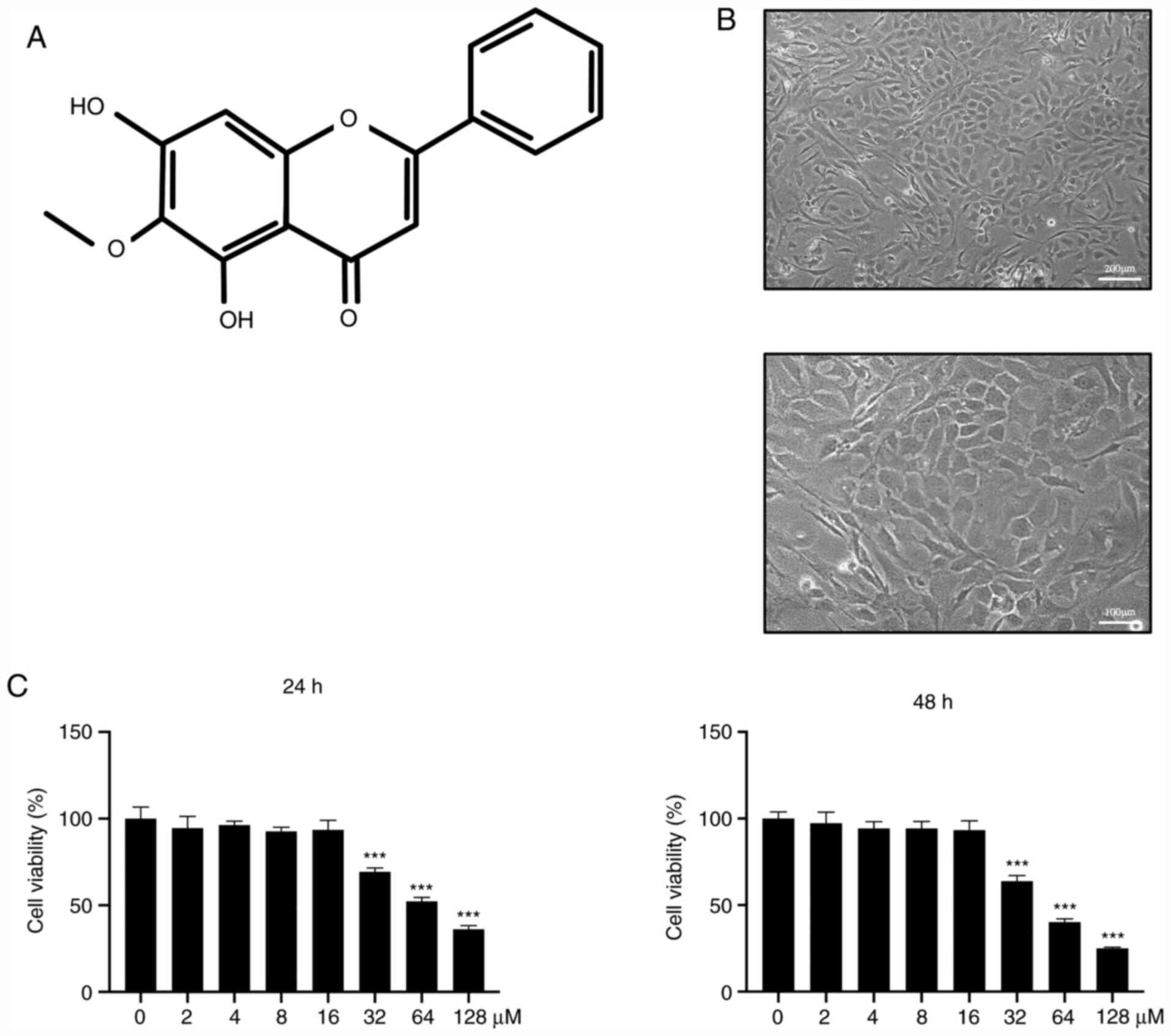
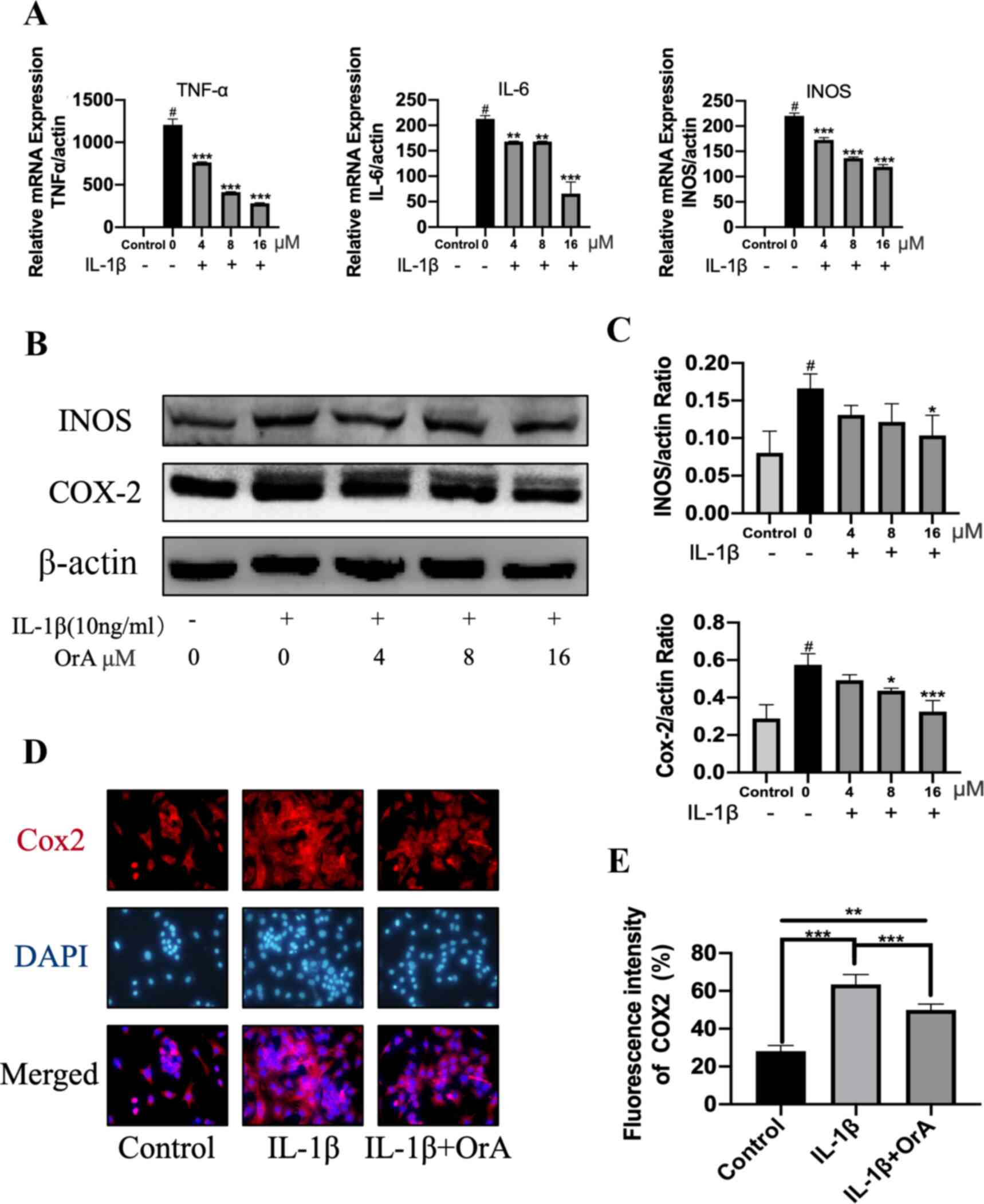
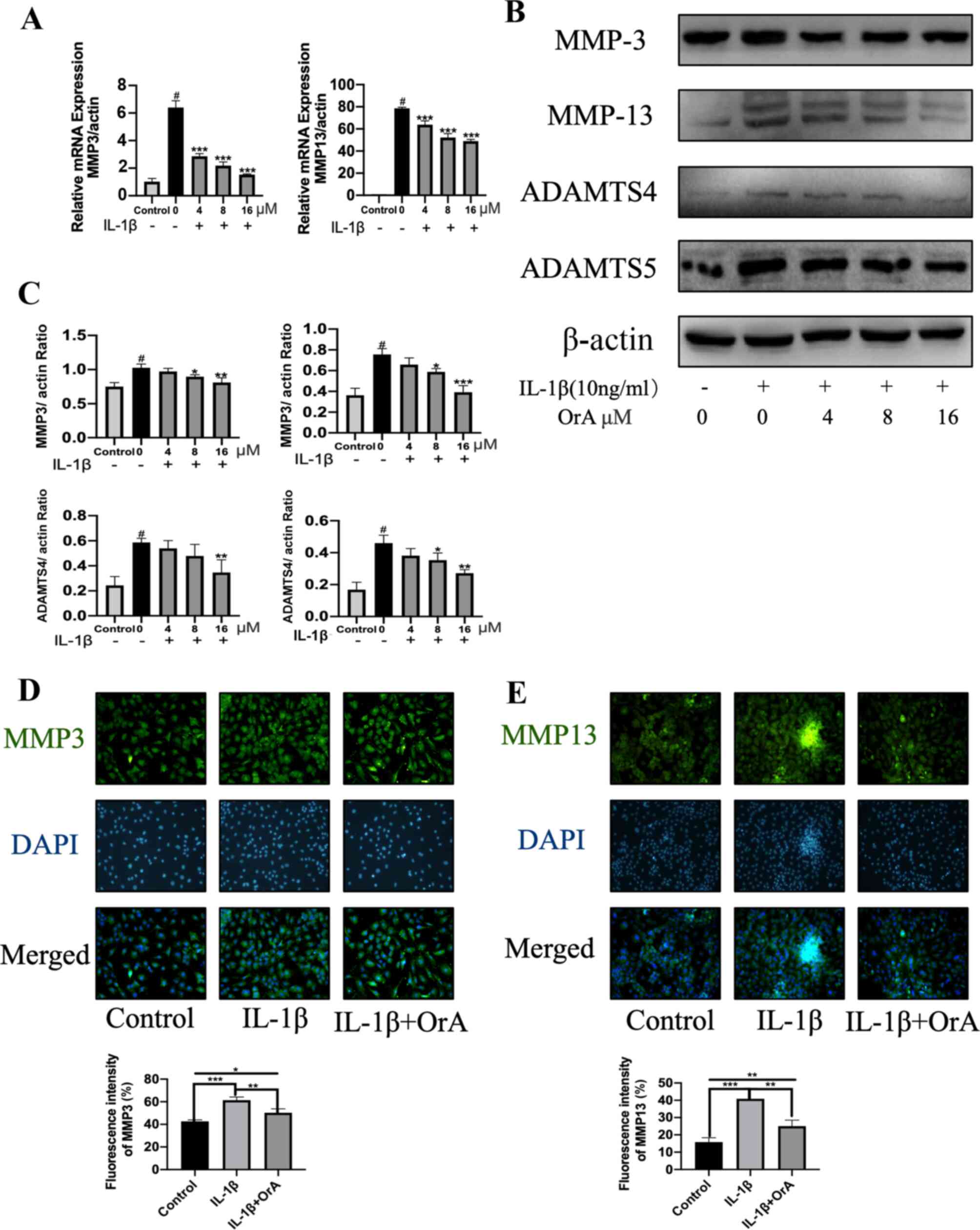
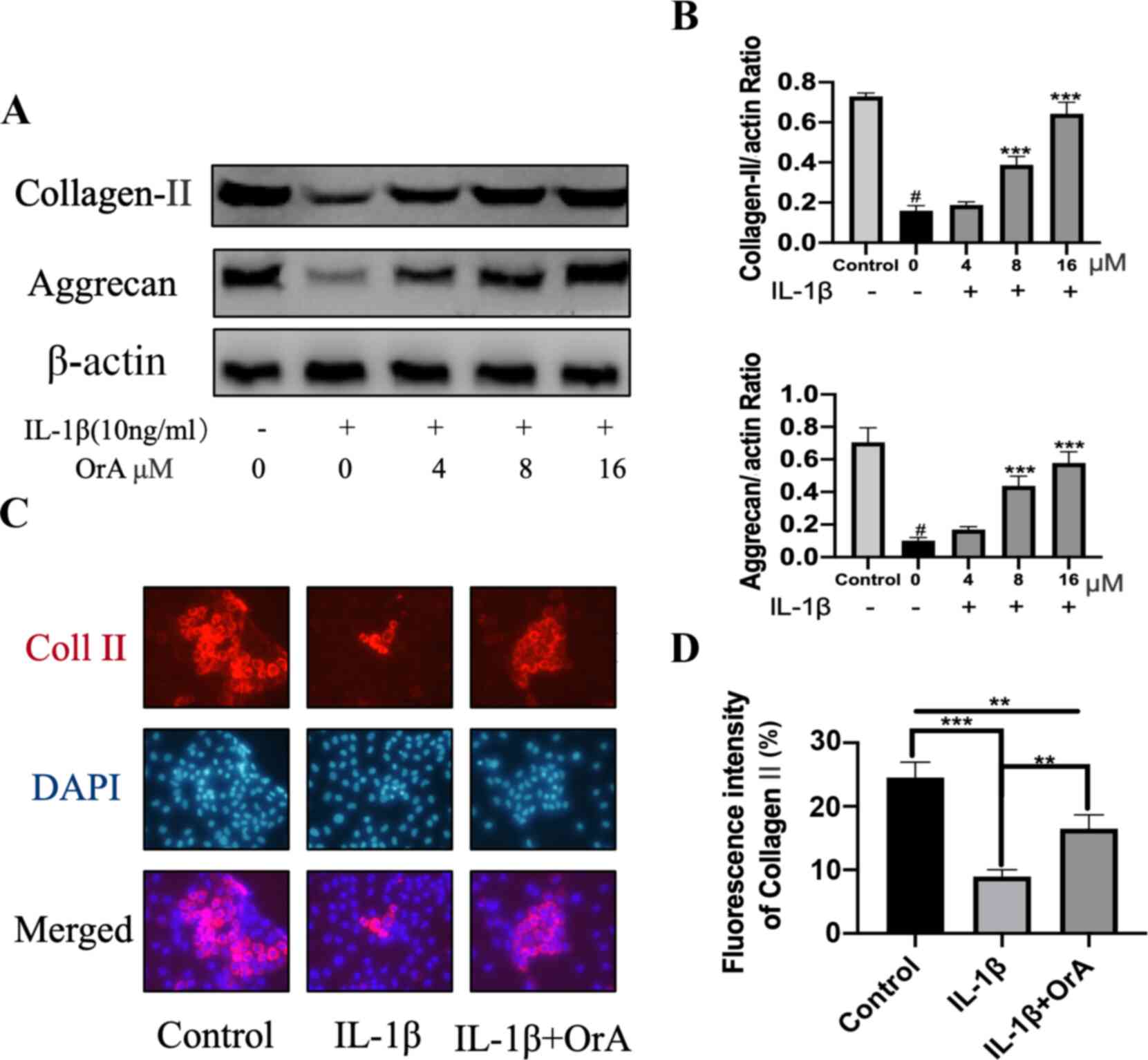
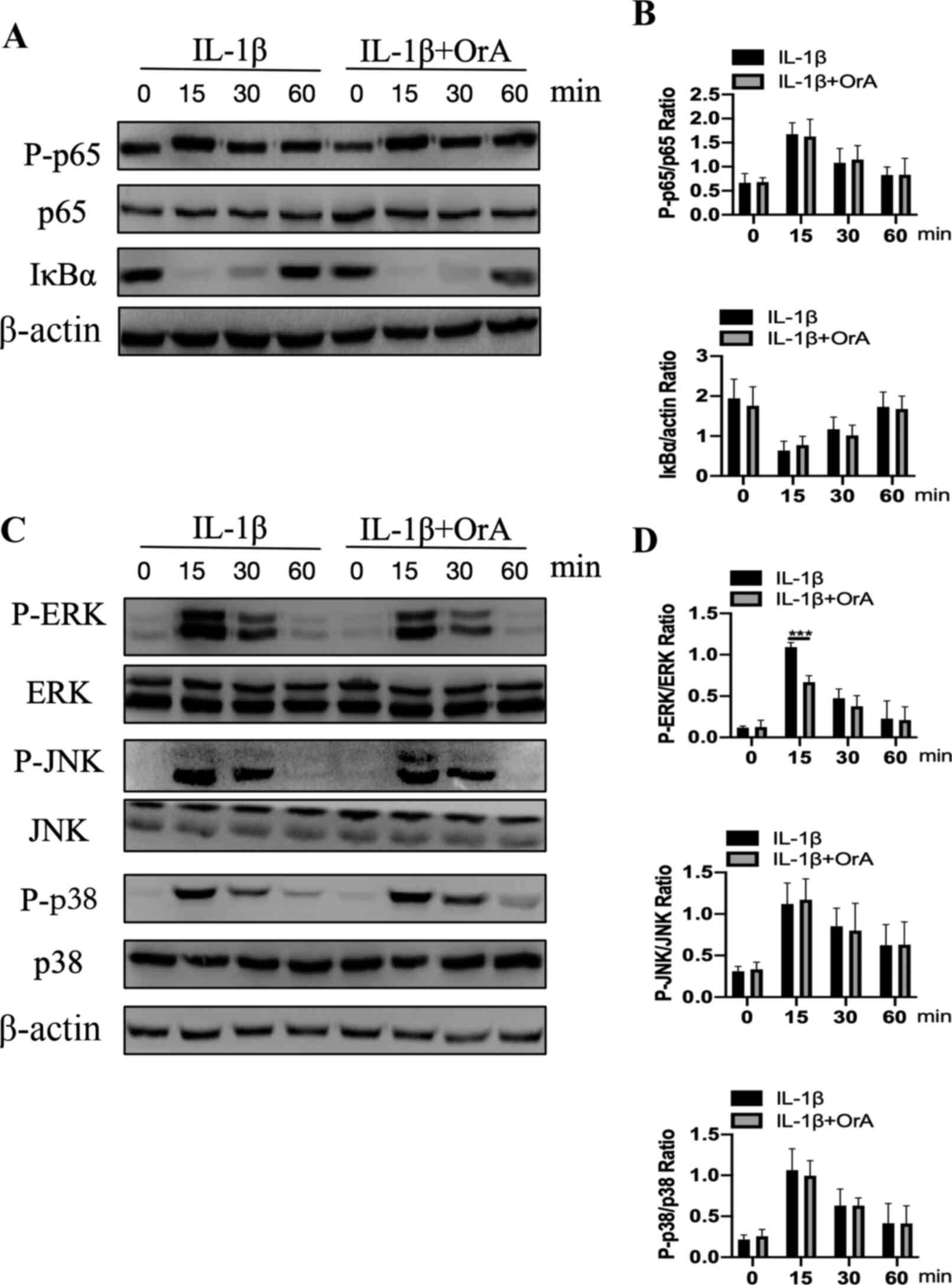
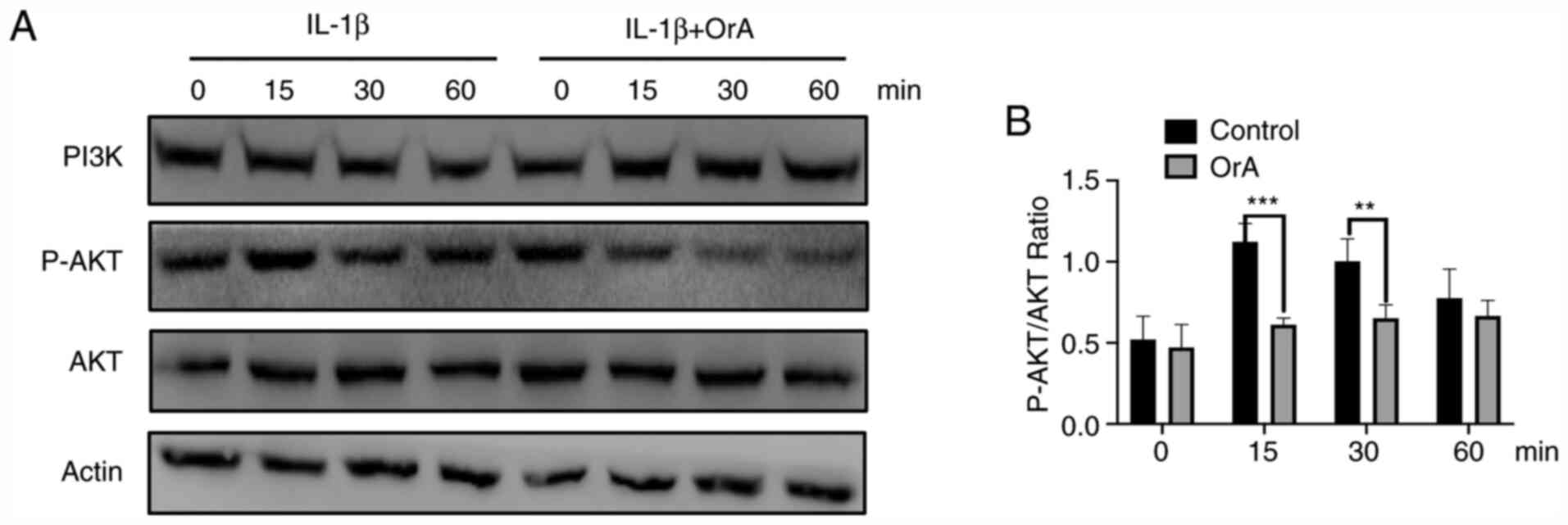
|
1
|
Ji Q, Xu X, Kang L, Xu Y, Xiao J, Goodman
SB, Zhu X, Li W, Liu J, Gao X, et al: Hematopoietic PBX-interacting
protein mediates cartilage degeneration during the pathogenesis of
osteoarthritis. Nat Commun. 10(313)2019.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
2
|
Ashford S and Williard J: Osteoarthritis:
A review. Nurse Pract. 39:1–8. 2014.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
3
|
Abramson SB: Inflammation in
osteoarthritis. J Rheumatol Suppl. 70:70–76. 2004.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
4
|
Chen YF, Jobanputra P, Barton P, Bryan S,
Fry-Smith A, Harris G and Taylor RS: Cyclooxygenase-2 selective
non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs (etodolac, meloxicam,
celecoxib, rofecoxib, etoricoxib, valdecoxib and lumiracoxib) for
osteoarthritis and rheumatoid arthritis: A systematic review and
economic evaluation. Health Technol Assess. 12:1–278.
2008.PubMed/NCBI View
Article : Google Scholar
|
|
5
|
Lane NE: Pain management in
osteoarthritis: The role of COX-2 inhibitors. J Rheumatol Suppl.
49:20–24. 1997.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
6
|
Hungin APS and Kean WF: Nonsteroidal
anti-inflammatory drugs: Overused or underused in osteoarthritis?
