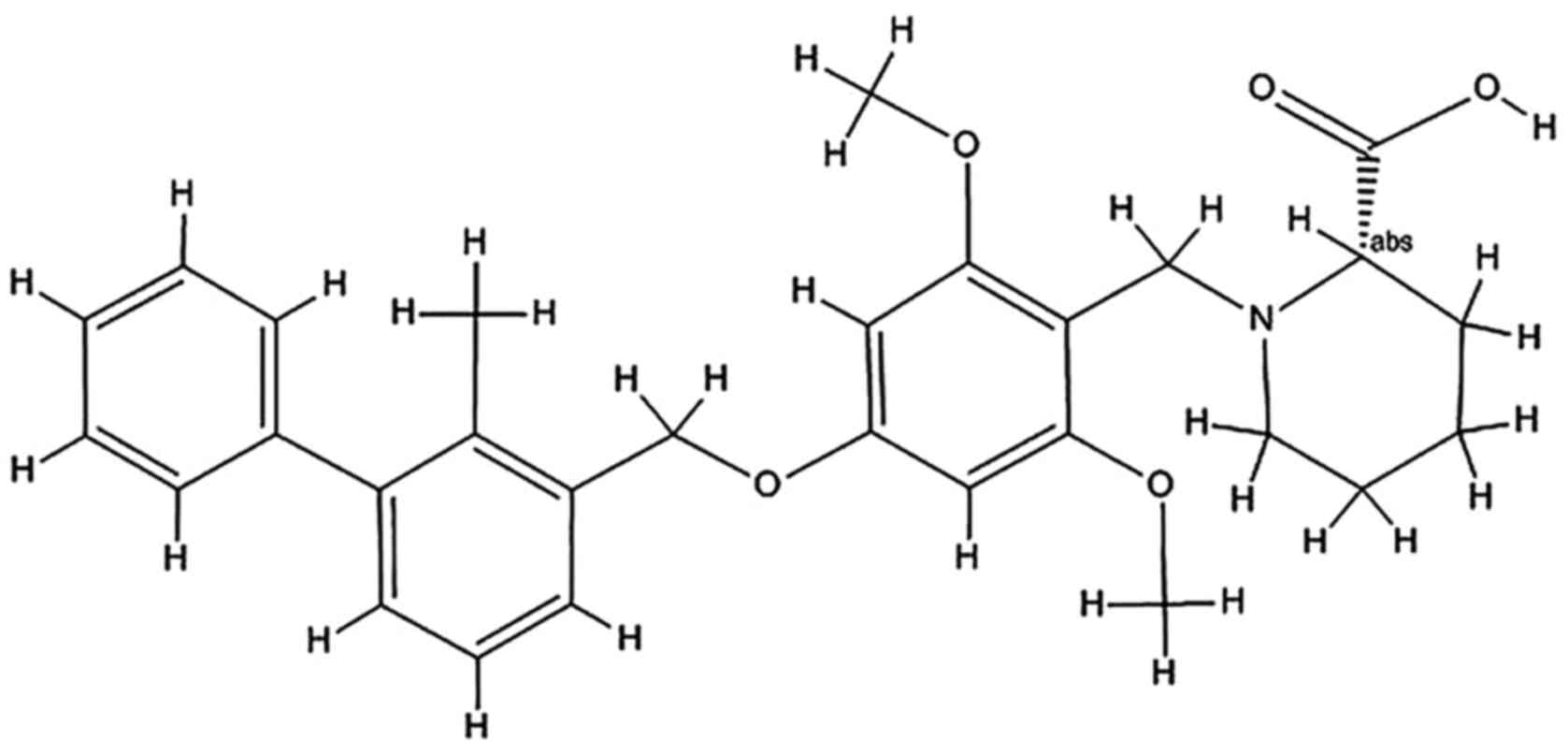
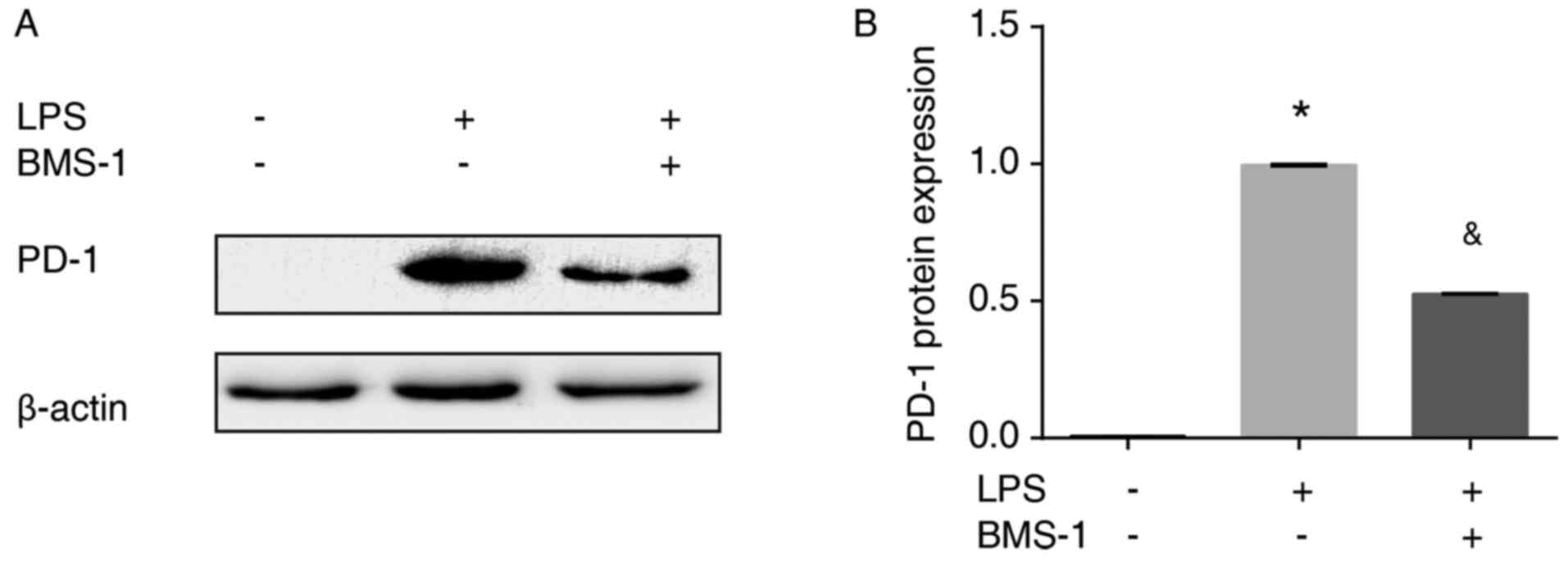
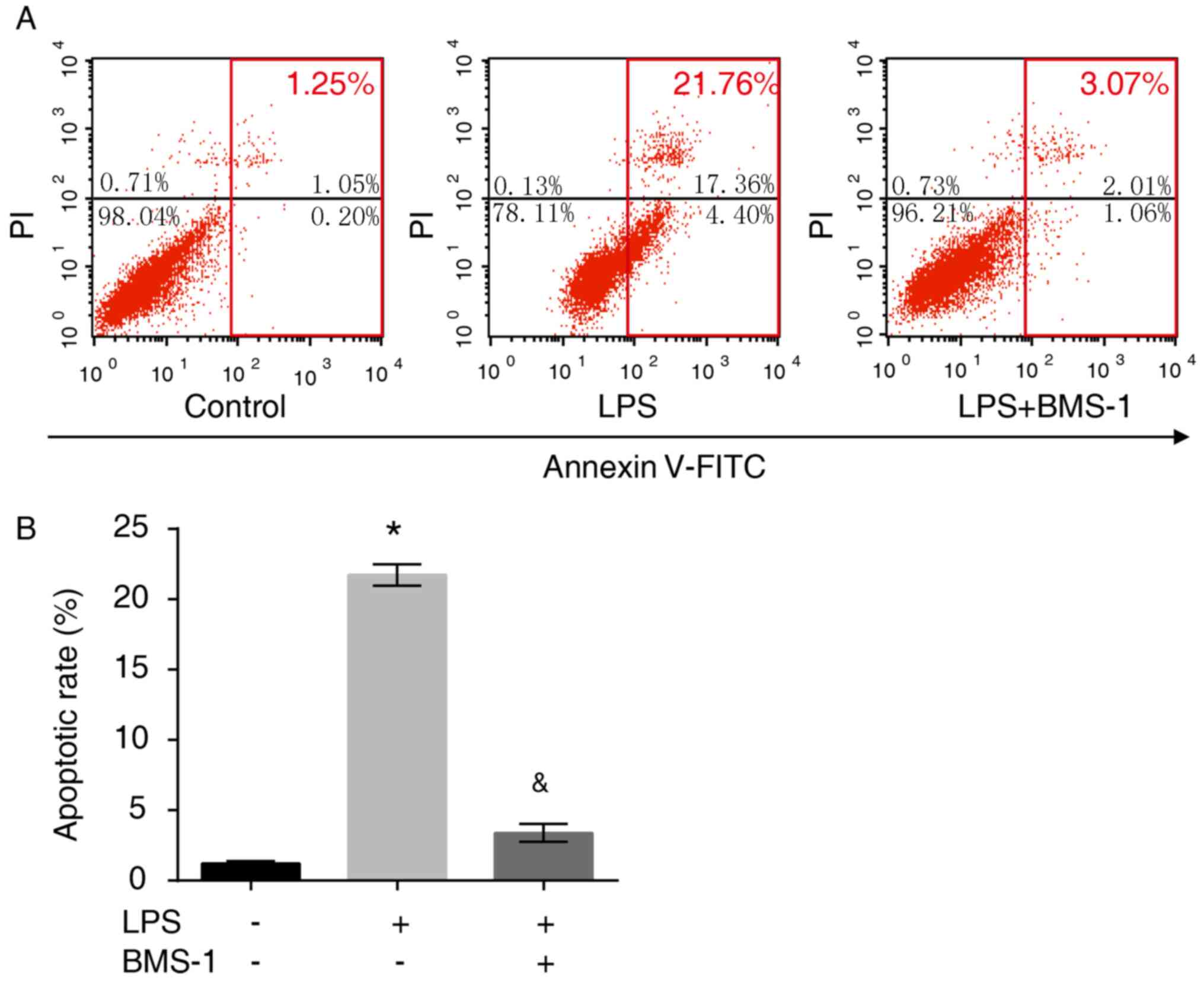
