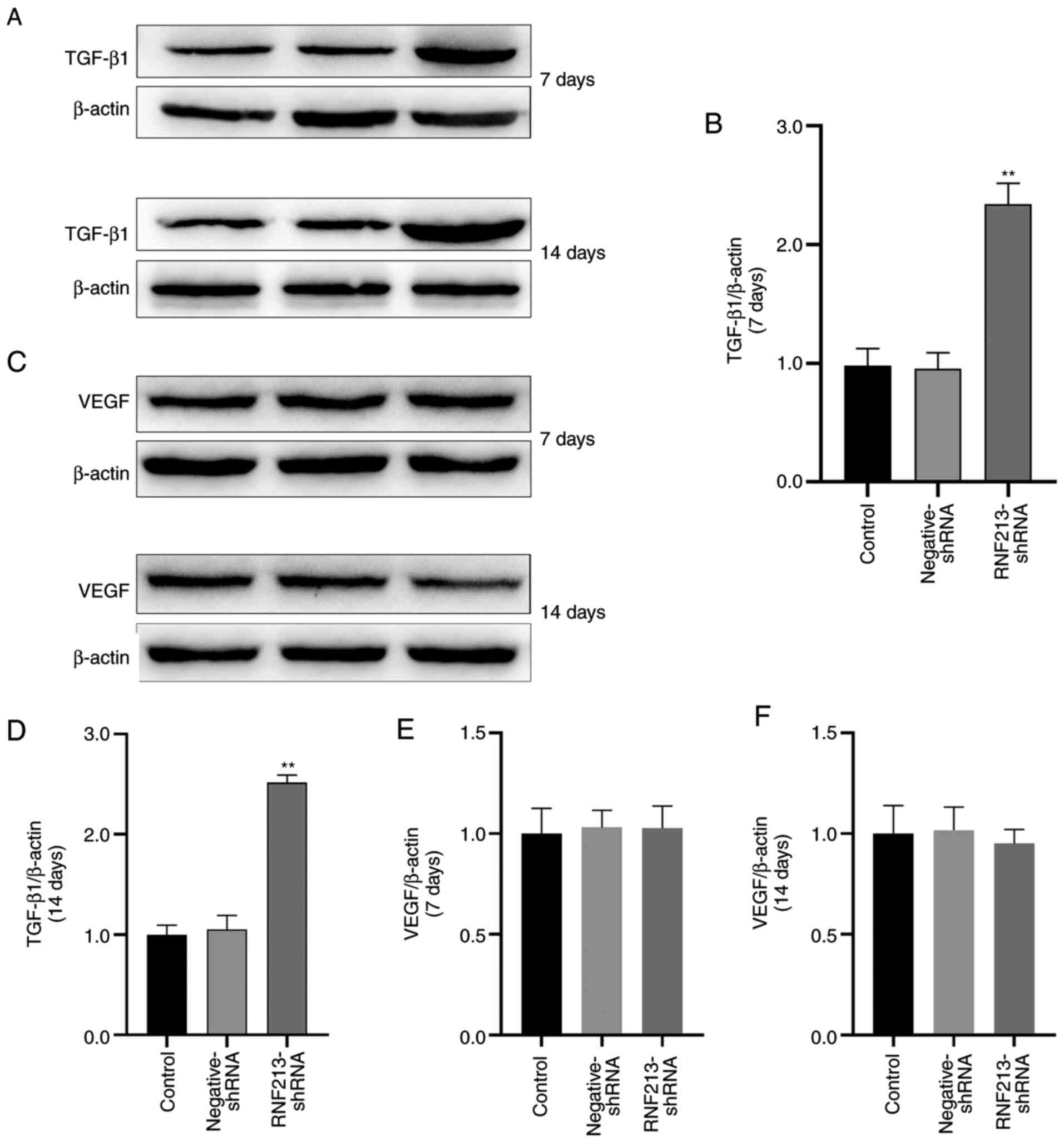
|
1
|
Suzuki J and Takaku A: Cerebrovascular
‘moyamoya’ disease. Disease showing abnormal net-like vessels in
base of brain. Arch Neurol. 20:288–299. 1969.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
2
|
Han W, Jin F, Zhang H, Yang M, Cui C, Wang
C and Jiang P: Association of Brain-Gut Peptides with Inflammatory
Cytokines in Moyamoya Disease. Mediators Inflamm.
