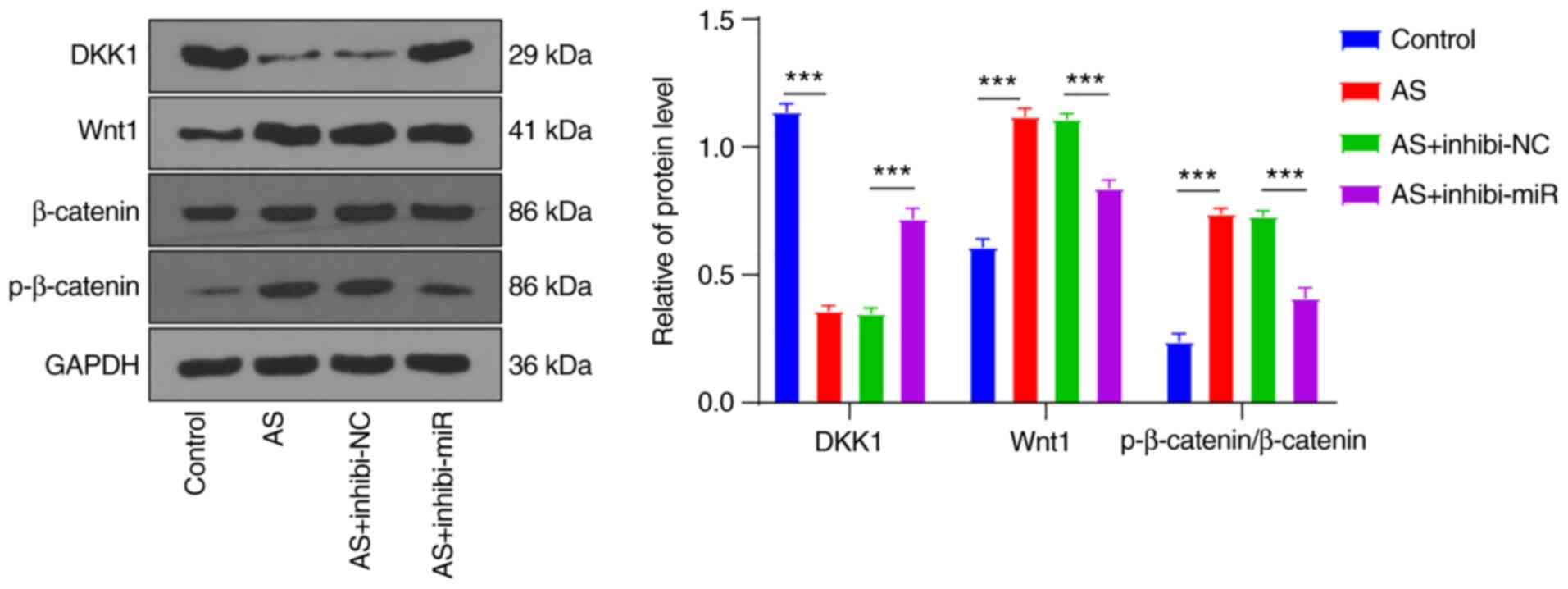
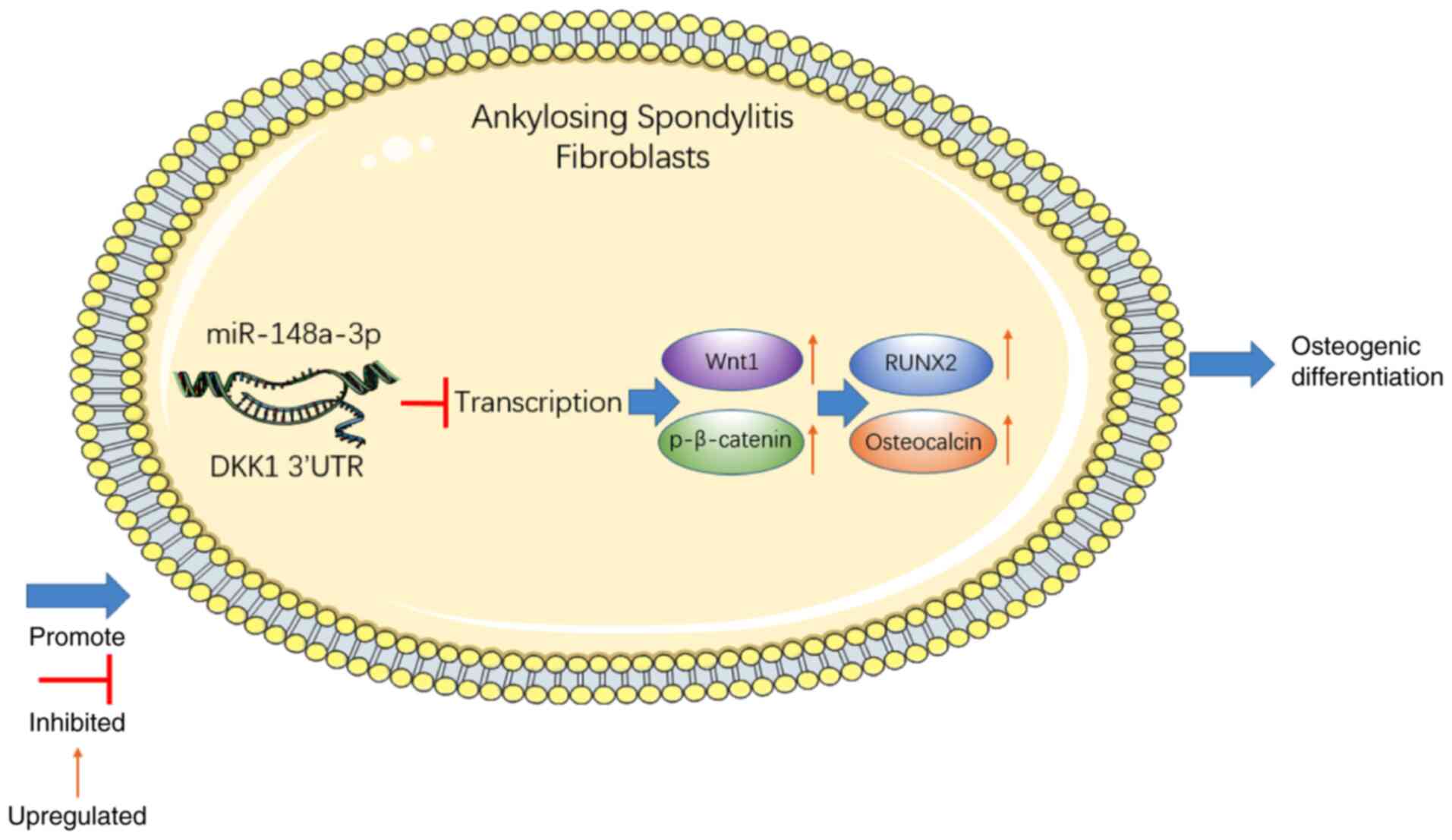
|
1
|
Smith JA: Update on ankylosing
spondylitis: Current concepts in pathogenesis. Curr Allergy Asthma
Rep. 15(489)2015.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
2
|
Zhang L, Zhang YJ, Chen J, Huang XL, Fang
GS, Yang LJ, Duan Y and Wang J: The association of HLA-B27 and
Klebsiella pneumoniae in ankylosing spondylitis: A systematic
review. Microb Pathog. 117:49–54. 2018.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
3
|
Golder V and Schachna L: Ankylosing
spondylitis: An update. Aust Fam Physician. 42:780–784.
2013.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
4
|
Pecourneau V, Degboe Y, Barnetche T,
Cantagrel A, Constantin A and Ruyssen-Witrand A: Effectiveness of
exercise programs in ankylosing spondylitis: A meta-analysis of
randomized controlled trials. Arch Phys Med Rehabil. 99:383–389.e1.