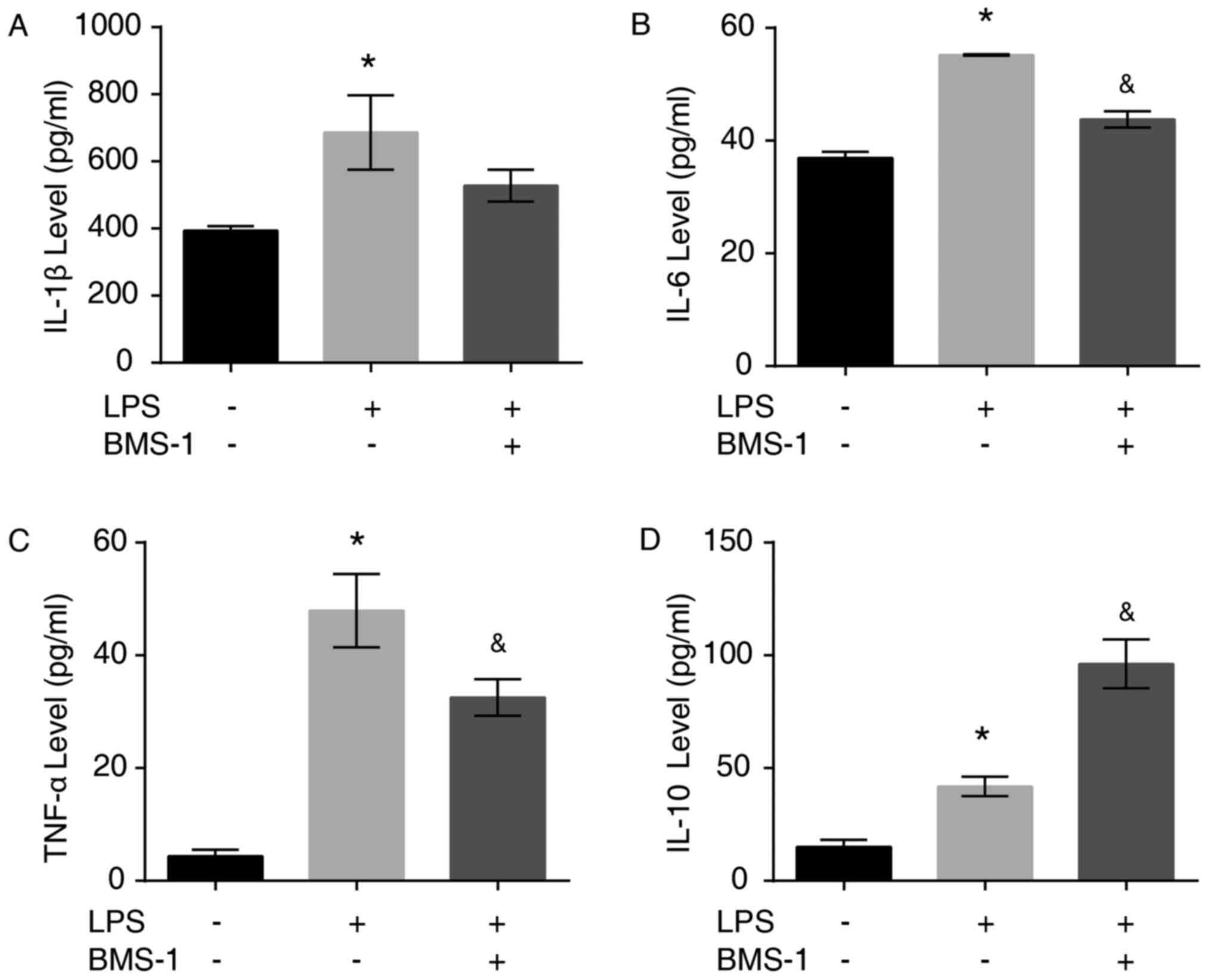
|
1
|
Singer M, Deutschman CS, Seymour CW,
Shankar-Hari M, Annane D, Bauer M, Bellomo R, Bernard GR, Chiche
JD, Coopersmith CM, et al: The third international consensus
definitions for sepsis and septic shock (Sepsis-3). JAMA.