2020(5847478)2020.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
3
|
Geng C, Cui C, Guo Y, Wang C, Zhang J, Han
W, Jin F, Chen D and Jiang P: Metabolomic Profiling Revealed
Potential Biomarkers in Patients With Moyamoya Disease. Front
Neurosci. 14(308)2020.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
4
|
Huang S, Guo Z, Shi M, Yang Y and Rao M:
Etiology and pathogenesis of Moyamoya Disease: An update on disease
prevalence. Int J Stroke. 12:246–253. 2017.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
5
|
Fang YC, Wei LF, Hu CJ and Tu YK:
Pathological Circulating Factors in Moyamoya Disease. Int J Mol
Sci. 22(22)2021.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
6
|
Kapoor S: The genetics of moyamoya
disease: Recent insights into the pathogenesis of the disease.
Neurosurgery. 72:E320–E321. 2013.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
7
|
Roder C, Nayak NR, Khan N, Tatagiba M,
Inoue I and Krischek B: Genetics of Moyamoya disease. J Hum Genet.
55:711–716. 2010.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
8
|
Yamauchi T, Tada M, Houkin K, Tanaka T,
Nakamura Y, Kuroda S, Abe H, Inoue T, Ikezaki K, Matsushima T, et
al: Linkage of familial moyamoya disease (spontaneous occlusion of
the circle of Willis) to chromosome 17q25. Stroke. 31:930–935.
2000.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
9
|
Sakurai K, Horiuchi Y, Ikeda H, Ikezaki K,
Yoshimoto T, Fukui M and Arinami T: A novel susceptibility locus
for moyamoya disease on chromosome 8q23. J Hum Genet. 49:278–281.
2004.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
10
|
Inoue TK, Ikezaki K, Sasazuki T,
Matsushima T and Fukui M: Linkage analysis of moyamoya disease on
chromosome 6. J Child Neurol. 15:179–182. 2000.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
11
|
Ikeda H, Sasaki T, Yoshimoto T, Fukui M
and Arinami T: Mapping of a familial moyamoya disease gene to
chromosome 3p24.2-p26. Am J Hum Genet. 64:533–537. 1999.PubMed/NCBI View
Article : Google Scholar
|
|
12
|
Kamada F, Aoki Y, Narisawa A, Abe Y,
Komatsuzaki S, Kikuchi A, Kanno J, Niihori T, Ono M, Ishii N, et
al: A genome-wide association study identifies RNF213 as the first
Moyamoya disease gene. J Hum Genet. 56:34–40. 2011.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
13
|
Wang X, Zhang Z, Liu W, Xiong Y, Sun W,
Huang X, Jiang Y, Ni G, Sun W, Zhou L, et al: Impacts and
interactions of PDGFRB, MMP-3, TIMP-2, and RNF213 polymorphisms on
the risk of Moyamoya disease in Han Chinese human subjects. Gene.
526:437–442. 2013.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
14
|
Ma J, Liu Y, Ma L, Huang S, Li H and You
C: RNF213 polymorphism and Moyamoya disease: A systematic review
and meta-analysis. Neurol India. 61:35–39. 2013.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
15
|
Wu Z, Jiang H, Zhang L, Xu X, Zhang X,
Kang Z, Song D, Zhang J, Guan M and Gu Y: Molecular analysis of
RNF213 gene for moyamoya disease in the Chinese Han population.
PLoS One. 7(e48179)2012.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
16
|
Liu W, Morito D, Takashima S, Mineharu Y,
Kobayashi H, Hitomi T, Hashikata H, Matsuura N, Yamazaki S, Toyoda
A, et al: Identification of RNF213 as a susceptibility gene for
moyamoya disease and its possible role in vascular development.
PLoS One. 6(e22542)2011.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
17
|
Togao O, Mihara F, Yoshiura T, Tanaka A,
Kuwabara Y, Morioka T, Matsushima T, Sasaki T and Honda H:
Prevalence of stenoocclusive lesions in the renal and abdominal
arteries in moyamoya disease. AJR Am J Roentgenol. 183:119–122.
2004.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
18
|
Koizumi A, Kobayashi H, Liu W, Fujii Y,
Senevirathna ST, Nanayakkara S, Okuda H, Hitomi T, Harada KH,
Takenaka K, et al: P.R4810K, a polymorphism of RNF213, the
susceptibility gene for moyamoya disease, is associated with blood
pressure. Environ Health Prev Med. 18:121–129. 2013.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
19
|
Liu S, Liu M, Li Q, Liu X, Wang Y, Mambiya
M, Zhang K, Yang L, Zhang Q, Shang M, et al: Association of single
nucleotide polymorphisms of MTHFR, TCN2, RNF213 with susceptibility
to hypertension and blood pressure. Biosci Rep.
