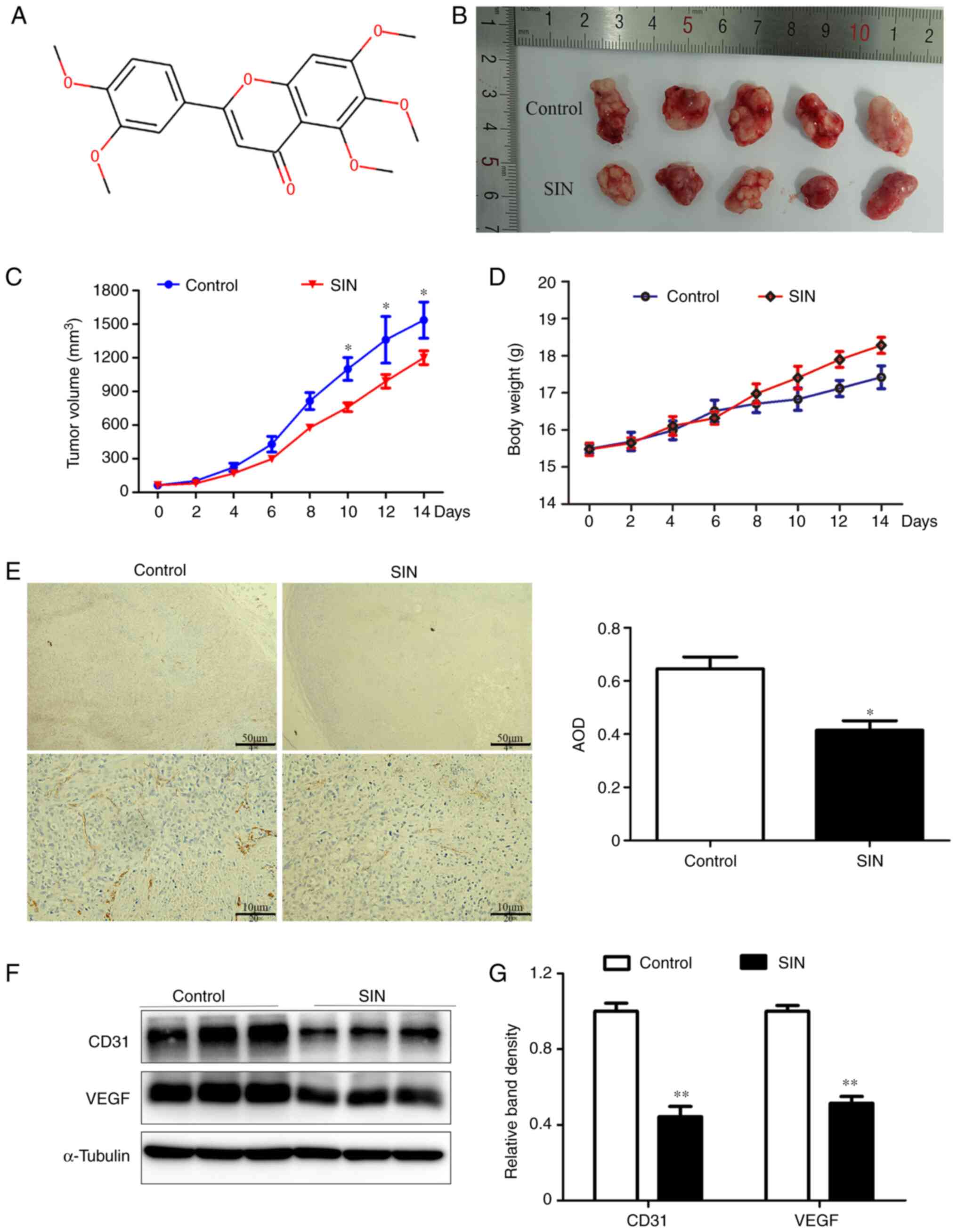
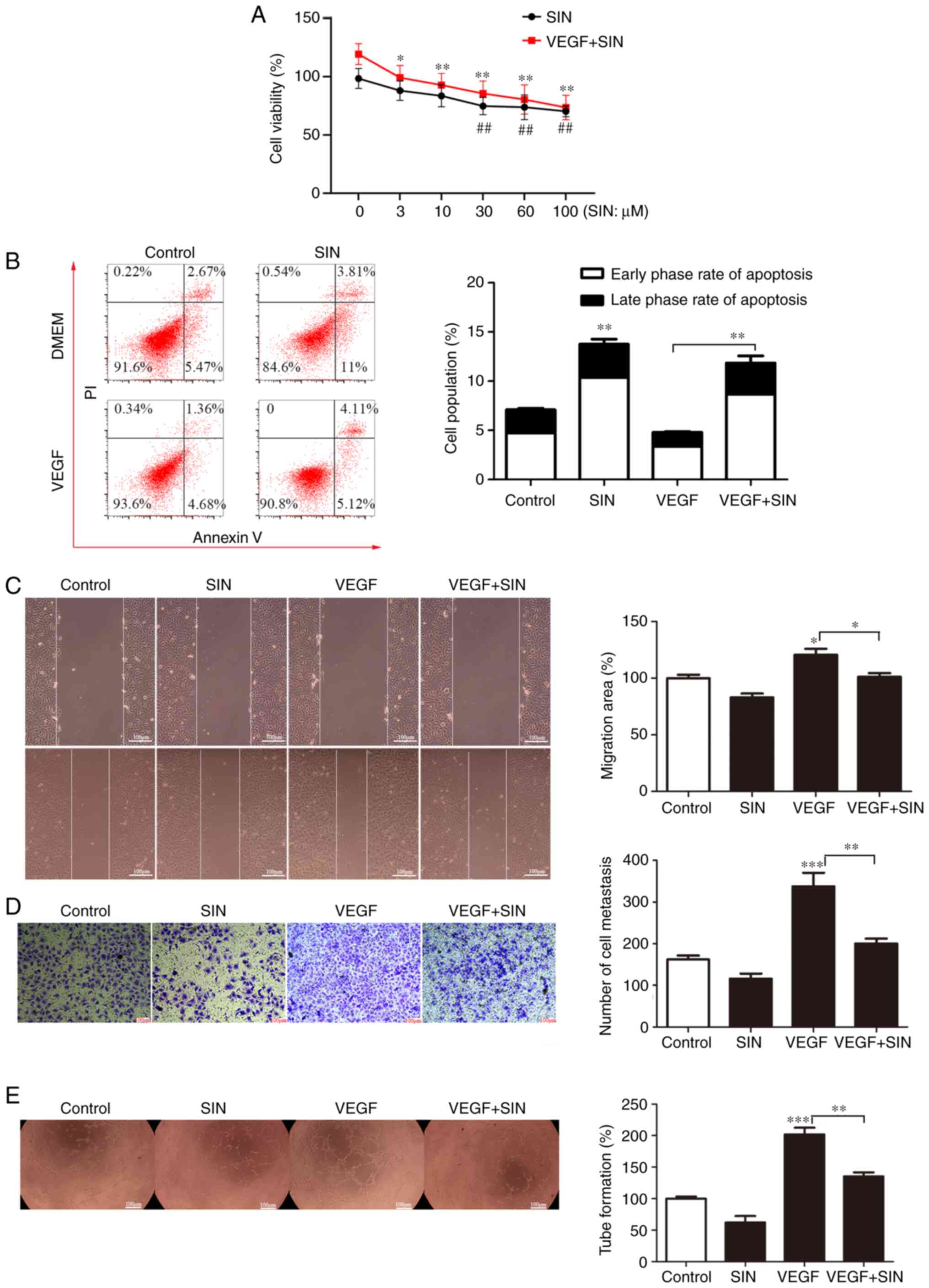
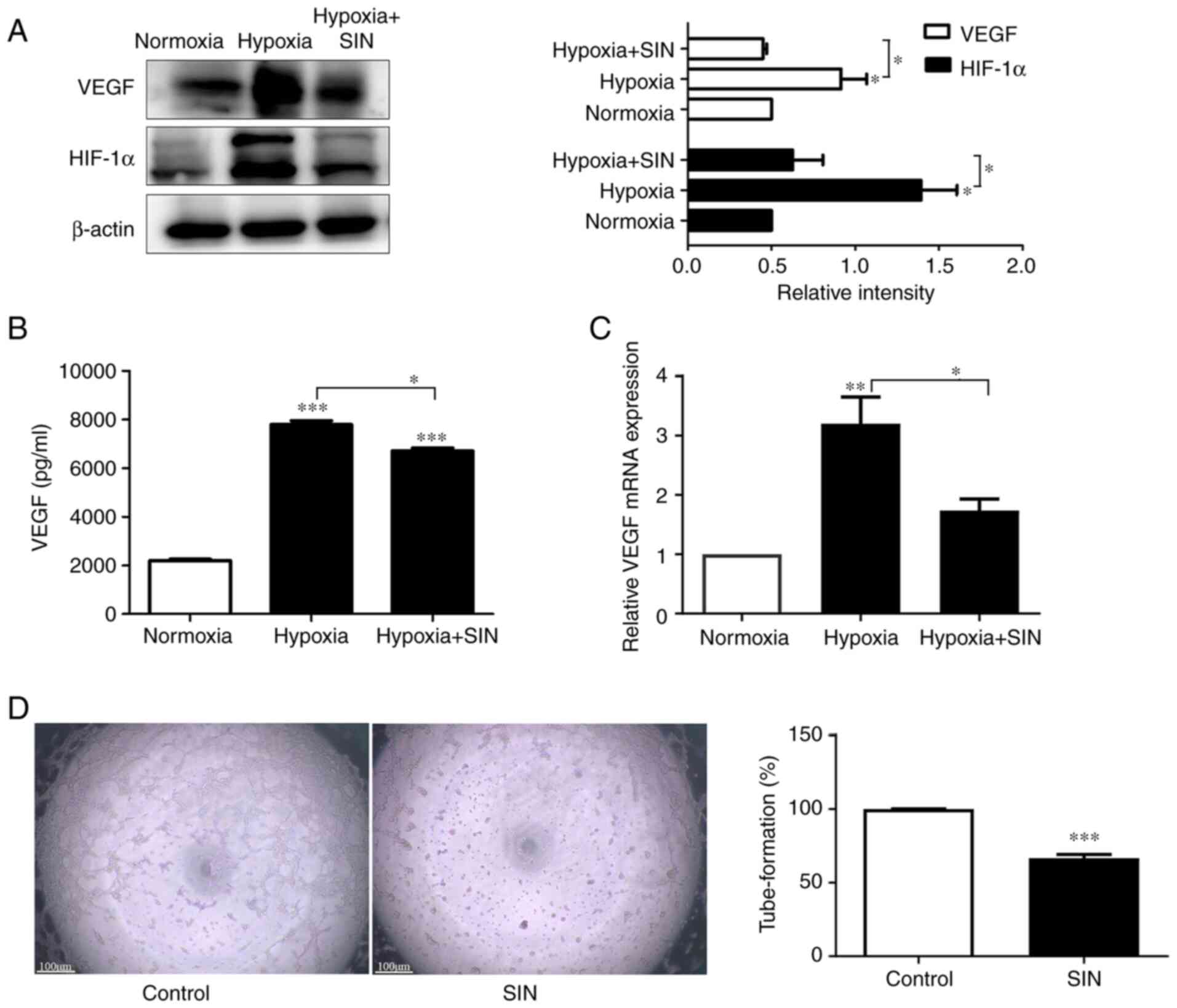
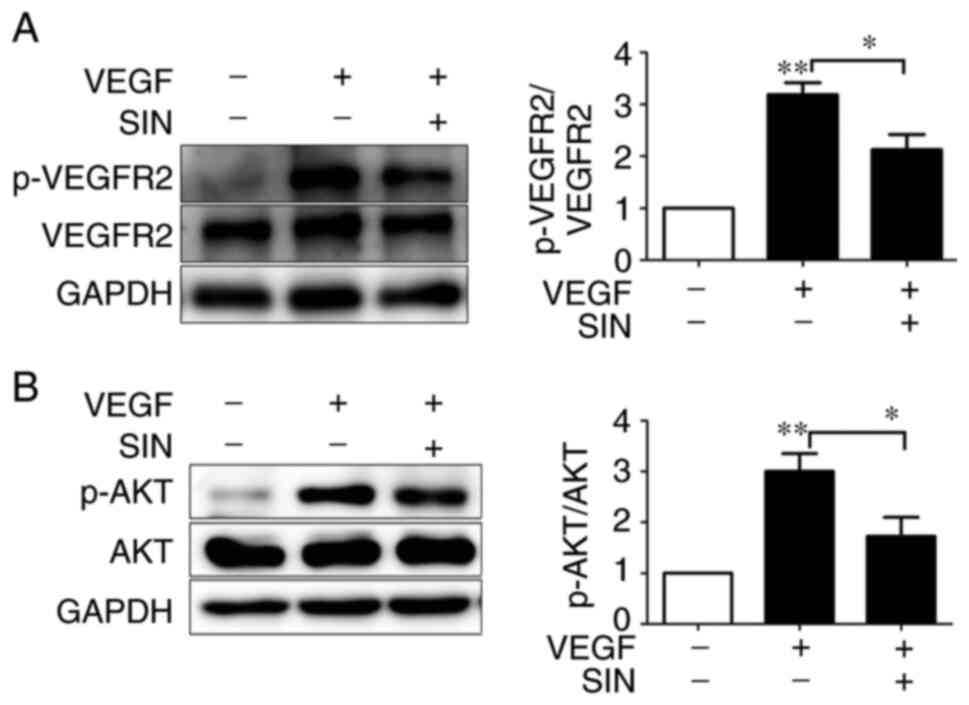
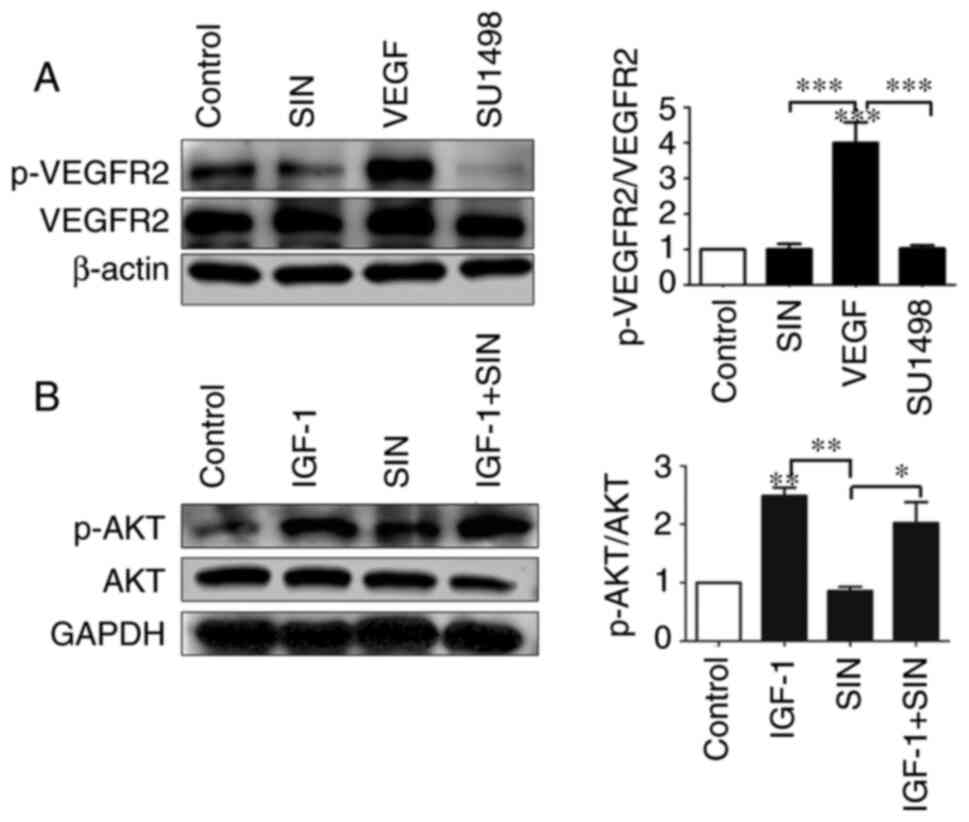
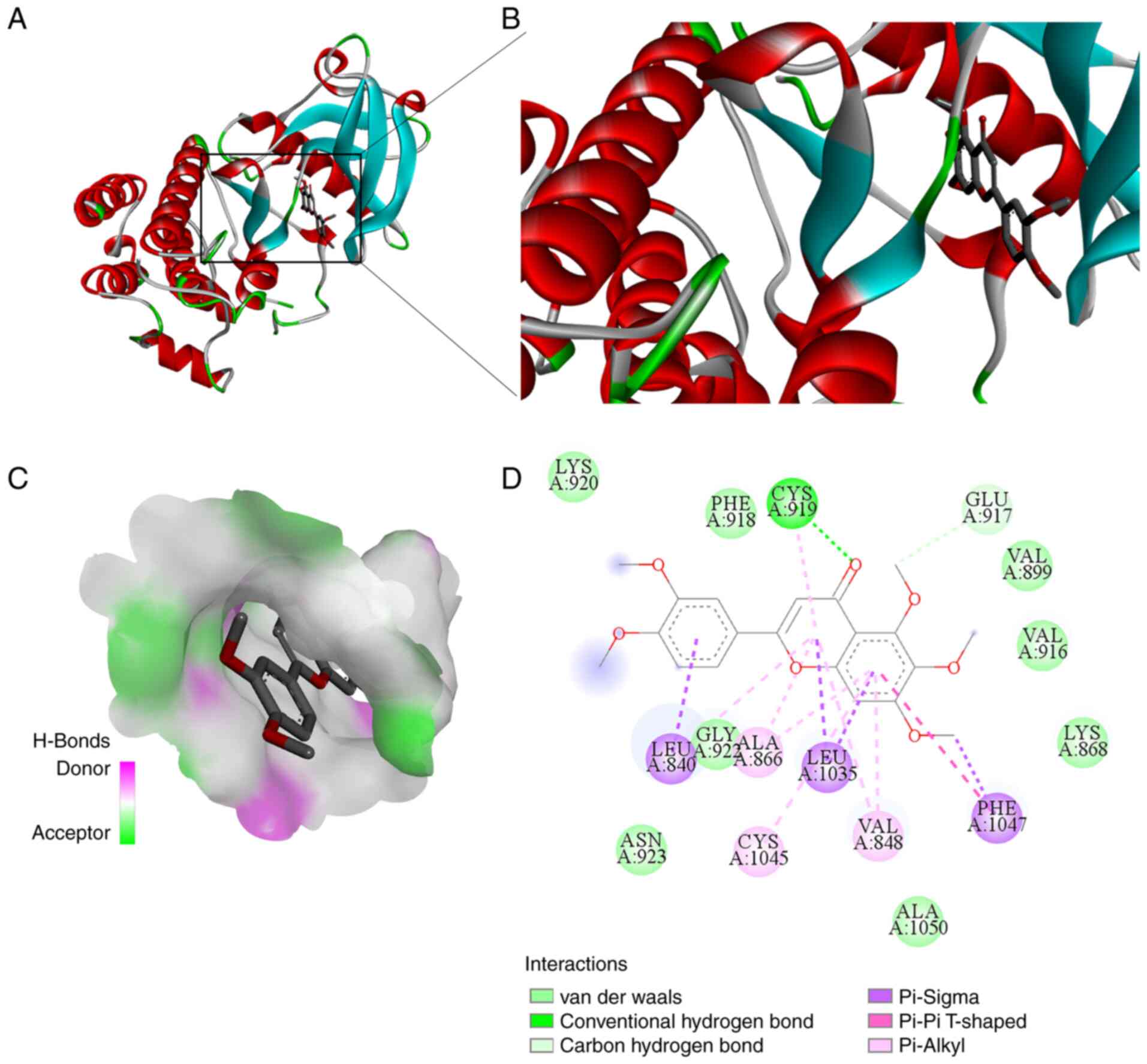
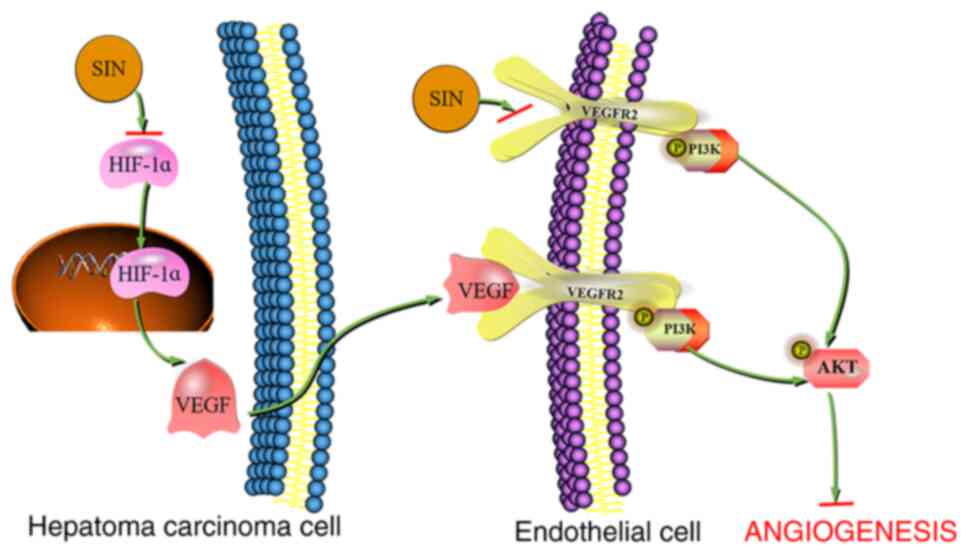
|
1
|
Carmeliet P and Jain RK: Principles and
