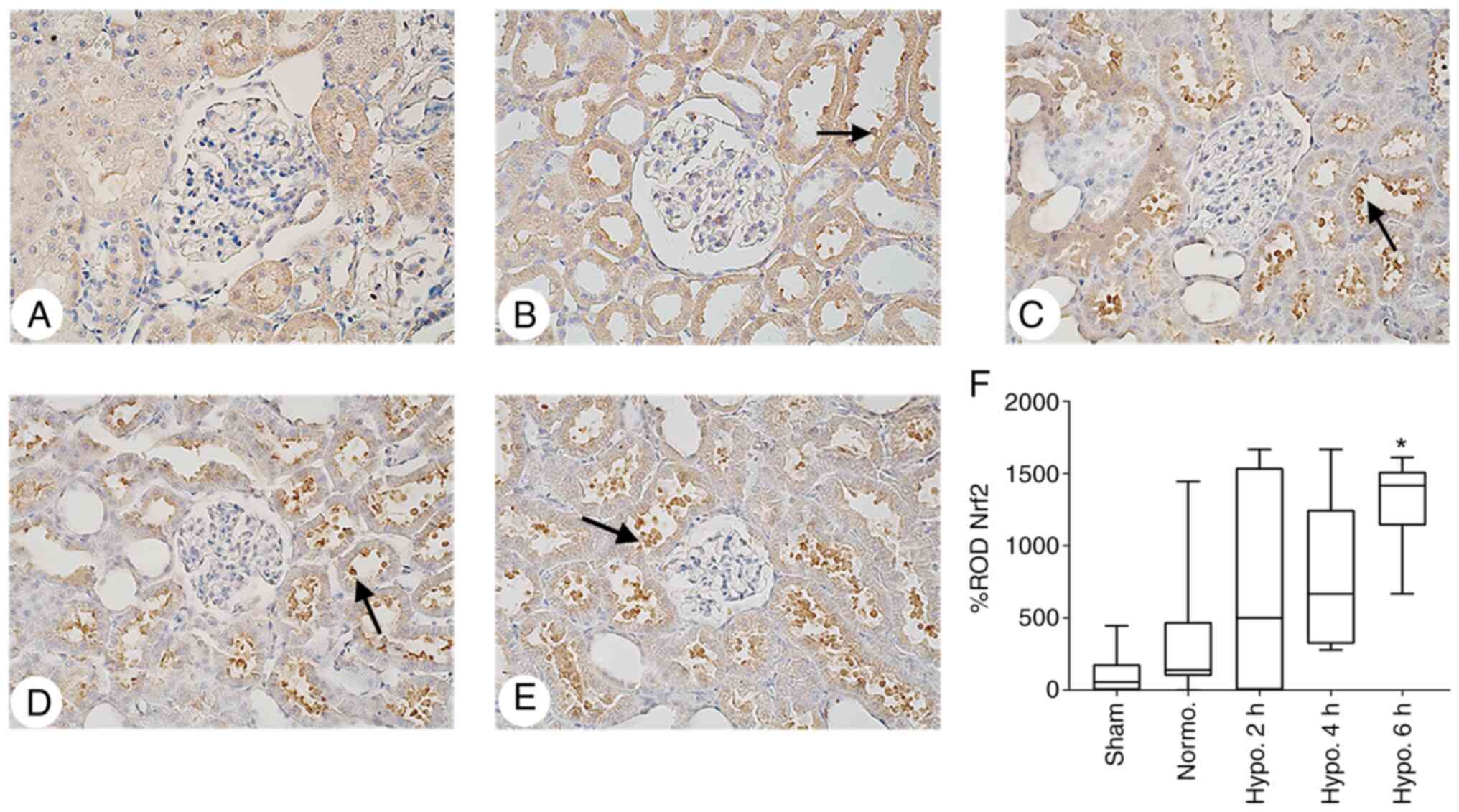
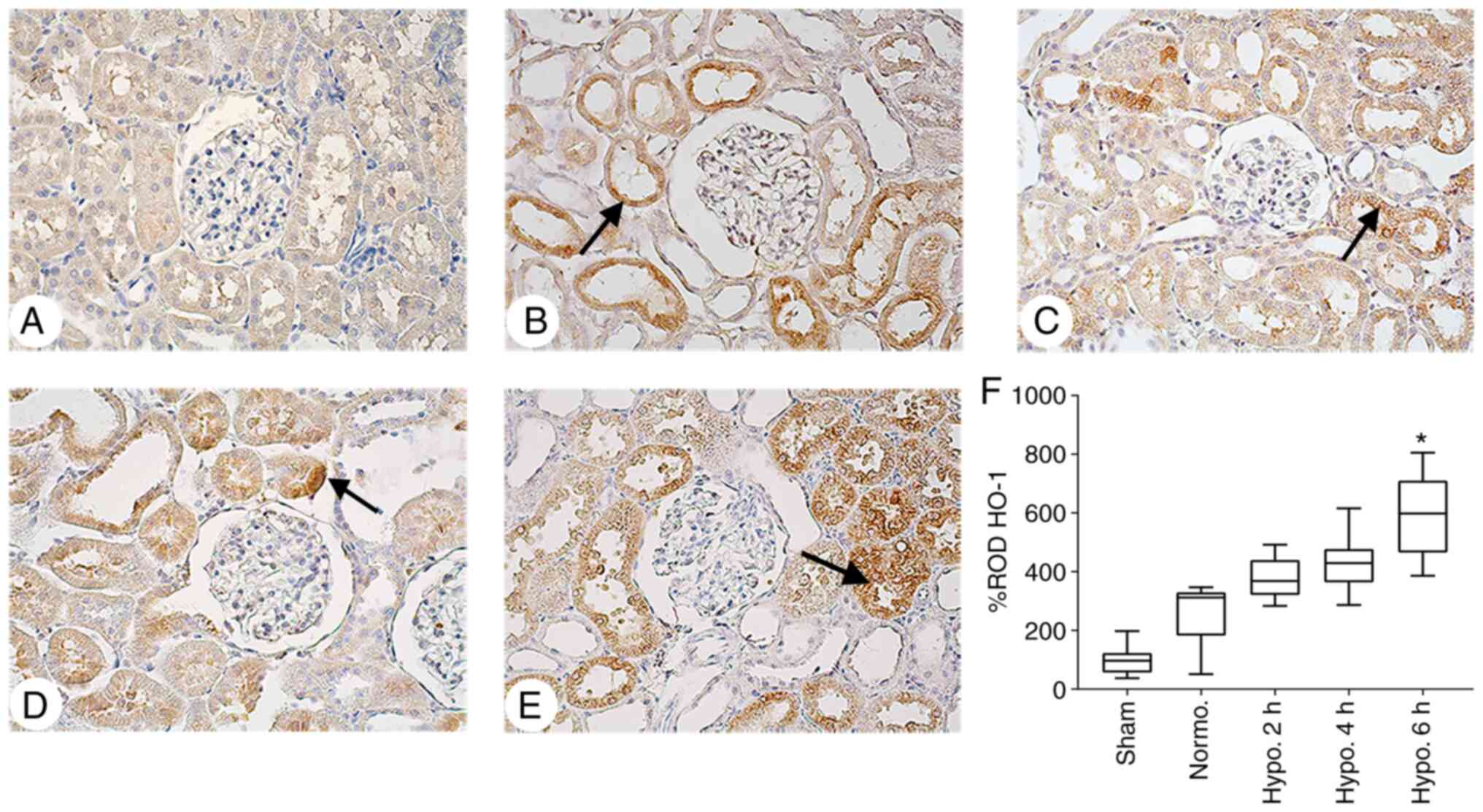
|
1
|
Girotra S, Chan PS and Bradley SM:
Post-resuscitation care following out-of-hospital and in-hospital
cardiac arrest. Heart. 101:1943–1949. 2015.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
2
|
Forman-Hoffman VL, Ault KL, Anderson WL,
Weiner JM, Stevens A, Campbell VA and Armour BS: Disability status,
mortality, and leading causes of death in the United States
community population. Med Care. 53:346–354. 2015.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
3
|
Roberts BW, Kilgannon JH, Chansky ME,
Mittal N, Wooden J, Parrillo JE and Trzeciak S: Multiple organ
dysfunction after return of spontaneous circulation in postcardiac
arrest syndrome. Crit Care Med. 41:1492–1501. 2013.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
4
|
Damman K, Valente MA, Voors AA, O'Connor
CM, van Veldhuisen DJ and Hillege HL: Renal impairment, worsening
renal function, and outcome in patients with heart failure: An
updated meta-analysis. Eur Heart J. 35:455–469. 2014.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
5
|
Hasper D, von Haehling S, Storm C, Jörres
A and Schefold JC: Changes in serum creatinine in the first 24
hours after cardiac arrest indicate prognosis: An observational
cohort study. Crit Care. 13(R168)2009.PubMed/NCBI View
Article : Google Scholar
|
|
6
|
Geri G, Guillemet L, Dumas F, Charpentier
J, Antona M, Lemiale V, Bougouin W, Lamhaut L, Mira JP, Vinsonneau
C and Cariou A: Acute kidney injury after out-of-hospital cardiac
arrest: Risk factors and prognosis in a large cohort. Intensive
