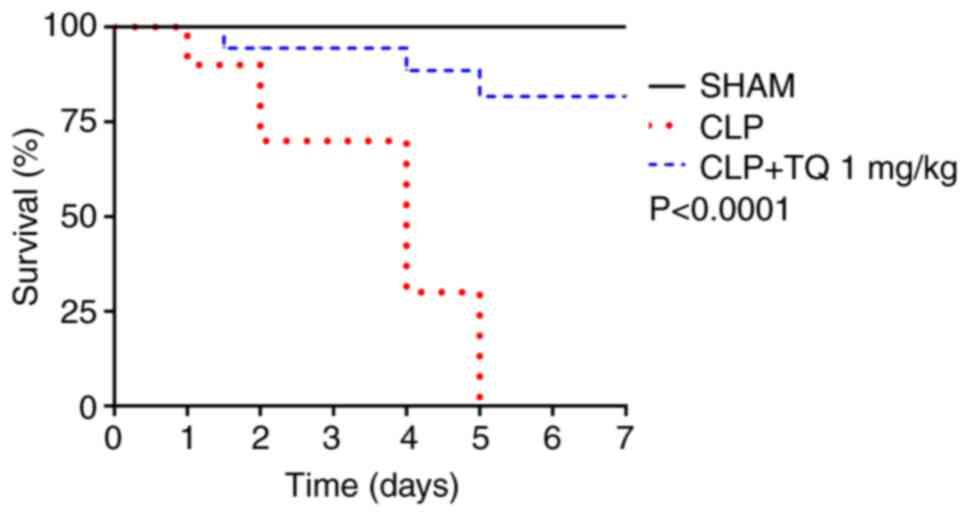
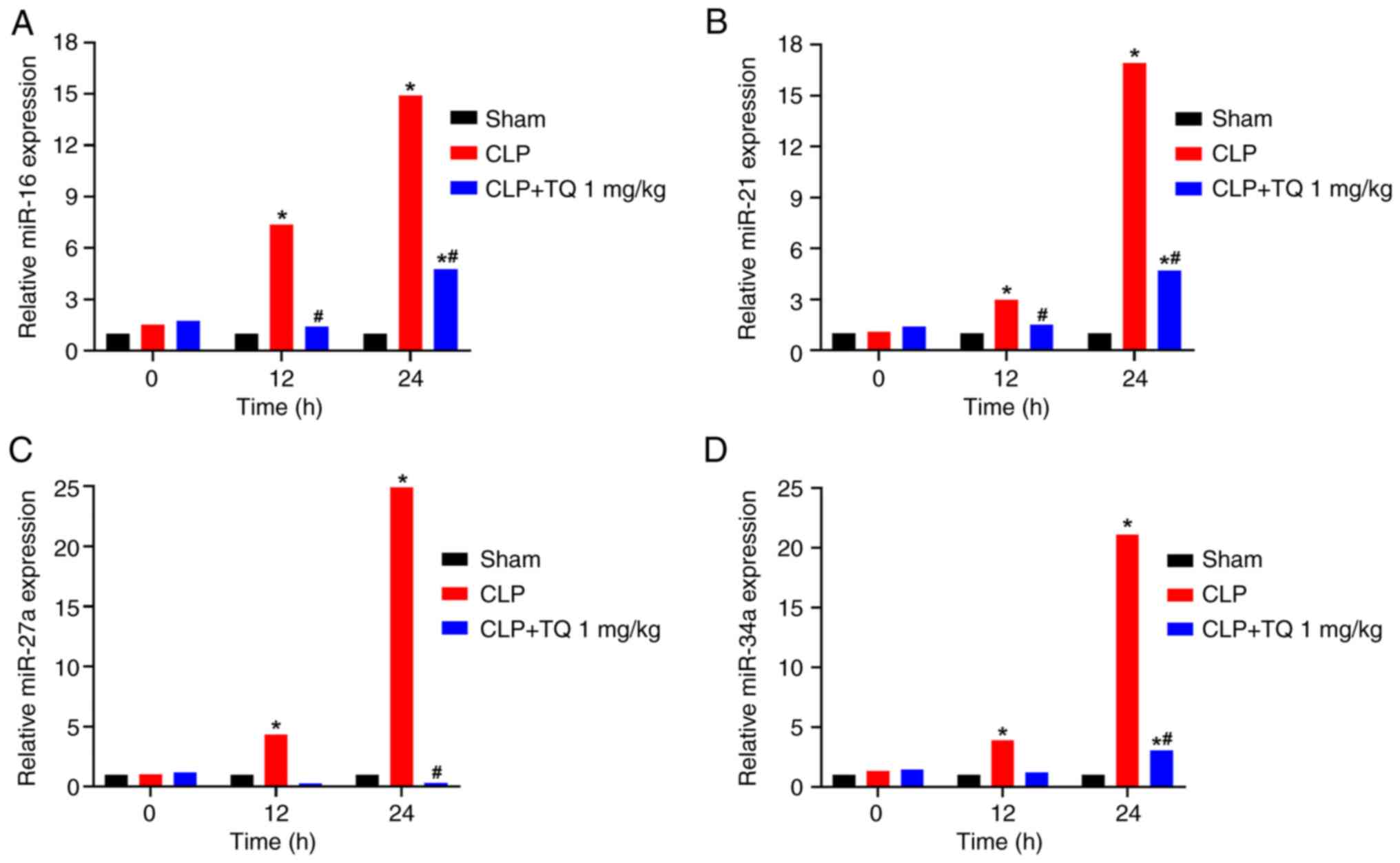
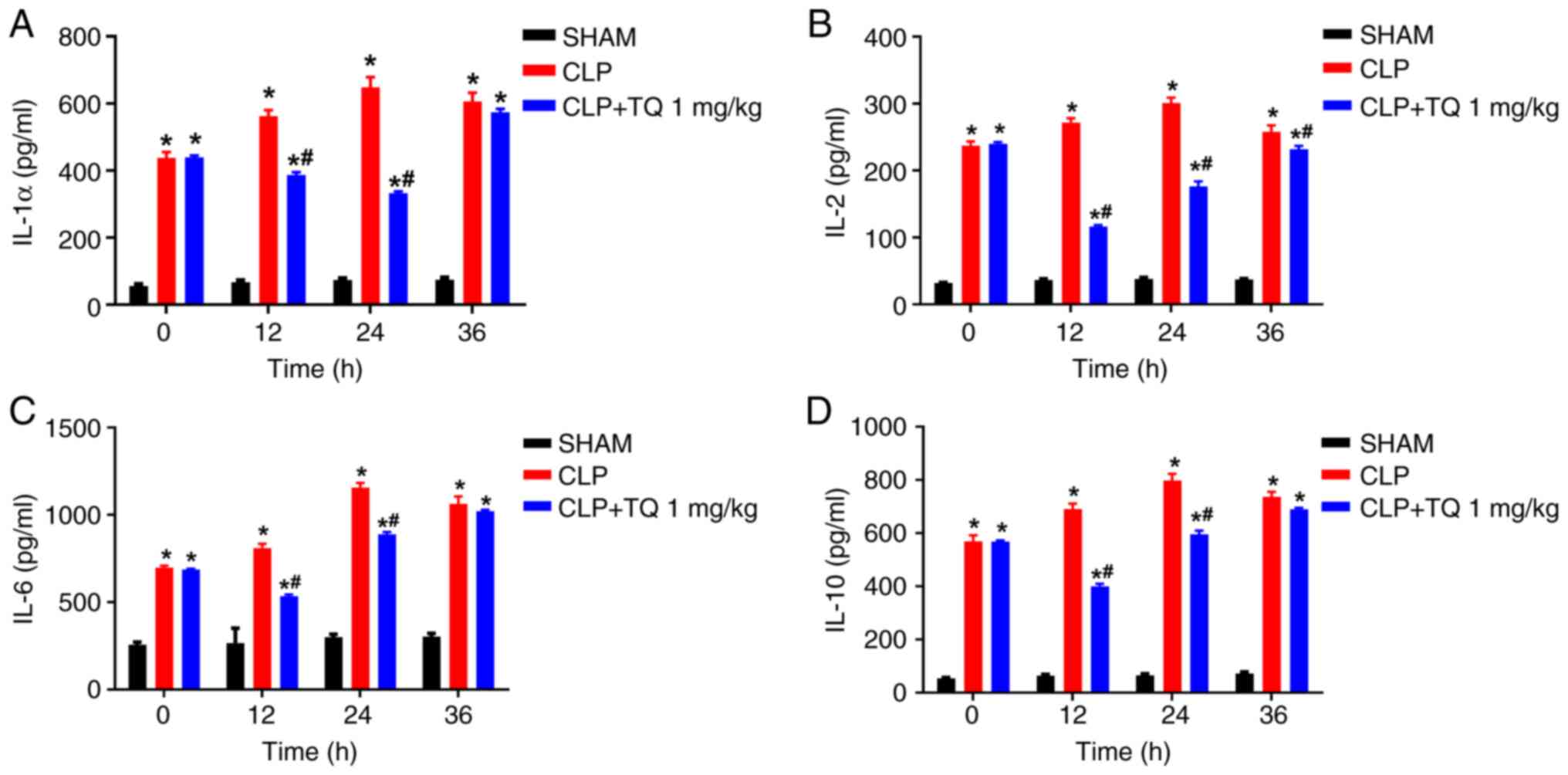
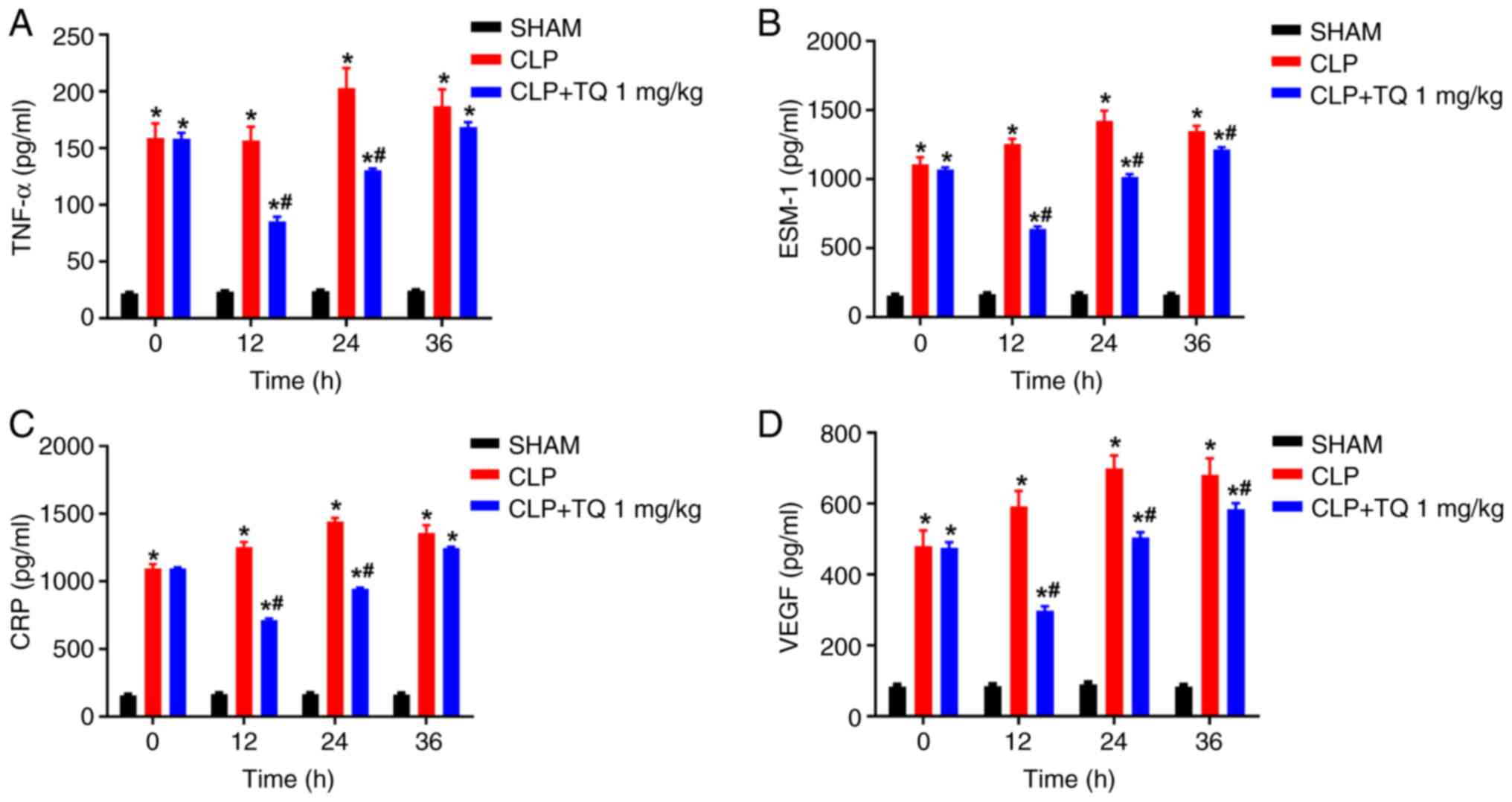
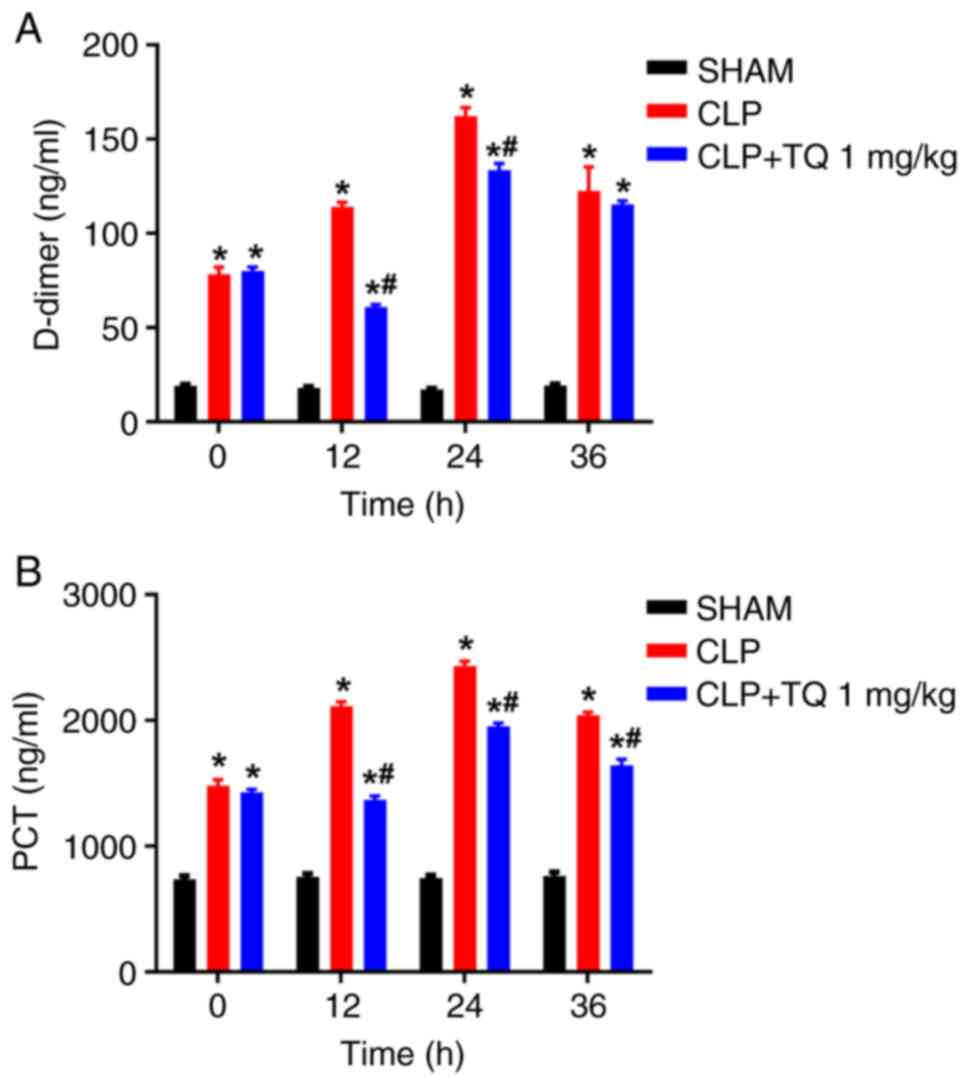
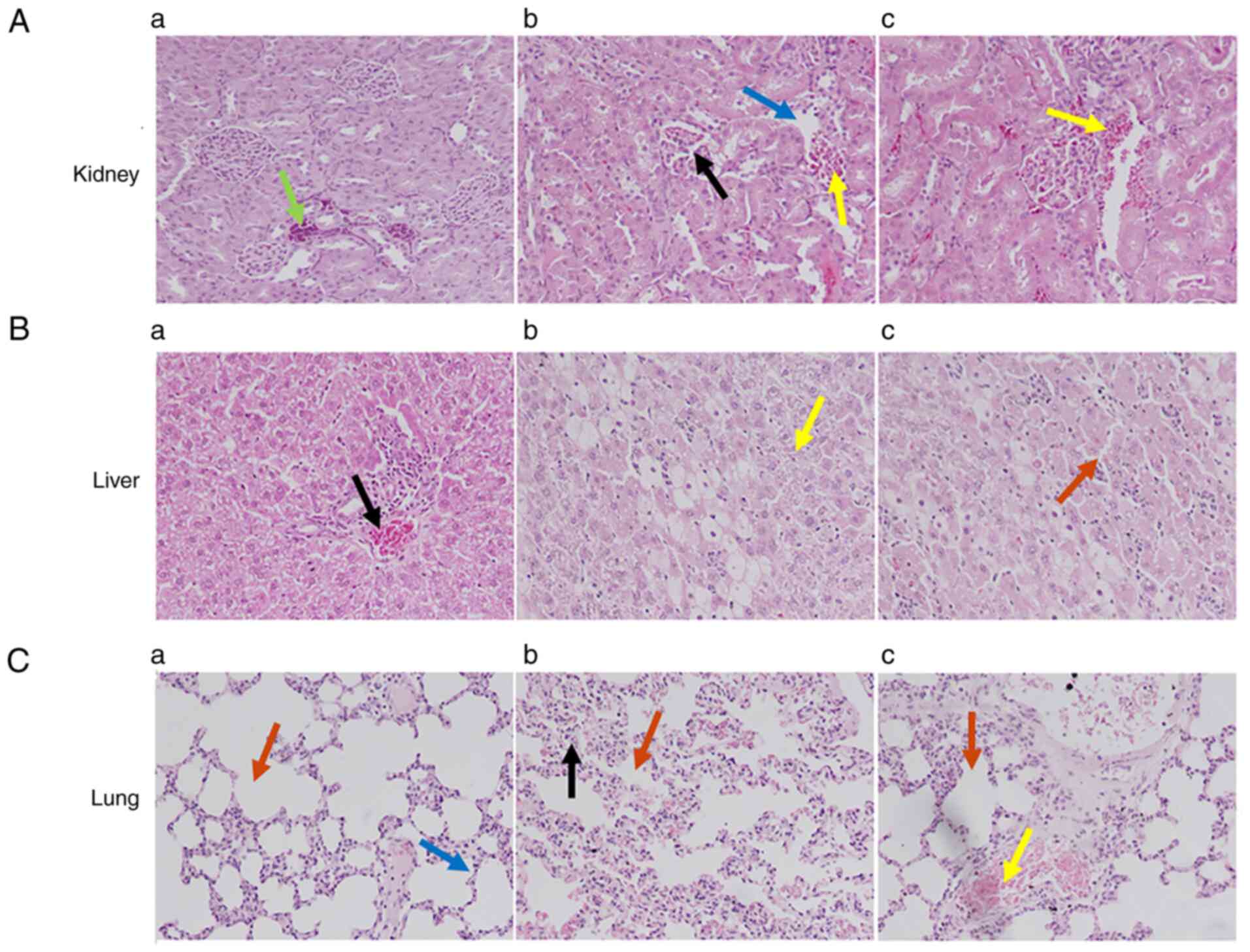
|
1
|
Fleischmann C, Scherag A, Adhikari NKJ,
Hartog CS, Tsaganos T, Schlattmann P, Angus DC and Reinhart K:
International Forum of Acute Care Trialists. Assessment of global
incidence and mortality of hospital-treated sepsis. Current
Estimates and Limitations. Am J Respir Crit Care Med. 193:259–272.
2016.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
2
|
Martin GS, Mannino DM, Eaton S and Moss M:
The epidemiology of sepsis in the United States from 1979 through
2000. New Engl J Med. 348:1546–1554. 2003.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
3
|
Angus DC and Wax RS: Epidemiology of