315:801–810. 2016.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
2
|
Kempker JA and Martin GS: The changing
epidemiology and definitions of sepsis. Clin Chest Med. 37:165–179.
2016.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
3
|
Wang YM, Ji R, Chen WW, Huang SW, Zheng
YJ, Yang ZT, Qu HP, Chen H, Mao EQ, Chen Y and Chen EZ: Paclitaxel
alleviated sepsis-induced acute lung injury by activating MUC1 and
suppressing TLR-4/NF-κB pathway. Drug Des Devel Ther. 13:3391–3404.
2019.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
4
|
Johnson ER and Matthay MA: Acute lung
injury: Epidemiology, pathogenesis, and treatment. J Aerosol Med
Pulm Drug Deliv. 23:243–252. 2010.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
5
|
Zahar JR, Timsit JF, Garrouste-Orgeas M,
Français A, Vesin A, Descorps-Declere A, Dubois Y, Souweine B,
Haouache H, Goldgran-Toledano D, et al: Outcomes in severe sepsis
and patients with septic shock: Pathogen species and infection
sites are not associated with mortality. Crit Care Med.
39:1886–1895. 2011.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
6
|
Matthay MA, Ware LB and Zimmerman GA: The
acute respiratory distress syndrome. J Clin Invest. 122:2731–2740.
2012.PubMed/NCBI View
Article : Google Scholar
|
|
7
|
Huang C, Zheng H, He W, Lu G, Li X, Deng Y
and Zeng M: Ghrelin ameliorates the human alveolar epithelial A549
cell apoptosis induced by lipopolysaccharide. Biochem Biophys Res
Commun. 474:83–90. 2016.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
8
|
Gill SE, Rohan M and Mehta S: Role of
pulmonary microvascular endothelial cell apoptosis in murine
sepsis-induced lung injury in vivo. Respir Res.
16(109)2015.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
9
|
Li B, Fang J, Zuo Z, Yin S, He T, Yang M,
Deng J, Shen L, Ma X, Yu S, et al: Activation of porcine alveolar
macrophages by actinobacillus pleuropneumoniae lipopolysaccharide
via the toll-like receptor 4/NF-κB-mediated pathway. Infect Immun.
86:e00642–17. 2018.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
10
|
Moldoveanu B, Otmishi P, Jani P, Walker J,
Sarmiento X, Guardiola J, Saad M and Yu J: Inflammatory mechanisms
in the lung. J Inflamm Res. 2:1–11. 2009.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
11
|
Pahuja M, Tran C, Wang H and Yin K:
Alveolar macrophage suppression in sepsis is associated with high
mobility group box 1 transmigration. Shock. 29:754–760.
2008.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
12
|
Yamazaki T, Akiba H, Iwai H, Matsuda H,
Aoki M, Tanno Y, Shin T, Tsuchiya H, Pardoll DM, Okumura K, et al:
Expression of programmed death 1 ligands by murine T cells and APC.
J Immunol. 169:5538–5545. 2002.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
13
|
Keir ME, Butte MJ, Freeman GJ and Sharpe
AH: PD-1 and its ligands in tolerance and immunity. Annu Rev
Immunol. 26:677–704. 2008.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
14
|
Shinohara T, Taniwaki M, Ishida Y,
Kawaichi M and Honjo T: Structure and chromosomal localization of
the human PD-1 gene (PDCD1). Genomics. 23:704–706. 1994.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
15
|
Hassan SS, Akram M, King EC, Dockrell HM
and Cliff JM: PD-1, PD-L1 and PD-L2 gene expression on T-cells and
natural killer cells declines in conjunction with a reduction in
PD-1 protein during the intensive phase of tuberculosis treatment.
