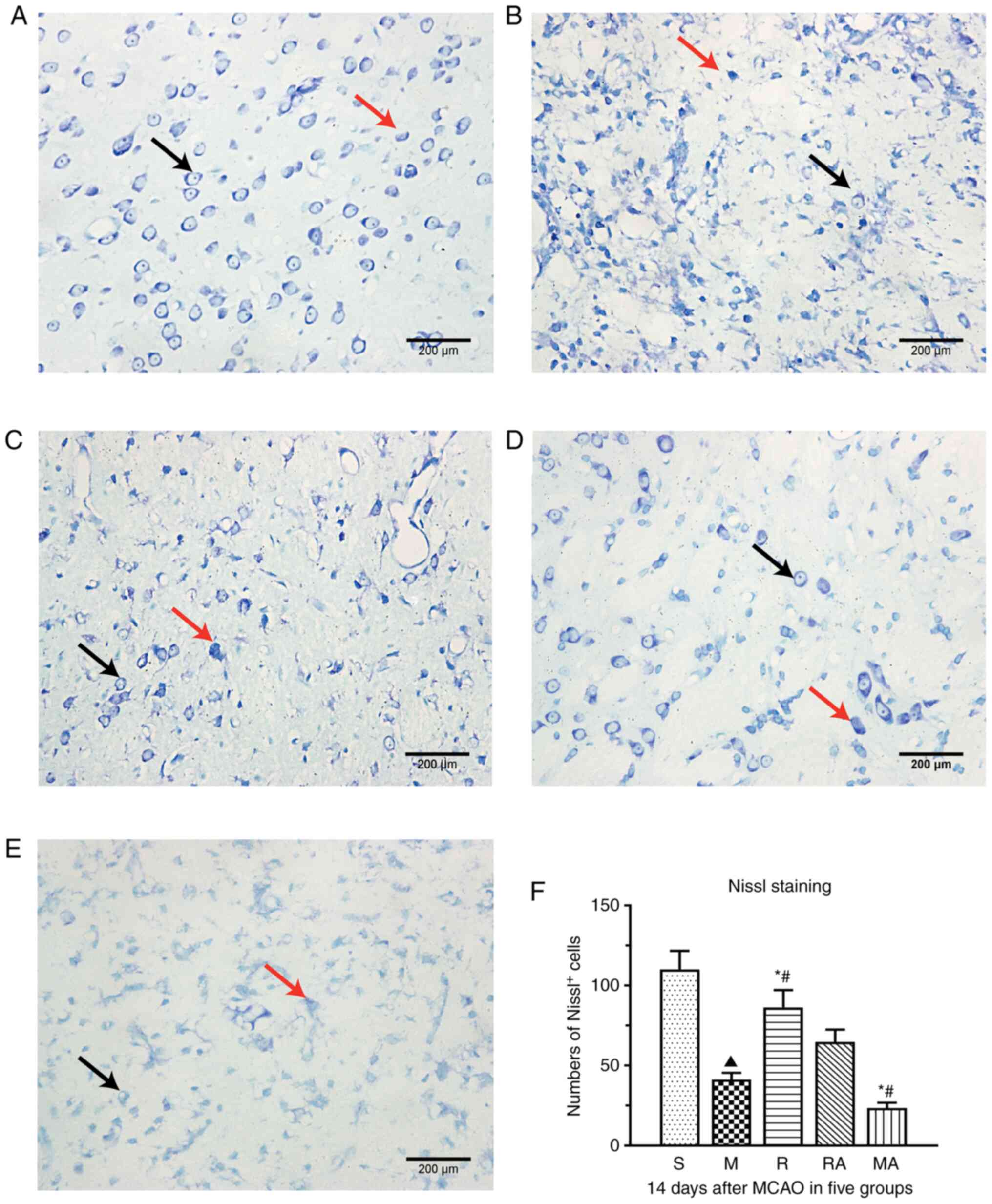
|
1
|
Sanai N, Tramontin AD, Quiñones-Hinojosa
A, Barbaro NM, Gupta N, Kunwar S, Lawton MT, McDermott MW, Parsa
AT, Verdugo JM, et al: Unique astrocyte ribbon in adult human brain
contains neural stem cells but lacks chain migration. Nature.