39(39)2019.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
20
|
Nomura S, Aihara Y, Akagawa H, Chiba K,
Yamaguchi K, Kawashima A, Okada Y and Kawamata T: Can Moyamoya
Disease Susceptibility Gene Affect Extracranial Systemic Artery
Stenosis? J Stroke Cerebrovasc Dis. 29(104532)2020.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
21
|
Wang X, Wang Y, Nie F, Li Q, Zhang K, Liu
M, Yang L, Zhang Q, Liu S, Zeng F, et al: Association of Genetic
Variants With Moyamoya Disease in 13 000 Individuals: A
Meta-Analysis. Stroke. 51:1647–1655. 2020.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
22
|
Sun X, Luo M, Li J, Lai R, Lin J, Wang Y,
Xu X, Wu S and Sheng W: Prevalence of RNF213 variants in
symptomatic intracranial arterial stenosis/occlusion in China. Mol
Genet Genomics. 295:635–643. 2020.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
23
|
Wang Y, Zhang Z, Wei L, Zhang Q, Zou Z,
Yang L, Li D, Shang M, Han C, Mambiya M, et al: Predictive role of
heterozygous p.R4810K of RNF213in the phenotype of Chinese moyamoya
disease. Neurology. 94:e678–e686. 2020.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
24
|
Smith ER: Moyamoya Biomarkers. J Korean
Neurosurg Soc. 57:415–421. 2015.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
25
|
Hu JT, Luo J and Chen QX: The
Susceptibility Pathogenesis of Moyamoya Disease. World Neurosurg.
101:731–741. 2017.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
26
|
Zhang P, Xing C, Rhodes SD, He Y, Deng K,
Li Z, He F, Zhu C, Nguyen L, Zhou Y, et al: Loss of Asxl1 Alters
Self-Renewal and Cell Fate of Bone Marrow Stromal Cell, Leading to
Bohring-Opitz-like Syndrome in Mice. Stem Cell Reports. 6:914–925.
2016.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
27
|
Hu Y, Li X, Huang G, Wang J and Lu W:
Fasudil may induce the differentiation of bone marrow mesenchymal
stem cells into neuron like cells via the Wnt/β catenin pathway.
Mol Med Rep. 19:3095–3104. 2019.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
28
|
Kawanishi S, Takata K, Itezono S, Nagayama
H, Konoya S, Chisaki Y, Toda Y, Nakata S, Yano Y, Kitamura Y, et
al: Bone-Marrow-Derived Microglia-Like Cells Ameliorate Brain
Amyloid Pathology and Cognitive Impairment in a Mouse Model of
Alzheimer's Disease. J Alzheimers Dis. 64:563–585. 2018.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
29
|
Kinnaird T, Stabile E, Burnett MS, Lee CW,
Barr S, Fuchs S and Epstein SE: Marrow-derived stromal cells
express genes encoding a broad spectrum of arteriogenic cytokines
and promote in vitro and in vivo arteriogenesis through paracrine
mechanisms. Circ Res. 94:678–685. 2004.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
30
|
Zhu M, Chu Y, Shang Q, Zheng Z, Li Y, Cao
L, Chen Y, Cao J, Lee OK, Wang Y, et al: Mesenchymal stromal cells
pretreated with pro-inflammatory cytokines promote skin wound
healing through VEGFC-mediated angiogenesis. Stem Cells Transl Med.
9:1218–1232. 2020.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
31
|
Zheng Z, Zhang L, Qu Y, Xiao G, Li S, Bao
S, Lu QR and Mu D: Mesenchymal Stem Cells Protect Against
Hypoxia-Ischemia Brain Damage by Enhancing Autophagy Through Brain
Derived Neurotrophic Factor/Mammalin Target of Rapamycin Signaling
Pathway. Stem Cells. 36:1109–1121. 2018.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
32
|
Griessenauer CJ, Farrell S, Sarkar A, Zand
R, Abedi V, Holland N, Michael A, Cummings CL, Metpally R, Carey
DJ, et al: Genetic susceptibility to cerebrovascular disease: A
systematic review. J Cereb Blood Flow Metab. 38:1853–1871.