Am J Med. 110 (Suppl):S8–S11. 2001.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
7
|
Felson DT: Risk factors for
osteoarthritis: Understanding joint vulnerability. Clin Orthop
Relat Res. 427:16–21. 2004.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
8
|
Goldring MB and Otero M: Inflammation in
osteoarthritis. Curr Opin Rheumatol. 23:471–478. 2011.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
9
|
Mokuda S, Nakamichi R, Matsuzaki T, Ito Y,
Sato T, Miyata K, Inui M, Olmer M, Sugiyama E, Lotz M and Asahara
H: Wwp2 maintains cartilage homeostasis through regulation of
Adamts5. Nat Commun. 10(2429)2019.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
10
|
Lee JH, Shehzad O, Ko SK, Kim YS and Kim
HP: Matrix metalloproteinase-13 downregulation and potential
cartilage protective action of the Korean Red Ginseng preparation.
J Ginseng Res. 39:54–60. 2015.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
11
|
Gao Y, Liu S, Huang J, Guo W, Chen J,
Zhang L, Zhao B, Peng J, Wang A, Wang Y, et al: The ECM-cell
interaction of cartilage extracellular matrix on chondrocytes.
Biomed Res Int. 2014(648459)2014.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
12
|
Wang M, Sampson ER, Jin H, Li J, Ke QH, Im
HJ and Chen D: MMP13 is a critical target gene during the
progression of osteoarthritis. Arthritis Res Ther.
15(R5)2013.PubMed/NCBI View
Article : Google Scholar
|
|
13
|
Kubota E, Imamura H, Kubota T, Shibata T
and Murakami KI: Interleukin-1 beta and stromelysin (MMP3) activity
of synovial fluid as possible markers of osteoarthritis in the
temporomandibular joint. J Oral Maxillofac Surg. 55:20–28.
1997.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
14
|
Studer R, Jaffurs D, Stefanovic-Racic M,
Robbins PD and Evans CH: Nitric oxide in osteoarthritis.
Osteoarthritis Cartilage. 7:377–379. 1999.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
15
|
Smith RL: Degradative enzymes in
osteoarthritis. Front Biosci. 4(D704-D712)1999.PubMed/NCBI View
Article : Google Scholar
|
|
16
|
Tchetina EV, Squires G and Poole AR:
Increased type II collagen degradation and very early focal
cartilage degeneration is associated with upregulation of
chondrocyte differentiation related genes in early human articular
cartilage lesions. J Rheumatol. 32:876–886. 2005.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
17
|
Vertel BM: The ins and outs of aggrecan.
Trends Cell Biol. 5:458–464. 1995.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
18
|
Ding J, Ghali O, Lencel P, Broux O,
Chauveau C, Devedjian JC, Hardouin P and Magne D: TNF-alpha and
IL-1beta inhibit RUNX2 and collagen expression but increase
alkaline phosphatase activity and mineralization in human
mesenchymal stem cells. Life Sci. 84:499–504. 2009.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
19
|
Wang J, Markova D, Anderson DG, Zheng Z,
Shapiro IM and Risbud MV: TNF-α and IL-1β promote a
disintegrin-like and metalloprotease with thrombospondin type I
motif-5-mediated aggrecan degradation through syndecan-4 in
intervertebral disc. J Biol Chem. 286:39738–39749. 2011.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
20
|
Zou M, Hu C, You Q, Zhang A, Wang X and
Guo Q: Oroxylin A induces autophagy in human malignant glioma cells
via the mTOR-STAT3-Notch signaling pathway. Mol Carcinog.
54:1363–1375. 2015.PubMed/NCBI View
Article : Google Scholar
|
|
21
|
Yao J, Hu R, Sun J, Lin B, Zhao L, Sha Y,
Zhu B, You QD, Yan T and Guo QL: Oroxylin a prevents
inflammation-related tumor through down-regulation of inflammatory
gene expression by inhibiting NF-κB signaling. Mol Carcinog.
53:145–158. 2014.PubMed/NCBI View
Article : Google Scholar
|
|
22
|
Ye M, Wang Q, Zhang W, Li Z, Wang Y and Hu
R: Oroxylin A exerts anti-inflammatory activity on
lipopolysaccharide-induced mouse macrophage via Nrf2/ARE
activation. Biochem Cell Biol. 92:337–348. 2014.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
23
|
Li J, Tong D, Liu J, Chen F and Shen Y:
Oroxylin A attenuates cigarette smoke-induced lung inflammation by
activating Nrf2. Int Immunopharmacol. 40:524–529. 2016.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
24
|
Han Q, Wang H, Xiao C, Fu BD and Du CT:
Oroxylin A inhibits H2O2-induced oxidative
stress in PC12 cells. Nat Prod Res. 31:1339–1342. 2017.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
25
|
Zou M, Lu N, Hu C, Liu W, Sun Y, Wang X,
You Q, Gu C, Xi T and Guo Q: Beclin 1-mediated autophagy in
hepatocellular carcinoma cells: Implication in anticancer
efficiency of oroxylin A via inhibition of mTOR signaling. Cell
Signal. 24:1722–1732. 2012.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
26
|
Sun Y, Lu N, Ling Y, Gao Y, Chen Y, Wang
L, Hu R, Qi Q, Liu W, Yang Y, et al: Oroxylin A suppresses invasion
through down-regulating the expression of matrix
metalloproteinase-2/9 in MDA-MB-435 human breast cancer cells. Eur
J Pharmacol. 603:22–28. 2009.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
27
|
Choi HW, Shin PG, Lee JH, Choi WS, Kang
MJ, Kong WS, Kang MJ, Kong WS, Oh MJ, Seo YB and Kim GD:
Anti-inflammatory effect of lovastatin is mediated via the
modulation of NF-κB and inhibition of HDAC1 and the PI3K/Akt/mTOR
pathway in RAW264. 7 macrophages. Int J Mol Med. 41:1103–119.