427:740–744. 2004.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
2
|
Kannangara TS, Carter A, Xue Y, Dhaliwal
JS, Beique JC and Lagace DC: Excitable adult-generated GABAergic
neurones acquire functional innervation in the cortex after stroke.
Stem Cell Rep. 11:1327–1336. 2018.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
3
|
Tsintou M, Dalamagkas K and Makris N:
Taking central nervous system regenerative therapies to the clinic:
Curing rodents versus nonhuman primates versus humans. Neural Regen
Res. 15:425–437. 2020.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
4
|
Luo J, Hu X, Zhang L, Li L, Zheng H, Li M
and Zhang Q: Physical exercise regulates neural stem cells
proliferation and migration via SDF-1α/CXCR4 pathway in rats after
ischemic stroke. Neurosci Lett. 578:203–208. 2014.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
5
|
Zhao S, Qu H, Zhao Y, Xiao T, Zhao M, Li
Y, Jolkkonen J, Cao Y and Zhao C: CXCR4 antagonist AMD3100 reverses
the neurogenesis and behavioral recovery promoted by forced
limb-use in stroke rats. Restor Neurol Neurosci. 33:809–821.
2015.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
6
|
Jin K, Wang X, Xie L, Mao XO and Greenberg
DA: Transgenic ablation of doublecortin-expressing cells suppresses
adult neurogenesis and worsens stroke outcome in mice. Proc Natl
Acad Sci USA. 107:7993–7998. 2010.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
7
|
Hummel FC and Cohen LG: Non-invasive brain
stimulation: A new strategy to improve neurorehabilitation after
stroke? Lancet Neurol. 5:708–712. 2006.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
8
|
Yuan X, Yang Y, Cao N and Jiang C:
Promotion of poststroke motor-function recovery with repetitive
transcranial magnetic stimulation by regulating the
interhemispheric imbalance. Brain Sci. 10(648)2020.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
9
|
Fisicaro F, Lanza G, Grasso AA, Pennisi G,
Bella R, Paulus W and Pennisi M: Repetitive transcranial magnetic
stimulation in stroke rehabilitation: Review of the current
evidence and pitfalls. Ther Adv Neurol Disord.
12(1278099885)2019.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
10
|
Gleeson JG, Lin PT, Flanagan LA and Walsh
CA: Doublecortin is a microtubule-associated protein and is
expressed widely by migrating neurons. Neuron. 23:257–271.
1999.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
11
|
Couillard-Despres S, Winner B, Schaubeck
S, Aigner R, Vroemen M, Weidner N, Bogdahn U, Winkler J, Kuhn HG
and Aigner L: Doublecortin expression levels in adult brain reflect
neurogenesis. Eur J Neurosci. 21:1–14. 2005.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
12
|
Cui M, Ge H, Zeng H, Yan H, Zhang L, Feng
H and Chen Y: Repetitive transcranial magnetic stimulation promotes
neural stem cell proliferation and differentiation after
intracerebral hemorrhage in mice. Cell Transplant. 28:568–584.
2019.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
13
|
Sherafat MA, Heibatollahi M, Mongabadi S,
Moradi F, Javan M and Ahmadiani A: Electromagnetic field
stimulation potentiates endogenous myelin repair by recruiting
subventricular neural stem cells in an experimental model of white
matter demyelination. J Mol Neurosci. 48:144–153. 2012.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
14
|
Li M and Ransohoff RM: Multiple roles of
chemokine CXCL12 in the central nervous system: A migration from
immunology to neurobiology. Prog Neurobiol. 84:116–131.
2008.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
15
|
Ho SY, Ling TY, Lin HY, Liou JT, Liu FC,
Chen IC, Lee SW, Hsu Y, Lai DM and Liou HH: SDF-1/CXCR4 signaling
maintains stemness signature in mouse neural stem/progenitor cells.
Stem Cells Int. 2017(2493752)2017.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
16
|
Hatami M, Conrad S, Naghsh P,
Alvarez-Bolado G and Skutella T: Cell-biological requirements for
the generation of dentate gyrus granule neurons. Front Cell
Neurosci. 12(402)2018.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
17
|
Lu M, Grove EA and Miller RJ: Abnormal
development of the hippocampal dentate gyrus in mice lacking the
CXCR4 chemokine receptor. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA. 99:7090–7095.