mechanisms of vessel normalization for cancer and other angiogenic
diseases. Nat Rev Drug Discov. 10:417–427. 2011.PubMed/NCBI View
Article : Google Scholar
|
|
2
|
Carmeliet P: Angiogenesis in life, disease
and medicine. Nature. 438:932–936. 2005.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
3
|
Xue C, Shao S, Yan Y, Yang S, Bai S, Wu Y,
Zhang J, Liu R, Ma H, Chai L, et al: Association between G-protein
coupled receptor 4 expression and microvessel density,
clinicopathological characteristics and survival in hepatocellular
carcinoma. Oncol Lett. 19:2609–2620. 2020.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
4
|
Welker MW and Trojan J: Anti-angiogenesis
in hepatocellular carcinoma treatment: Current evidence and future
perspectives. World J Gastroenterol. 17:3075–3081. 2011.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
5
|
Edeline J, Boucher E, Rolland Y, Vauléon
E, Pracht M, Perrin C, Le Roux C and Raoul JL: Comparison of tumor
response by response evaluation criteria in solid tumors (RECIST)
and modified RECIST in patients treated with sorafenib for
hepatocellular carcinoma. Cancer. 118:147–156. 2012.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
6
|
Zhang H, Tian G, Zhao C, Han Y,
DiMarco-Crook C, Lu C, Bao Y, Li C, Xiao H and Zheng J:
Characterization of polymethoxyflavone demethylation during drying
processes of citrus peels. Food Funct. 10:5707–5717.