sepsis: An update. Crit Care Med. 29 (7 Suppl):S109–S116.
2001.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
4
|
Bone RC, Balk RA, Cerra FB, Dellinger RP,
Fein AM, Knaus WA, Schein RM and Sibbald WJ: Definitions for sepsis
and organ failure and guidelines for the use of innovative
therapies in sepsis. Chest. 101:1644–1655. 1992.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
5
|
Singer M, Deutschman CS, Seymour CW,
Shankar-Hari M, Annane D, Bauer M, Bellomo R, Bernard GR, Chiche
JD, Coopersmith CM, et al: The third international consensus
definitions for sepsis and septic shock (Sepsis-3). JAMA.
315:801–810. 2016.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
6
|
Koyama I, Matsunaga T, Harada T, Hokari S
and Komoda T: Alkaline phosphatases reduce toxicity of
lipopolysaccharides in vivo and in vitro through dephosphorylation.
Clin Biochem. 35:455–461. 2002.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
7
|
Männel DN: Advances in sepsis research
derived from animal models. Int J Med Microbiol. 297:393–400.
2007.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
8
|
Bentala H, Verweij WR, der Vlag AH-V, van
Loenen-Weemaes AM, Meijer DKF and Poelstra K: Removal of phosphate
from lipid a as a strategy to detoxify lipopolysaccharide. Shock.
18:561–566. 2002.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
9
|
Annane D, Buisson CB, Cariou A, Martin C,
Misset B, Renault A, Lehmann B, Millul V, Maxime V and Bellissant
E: APROCCHSS Investigators for the TRIGGERSEP Network. Design and
conduct of the activated protein C and corticosteroids for human
septic shock (APROCCHSS) trial. Ann Intensive Care.
6(43)2016.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
10
|