2018.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
33
|
Stienen MN, Smoll NR, Weisshaupt R,
Fandino J, Hildebrandt G, Studerus-Germann A and Schatlo B: Delayed
cerebral ischemia predicts neurocognitive impairment following
aneurysmal subarachnoid hemorrhage. World Neurosurg. 82:e599–e605.
2014.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
34
|
Baek HJ, Chung SY, Park MS, Kim SM, Park
KS and Son HU: Preliminary study of neurocognitive dysfunction in
adult moyamoya disease and improvement after superficial temporal
artery-middle cerebral artery bypass. J Korean Neurosurg Soc.
56:188–193. 2014.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
35
|
Li F, Zhang J, Liao R, Duan Y, Tao L, Xu Y
and Chen A: Mesenchymal stem cell derived extracellular vesicles
prevent neural stem cell hypoxia injury via promoting miR-210-3p
expression. Mol Med Rep. 22:3813–3821. 2020.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
36
|
Research Committee on the Pathology and
Treatment of Spontaneous Occlusion of the Circle of Willis; Health
Labour Sciences Research Grant for Research on Measures for
Infractable Diseases. Guidelines for diagnosis and treatment of
moyamoya disease (spontaneous occlusion of the circle of Willis).
Neurol Med Chir (Tokyo). 52:245–266. 2012.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
37
|
Livak KJ and Schmittgen TD: Analysis of
relative gene expression data using real-time quantitative PCR and
the 2(-Delta Delta C(T)) Method. Methods. 25:402–408.
2001.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
38
|
Fujimura M and Tominaga T: Significance of
Cerebral Blood Flow Analysis in the Acute Stage after
Revascularization Surgery for Moyamoya Disease. Neurol Med Chir
(Tokyo). 55:775–781. 2015.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
39
|
Lee JS, Hong JM, Moon GJ, Lee PH, Ahn YH
and Bang OY: STARTING collaborators. A long-term follow-up study of
intravenous autologous mesenchymal stem cell transplantation in
patients with ischemic stroke. Stem Cells. 28:1099–1106.
2010.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
40
|
Wakai K, Tamakoshi A, Ikezaki K, Fukui M,
Kawamura T, Aoki R, Kojima M, Lin Y and Ohno Y: Epidemiological
features of moyamoya disease in Japan: Findings from a nationwide
survey. Clin Neurol Neurosurg. 99 (Suppl 2):S1–S5. 1997.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
41
|
Baba T, Houkin K and Kuroda S: Novel
epidemiological features of moyamoya disease. J Neurol Neurosurg
Psychiatry. 79:900–904. 2008.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
42
|
Kuroda S and Houkin K: Moyamoya disease:
Current concepts and future perspectives. Lancet Neurol.
7:1056–1066. 2008.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
43
|
Mayeku J and Lopez-Gonzalez MA: Current
Surgical Options for Moyamoya Disease. Cureus.
12(e11332)2020.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
44
|
Yamada S, Oki K, Itoh Y, Kuroda S and
Suzuki N: Effects of Surgery and Antiplatelet Therapy in Ten-Year
Follow-Up from the Registry Study of Research Committee on Moyamoya
Disease in Japan. J Stroke Cerebrovasc Dis. 25:340–349.
2016.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
45
|
Arias EJ, Derdeyn CP, Dacey RG and Zipfel
GJ: Advances and surgical considerations in the treatment of
moyamoya disease. Neurosurgery. 74 (Suppl 1):S116–125.
2014.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
46
|
Tokairin K, Kazumata K, Gotoh S, Sugiyama
T and Kobayashi H: Neuroendoscope-Assisted Aneurysm Trapping for
Ruptured Intraventricular Aneurysms in Moyamoya Disease Patients.
World Neurosurg. 141:278–283. 2020.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
47
|
Kang HS, Kim JH, Phi JH, Kim YY, Kim JE,
Wang KC, Cho BK and Kim SK: Plasma matrix metalloproteinases,
cytokines and angiogenic factors in moyamoya disease. J Neurol
Neurosurg Psychiatry. 81:673–678. 2010.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
48
|
Sakamoto S, Kiura Y, Yamasaki F, Shibukawa
M, Ohba S, Shrestha P, Sugiyama K and Kurisu K: Expression of
vascular endothelial growth factor in dura mater of patients with
moyamoya disease. Neurosurg Rev. 31:77–81; discussion 81.
2008.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
49
|
Yamamoto M, Aoyagi M, Tajima S, Wachi H,
Fukai N, Matsushima Y and Yamamoto K: Increase in elastin gene
expression and protein synthesis in arterial smooth muscle cells
derived from patients with Moyamoya disease. Stroke. 28:1733–1738.