2019.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
7
|
Huang B, Zhai M, Qin A, Wu J, Jiang X and
Qiao Z: Sinensetin flavone exhibits potent anticancer activity
against drug-resistant human gallbladder adenocarcinoma cells by
targeting PTEN/PI3K/AKT signalling pathway, induces cellular
apoptosis and inhibits cell migration and invasion. J BUON.
25:1251–1256. 2020.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
8
|
Tan KT, Lin MX, Lin SC, Tung YT, Lin SH
and Lin CC: Sinensetin induces apoptosis and autophagy in the
treatment of human T-cell lymphoma. Anticancer Drugs. 30:485–494.
2019.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
9
|
Dong Y, Ji G, Cao A, Shi J, Shi H, Xie J
and Wu D: Effects of sinensetin on proliferation and apoptosis of
human gastric cancer AGS cells. Zhongguo Zhong Yao Za Zhi.
36:790–794. 2011.PubMed/NCBI(In Chinese).
|
|
10
|
Kim SM, Ha SE, Lee HJ, Rampogu S, Vetrivel
P, Kim HH, Venkatarame Gowda Saralamma V, Lee KW and Kim GS:
Sinensetin induces autophagic cell death through p53-related
AMPK/mTOR signaling in hepatocellular carcinoma HepG2 cells.
Nutrients. 12(2462)2020.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
11
|
Stevens M and Oltean S: Modulation of
receptor tyrosine kinase activity through alternative splicing of
ligands and receptors in the VEGF-A/VEGFR axis. Cells.
8(288)2019.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
12
|
Guo D, Wang Q, Li C, Wang Y and Chen X:
VEGF stimulated the angiogenesis by promoting the mitochondrial
functions. Oncotarget. 8:77020–77027. 2017.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
13
|
Yan ZX, Luo Y and Liu NF: Blockade of
angiopoietin-2/Tie2 signaling pathway specifically promotes
inflammation-induced angiogenesis in mouse cornea. Int J
Ophthalmol. 10:1187–1194. 2017.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
14
|
Al-Aqtash RA, Zihlif MA, Hammad H, Nassar
ZD, Meliti JA and Taha MO: Ligand-based computational modelling of
platelet-derived growth factor beta receptor leading to new
angiogenesis inhibitory leads. Comput Biol Chem. 71:170–179.
2017.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
15
|
Shibuya M: Vascular endothelial growth
factor (VEGF) and its receptor (VEGFR) signaling in angiogenesis: A
crucial target for anti- and pro-angiogenic therapies. Genes
Cancer. 2:1097–1105. 2011.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
16
|
Li S, Xu G, Gao F, Bi J and Huo R:
Expression and association of VEGF-Notch pathways in infantile
hemangiomas. Exp Ther Med. 14:3737–3743. 2017.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
17
|
Dulloo I, Phang BH, Othman R, Tan SY,
Vijayaraghavan A, Goh LK, Martin-Lopez M, Marques MM, Li CW, Wang
de Y, et al: Hypoxia-inducible TAp73 supports tumorigenesis by
regulating the angiogenic transcriptome. Nat Cell Biol. 17:511–523.
2015.PubMed/NCBI View
Article : Google Scholar
|
|
18
|
Schlieve CR, Mojica SG, Holoyda KA, Hou X,
Fowler KL and Grikscheit TC: Vascular endothelial growth factor
(VEGF) bioavailability regulates angiogenesis and intestinal stem
and progenitor cell proliferation during postnatal small intestinal
development. PLoS One. 11(e0151396)2016.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
19
|
Nicolas S, Abdellatef S, Haddad MA,
Fakhoury I and El-Sibai M: Hypoxia and EGF stimulation regulate
VEGF expression in human glioblastoma multiforme (GBM) cells by
differential regulation of the PI3K/Rho-GTPase and MAPK pathways.