Ayala A and Chaudry IH: IMMUNE dysfunction
in murine polymicrobial sepsis. Shock. 5 (Suppl 1):S27–S38.
1996.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
11
|
Lang JD and Matute-Bello G: Lymphocytes,
apoptosis and sepsis: Making the jump from mice to humans. Crit
Care. 13(109)2009.PubMed/NCBI View
Article : Google Scholar
|
|
12
|
Matsuda H, Ishikado A, Nishida N, Ninomiya
K, Fujiwara H, Kobayashi Y and Yoshikawa M: Hepatoprotective,
superoxide scavenging, and antioxidative activities of aromatic
constituents from the bark of Betula platyphylla var. japonica.
Bioorg Med Chem Lett. 8:2939–2944. 1998.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
13
|
Wesche DE, Lomas-Neira JL, Perl M, Chung
CS and Ayala A: Leukocyte apoptosis and its significance in sepsis
and shock. J Leuk Biol. 78:325–337. 2005.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
14
|
Coopersmith CM, Chang KC, Swanson PE,
Tinsley KW, Stromberg PE, Buchman TG, Karl IE and Hotchkiss RS:
Overexpression of Bcl-2 in the intestinal epithelium improves
survival in septic mice. Crit Care Med. 30:195–201. 2002.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
15
|
Coopersmith CM: Inhibition of intestinal
epithelial apoptosis and survival in a murine model of
pneumonia-induced sepsis. JAMA. 287:1716–1721. 2002.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
16
|
Sonkoly E and Pivarcsi A: MicroRNAs in
inflammation. Int Rev Immunol. 28:535–561. 2009.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
17
|
Ratti M, Lampis A, Ghidini M, Salati M,
Mirchev MB, Valeri N and Hahne JC: MicroRNAs (miRNAs) and long
non-coding RNAs (lncRNAs) as new tools for cancer therapy: First
steps from bench to bedside. Target Oncol. 15:261–278.