1997.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
50
|
Ng YS, Krilleke D and Shima DT: VEGF
function in vascular pathogenesis. Exp Cell Res. 312:527–537.
2006.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
51
|
Jin K, Zhu Y, Sun Y, Mao XO, Xie L and
Greenberg DA: Vascular endothelial growth factor (VEGF) stimulates
neurogenesis in vitro and in vivo. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA.
99:11946–11950. 2002.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
52
|
Fujii T, Yonemitsu Y, Onimaru M, Inoue M,
Hasegawa M, Kuwano H and Sueishi K: VEGF function for upregulation
of endogenous PlGF expression during FGF-2-mediated therapeutic
angiogenesis. Atherosclerosis. 200:51–57. 2008.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
53
|
Chen CY, Rao SS, Ren L, Hu XK, Tan YJ, Hu
Y, Luo J, Liu YW, Yin H, Huang J, et al: Exosomal DMBT1 from human
urine-derived stem cells facilitates diabetic wound repair by
promoting angiogenesis. Theranostics. 8:1607–1623. 2018.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
54
|
Perl M, Chung CS and Ayala A: Apoptosis.
Crit Care Med. 33 (Suppl):S526–S529. 2005.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
55
|
Kim DW, Jo YY, Garagiola U, Choi JY, Kang
YJ, Oh JH and Kim SG: Increased Level of Vascular Endothelial
Growth Factors by 4-hexylresorcinol is Mediated by Transforming
Growth Factor-β1 and Accelerates Capillary Regeneration in the
Burns in Diabetic Animals. Int J Mol Sci. 21(21)2020.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
56
|
König HG, Kögel D, Rami A and Prehn JH:
TGF-{beta}1 activates two distinct type I receptors in neurons:
Implications for neuronal NF-{kappa}B signaling. J Cell Biol.
168:1077–1086. 2005.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
57
|
Nabel EG, Shum L, Pompili VJ, Yang ZY, San
H, Shu HB, Liptay S, Gold L, Gordon D and Derynck R: Direct
transfer of transforming growth factor beta 1 gene into arteries
stimulates fibrocellular hyperplasia. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA.
90:10759–10763. 1993.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
58
|
Hojo M, Hoshimaru M, Miyamoto S, Taki W,
Nagata I, Asahi M, Matsuura N, Ishizaki R, Kikuchi H and Hashimoto
N: Role of transforming growth factor-β1 in the pathogenesis of
moyamoya disease. J Neurosurg. 89:623–629. 1998.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
59
|
Huang Y, Cheng D, Zhang J and Zhao W:
Association between the rs112735431 polymorphism of the RNF213 gene
and moyamoya disease: A case-control study and meta-analysis. J
Clin Neurosci. 32:14–18. 2016.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
60
|
Park MG, Shin JH, Lee SW, Park HR and Park
KP: RNF213 rs112735431 polymorphism in intracranial artery
steno-occlusive disease and moyamoya disease in Koreans. J Neurol
Sci. 375:331–334. 2017.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
61
|
Zhang Q, Liu Y, Zhang D, Wang R, Zhang Y,
Wang S, Yu L, Lu C, Liu F, Zhou J, et al: RNF213 as the major
susceptibility gene for Chinese patients with moyamoya disease and
its clinical relevance. J Neurosurg. 126:1106–1113. 2017.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
62
|
Hitomi T, Habu T, Kobayashi H, Okuda H,
Harada KH, Osafune K, Taura D, Sone M, Asaka I, Ameku T, et al: The
moyamoya disease susceptibility variant RNF213 R4810K (rs112735431)
induces genomic instability by mitotic abnormality. Biochem Biophys
Res Commun. 439:419–426. 2013.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
63
|
Liu G, Beggs H, Jürgensen C, Park HT, Tang
H, Gorski J, Jones KR, Reichardt LF, Wu J and Rao Y: Netrin
requires focal adhesion kinase and Src family kinases for axon
outgrowth and attraction. Nat Neurosci. 7:1222–1232.