Cells. 8(1397)2019.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
20
|
Tang Q, He X, Liao H, He L, Wang Y, Zhou
D, Ye S and Chen Q: Ultrasound microbubble contrast agent-mediated
suicide gene transfection in the treatment of hepatic cancer. Oncol
Lett. 4:970–972. 2012.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
21
|
Xiong YJ, Deng ZB, Liu JN, Qiu JJ, Guo L,
Feng PP, Sui JR, Chen DP and Guo HS: Enhancement of epithelial cell
autophagy induced by sinensetin alleviates epithelial barrier
dysfunction in colitis. Pharmacol Res. 148(104461)2019.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
22
|
Liu F, Wang B, Li L, Dong F, Chen X, Li Y,
Dong X, Wada Y, Kapron CM and Liu J: Low-dose cadmium upregulates
VEGF expression in lung adenocarcinoma cells. Int J Environ Res
Public Health. 12:10508–10521. 2015.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
23
|
Livak KJ and Schmittgen TD: Analysis of
relative gene expression data using real-time quantitative PCR and
the 2(-Delta Delta C(T)) method. Methods. 25:402–408.
2001.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
24
|
Wang R, Liu Y, Hu X, Pan J, Gong D and
Zhang G: New insights into the binding mechanism between osthole
and β-lactoglobulin: Spectroscopic, chemometrics and docking
studies. Food Res Int. 120:226–234. 2019.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
25
|
Cao X, Wang S, Bi R, Tian S, Huo Y and Liu
J: Toxic effects of Cr(VI) on the bovine hemoglobin and human
vascular endothelial cells: Molecular interaction and cell damage.
Chemosphere. 222:355–363. 2019.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
26
|
Okamura S, Osaki T, Nishimura K, Ohsaki H,
Shintani M, Matsuoka H, Maeda K, Shiogama K, Itoh T and Kamoshida
S: Thymidine kinase-1/CD31 double immunostaining for identifying
activated tumor vessels. Biotech Histochem. 94:60–64.
2019.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
27
|
Holmqvist K, Cross MJ, Rolny C, Hägerkvist
R, Rahimi N, Matsumoto T, Claesson-Welsh L and Welsh M: The adaptor
protein shb binds to tyrosine 1175 in vascular endothelial growth
factor (VEGF) receptor-2 and regulates VEGF-dependent cellular
migration. J Biol Chem. 279:22267–22275. 2004.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
28
|
Farhat FS, Tfayli A, Fakhruddin N, Mahfouz
R, Otrock ZK, Alameddine RS, Awada AH and Shamseddine A:
Expression, prognostic and predictive impact of VEGF and bFGF in
non-small cell lung cancer. Crit Rev Oncol Hematol. 84:149–160.
2012.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
29
|
Forsythe JA, Jiang BH, Iyer NV, Agani F,
Leung SW, Koos RD and Semenza GL: Activation of vascular
endothelial growth factor gene transcription by hypoxia-inducible
factor 1. Mol Cell Biol. 16:4604–4613. 1996.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
30
|
Semenza GL, Agani F, Booth G, Forsythe J,
Iyer N, Jiang BH, Leung S, Roe R, Wiener C and Yu A: Structural and
functional analysis of hypoxia-inducible factor 1. Kidney Int.
51:553–555. 1997.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
31
|
Ye J and Yuan L: Inhibition of p38 MAPK
reduces tumor conditioned medium-induced angiogenesis in
co-cultured human umbilical vein endothelial cells and fibroblasts.
Biosci Biotechno lBiochem. 71:1162–1169. 2007.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
32
|
Liu J, Yuan L, Molema G, Regan E, Janes L,
Beeler D, Spokes KC, Okada Y, Minami T, Oettgen P and Aird WC:
Vascular bed-specific regulation of the von Willebrand factor
promoter in the heart and skeletal muscle. Blood. 117:342–351.
2011.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
33
|
Shibuya M: Structure and function of
VEGF/VEGF-receptor system involved in angiogenesis. Cell Struct
Funct. 26:25–35. 2001.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
34
|
Shu-Ya T, Qiu-Yang Z, Jing-Jing L, Jin Y
and Biao Y: Suppression of pathological ocular neovascularization
by a small molecule, SU1498. Biomed Pharmacother.