2020.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
18
|
Ardekani AM and Naeini MM: The role of
microRNAs in human diseases. Avicenna J Med Biotechnol. 2:161–179.
2010.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
19
|
Taganov KD, Boldin MP, Chang KJ and
Baltimore D: NF-kappaB-dependent induction of microRNA miR-146, an
inhibitor targeted to signaling proteins of innate immune
responses. Proc Natl Acad Sci. 103:12481–12486. 2006.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
20
|
Ceppi M, Pereira PM, Dunand-Sauthier I,
Barras E, Reith W, Santos MA and Pierre P: MicroRNA-155 modulates
the interleukin-1 signaling pathway in activated human
monocyte-derived dendritic cells. Proc Natl Acad Sci.
106:2735–2740. 2009.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
21
|
Essandoh K and Fan GC: Role of
extracellular and intracellular microRNAs in sepsis. Biochim
Biophys Acta. 1842:2155–2162. 2014.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
22
|
Krol J, Loedige I and Filipowicz W: The
widespread regulation of microRNA biogenesis, function and decay.
Nat Rev Genet. 11:597–610. 2010.PubMed/NCBI View
Article : Google Scholar
|
|
23
|
Wang HJ, Zhang PJ, Chen WJ, Feng D, Jia YH
and Xie LX: Four serum microRNAs identified as diagnostic
biomarkers of sepsis. J Trauma Acute Care Surg. 73:850–854.
2012.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
24
|
Wang Z, Ruan Z, Mao Y, Dong W, Zhang Y,
Yin N and Jiang L: miR-27a is up regulated and promotes
inflammatory response in sepsis. Cell Immunol. 290:190–195.
2014.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
25
|
Sheedy FJ: Turning 21: Induction of miR-21
as a key switch in the inflammatory response. Front Immunol.
6(19)2015.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
26
|
Woo CC, Kumar AP, Sethi G and Tan KHB:
Thymoquinone: Potential cure for inflammatory disorders and cancer.
Biochem Pharmacol. 83:443–451. 2012.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
27
|
Alkharfy KM, Ahmad A, Raish M and
Vanhoutte PM: Thymoquinone modulates nitric oxide production and
improves organ dysfunction of sepsis. Life Sci. 143:131–138.
2015.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
28
|
Hubbard WJ, Choudhry M, Schwacha MG, Kerby
JD, Rue LW III, Bland KI and Chaudry IH: Cecal ligation and
puncture. Shock. 24:52–57. 2005.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
29
|
Livak KJ and Schmittgen TD: Analysis of
relative gene expression data using real-time quantitative PCR and
the 2(-Delta Delta C(T)) method. Methods. 25:402–408.
2001.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
30
|
Bancroft J and Gamble M: Theory and
practice of histological techniques. Churchill Livingstone Pub,
Edinburgh, 2002.
|
|
31
|
Drury R and Wallington E: Carlton's
histological techniques, 4th ed. 1967. Oxford University Press, New
York, Toronto, 1967.
|
|
32
|
Calandra T, Glauser MP, Schellekens J and
Verhoef J: Treatment of gram-negative septic shock with human igg
antibody to escherichia coli J5: A prospective, double-blind,
randomized trial. J Infect Dis. 158:312–319. 1988.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
33
|
Frazier WJ and Hall MW: Immunoparalysis
and adverse outcomes from critical illness. Pediatr Clin North Am.
55:647–668. 2008.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
34
|
Dejager L, Pinheiro I, Dejonckheere E and
Libert C: Cecal ligation and puncture: The gold standard model for
polymicrobial sepsis? Trends Microbiol. 19:198–208. 2011.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
35
|
Menezes G, Amaral S, Alvarenga D and Cara
D: Surgical procedures to an experimental polymicrobial sepsis:
Cecal Ligation and Puncture. Braz J Vet Pathol. 1:77–80. 2008.
|
|
36
|
Mittal M, Siddiqui MR, Tran K, Reddy SP
and Malik AB: Reactive oxygen species in inflammation and tissue
injury. Antiox Redox Signal. 20:1126–1167. 2014.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
37
|
Precone V, Stornaiuolo G, Amato A,
Brancaccio G, Nardiello S and Gaeta GB: Different changes in
mitochondrial apoptotic pathway in lymphocytes and granulocytes in
cirrhotic patients with sepsis. Liver Int. 33:834–842.