2018.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
28
|
Chen YC, Yang LL and Lee TJF: Oroxylin A
inhibition of lipopolysaccharide-induced iNOS and COX-2 gene
expression via suppression of nuclear factor-κB activation. Biochem
Pharmacol. 59:1445–1457. 2000.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
29
|
Livak KJ and Schmittgen TD: Analysis of
relative gene expression data using real-time quantitative PCR and
the 2(-Delta Delta C(T)) method. Methods. 25:402–408.
2001.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
30
|
Sherwin CM, Christiansen SB, Duncan IJ,
Erhard HW, Lay DC, Mench JA, O'Connorg CE and Petherick CJ:
Guidelines for the ethical use of animals in applied ethology
studies. Appl Anim Behav Sci. 81:291–305. 2003. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
31
|
Derrell CJ, Gebhart GF, Gonder JC, Keeling
ME and Kohn DF: Special Report: The 1996 Guide for the care and use
of laboratory animals. ILAR J. 38:41–48. 1997.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
32
|
Glasson SS, Askew R, Sheppard B, Carito B,
Blanchet T, Ma HL, Flannery CR, Peluso D, Kanki K, Yang Z, et al:
Deletion of active ADAMTS5 prevents cartilage degradation in a
murine model of osteoarthritis. Nature. 434:644–648.
2005.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
33
|
Poole AR, Kobayashi M, Yasuda T, Laverty
S, Mwale F, Kojima T, Sakai T, Wahl C, El-Maadawy S, Webb G, et al:
Type II collagen degradation and its regulation in articular
cartilage in osteoarthritis. Ann Rheum Dis. 61 (Suppl 2):ii78–ii81.
2002.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
34
|
Song RH, Tortorella MD, Malfait AM, Alston
JT, Yang Z, Arner EC and Griggs DW: Aggrecan degradation in human
articular cartilage explants is mediated by both ADAMTS-4 and
ADAMTS-5. Arthritis Rheum. 56:575–585. 2014.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
35
|
Glyn-Jones S, Palmer AJR, Agricola R,
Price AJ, Vincent TL, Weinans H and Carr AJ: Osteoarthritis.
Lancet. 386:376–387. 2015.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
36
|
Zhang Y and Jordan JM: Epidemiology of
osteoarthritis. Clin Geriatr Med. 26:355–369. 2010.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
37
|
Sarzi-Puttini P, Cimmino MA, Scarpa R,
Caporali R, Parazzini F, Zaninelli A, Atzeni F and Canesi B:
Osteoarthritis: An overview of the disease and its treatment
strategies. Semin Arthritis Rheum. 35:1–10. 2005.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
38
|
Giercksky KE, Huseby G and Rugstad HE:
Epidemiology of NSAID-related gastrointestinal side effects. Scand
J Gastroenterol Suppl. 163:3–8. 1989.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
39
|
Lichtenberger LM, Zhou Y, Dial EJ and
Raphael RM: NSAID injury to the gastrointestinal tract: Evidence
that NSAIDs interact with phospholipids to weaken the hydrophobic
surface barrier and induce the formation of unstable pores in
membranes. J Pharm Pharmacol. 58:1421–1428. 2010.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
40
|
Song X, Chen Y, Sun Y, Lin B, Qin Y, Hui
H, Li Z, You Q, Lu N and Guo Q: Oroxylin A, a classical natural
product, shows a novel inhibitory effect on angiogenesis induced by
lipopolysaccharide. Pharmacol Rep. 64:1189–1199. 2012.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
41
|
Sun X, Chang X, Wang Y, Xu B and Cao X:
Oroxylin A suppresses the cell proliferation, migration, and EMT
via NF-κB signaling pathway in human breast cancer cells. Biomed
Res Int. 2019(9241769)2019.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
42
|
Roos EM and Arden NK: Strategies for the
prevention of knee osteoarthritis. Nat Rev Rheumatol.