Care Med. 41:1273–1280. 2015.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
7
|
Laurent I, Monchi M, Chiche JD, Joly LM,
Spaulding C, Bourgeois B, Cariou A, Rozenberg A, Carli P, Weber S
and Dhainaut JF: Reversible myocardial dysfunction in survivors of
out-of-hospital cardiac arrest. J Am Coll Cardiol. 40:2110–2116.
2002.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
8
|
Madl C and Holzer M: Brain function after
resuscitation from cardiac arrest. Curr Opin Crit Care. 10:213–217.
2004.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
9
|
Nath KA and Norby SM: Reactive oxygen
species and acute renal failure. Am J Med. 109:665–678.
2000.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
10
|
Tsuda H, Kawada N, Kaimori JY, Kitamura H,
Moriyama T, Rakugi H, Takahara S and Isaka Y: Febuxostat suppressed
renal ischemia-reperfusion injury via reduced oxidative stress.
Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 427:266–272. 2012.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
11
|
Feng L, Ke N, Cheng F, Guo Y, Li S, Li Q
and Li Y: The protective mechanism of ligustrazine against renal
ischemia/reperfusion injury. J Surg Res. 166:298–305.
2011.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
12
|
Jaiswal AK: Nrf2 signaling in coordinated
activation of antioxidant gene expression. Free Radic Biol Med.
36:1199–1207. 2004.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
13
|
Jiang G, Liu X, Wang M, Chen H, Chen Z and
Qiu T: Oxymatrine ameliorates renal ischemia-reperfusion injury
from oxidative stress through Nrf2/HO-1 pathway. Acta Cir Bras.
30:422–429. 2015.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