2013.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
38
|
Moon HG, Yang J, Zheng Y and Jin Y:
MiR-15a/16 regulates macrophage phagocytosis after bacterial
infection. J Immunol. 193:4558–4567. 2014.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
39
|
Gao Y and Yu Z: MicroRNA-16 inhibits
interleukin-13-induced inflammatory cytokine secretion and mucus
production in nasal epithelial cells by suppressing the IκB kinase
β/nuclear factor-κB pathway. Mol Med Rep. 18:4042–4050.
2018.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
40
|
Löffler D, Brocke-Heidrich K, Pfeifer G,
Stocsits C, Hackermüller J, Kretzschmar AK, Burger R, Gramatzki M,
Blumert C, Bauer K, et al: Interleukin-6-dependent survival of
multiple myeloma cells involves the Stat3-mediated induction of
microRNA-21 through a highly conserved enhancer. Blood.
110:1330–1333. 2007.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
41
|
Sheedy FJ, Palsson-McDermott E, Hennessy
EJ, Martin C, O'Leary JJ, Ruan Q, Johnson DS, Chen Y and O'Neill
LAJ: Negative regulation of TLR4 via targeting of the
proinflammatory tumor suppressor PDCD4 by the microRNA miR-21. Nat
Immunol. 11:141–147. 2010.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
42
|
McClure C, Brudecki L, Ferguson DA, Yao
ZQ, Moorman JP, McCall CE and Gazzar ME: MicroRNA 21 (miR-21) and
miR-181b couple with nfi-a to generate myeloid-derived suppressor
cells and promote immunosuppression in late sepsis. Infect Immun.
82:3816–3825. 2014.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
43
|
Goodwin AJ, Guo C, Cook JA, Wolf B,
Halushka PV and Fan H: Plasma levels of microRNA are altered with
the development of shock in human sepsis: An observational study.
Crit Care. 19:2015.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
44
|
McClure C, Ali E, Youssef D, Yao ZQ,
McCall CE and El Gazzar M: NFI-A disrupts myeloid cell
differentiation and maturation in septic mice. J Leukoc Biol.
99:201–211. 2016.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
45
|
Lu TX and Rothenberg ME: Diagnostic,
functional, and therapeutic roles of microRNA in allergic diseases.
J Allergy Clin Immunol. 132:3–13; quiz 14. 2013.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
46
|
Jiang C, Ting AT and Seed B: PPAR-gamma
agonists inhibit production of monocyte inflammatory cytokines.
Nature. 391:82–86. 1998.PubMed/NCBI View
Article : Google Scholar
|
|
47
|
Chawla A: Control of macrophage activation
and function by PPARs. Circul Res. 106:1559–1569. 2010.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
48
|
Mantzarlis K, Tsolaki V and Zakynthinos E:
Role of oxidative stress and mitochondrial dysfunction in sepsis
and potential therapies. Oxid Med Cell Longev.
2017(5985209)2017.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
49
|
Ackermann EJ, Taylor JK, Narayana R and
Bennett CF: The role of antiapoptotic Bcl-2 family members in
endothelial apoptosis elucidated with antisense oligonucleotides. J
Biol Chem. 274:11245–11252. 1999.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
50
|
Potente M and Dimmeler S: Emerging roles
of SIRT1 in vascular endothelial homeostasis. Cell Cycle.
7:2117–2122. 2008.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
51
|
Zhang JM and An J: Cytokines,
inflammation, and pain. Int Anesthesiol Clin. 45:27–37.
2007.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
52
|
Schulte W, Bernhagen J and Bucala R:
Cytokines in sepsis: Potent immunoregulators and potential
therapeutic targets-an updated view. Mediators Inflamm.
2013(165974)2013.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
53
|
Parameswaran N and Patial S: Tumor
necrosis factor-α signaling in macrophages. Crit Rev Eukaryot Gene
Expr. 20:87–103. 2010.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
54
|
Cohen J: The immunopathogenesis of sepsis.
Nature. 420:885–891. 2002.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
55
|
Fong Y, Tracey KJ, Moldawer LL, Hesse DG,
Manogue KB, Kenney JS, Lee AT, Kuo GC, Allison AC and Lowry SF:
Antibodies to cachectin/tumor necrosis factor reduce interleukin 1
beta and interleukin 6 appearance during lethal bacteremia. J Exp
Med. 170:1627–1633. 1989.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
56
|
Alkharfy KM, Ahmad A, Jan BL and Raish M:
Thymoquinone reduces mortality and suppresses early acute
inflammatory markers of sepsis in a mouse model. Biomed
Pharmacother. 98:801–805. 2018.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
57
|
Hoyer KK, Dooms H, Barron L and Abbas AK:
Interleukin-2 in the development and control of inflammatory
disease. Immunol Rev. 226:19–28. 2008.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
58
|
Tanaka T, Narazaki M and Kishimoto T: IL-6
in inflammation, immunity, and disease. Cold Spring Harb Perspect
Biol. 6:a016295. 2014.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
59
|
Pestka S, Krause CD, Sarkar D, Walter MR,
Shi Y and Fisher PB: Interleukin-10andrelatedcytokines
andreceptors. Ann Rev Immunol. 22:929–979. 2004.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
60
|
Couper KN, Blount DG and Riley EM: IL-10:
The master regulator of immunity to infection. J Immunol.