2018.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
5
|
Ranganathan V, Gracey E, Brown MA, Inman
RD and Haroon N: Pathogenesis of ankylosing spondylitis-recent
advances and future directions. Nat Rev Rheumatol. 13:359–367.
2017.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
6
|
Wenker KJ and Quint JM: Ankylosing
Spondylitis. In: StatPearls [Internet]. StatPearls Publishing,
Treasure Island, FL, 2021.
|
|
7
|
Blair HA: Secukinumab: A review in
ankylosing spondylitis. Drugs. 79:433–443. 2019.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
8
|
Li Z, Wong SH, Shen J, Chan MTV and Wu
WKK: The role of MicroRNAS in ankylosing spondylitis. Medicine
(Baltimore). 95(e3325)2016.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
9
|
Yan L, Liang M, Hou X, Zhang Y, Zhang H,
Guo Z, Jinyu J, Feng Z and Mei Z: The role of microRNA-16 in the
pathogenesis of autoimmune diseases: A comprehensive review. Biomed
Pharmacother. 112(108583)2019.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
10
|
Motta F, Carena MC, Selmi C and Vecellio
M: MicroRNAs in ankylosing spondylitis: Function, potential and
challenges. J Transl Autoimmun. 3(100050)2020.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
11
|
Vonk LA, Kragten AH, Dhert WJ, Saris DB
and Creemers LB: Overexpression of hsa-miR-148a promotes cartilage
production and inhibits cartilage degradation by osteoarthritic
chondrocytes. Osteoarthritis Cartilage. 22:145–153. 2014.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
12
|
Liu H, Su H, Wang X and Hao W: MiR-148a
regulates bone marrow mesenchymal stem cells-mediated fracture
healing by targeting insulin-like growth factor 1. J Cell Biochem:
Oct 18, 2018 (Epub ahead of print). doi: 10.1002/jcb.27121.
|
|
13
|
Tian L, Zheng F, Li Z, Wang H, Yuan H,
Zhang X, Ma Z, Li X, Gao X and Wang B: miR-148a-3p regulates
adipocyte and osteoblast differentiation by targeting
lysine-specific demethylase 6b. Gene. 627:32–39. 2017.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
14
|
Huang S, Li Y, Wu P, Xiao Y, Duan N, Quan
J and Du W: microRNA-148a-3p in extracellular vesicles derived from
bone marrow mesenchymal stem cells suppresses SMURF1 to prevent
osteonecrosis of femoral head. J Cell Mol Med. 24:11512–11523.
2020.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
15
|
Ma C, Wen B, Zhang Q, Shao PP, Gu W, Qu K,
Shi Y and Wang B: Emodin induces apoptosis and autophagy of
fibroblasts obtained from patient with ankylosing spondylitis. Drug
Des Devel Ther. 13:601–609. 2019.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
16
|
Hamdi W, Chelli-Bouaziz M, Ahmed MS,
Ghannouchi MM, Kaffel D, Ladeb MF and Kchir MM: Correlations among
clinical, radiographic, and sonographic scores for enthesitis in
ankylosing spondylitis. Joint Bone Spine. 78:270–274.
2011.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
17
|
Li DH, He CR, Liu FP, Li J, Gao JW, Li Y
and Xu WD: Annexin A2, up-regulated by IL-6, promotes the
ossification of ligament fibroblasts from ankylosing spondylitis
patients. Biomed Pharmacother. 84:674–679. 2016.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
18
|
Qin X, Zhu B, Jiang T, Tan J, Wu Z, Yuan
Z, Zheng L and Zhao J: miR-17-5p regulates heterotopic ossification
by targeting ANKH in ankylosing spondylitis. Mol Ther Nucleic
Acids. 18:696–707. 2019.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
19
|
Liu L, Zuo Y, Xu Y, Zhang Z, Li Y and Pang
J: MiR-613 inhibits proliferation and invasion and induces
apoptosis of rheumatoid arthritis synovial fibroblasts by direct
down-regulation of DKK1. Cell Mol Biol Lett. 24(8)2019.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
20
|
Huang J, Song G, Yin Z, Fu Z and Zhang L:
Altered expression of microRNAs targeting Dkk-1 in peripheral blood
mononuclear cells of patients with ankylosing spondylitis. Cent Eur
J Immunol. 44:59–64. 2019.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
21
|
Ma S, Wang DD, Ma CY and Zhang YD:
microRNA-96 promotes osteoblast differentiation and bone formation
in ankylosing spondylitis mice through activating the Wnt signaling
pathway by binding to SOST. J Cell Biochem. 120:15429–15442.
