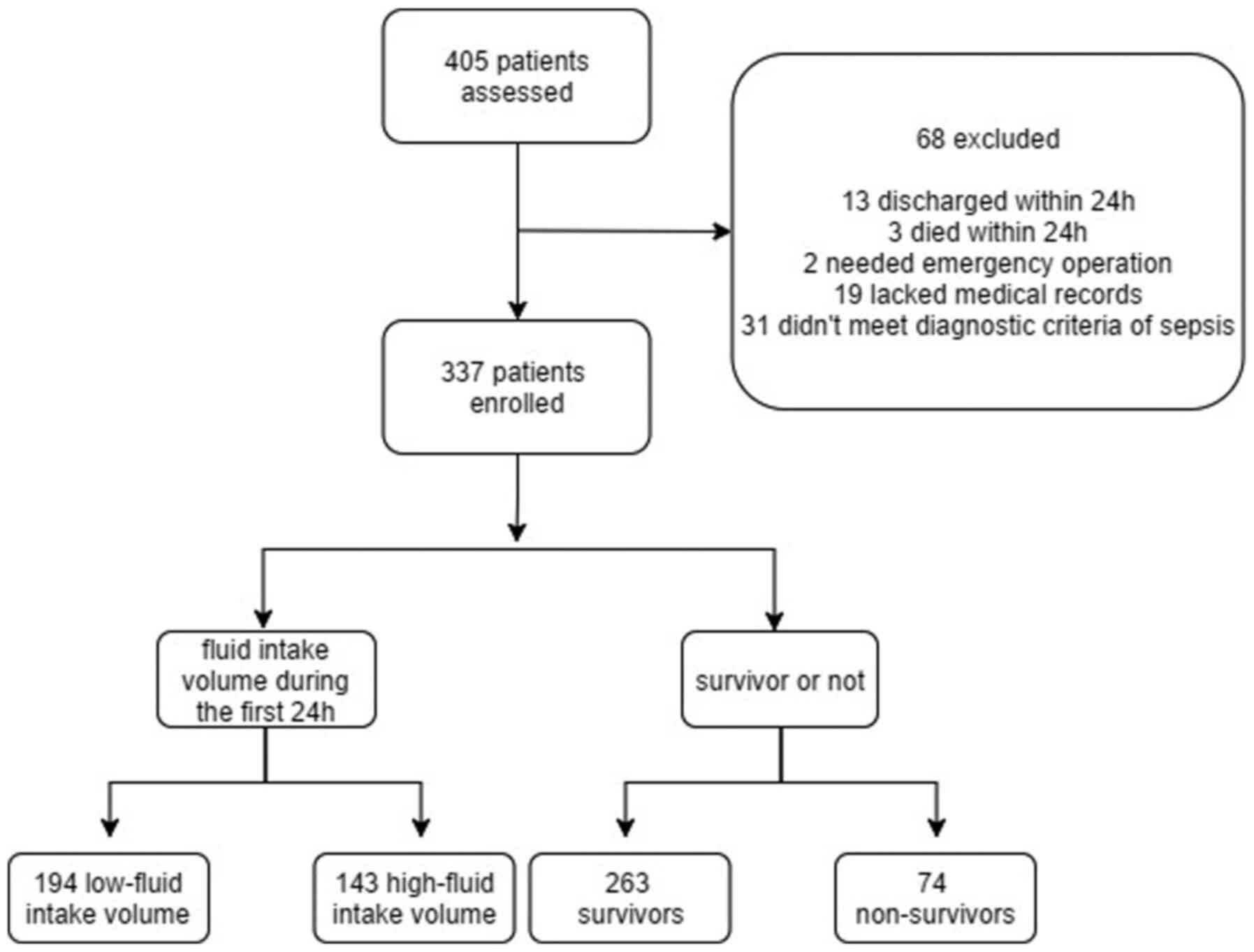
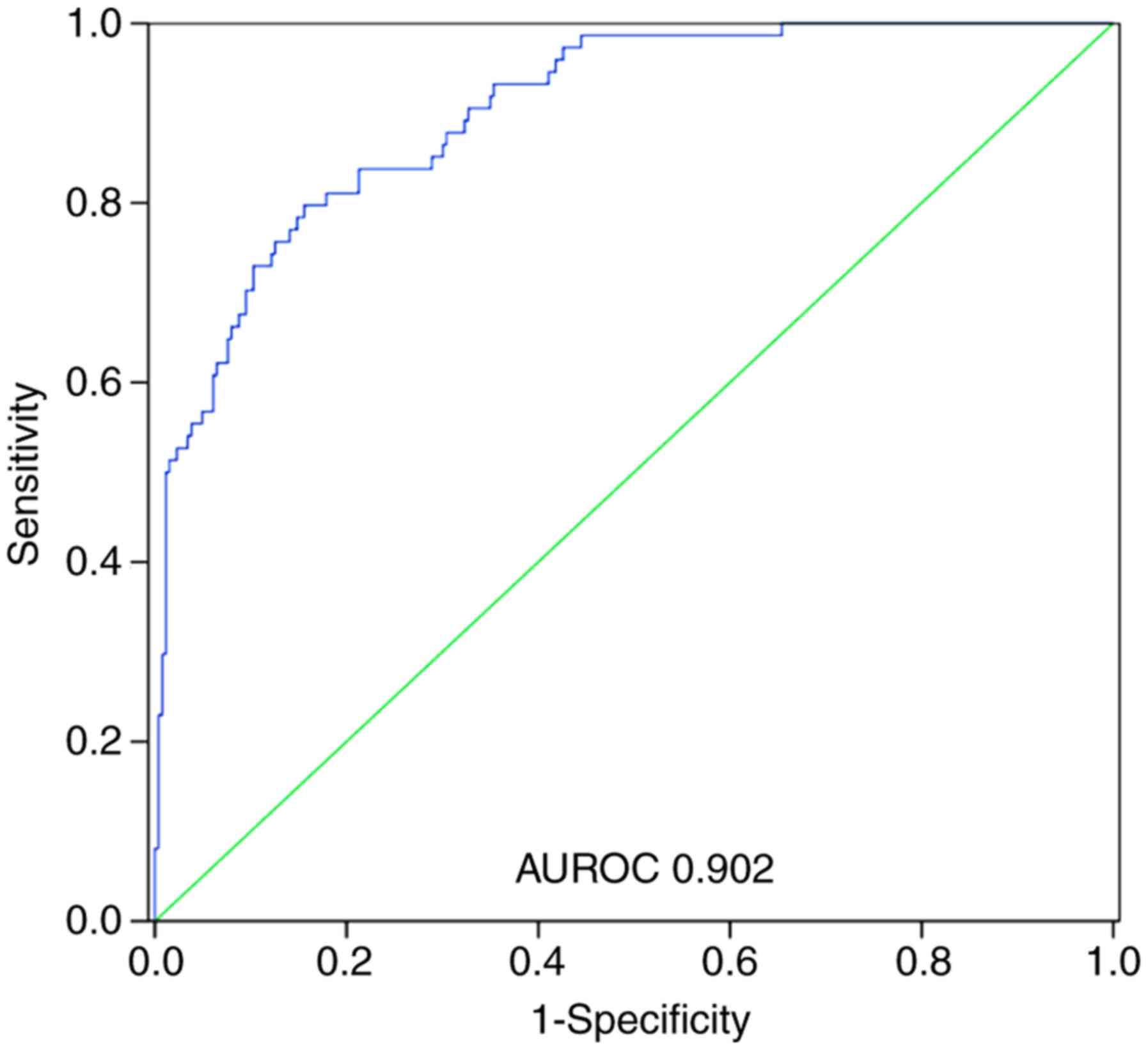
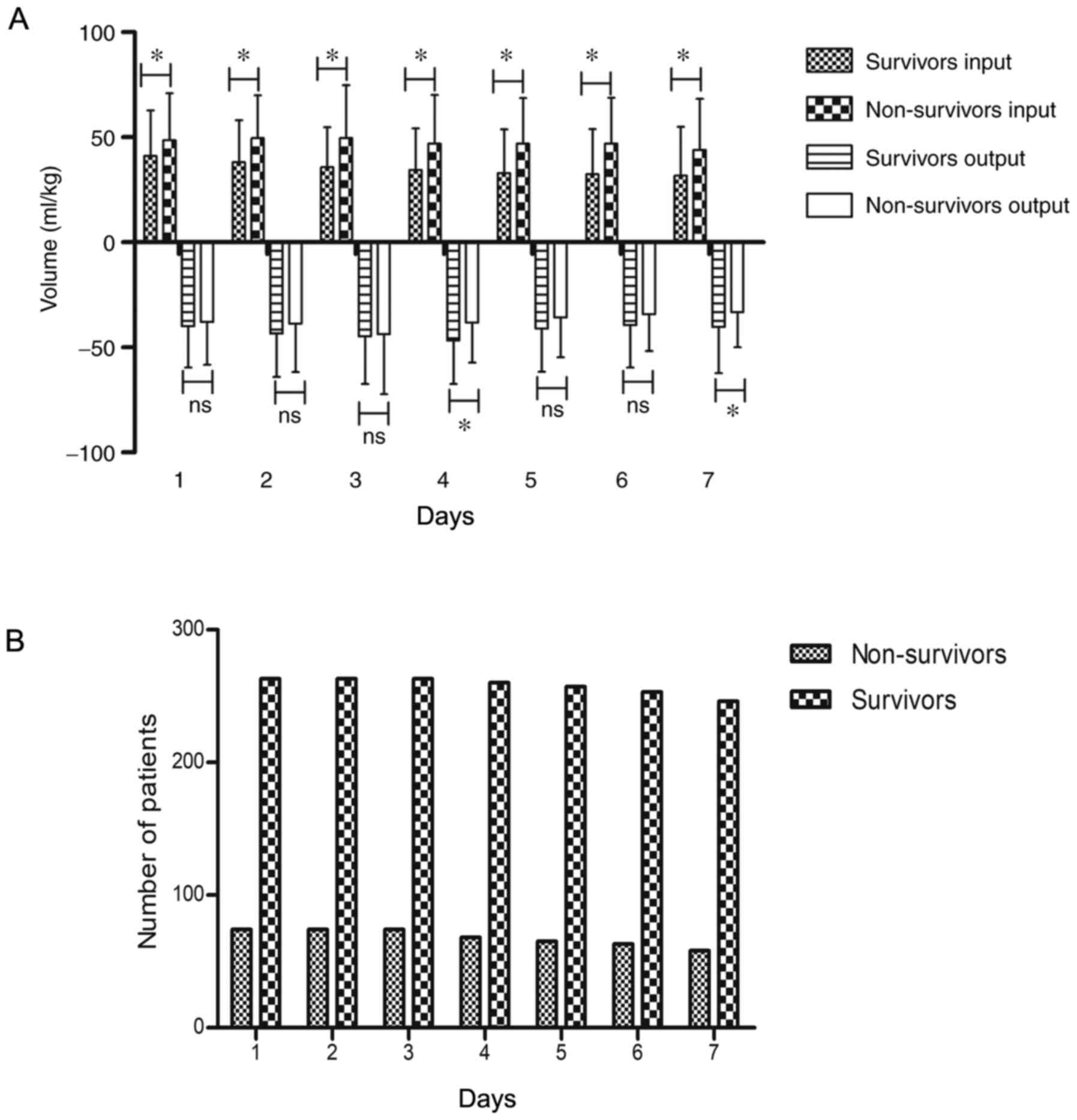
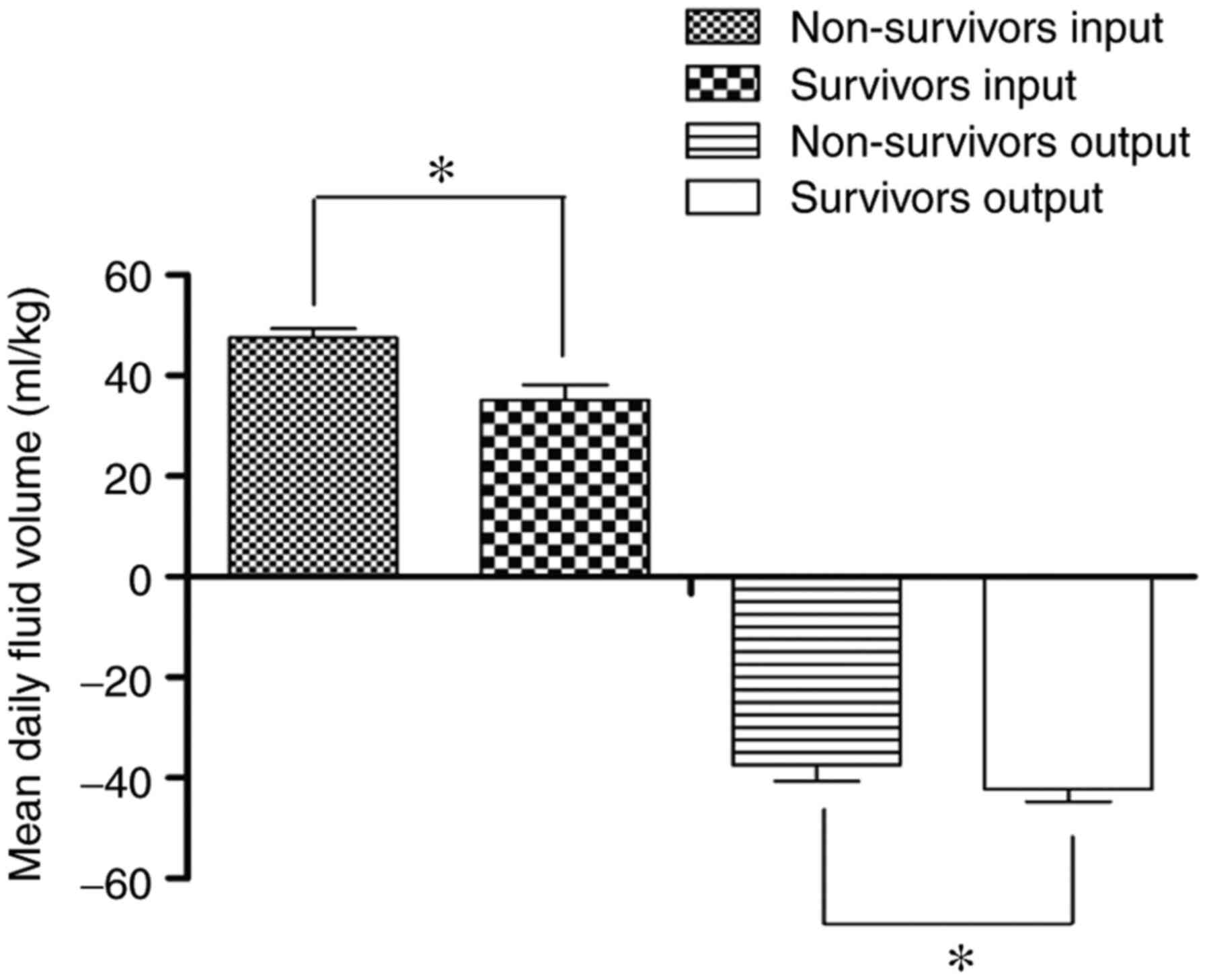
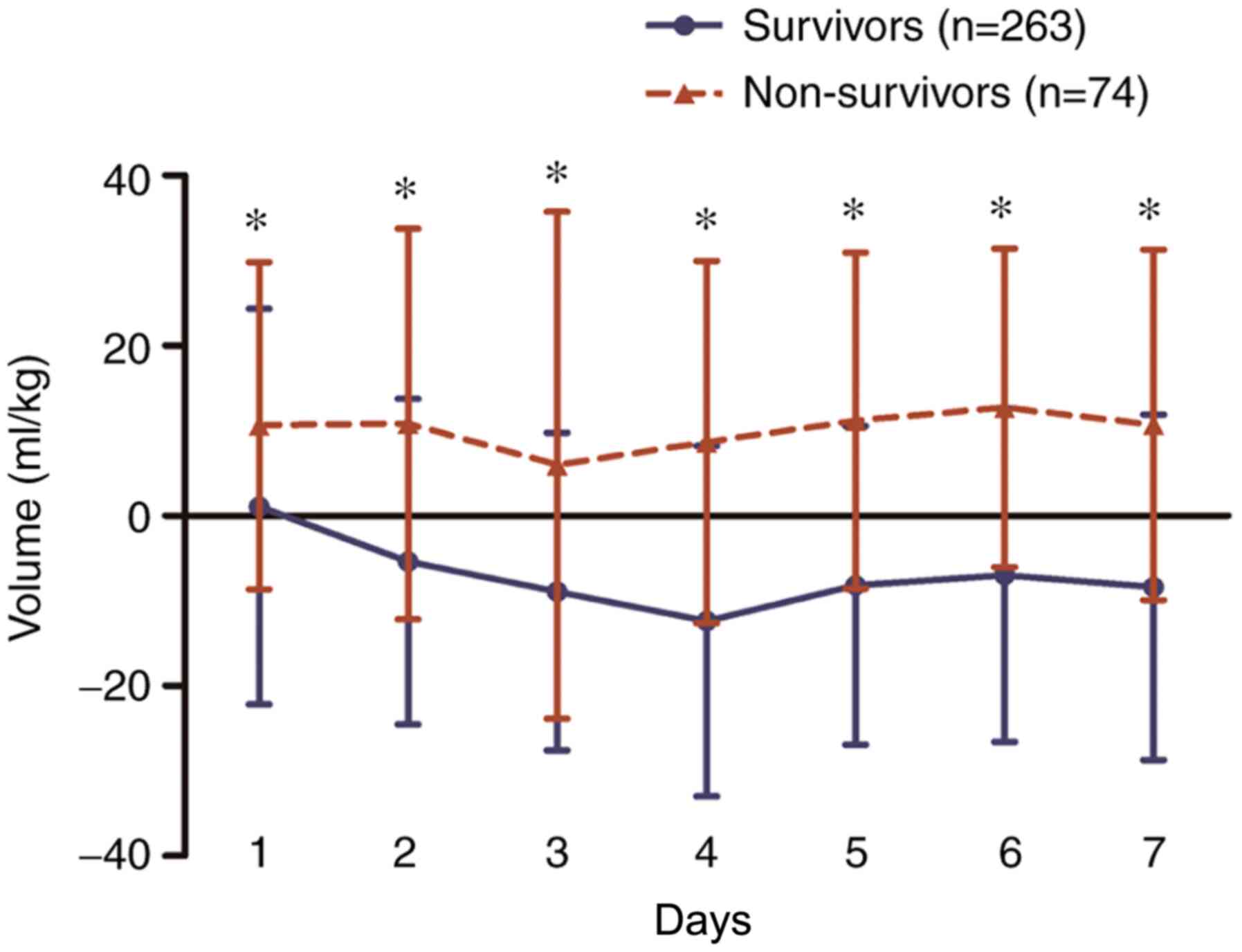
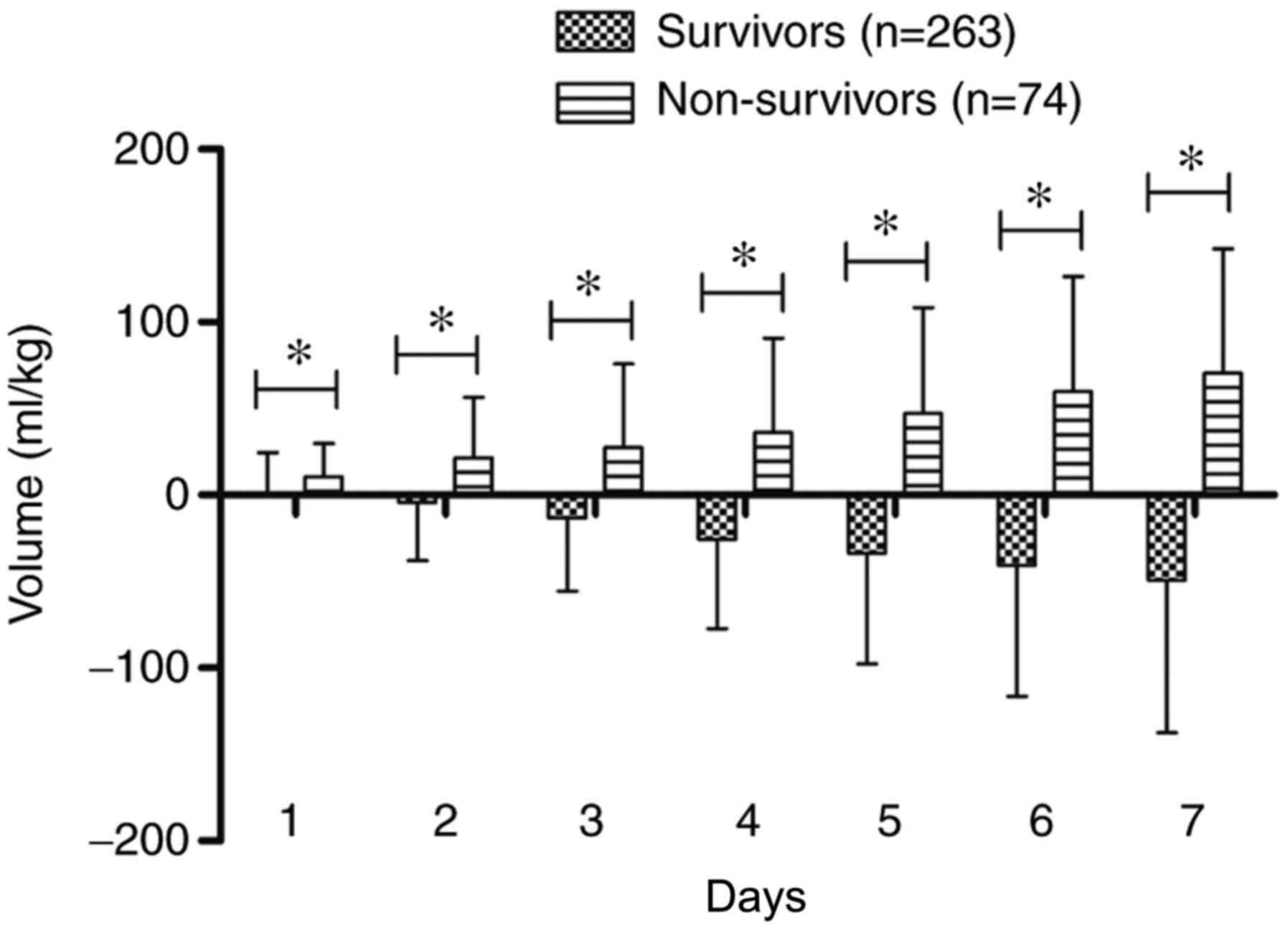
|
1
|
Singer M, Deutschman CS, Seymour CW,
Shankar-Hari M, Annane D, Bauer M, Bellomo R, Bernard GR, Chiche