2002.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
18
|
Zanin JP, Abercrombie E and Friedman WJ:
Proneurotrophin-3 promotes cell cycle withdrawal of developing
cerebellar granule cell progenitors via the p75 neurotrophin
receptor. Elife. 5(e16654)2016.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
19
|
Ma Q, Jones D, Borghesani PR, Segal RA,
Nagasawa T, Kishimoto T, Bronson RT and Springer TA: Impaired
B-lymphopoiesis, myelopoiesis, and derailed cerebellar neuron
migration in CXCR4- and SDF-1-deficient mice. Proc Natl Acad Sci
USA. 95:9448–9453. 1998.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
20
|
Tsai LK, Wang Z, Munasinghe J, Leng Y,
Leeds P and Chuang DM: Mesenchymal stem cells primed with valproate
and lithium robustly migrate to infarcted regions and facilitate
recovery in a stroke model. Stroke. 42:2932–2939. 2011.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
21
|
Sanchez AB, Medders KE, Maung R,
Sanchez-Pavon P, Ojeda-Juárez D and Kaul M: CXCL12-induced
neurotoxicity critically depends on NMDA receptor-gated and L-type
Ca2+ channels upstream of p38 MAPK. J Neuroinflammation.
13(252)2016.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
22
|
Hwang SJ, Song YM, Cho TH, Kim RY, Lee TH,
Kim SJ, Seo YK and Kim IS: The implications of the response of
human mesenchymal stromal cells in three-dimensional culture to
electrical stimulation for tissue regeneration. Tissue Eng Part A.
18:432–445. 2012.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
23
|
Wang X, Gao Y, Shi H, Liu N, Zhang W and
Li H: Influence of the intensity and loading time of direct current
electric field on the directional migration of rat bone marrow
mesenchymal stem cells. Front Med. 10:286–296. 2016.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
24
|
Morimoto J, Yasuhara T, Kameda M, Umakoshi
M, Kin I, Kuwahara K, Kin K, Okazaki M, Takeuchi H, Sasaki T, et
al: Electrical stimulation enhances migratory ability of
transplanted bone marrow stromal cells in a rodent ischemic stroke
model. Cell Physiol Biochem. 46:57–68. 2018.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
25
|
Nicolai J, Burbassi S, Rubin J and Meucci
O: CXCL12 inhibits expression of the NMDA receptor's NR2B subunit
through a histone deacetylase-dependent pathway contributing to
neuronal survival. Cell Death Dis. 1(e33)2010.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
26
|
Huang J, Li Y, Tang Y, Tang G, Yang GY and
Wang Y: CXCR4 antagonist AMD3100 protects blood-brain barrier
integrity and reduces inflammatory response after focal ischemia in
mice. Stroke. 44:190–197. 2013.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
27
|
Wu KJ, Yu SJ, Shia KS, Wu CH, Song JS,
Kuan HH, Yeh KC, Chen CT, Bae E and Wang Y: A novel CXCR4
Antagonist CX549 induces neuroprotection in stroke brain. Cell
Transplant. 26:571–583. 2017.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
28
|
Baek A, Kim JH, Pyo S, Jung JH, Park EJ,
Kim SH and Cho SR: The differential effects of repetitive magnetic
stimulation in an in vitro neuronal model of ischemia/reperfusion
injury. Front Neurol. 9(50)2018.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
29
|
Zong X, Dong Y, Li Y, Yang L, Li Y, Yang
B, Tucker L, Zhao N, Brann DW, Yan X, et al: Beneficial effects of
theta-burst transcranial magnetic stimulation on stroke injury via
improving neuronal microenvironment and mitochondrial integrity.
Transl Stroke Res. 11:450–467. 2020.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
30
|
Longa EZ, Weinstein PR, Carlson S and
Cummins R: Reversible middle cerebral artery occlusion without
craniectomy in rats. Stroke. 20:84–91. 1989.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
31
|
Sha R, Zhang B, Han X, Peng J, Zheng C,
Zhang F and Huang X: Electroacupuncture alleviates ischemic brain
injury by inhibiting the miR-223/NLRP3 pathway. Med Sci Monitor.