PLoS One. 10(e0137646)2015.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
16
|
Dong H, Zhu G, Tamada K and Chen L: B7-H1,
a third member of the B7 family, co-stimulates T-cell proliferation
and interleukin-10 secretion. Nat Med. 5:1365–1369. 1999.PubMed/NCBI View
Article : Google Scholar
|
|
17
|
Latchman Y, Wood CR, Chernova T, Chaudhary
D, Borde M, Chernova I, Iwai Y, Long AJ, Brown JA, Nunes R, et al:
PD-L2 is a second ligand for PD-1 and inhibits T cell activation.
Nat Immunol. 2:261–268. 2001.PubMed/NCBI View
Article : Google Scholar
|
|
18
|
Taube JM, Klein A, Brahmer JR, Xu H, Pan
X, Kim JH, Chen L, Pardoll DM, Topalian SL and Anders RA:
Association of PD-1, PD-1 ligands, and other features of the tumor
immune microenvironment with response to anti-PD-1 therapy. Clin
Cancer Res. 20:5064–5074. 2014.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
19
|
Huang X, Venet F, Wang YL, Lepape A, Yuan
Z, Chen Y, Swan R, Kherouf H, Monneret G, Chung CS and Ayala A:
PD-1 expression by macrophages plays a pathologic role in altering
microbial clearance and the innate inflammatory response to sepsis.
Proc Natl Acad Sci USA. 106:6303–6308. 2009.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
20
|
Bao X, Sun H and Yang Q: The role and
mechanism of costimulatory molecular programmed death ligand-1 in
acute lung injury. Zhonghua Crisis Emerg Med. 28:498–503. 2016.
|
|
21
|
Zhao Y, Jia Y, Shi T, Wang W, Shao D,
Zheng X, Sun M, He K and Chen L: Depression promotes hepatocellular
carcinoma progression through a glucocorticoids mediated
up-regulation of PD-1 expression in tumor infiltrating NK cells.
Carcinogenesis: Feb 4, 2019 (Epub ahead of print). doi:
10.1093/carcin/bgz017.
|
|
22
|
Zhou Z, Su Y and Fa XE: Isorhynchophylline
exerts anti-inflammatory and anti-oxidative activities in
LPS-stimulated murine alveolar macrophages. Life Sci. 223:137–145.
2019.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
23
|
Livak KJ and Schmittgen TD: Analysis of
relative gene expression data using real-time quantitative PCR and
the 2(-Delta Delta C(T)) method. Methods. 25:402–408.
2001.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
24
|
Niesler U, Palmer A, Radermacher P and
Huber-Lang MS: Role of alveolar macrophages in the inflammatory
response after trauma. Shock. 42:3–10. 2014.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
25
|
Kubota Y, Iwasaki Y, Harada H, Yokomura I,
Ueda M, Hashimoto S and Nakagawa M: Role of alveolar macrophages in
Candida-induced acute lung injury. Clin Diagn Lab Immunol.
8:1258–1262. 2001.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
26
|
Yang L, Zhang Z, Zhuo Y, Cui L, Li C, Li
D, Zhang S, Cui N, Wang X and Gao H: Resveratrol alleviates
sepsis-induced acute lung injury by suppressing inflammation and
apoptosis of alveolar macrophage cells. Am J Transl Res.
10:1961–1975. 2018.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
27
|
Fu Y, Zhou J, Liu K, Hou L and Zhang W:
Effects of miR-155 on IL-6, IL-10 and MIP-2 in alveolar macrophages
of acute lung injury induced by sepsis. Chin J Crit Care Med.
5:159–164. 2019.
|
|
28
|
Nam S, Lee A, Lim J and Lim JS: Analysis
of the expression and regulation of PD-1 protein on the surface of
myeloid-derived suppressor cells (MDSCs). Biomol Ther (Seoul).
27:63–70. 2019.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
29
|
Mitsi E, Kamng'ona R, Rylance J, Solórzano
C, Jesus Reiné J, Mwandumba HC, Ferreira DM and Jambo KC: Human
alveolar macrophages predominately express combined classical M1
and M2 surface markers in steady state. Respir Res.
19(66)2018.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
30
|
Italiani P and Boraschi D: From monocytes
to M1/M2 macrophages: Phenotypical vs functional differentiation.
Front Immunol. 5(514)2014.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
31
|
Yin D, Wang W, Han W and Fan C: Targeting
Notch-activated M1 macrophages attenuate lung tissue damage in a
rat model of ventilator induced lunginjury. Int J Mol Med.
44:1388–1398. 2019.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|