JD, Coopersmith CM, Hotchkiss RS, et al: The third international
consensus definitions for sepsis and septic shock (Sepsis-3). JAMA.
315:801–810. 2016.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
2
|
Cohen J, Vincent JL, Adhikari NK, Machado
FR, Angus DC, Calandra T, Jaton K, Giulieri S, Delaloye J, Opal S,
et al: Sepsis: A roadmap for future research. Lancet Infect Dis.
15:581–614. 2015.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
3
|
Dellinger RP, Levy MM, Rhodes A, Annane D,
Gerlach H, Opal SM, Sevransky JE, Sprung CL, Douglas IS, Jaeschke
R, et al: Surviving sepsis campaign: International guidelines for
management of severe sepsis and septic shock, 2012. Intensive Care
Med. 39:165–228. 2013.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
4
|
Dellinger RP, Levy MM, Carlet JM, Bion J,
Parker MM, Jaeschke R, Reinhart K, Angus DC, Brun-Buisson C, Beale
R, et al: Surviving sepsis campaign: International guidelines for
management of severe sepsis and septic shock: 2008. Crit Care Med.
36:296–327. 2008.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
5
|
Vincent JL and De Backer D: Circulatory
shock. N Engl J Med. 369:1726–1734. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
6
|
Hoste EA, Maitland K, Brudney CS, Mehta R,
Vincent JL, Yates D, Kellum JA, Mythen MG and Shaw AD: ADQI XII
Investigators Group. Four phases of intravenous fluid therapy: A
conceptual model. Br J Anaesth. 113:740–747. 2014.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
7
|
Besen BA and Taniguchi LU: Negative fluid
balance in sepsis: When and how? Shock. 47 (1S Suppl 1):S35–S40.