25:4723–4733. 2019.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
32
|
Chen J, Sanberg PR, Li Y, Wang L, Lu M,
Willing AE, Sanchez-Ramos J and Chopp M: Intravenous administration
of human umbilical cord blood reduces behavioral deficits after
stroke in rats. Stroke. 32:2682–2688. 2001.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
33
|
Balkaya M, Krober JM, Rex A and Endres M:
Assessing post-stroke behavior in mouse models of focal ischemia. J
Cereb Blood Flow Metab. 33:330–338. 2013.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
34
|
Richter L, Neumann G, Oung S, Schweikard A
and Trillenberg P: Optimal coil orientation for transcranial
magnetic stimulation. PLoS One. 8(e60358)2013.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
35
|
Zhang XY, Sui YF, Guo TC, Wang SH, Hu Y
and Lu YS: Effect of paired associative stimulation on motor cortex
excitability in rats. Curr Med Sci. 38:903–909. 2018.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
36
|
Shin HI, Han TR and Paik NJ: Effect of
consecutive application of paired associative stimulation on motor
recovery in a rat stroke model: A preliminary study. Int J
Neurosci. 118:807–820. 2008.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
37
|
Peng JJ, Sha R, Li MX, Chen LT, Han XH,
Guo F, Chen H and Huang XL: Repetitive transcranial magnetic
stimulation promotes functional recovery and differentiation of
human neural stem cells in rats after ischemic stroke. Exp Neurol.
313:1–9. 2019.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
38
|
Guo F, Han X, Zhang J, Zhao X, Lou J, Chen
H and Huang X: Repetitive transcranial magnetic stimulation
promotes neural stem cell proliferation via the regulation of
MiR-25 in a rat model of focal cerebral ischemia. PLoS One.
9(e109267)2014.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
39
|
Nygren J, Wieloch T, Pesic J, Brundin P
and Deierborg T: Enriched environment attenuates cell genesis in
subventricular zone after focal ischemia in mice and decreases
migration of newborn cells to the striatum. Stroke. 37:2824–2829.
2006.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
40
|
Chen H, Qian K, Chen W, Hu B, Blackbourn
LW IV, Du Z, Ma L, Liu H, Knobel KM, Ayala M, et al: Human-derived
neural progenitors functionally replace astrocytes in adult mice. J
Clin Invest. 125:1033–1042. 2015.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
41
|