14
|
Zhang Y, Rong S, Feng Y, Zhao L, Hong J,
Wang R and Yuan W: Simvastatin attenuates renal
ischemia/reperfusion injury from oxidative stress via targeting
Nrf2/HO-1 pathway. Exp Ther Med. 14:4460–4466. 2017.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
15
|
Williams GR Jr and Spencer FC: The
clinical use of hypothermia following cardiac arrest. Ann Surg.
148:462–468. 1958.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
16
|
Palmers PJ, Hiltrop N, Ameloot K,
Timmermans P, Ferdinande B, Sinnaeve P, Nieuwendijk R and Malbrain
ML: From therapeutic hypothermia towards targeted temperature
management: A decade of evolution. Anaesthesiol Intensive Ther.
47:156–161. 2015.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
17
|
Hypothermia after Cardiac Arrest Study
Group. Mild therapeutic hypothermia to improve the neurologic
outcome after cardiac arrest. N Engl J Med. 346:549–556.
2002.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
18
|
Ostadal P, Mlcek M, Kruger A, Horakova S,
Skabradova M, Holy F, Svoboda T, Belohlavek J, Hrachovina V,
Taborsky L, et al: Mild therapeutic hypothermia is superior to
controlled normothermia for the maintenance of blood pressure and
cerebral oxygenation, prevention of organ damage and suppression of
oxidative stress after cardiac arrest in a porcine model. J Transl
Med. 11(124)2013.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
19
|
Gong P, Li CS, Hua R, Zhao H, Tang ZR, Mei
X, Zhang MY and Cui J: Mild hypothermia attenuates mitochondrial
oxidative stress by protecting respiratory enzymes and upregulating
MnSOD in a pig model of cardiac arrest. PLoS One.