128(110248)2020.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
35
|
Chen S, Hu M, Shen M, Wang S, Wang C, Chen
F, Tang Y, Wang X, Zeng H, Chen M, et al: IGF-1 facilitates
thrombopoiesis primarily through Akt activation. Blood.
132:210–222. 2018.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
36
|
Huang X, Zhou G, Wu W, Ma G, D'Amore PA,
Mukai S and Lei H: Editing VEGFR2 blocks VEGF-induced activation of
Akt and tube formation. Invest Ophthalmol Vis Sci. 58:1228–1236.
2017.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
37
|
Hosseini-Koupaei M, Shareghi B, Saboury AA
and Davar F: Molecular investigation on the interaction of spermine
with proteinase K by multispectroscopic techniques and molecular
simulation studies. Int J Biol Macromol. 94:406–414.
2017.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
38
|
Liu D, Cao X, Kong Y, Mu T and Liu J:
Inhibitory mechanism of sinensetin on α-glucosidase and
non-enzymatic glycation: Insights from spectroscopy and molecular
docking analyses. Int J Biol Macromol. 166:259–267. 2021.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
39
|
Hu B, An HM, Wang SS, Chen JJ and Xu L:
Preventive and therapeutic effects of Chinese herbal compounds
against hepatocellular carcinoma. Molecules. 21(142)2016.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
40
|
Liao CY, Lee CC, Tsai CC, Hsueh CW, Wang
CC, Chen IH, Tsai MK, Liu MY, Hsieh AT, Su KJ, et al: Novel
investigations of flavonoids as chemopreventive agents for
hepatocellular carcinoma. Biomed Res Int.
2015(840542)2015.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
41
|
Kim SM, Rampogu S, Vetrivel P, Kulkarni
AM, Ha SE, Kim HH, Lee KW and Kim GS: Transcriptome analysis of
sinensetin-treated liver cancer cells guided by biological network
analysis. Oncol Lett. 21(355)2021.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
42
|
Hanahan D and Weinberg RA: Hallmarks of
cancer: The next generation. Cell. 144:646–674. 2011.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
43
|
Figueiredo CC, Pereira NB, Pereira LX,
Oliveira LAM, Campos PP, Andrade SP and Moro L: Double
immunofluorescence labeling for CD31 and CD105 as a marker for
polyether polyurethane-induced angiogenesis in mice. Histol
Histopathol. 34:257–264. 2019.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
44
|
Salvucci O, Maric D, Economopoulou M,
Sakakibara S, Merlin S, Follenzi A and Tosato G: EphrinB reverse
signaling contributes to endothelial and mural cell assembly into
vascular structures. Blood. 114:1707–1716. 2009.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
45
|
Lam IK, Alex D, Wang YH, Liu P, Liu AL, Du
GH and Lee SM: In vitro and in vivo structure and activity
relationship analysis of polymethoxylated flavonoids: identifying
sinensetin as a novel antiangiogenesis agent. Mol Nutr Food Res.
56:945–956. 2012.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
46
|
Alon T, Hemo I, Itin A, Pe'er J, Stone J
and Keshet E: Vascular endothelial growth factor acts as a survival
factor for newly formed retinal vessels and has implications for
retinopathy of prematurity. Nat Med. 1:1024–1028. 1995.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
47
|
Hida K, Kawamoto T, Ohga N, Akiyama K,
Hida Y and Shindoh M: Altered angiogenesis in the tumor
microenvironment. Pathol Int. 61:630–637. 2011.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
48
|
Poon RT, Fan ST and Wong J: Clinical
implications of circulating angiogenic factors in cancer patients.
J Clin Oncol. 19:1207–1225. 2001.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
49
|
Rapisarda A and Melillo G: Role of the
VEGF/VEGFR axis in cancer biology and therapy. Adv Cancer Res.
114:237–267. 2012.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
50
|
Jászai J and Schmidt MHH: Trends and
challenges in tumor anti-angiogenic therapies. Cells.
8(1102)2019.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
51
|
Boguslawski G, McGlynn PW, Harvey KA and
Kovala AT: SU1498, an inhibitor of vascular endothelial growth
factor receptor 2, causes accumulation of phosphorylated ERK
kinases and inhibits their activity in vivo and in vitro. J Biol
Chem. 279:5716–5724. 2004.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
52
|
Zhang J, Cao J, Weng Q, Wu R, Yan Y, Jing
H, Zhu H, He Q and Yang B: Suppression of hypoxia-inducible factor
1α (HIF-1α) by tirapazamine is dependent on eIF2α phosphorylation
rather than the mTORC1/4E-BP1 pathway. PLoS One.
5(e13910)2010.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|