Zhan L, Yan H, Zhou H, Sun W, Hou Q and Xu
E: Hypoxic preconditioning attenuates neuronal cell death by
preventing MEK/ERK signaling pathway activation after transient
global cerebral ischemia in adult rats. Mol Neurobiol. 48:109–119.
2013.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
42
|
Ji Y, Teng L, Zhang R, Sun J and Guo Y:
NRG-1β exerts neuroprotective effects against ischemia
reperfusion-induced injury in rats through the JNK signaling
pathway. Neuroscience. 362:13–24. 2017.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
43
|
Tan F, Wang J, Liu JX, Wang C, Li M and Gu
Y: Electroacupuncture stimulates the proliferation and
differentiation of endogenous neural stem cells in a rat model of
ischemic stroke. Exp Ther Med. 16:4943–4950. 2018.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
44
|
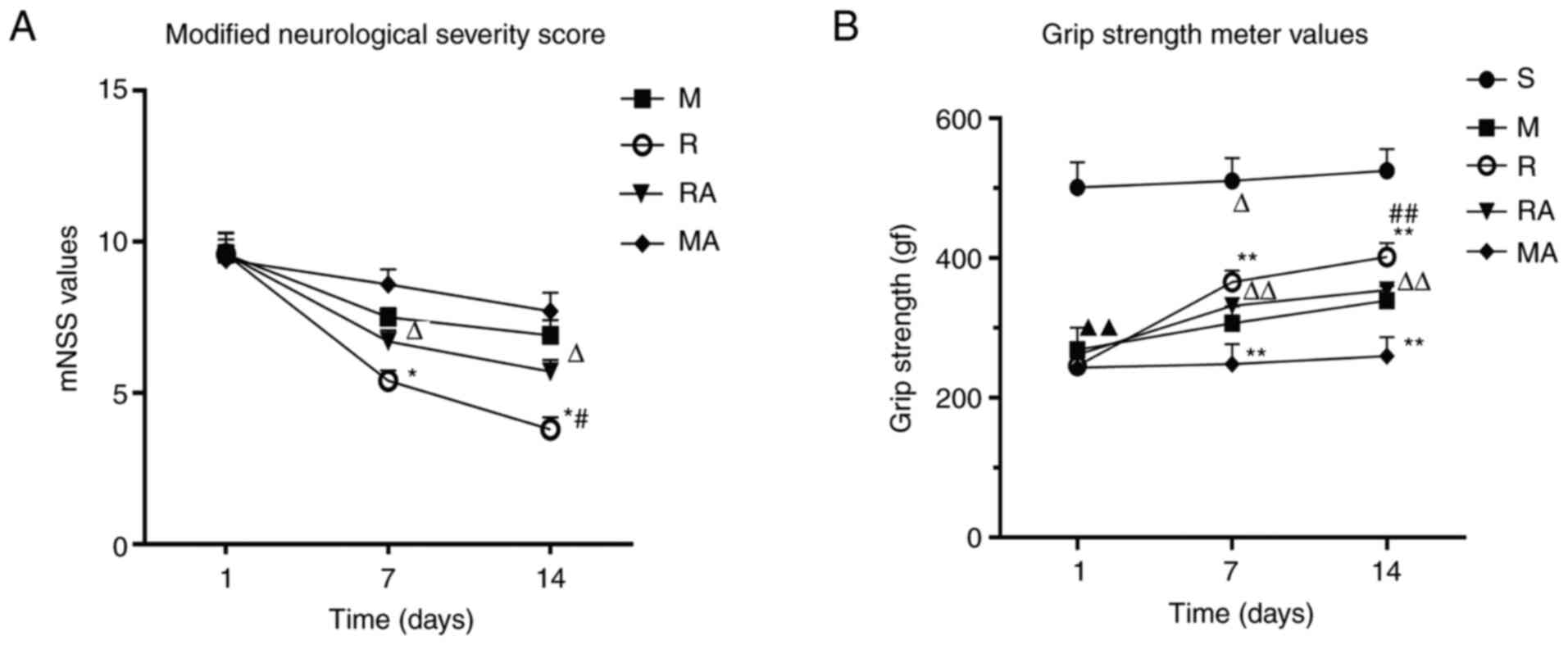
Meyer OA, Tilson HA, Byrd WC and Riley MT:
A method for the routine assessment of fore- and hindlimb grip
strength of rats and mice. Neurobehav Toxicol. 1:233–236.
1979.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
45
|
Fu DL, Li JH, Shi YH, Zhang XL, Lin Y and
Zheng GQ: Sanhua decoction, a classic herbal prescription, exerts
neuroprotection through regulating phosphorylated tau level and
promoting adult endogenous neurogenesis after cerebral
ischemia/reperfusion injury. Front Physiol. 11(57)2020.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
46
|
Jin Y, Raviv N, Barnett A, Bambakidis NC,
Filichia E and Luo Y: The shh signaling pathway is upregulated in
multiple cell types in cortical ischemia and influences the outcome
of stroke in an animal model. PLoS One. 10(e124657)2015.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
47
|
Wang X, Mao X, Xie L, Sun F, Greenberg DA
and Jin K: Conditional depletion of neurogenesis inhibits long-term
recovery after experimental stroke in mice. PLoS One.
7(e38932)2012.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
48
|
Gao F, Wang S, Guo Y, Wang J, Lou M, Wu J,
Ding M, Tian M and Zhang H: Protective effects of repetitive
transcranial magnetic stimulation in a rat model of transient
cerebral ischaemia: A microPET study. Eur J Nucl Med Mol Imaging.
37:954–961. 2010.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
49
|
Li L, El-Hayek YH, Liu B, Chen Y, Gomez E,
Wu X, Ning K, Li L, Chang N, Zhang L, et al: Direct-current
electrical field guides neuronal stem/progenitor cell migration.