2017.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
8
|
Cinel I, Kasapoglu US, Gul F and Dellinger
RP: The initial resuscitation of septic shock. J Crit Care.
57:108–117. 2020.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
9
|
Marik PE and Lemson J: Fluid
responsiveness: An evolution of our understanding. Br J Anaesth.
112:617–620. 2014.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
10
|
Acheampong A and Vincent JL: A positive
fluid balance is an independent prognostic factor in patients with
sepsis. Crit Care. 19(251)2015.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
11
|
Bagshaw SM, Brophy PD, Cruz D and Ronco C:
Fluid balance as a biomarker: Impact of fluid overload on outcome
in critically ill patients with acute kidney injury. Crit Care.
12(169)2008.PubMed/NCBI View
Article : Google Scholar
|
|
12
|
Sirvent JM, Ferri C, Baró A, Murcia C and
Lorencio C: Fluid balance in sepsis and septic shock as a
determining factor of mortality. Am J Emerg Med. 33:186–189.
2015.
|
|
13
|
Alsous F, Khamiees M, DeGirolamo A,
Amoateng-Adjepong Y and Manthous CA: Negative fluid balance
predicts survival in patients with septic shock: A retrospective
pilot study. Chest. 117:1749–1754. 2000.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
14
|
Brotfain E, Koyfman L, Toledano R, Borer
A, Fucs L, Galante O, Frenkel A, Kutz R and Klein M: Positive fluid
balance as a major predictor of clinical outcome of patients with
sepsis/septic shock after ICU discharge. Am J Emerg Med.
34:2122–2126. 2016.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
15
|
de Oliveira FS, Freitas FG, Ferreira EM,
de Castro I, Bafi AT, de Azevedo LC and Machado FR: Positive fluid
balance as a prognostic factor for mortality and acute kidney
injury in severe sepsis and septic shock. J Crit Care. 30:97–101.
2015.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
16
|
Sakr Y, Rubatto Birri PN, Kotfis K,
Nanchal R, Shah B, Kluge S, Schroeder ME, Marshall JC and Vincent
JL: Intensive Care Over Nations Investigators. Higher fluid balance
increases the risk of death from sepsis: Results from a large
international audit. Crit Care Med. 45:386–394. 2017.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
17
|
de Almeida JP, Palomba H, Galas FR,
Fukushima JT, Duarte FA, Nagaoka D, Torres V, Yu L, Vincent JL,
Auler JO Jr and Hajjar LA: Positive fluid balance is associated
with reduced survival in critically ill patients with cancer. Acta
Anaesthesiol Scand. 56:712–717. 2012.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
18
|
Dhondup T, Tien JC, Marquez A, Kennedy CC,
Gajic O and Kashani KB: Association of negative fluid balance
during the de-escalation phase of sepsis management with mortality:
A cohort study. J Crit Care. 55:16–21. 2020.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
19
|
National Heart Lung and Blood Institute
Acute Respiratory Distress Syndrome (ARDS) Clinical Trials Network.
Wiedemann HP, Wheeler AP, Bernard GR, Thompson BT, Hayden D,
deBoisblanc B, Connors AF Jr, Hite RD and Harabin AL: Comparison of
two fluid-management strategies in acute lung injury. N Engl J Med.
354:2564–2575. 2006.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
20
|
Silversides JA, Major E, Ferguson AJ, Mann
EE, McAuley DF, Marshall JC, Blackwood B and Fan E: Conservative
fluid management or deresuscitation for patients with sepsis or
acute respiratory distress syndrome following the resuscitation
phase of critical illness: A systematic review and meta-analysis.