7(e35313)2012.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
20
|
Dohi K, Miyamoto K, Fukuda K, Nakamura S,
Hayashi M, Ohtaki H, Shioda S and Aruga T: Status of systemic
oxidative stress during therapeutic hypothermia in patients with
post-cardiac arrest syndrome. Oxid Med Cell Longev.
2013(562429)2013.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
21
|
Legriel S, Lemiale V, Schenck M, Chelly J,
Laurent V, Daviaud F, Srairi M, Hamdi A, Geri G, Rossignol T, et
al: Hypothermia for neuroprotection in convulsive status
epilepticus. N Engl J Med. 375:2457–2467. 2016.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
22
|
Moler FW, Silverstein FS, Holubkov R,
Slomine BS, Christensen JR, Nadkarni VM, Meert KL, Browning B,
Pemberton VL, Page K, et al: Therapeutic hypothermia after
in-hospital cardiac arrest in children. N Engl J Med. 376:318–329.
2017.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
23
|
Nielsen N, Wetterslev J, Cronberg T,
Erlinge D, Gasche Y, Hassager C, Horn J, Hovdenes J, Kjaergaard J,
Kuiper M, et al: Targeted temperature management at 33˚C versus
36˚C after cardiac arrest. N Engl J Med. 369:2197–2206.
2013.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
24
|
Tujjar O, Mineo G, Dell'Anna A,
Poyatos-Robles B, Donadello K, Scolletta S, Vincent JL and Taccone
FS: Acute kidney injury after cardiac arrest. Crit Care.
19(169)2015.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
25
|
Islam A, Kim SE, Yoon JC, Jawad A, Tian W,
Yoo YJ, Kim IS, Ahn D, Park BY, Hwang Y, et al: Protective effects
of therapeutic hypothermia on renal injury in an asphyxial cardiac
arrest rat model. J Thermal Biol. 94(102761)2020.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
26
|
Drabek T, Foley LM, Janata A, Stezoski J,
Hitchens TK, Manole MD and Kochanek PM: Global and regional
differences in cerebral blood flow after asphyxial versus
ventricular fibrillation cardiac arrest in rats using ASL-MRI.
Resuscitation. 85:964–971. 2014.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
27
|
Aoki T, Okuma Y, Becker LB, Hayashida K
and Shinozaki K: Methodological issue of mitochondrial isolation in
acute-injury rat model: Asphyxia cardiac arrest and resuscitation.
Front Med (Lausanne). 8(666735)2021.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
28
|
Junyun H, Hongyang L, Ruoxian D, Young L,
Shanbao T and Xiaofeng J: Real-time monitoring of cerebral blood
flow by laser speckle contrast imaging after cardiac arrest in rat.
Annu Int Conf IEEE Eng Med Biol Soc. 2015:6971–6974.
2015.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
29
|
Lu J, Qian HY, Liu LJ, Zhou BC, Xiao Y,
Mao JN, An GY, Rui MZ, Wang T and Zhu CL: Mild hypothermia
alleviates excessive autophagy and mitophagy in a rat model of
asphyxial cardiac arrest. Neurol Sci. 35:1691–1699. 2014.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
30
|
Park Y, Ahn JH, Cho JH, Tae HJ, Lee TK,
Kim B, Lee JC, Park JH, Shin MC, Ohk TG, et al: Effects of
hypothermia on inflammatory cytokine expression in rat liver
following asphyxial cardiac arrest. Exp Ther Med.
21(626)2021.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
31
|
Tong F and Zhou X: The Nrf2/HO-1 pathway
mediates the antagonist effect of L-arginine on renal
ischemia/reperfusion injury in rats. Kidney Blood Press Res.
42:519–529. 2017.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
32
|
Akanda MR, Kim IS, Ahn D, Tae HJ, Nam HH,
Choo BK, Kim K and Park BY: Anti-inflammatory and gastroprotective
roles of rabdosia inflexa through downregulation of
pro-inflammatory cytokines and MAPK/NF-kappaB signaling pathways.