Stem Cells. 26:2193–2200. 2008.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
50
|
Luo Y: Cell-based therapy for stroke. J
Neural Transm (Vienna). 118:61–74. 2011.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
51
|
Leu S, Lin YC, Yuen CM, Yen CH, Kao YH,
Sun CK and Yip HK: Adipose-derived mesenchymal stem cells markedly
attenuate brain infarct size and improve neurological function in
rats. J Transl Med. 8(63)2010.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
52
|
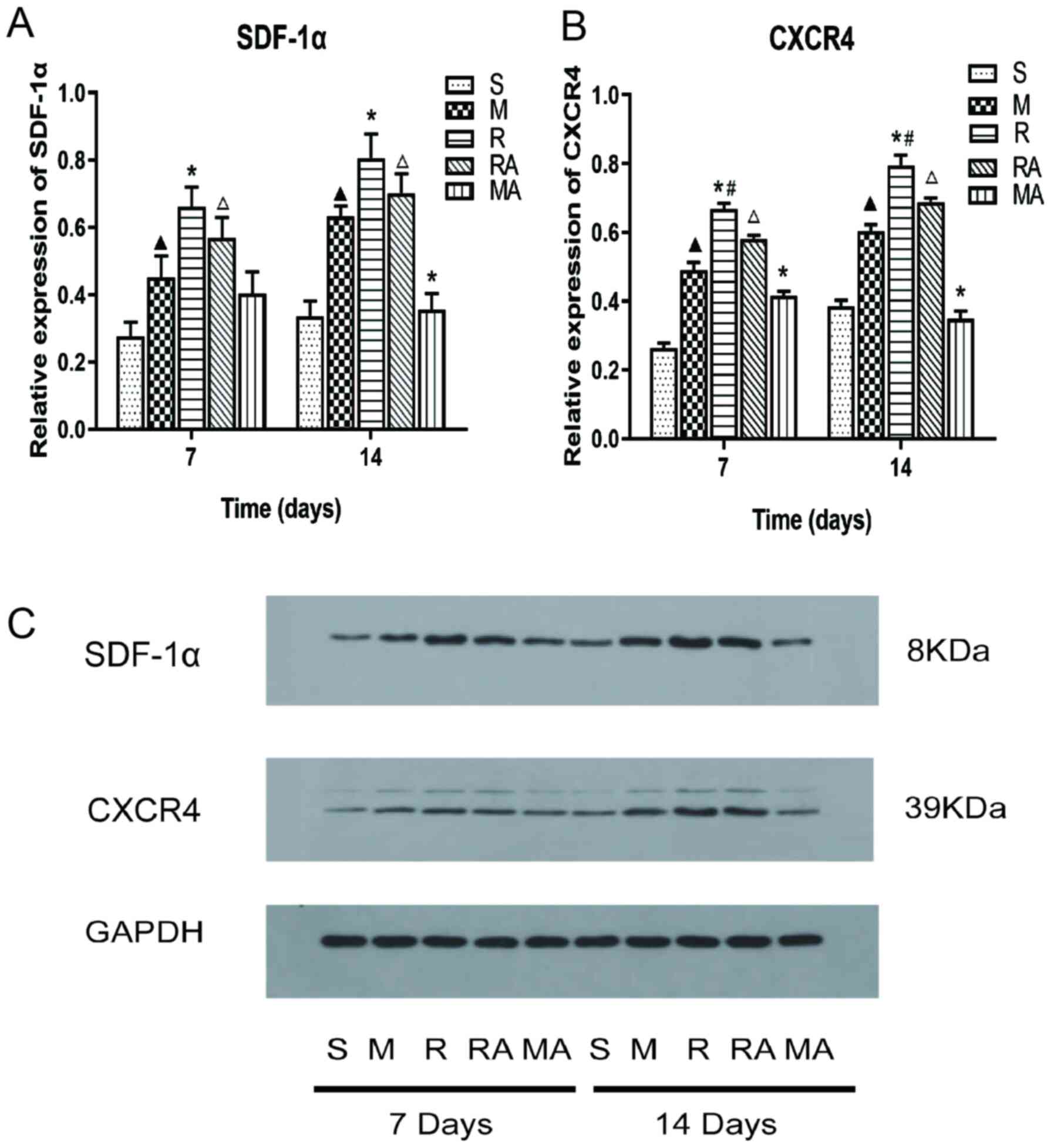
Yoo J, Seo JJ, Eom JH and Hwang DY:
Effects of stromal cell-derived factor 1α delivered at different
phases of transient focal ischemia in rats. Neuroscience.