2004.PubMed/NCBI View
Article : Google Scholar
|
|
64
|
Abe K, Yamashita T, Takizawa S, Kuroda S,
Kinouchi H and Kawahara N: Stem cell therapy for cerebral ischemia:
From basic science to clinical applications. J Cereb Blood Flow
Metab. 32:1317–1331. 2012.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
65
|
Harris VK, Yan QJ, Vyshkina T, Sahabi S,
Liu X and Sadiq SA: Clinical and pathological effects of
intrathecal injection of mesenchymal stem cell-derived neural
progenitors in an experimental model of multiple sclerosis. J
Neurol Sci. 313:167–177. 2012.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
66
|
Gamie Z, Tran GT, Vyzas G, Korres N,
Heliotis M, Mantalaris A and Tsiridis E: Stem cells combined with
bone graft substitutes in skeletal tissue engineering. Expert Opin
Biol Ther. 12:713–729. 2012.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
67
|
Deryugina EI and Müller-Sieburg CE:
Stromal cells in long-term cultures: Keys to the elucidation of
hematopoietic development? Crit Rev Immunol. 13:115–150.
1993.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
68
|
Lisignoli G, Remiddi G, Cattini L,
Cocchini B, Zini N, Fini M, Grassi F, Piacentini A and Facchini A:
An elevated number of differentiated osteoblast colonies can be
obtained from rat bone marrow stromal cells using a gradient
isolation procedure. Connect Tissue Res. 42:49–58. 2001.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
69
|
Li YH, Wang ZD, Wang W, Ding CW, Zhang HX
and Li JM: The biocompatibility of calcium phosphate cements
containing alendronate-loaded PLGA microparticles in vitro. Exp
Biol Med (Maywood). 240:1465–1471. 2015.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
70
|
Dominici M, Le Blanc K, Mueller I,
Slaper-Cortenbach I, Marini F, Krause D, Deans R, Keating A,
Prockop Dj and Horwitz E: Minimal criteria for defining multipotent
mesenchymal stromal cells. The International Society for Cellular
Therapy position statement. Cytotherapy. 8:315–317. 2006.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
71
|
Moteki Y, Onda H, Kasuya H, Yoneyama T,
Okada Y, Hirota K, Mukawa M, Nariai T, Mitani S and Akagawa H:
Systematic Validation of RNF213 Coding Variants in Japanese
Patients With Moyamoya Disease. J Am Heart Assoc.
4(e001862)2015.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
72
|
Bang OY, Ryoo S, Kim SJ, Yoon CH, Cha J,
Yeon JY, Kim KH, Kim GM, Chung CS, Lee KH, et al: Adult Moyamoya
Disease: A Burden of Intracranial Stenosis in East Asians? PLoS
One. 10(e0130663)2015.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
73
|
Nomura S, Yamaguchi K, Akagawa H,
Kawashima A, Moteki Y, Ishikawa T, Aihara Y, Saito T, Okada Y and
Kawamata T: Genotype-Phenotype Correlation in Long-Term Cohort of
Japanese Patients with Moyamoya Disease. Cerebrovasc Dis.
47:105–111. 2019.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
74
|
Kim EH, Yum MS, Ra YS, Park JB, Ahn JS,
Kim GH, Goo HW, Ko TS and Yoo HW: Importance of RNF213 polymorphism
on clinical features and long-term outcome in moyamoya disease. J
Neurosurg. 124:1221–1227. 2016.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
75
|
Fujimura M, Sonobe S, Nishijima Y, Niizuma
K, Sakata H, Kure S and Tominaga T: Genetics and Biomarkers of
Moyamoya Disease: Significance of RNF213 as a Susceptibility Gene.
J Stroke. 16:65–72. 2014.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
76
|
Reid AJ, Bhattacharjee MB, Regalado ES,
Milewicz AL, El-Hakam LM, Dauser RC and Milewicz DM: Diffuse and
uncontrolled vascular smooth muscle cell proliferation in rapidly
progressing pediatric moyamoya disease. J Neurosurg Pediatr.
6:244–249. 2010.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
77
|
Han W, Qiao Y, Zhang H, Geng C, Zhu X,
Liao D, Guo Y, Yang M, Chen D and Jiang P: Circulating sortilin
levels are associated with inflammation in patients with moyamoya
disease. Metab Brain Dis. 36:103–109. 2021.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
78
|
Corey S and Luo Y: Circular RNAs and
neutrophils: Key factors in tackling asymptomatic moyamoya disease.
Brain Circ. 5:150–155. 2019.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
79
|
Park YS, Jeon YJ, Kim HS, Chae KY, Oh SH,
Han IB, Kim HS, Kim WC, Kim OJ, Kim TG, et al: The role of VEGF and
KDR polymorphisms in moyamoya disease and collateral
revascularization. PLoS One. 7(e47158)2012.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|