2019.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
22
|
World Medical Association. World medical
association declaration of Helsinki: Ethical principles for medical
research involving human subjects. JAMA. 310:2191–2194.
2013.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
23
|
Raychaudhuri SP and Deodhar A: The
classification and diagnostic criteria of ankylosing spondylitis. J
Autoimmun. 48-49:128–133. 2014.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
24
|
Ding L, Yin Y, Hou Y, Jiang H, Zhang J,
Dai Z and Zhang G: microRNA-214-3p suppresses ankylosing
spondylitis fibroblast osteogenesis via BMP-TGF β axis and
BMP2. Front Endocrinol (Lausanne). 11(609753)2020.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
25
|
Livak KJ and Schmittgen TD: Analysis of
relative gene expression data using real-time quantitative PCR and
the 2(-Delta Delta C(T)) method. Methods. 25:402–408.
2001.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
26
|
Liu Z, Yao X, Yan G, Xu Y, Yan J, Zou W
and Wang G: Mediator MED23 cooperates with RUNX2 to drive
osteoblast differentiation and bone development. Nat Commun.
7(11149)2016.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
27
|
Franck H and Keck E: Serum osteocalcin and
vitamin D metabolites in patients with ankylosing spondylitis. Ann
Rheum Dis. 52:343–346. 1993.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
28
|
Heo JS, Choi Y, Kim HS and Kim HO:
Comparison of molecular profiles of human mesenchymal stem cells
derived from bone marrow, umbilical cord blood, placenta and
adipose tissue. Int J Mol Med. 37:115–125. 2016.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
29
|
Shao F, Liu Q, Zhu Y, Fan Z, Chen W, Liu
S, Li X, Guo W, Feng GS, Yu H, et al: Targeting chondrocytes for
arresting bony fusion in ankylosing spondylitis. Nat Commun.
12(6540)2021.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
30
|
Tan H, Ren R, Zhang J, Huang Z, Niu Q and
Yang B: Analysis of inflammation-related microRNA expression in
patients with ankylosing spondylitis. Immunol Res. 70:23–32.
2022.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
31
|
Zhao J, Zhang Y and Liu B: MicroRNA2045p
inhibits the osteogenic differentiation of ankylosing spondylitis
fibroblasts by regulating the Notch2 signaling pathway. Mol Med
Rep. 22:2537–2544. 2020.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
32
|
Vasko R, Streich JH, Blaschke S, Muller
GA, Mai B, Kostrzewa M, Sparbier K, Korsten P, Bohr S and Dihazi H:
Vimentin fragments are potential markers of rheumatoid synovial
fibroblasts. Clin Exp Rheumatol. 34:513–520. 2016.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
33
|
Kook SH, Heo JS and Lee JC: Crucial roles
of canonical Runx2-dependent pathway on Wnt1-induced osteoblastic
differentiation of human periodontal ligament fibroblasts. Mol Cell
Biochem. 402:213–223. 2015.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
34
|
Tsao YT, Huang YJ, Wu HH, Liu YA, Liu YS
and Lee OK: Osteocalcin mediates biomineralization during
osteogenic maturation in human mesenchymal stromal cells. Int J Mol
Sci. 18(159)2017.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
35
|
He H, Cai M, Zhu J, Xiao W, Liu B, Shi Y,
Yang X, Liang X, Zheng T, Hu S, et al: miR-148a-3p promotes rabbit
preadipocyte differentiation by targeting PTEN. In Vitro Cell Dev
Biol Anim. 54:241–249. 2018.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
36
|
Yucong Z, Lu L, Shengfa L, Yongliang Y,
Ruguo S and Yikai L: Serum functional dickkopf-1 levels are
inversely correlated with radiographic severity of ankylosing