209:171–186. 2012.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
53
|
Dziembowska M, Tham TN, Lau P, Vitry S,
Lazarini F and Dubois-Dalcq M: A role for CXCR4 signaling in
survival and migration of neural and oligodendrocyte precursors.
Glia. 50:258–269. 2005.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
54
|
Feng J, Liu J, Zhang X, Zhang L, Jiang J,
Nolta J and Zhao M: Guided migration of neural stem cells derived
from human embryonic stem cells by an electric field. Stem Cells.
30:349–355. 2012.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
55
|
Chiazza F, Tammen H, Pintana H, Lietzau G,
Collino M, Nyström T, Klein T, Darsalia V and Patrone C: The effect
of DPP-4 inhibition to improve functional outcome after stroke is
mediated by the SDF-1α/CXCR4 pathway. Cardiovasc Diabetol.
17(60)2018.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
56
|
Sun W, Liu J, Huan Y and Zhang C:
Intracranial injection of recombinant stromal-derived factor-1
alpha (SDF-1α) attenuates traumatic brain injury in rats. Inflamm
Res. 63:287–297. 2014.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
57
|
Lu X, Bao X, Li J, Zhang G, Guan J, Gao Y,
Wu P, Zhu Z, Huo X and Wang R: High-frequency repetitive
transcranial magnetic stimulation for treating moderate traumatic
brain injury in rats: A pilot study. Exp Ther Med. 13:2247–2254.
2017.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
58
|
Salcedo L, Lian L, Jiang H, Sopko N, Penn
M, Damaser M and Zutshi M: Low current electrical stimulation
upregulates cytokine expression in the anal sphincter. Int J
Colorectal Dis. 27:221–225. 2012.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
59
|
George PM and Steinberg GK: Novel stroke
therapeutics: Unraveling stroke pathophysiology and its impact on
clinical treatments. Neuron. 87:297–309. 2015.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
60
|
Belayev L, Hong S, Menghani H, Marcell SJ,
Obenaus A, Freitas RS, Khoutorova L, Balaszczuk V, Jun B, Oriá RB
and Bazan NG: Docosanoids promote neurogenesis and angiogenesis,
blood-brain barrier integrity, penumbra protection, and
neurobehavioral recovery after experimental ischemic stroke. Mol
Neurobiol. 55:7090–7106. 2018.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
61
|
Shohayeb B, Diab M, Ahmed M and Ng DCH:
Factors that influence adult neurogenesis as potential therapy.
Transl Neurodegener. 7(4)2018.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
62
|
Nih LR, Deroide N, Leré-Déan C, Lerouet D,
Soustrat M, Levy BI, Silvestre JS, Merkulova-Rainon T, Pocard M,
Margaill I and Kubis N: Neuroblast survival depends on mature
vascular network formation after mouse stroke: Role of endothelial
and smooth muscle progenitor cell co-administration. Eur J
Neurosci. 35:1208–1217. 2012.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
63
|
Yoon KJ, Lee Y and Han TR: Mechanism of
functional recovery after repetitive transcranial magnetic
stimulation (rTMS) in the subacute cerebral ischemic rat model:
Neural plasticity or anti-apoptosis? Exp Brain Res. 214:549–556.
2011.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
64
|
Guo F, Lou J, Han X, Deng Y and Huang X:
Repetitive transcranial magnetic stimulation ameliorates cognitive
impairment by enhancing neurogenesis and suppressing apoptosis in
the hippocampus in rats with ischemic stroke. Front Physiol.
8(559)2017.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
65
|
Czeh B, Welt T, Fischer AK, Erhardt A,
Schmitt W, Müller MB, Toschi N, Fuchs E and Keck ME: Chronic
psychosocial stress and concomitant repetitive transcranial
magnetic stimulation: effects on stress hormone levels and adult
hippocampal neurogenesis. Biol Psychiatry. 52:1057–1065.
2002.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|