Int J Mol Sci. 19(584)2018.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
33
|
Park Y, Tae HJ, Cho JH, Kim IS, Ohk TG,
Park CW, Moon JB, Shin MC, Lee TK, Lee JC, et al: The relationship
between low survival and acute increase of tumor necrosis factor α
expression in the lung in a rat model of asphyxial cardiac arrest.
Anat Cell Biol. 51:128–135. 2018.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
34
|
Kocoglu H, Ozturk H, Ozturk H, Yilmaz F
and Gulcu N: Effect of dexmedetomidine on ischemia-reperfusion
injury in rat kidney: A histopathologic study. Renal Failure.
31:70–74. 2009.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
35
|
Collard CD and Gelman S: Pathophysiology,
clinical manifestations, and prevention of ischemia-reperfusion
injury. Anesthesiology. 94:1133–1138. 2001.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
36
|
Tae HJ, Kang IJ, Lee TK, Cho JH, Lee JC,
Shin MC, Kim YS, Cho JH, Kim JD, Ahn JH, et al: Neuronal injury and
tumor necrosis factor-alpha immunoreactivity in the rat hippocampus
in the early period of asphyxia-induced cardiac arrest under
normothermia. Neural Regen Res. 12:2007–2013. 2017.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
37
|
Janata A, Magnet IA, Schreiber KL, Wilson
CD, Stezoski JP, Janesko-Feldman K, Kochanek PM and Drabek T:
Minocycline fails to improve neurologic and histologic outcome
after ventricular fibrillation cardiac arrest in rats. World J Crit
Care Med. 8:106–119. 2019.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
38
|
McCord JM: Oxygen-derived free radicals in
postischemic tissue injury. N Engl J Med. 312:159–163.
1985.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
39
|
Guidet BR and Shah SV: In vivo generation
of hydrogen peroxide by rat kidney cortex and glomeruli. Am J
Physiol. 256:F158–F164. 1989.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
40
|
Grekas D, Dioudis C, Papageorgiou G,
Iliadis S, Zilidis C, Alivanis P, Dimitriadou A and Tourkantonis A:
Lipid peroxidation after acute renal ischemia and reperfusion in
rats: The effect of trimetazidine. Ren Fail. 18:545–552.
1996.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
41
|
Xia Z, Wang W, Xiao Q, Ye Q, Zhang X and
Wang Y: Mild hypothermia protects renal function in
ischemia-reperfusion kidney: An experimental study in mice.
Transplant Proc. 50:3816–3821. 2018.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
42
|
Hackenhaar FS, Medeiros TM, Heemann FM,
Behling CS, Putti JS, Mahl CD, Verona C, da Silva ACA, Guerra MC,
Gonçalves CAS, et al: Therapeutic hypothermia reduces oxidative
damage and alters antioxidant defenses after cardiac arrest. Oxid
Med Cell Longev. 2017(8704352)2017.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
43
|
Kim HJ and Vaziri ND: Contribution of
impaired Nrf2-Keap1 pathway to oxidative stress and inflammation in
chronic renal failure. Am J Physiol Renal Physiol. 298:F662–F671.
2010.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
44
|
Kobayashi M and Yamamoto M: Molecular
mechanisms activating the Nrf2-Keap1 pathway of antioxidant gene
regulation. Antioxid Redox Signal. 7:385–394. 2005.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
45
|
Zhang L, Zhu Z, Liu J, Zhu Z and Hu Z:
Protective effect of N-acetylcysteine (NAC) on renal
ischemia/reperfusion injury through Nrf2 signaling pathway. J
Recept Signal Transduct Res. 34:396–400. 2014.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
46
|
Xia D and Zhang H: Effects of mild
hypothermia on expression of NF-E2-related factor 2 and
heme-oxygenase-1 in cerebral cortex and hippocampus after
cardiopulmonary resuscitation in rats. Iran J Basic Med Sci.
20:1002–1008. 2017.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
47
|
Lu X, Ma L, Sun S, Xu J, Zhu C and Tang W:
The effects of the rate of postresuscitation rewarming following
hypothermia on outcomes of cardiopulmonary resuscitation in a rat
model. Crit Care Med. 42:e106–113. 2014.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|