spondylitis. Clin Lab. 60:1527–1531. 2014.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
37
|
Zou YC, Yang XW, Yuan SG, Zhang P, Ye YL
and Li YK: Downregulation of dickkopf-1 enhances the proliferation
and osteogenic potential of fibroblasts isolated from ankylosing
spondylitis patients via the Wnt/β-catenin signaling pathway in
vitro. Connect Tissue Res. 57:200–211. 2016.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
38
|
Lin L, Qiu Q, Zhou N, Dong W, Shen J,
Jiang W, Fang J, Hao J and Hu Z: Dickkopf-1 is involved in
BMP9-induced osteoblast differentiation of C3H10T1/2 mesenchymal
stem cells. BMB Rep. 49:179–184. 2016.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
39
|
Negri S, Wang Y, Sono T, Qin Q, Hsu GC,
Cherief M, Xu J, Lee S, Tower RJ, Yu V, et al: Systemic DKK1
neutralization enhances human adipose-derived stem cell mediated
bone repair. Stem Cells Transl Med. 10:610–622. 2021.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
40
|
Bafico A, Liu G, Yaniv A, Gazit A and
Aaronson SA: Novel mechanism of Wnt signalling inhibition mediated
by Dickkopf-1 interaction with LRP6/Arrow. Nat Cell Biol.
3:683–686. 2001.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
41
|
Glinka A, Wu W, Delius H, Monaghan AP,
Blumenstock C and Niehrs C: Dickkopf-1 is a member of a new family
of secreted proteins and functions in head induction. Nature.
391:357–362. 1998.PubMed/NCBI View
Article : Google Scholar
|
|
42
|
Baron R and Rawadi G: Targeting the
Wnt/beta-catenin pathway to regulate bone formation in the adult
skeleton. Endocrinology. 148:2635–2643. 2007.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
43
|
Goldring SR and Goldring MB: Eating bone
or adding it: The Wnt pathway decides. Nat Med. 13:133–134.
2007.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
44
|
Johnson ML and Kamel MA: The Wnt signaling
pathway and bone metabolism. Curr Opin Rheumatol. 19:376–382.
2007.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
45
|
Jin L, Cao Y, Yu G, Wang J, Lin X, Ge L,
Du J, Wang L, Diao S, Lian X, et al: SFRP2 enhances the osteogenic
differentiation of apical papilla stem cells by antagonizing the
canonical WNT pathway. Cell Mol Biol Lett. 22(14)2017.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
46
|
Gu H, Wu L, Chen H, Huang Z, Xu J, Zhou K,
Zhang Y, Chen J, Xia J and Yin X: Identification of differentially
expressed microRNAs in the bone marrow of osteoporosis patients. Am
J Transl Res. 11:2940–2954. 2019.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
47
|
Lu H, Li X, Mu P, Qian B, Jiang W and Zeng
L: Dickkopf-1 promotes the differentiation and adipocytokines
secretion via canonical Wnt signaling pathway in primary cultured
human preadipocytes. Obes Res Clin Pract. 10:454–464.
2016.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
48
|
Shi C, Zhang M, Tong M, Yang L, Pang L,
Chen L, Xu G, Chi X, Hong Q, Ni Y, et al: miR-148a is associated
with obesity and modulates adipocyte differentiation of mesenchymal
stem cells through Wnt signaling. Sci Rep. 5(9930)2015.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
49
|
Llorente I, García-Castañeda N, Valero C,
González-Álvaro I and Castañeda S: Osteoporosis in rheumatoid
arthritis: Dangerous liaisons. Front Med (Lausanne).
7(601618)2020.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
50
|
He X and Dong Y: Ankylosis progressive
homolog upregulation inhibits cell viability and mineralization
during fibroblast ossification by regulating the Wnt/β-catenin
signaling pathway. Mol Med Rep. 22:4551–4560. 2020.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|