Intensive Care Med. 43:155–170. 2017.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
21
|
Douglas IS, Alapat PM, Corl KA, Exline MC,
Forni LG, Holder AL, Kaufman DA, Khan A, Levy MM, Martin GS, et al:
Fluid response evaluation in sepsis hypotension and shock: A
randomized clinical trial. Chest. Apr 27. 2020.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar : (Online ahead of
print).
|
|
22
|
Shen Y, Ru W, Huang X and Zhang W:
Time-related association between fluid balance and mortality in
sepsis patients: Interaction between fluid balance and
haemodynamics. Sci Rep. 8(10390)2018. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
23
|
Rivers E, Nguyen B, Havstad S, Ressler J,
Muzzin A, Knoblich B, Peterson E and Tomlanovich M: Early
Goal-Directed Therapy Collaborative Group. Early goal-directed
therapy in the treatment of severe sepsis and septic shock. N Engl
J Med. 345:1368–1377. 2001.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
24
|
Mouncey PR, Osborn TM, Power GS, Harrison
DA, Sadique MZ, Grieve RD, Jahan R, Harvey SE, Bell D, Bion JF, et
al: Trial of early, goal-directed resuscitation for septic shock. N
Engl J Med. 372:1301–1311. 2015.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
25
|
ProCESS Investigators, Yealy DM, Kellum
JA, Huang DT, Barnato AE, Weissfeld LA, Pike F, Terndrup T, Wang
HE, Hou PC, et al: A randomized trial of protocol-based care for
early septic shock. N Engl J Med. 370:1683–1693. 2014.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
26
|
ARISE Investigators; ANZICS Clinical
Trials Group, Peake SL, Delaney A, Bailey M, Bellomo R, Cameron PA,
Cooper DJ, Higgins AM, Holdgate A, et al: Goal-directed
resuscitation for patients with early septic shock. N Engl J Med.
371:1496–1506. 2014.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
27
|
Skrypnik D, Mostowska A, Jagodzinski PP
and Bogdański P: Association of rs699947 (-2578 C/A) and rs2010963
(-634 G/C) single nucleotide polymorphisms of the VEGF gene, VEGF-A
and leptin serum level, and cardiovascular risk in patients with
excess body mass: A case-control study. J Clin Med.
9(469)2020.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
28
|
Rhodes A, Evans LE, Alhazzani W, Levy MM,
Antonelli M, Ferrer R, Kumar A, Sevransky JE, Sprung CL, Nunnally
ME, et al: Surviving sepsis campaign: International guidelines for
management of sepsis and septic shock: 2016. Intensive Care Med.
43:304–377. 2017.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
29
|
Levy MM, Dellinger RP, Townsend SR,
Linde-Zwirble WT, Marshall JC, Bion J, Schorr C, Artigas A, Ramsay
G, Beale R, et al: The surviving sepsis campaign: Results of an
international guideline-based performance improvement program
targeting severe sepsis. Crit Care Med. 38:367–374. 2010.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
30
|
Levy MM, Rhodes A, Phillips GS, Townsend
SR, Schorr CA, Beale R, Osborn T, Lemeshow S, Chiche JD, Artigas A
and Dellinger RP: Surviving sepsis campaign: Association between
performance metrics and outcomes in a 7.5-year study. Crit Care
Med. 43:3–12. 2015.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
31
|
Boyd JH, Forbes J, Nakada TA, Walley KR
and Russell JA: Fluid resuscitation in septic shock: A positive
fluid balance and elevated central venous pressure are associated
with increased mortality. Crit Care Med. 39:259–265.
2011.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
32
|
Tigabu BM, Davari M, Kebriaeezadeh A and
Mojtahedzadeh M: Fluid volume, fluid balance and patient outcome in
severe sepsis and septic shock: A systematic review. J Crit Care.
48:153–159. 2018.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
33
|
Huang AC, Lee TY, Ko MC, Huang CH, Wang
TY, Lin TY and Lin SM: Fluid balance correlates with clinical
course of multiple organ dysfunction syndrome and mortality in
patients with septic shock. PLoS One. 14(e0225423)2019.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
34
|
Soares M, Caruso P, Silva E, Teles JM,
Lobo SM, Friedman G, Dal Pizzol F, Mello PV, Bozza FA, Silva UV, et
al: Characteristics and outcomes of patients with cancer requiring
admission to intensive care units: A prospective multicenter study.
Crit Care Med. 38:9–15. 2010.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|