12(92)2016.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
43
|
Luo Y, Sinkeviciute D, He Y, Karsdal M,
Henrotin Y, Mobasheri A, Önnerfjord P and Bay-Jensen A: The minor
collagens in articular cartilage. Protein Cell. 8:560–572.
2017.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
44
|
Bonassar LJ, Sandy JD, Lark MW, Plaas AHK,
Frank EH and Grodzinsky AJ: Inhibition of cartilage degradation and
changes in physical properties induced by IL-1β and retinoic acid
using matrix metalloproteinase inhibitors. Arch Biochem Biophys.
344:404–412. 1997.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
45
|
Needleman P and Manning PT: Interactions
between the inducible cyclooxygenase (COX-2) and nitric oxide
synthase (iNOS) pathways: Implications for therapeutic intervention
in osteoarthritis. Osteoarthritis Cartilage. 7:367–370.
1999.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
46
|
More AS, Kumari RR, Gupta G, Lingaraju MC,
Balaganur V, Pathak NN, Kumar D, Kumar D, Sharma AK and Tandan SK:
Effect of iNOS inhibitor S-methylisothiourea in monosodium
iodoacetate-induced osteoathritic pain: Implication for
osteoarthritis therapy. Pharmacol Biochem Behav. 103:764–772.
2013.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
47
|
Watson DJ, Harper SE, Zhao PL, Quan H,
Bolognese JA and Simon TJ: Gastrointestinal tolerability of the
selective cyclooxygenase-2 (COX-2) inhibitor rofecoxib compared
with nonselective COX-1 and COX-2 inhibitors in osteoarthritis.
Arch Intern Med. 160:2998–3003. 2000.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
48
|
Wong M and Carter DR: Articular cartilage
functional histomorphology and mechanobiology: A research
perspective. Bone. 33:1–13. 2003.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
49
|
Rahmati M, Nalesso G, Mobasheri A and
Mozafari M: Aging and osteoarthritis: Central role of the
extracellular matrix. Ageing Res Rev. 40:20–30. 2017.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
50
|
Pattoli MA, MacMaster JF, Gregor KR and
Burke JR: Collagen and aggrecan degradation is blocked in
interleukin-1-treated cartilage explants by an inhibitor of IκB
kinase through suppression of metalloproteinase expression. J
Pharmacol Exp Ther. 315:382–388. 2005.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
51
|
Stanton H, Rogerson FM, East CJ, Golub SB,
Lawlor KE, Meeker CT, Little CB, Last K, Farmer PJ, Campbell IK, et
al: ADAMTS5 is the major aggrecanase in mouse cartilage in vivo and
in vitro. Nature. 434:648–652. 2005.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
52
|
Song RH, Tortorella MD, Malfait AM, Alston
JT, Yang Z, Arner EC and Griggs DW: Aggrecan degradation in human
articular cartilage explants is mediated by both ADAMTS-4 and
ADAMTS-5. Arthritis Rheum. 56:575–585. 2007.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
53
|
Shi J, Zhang C, Yi Z and Lan C: Explore
the variation of MMP3, JNK, p38 MAPKs, and autophagy at the early
stage of osteoarthritis. IUBMB Life. 68:293–302. 2016.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
54
|
Chow YY and Chin KY: The role of
inflammation in the pathogenesis of osteoarthritis. Mediators
Inflamm. 2020(8293921)2020.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
55
|
Gao SC, Yin HB, Liu HX and Sui YH:
Research progress on MAPK signal pathway in the pathogenesis of
osteoarthritis. Zhongguo Gu Shang. 27:441–444. 2014.PubMed/NCBI(In Chinese).
|
|
56
|
Liu Z, Cai H, Zheng X, Zhang B and Xia C:
The involvement of mutual inhibition of ERK and mTOR in
PLCγ1-mediated MMP-13 expression in human osteoarthritis
chondrocytes. Int J Mol Sci. 16:17857–17869. 2015.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
57
|
Hashizume M and Mihara M: High molecular
weight hyaluronic acid inhibits IL-6-induced MMP production from
human chondrocytes by up-regulating the ERK inhibitor, MKP-1.
Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 403:184–189. 2010.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
58
|
Xue JF, Shi ZM, Zou J and Li XL:
Inhibition of PI3K/AKT/mTOR signaling pathway promotes autophagy of
articular chondrocytes and attenuates inflammatory response in rats
with osteoarthritis. Biomed Pharmacother. 89:1252–1261.
2017.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
59
|
Cheng CC, Uchiyama Y, Hiyama A, Gajghate
S, Shapiro IM and Risbud MV: PI3K/AKT regulates aggrecan gene
expression by modulating Sox9 expression and activity in nucleus
pulposus cells of the intervertebral disc. J Cell Physiol.
221:668–676. 2009.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|