180:5771–5777. 2008.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
61
|
Howard M, Muchamuel T, Andrade S and Menon
S: Interleukin 10 protects mice from lethal endotoxemia. J Exp Med.
177:1205–1208. 1993.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
62
|
Calfee CS and Pugin J: The search for
diagnostic markers in sepsis. Am J Respir Crit Care Med. 186:2–4.
2012.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
63
|
Benzaquen LR, Yu H and Rifai N: High
sensitivity c-reactive protein: An emerging role in cardiovascular
risk assessment. Crit Rev Clin Lab Sci. 39:459–497. 2002.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
64
|
Gabay C and Kushner I: Acute-phase
proteins and other systemic responses to inflammation. N Engl J
Med. 340:448–454. 1999.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
65
|
Senger DR, Galli SJ, Dvorak AM, Perruzzi
CA, Harvey VS and Dvorak HF: Tumor cells secrete a vascular
permeability factor that promotes accumulation of ascites fluid.
Science. 219:983–985. 1983.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
66
|
Leung D, Cachianes G, Kuang W, Goeddel D
and Ferrara N: Vascular endothelial growth factor is a secreted
angiogenic mitogen. Science. 246:1306–1309. 1989.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
67
|
Hotchkiss RS and Karl IE: The
pathophysiology and treatment of sepsis. N Engl J Med. 348:138–150.
2003.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
68
|
Voelkel NF, Cool C, Taraceviene-Stewart L,
Geraci MW, Yeager M, Bull T, Kasper M and Tuder RM: Janus face of
vascular endothelial growth factor: The obligatory survival factor
for lung vascular endothelium controls precapillary artery
remodeling in severe pulmonary hypertension. Crit Care Med. 30 (5
Suppl):S251–S256. 2002.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
69
|
Pickkers P, Sprong T, Eijk LV, Hoeven HVD,
Smits P and Deuren MV: Vascular endothelial growth factor is
increased during the first 48 hours of human septic shock and
correlates with vascular permeability. Shock. 24:508–512.
2005.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
70
|
van der Flier M, van Leeuwen HJ, van
Kessel KP, Kimpen JL, Hoepelman AI and Geelen SP: Plasma vascular
endothelial growth factor in severe sepsis. Shock. 23:35–38.
2005.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
71
|
Yano K, Liaw PC, Mullington JM, Shih SC,
Okada H, Bodyak N, Kang PM, Toltl L, Belikoff B, Buras J, et al:
Vascular endothelial growth factor is an important determinant of
sepsis morbidity and mortality. J Exp Med. 203:1447–1458.
2006.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
72
|
Thickett DR, Armstrong L, Christie SJ and
Millar AB: Vascular endothelial growth factor may contribute to
increased vascular permeability in acute respiratory distress
syndrome. Am J Respir Crit Care Med. 164:1601–1605. 2001.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
73
|
Marshall JC, Vincent JL, Fink MP, Cook DJ,
Rubenfeld G, Foster D, Fisher CJ Jr, Faist E and Reinhart K:
Measures, markers, and mediators: Toward a staging system for
clinical sepsis. A report of the fifth toronto sepsis roundtable,
toronto, ontario, canada, october 25-26, 2000. Crit Care Med.
31:1560–1567. 2003.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
74
|
Peters K, Unger RE, Brunner J and
Kirkpatrick CJ: Molecular basis of endothelial dysfunction in
sepsis. Cardiovasc Res. 60:49–57. 2003.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
75
|
Lee W, Ku SK, Kim SW and Bae JS: Endocan
elicits severe vascular inflammatory responses in vitro and in
vivo. J Cell Physiol. 229:620–630. 2014.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
76
|
Becker KL, Snider R and Nylen ES:
Procalcitonin assay in systemic inflammation, infection, and
sepsis: Clinical utility and limitations. Crit Care Med.
36:941–952. 2008.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
77
|
Nakamura A, Wada H, Ikejiri M, Hatada T,
Sakurai H, Matsushima Y, Nishioka J, Maruyama K, Isaji S, Takeda T
and Nobori T: Efficacy of procalcitonin in the early diagnosis of
bacterial infections in a critical care unit. Shock. 31:586–591.
2009.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
78
|
Çetinkaya M, Özkan H, Köksal N, Çelebi S
and Hacımustafaoğlu M: Comparison of serum amyloid A concentrations
with those of C-reactive protein and procalcitonin in diagnosis and
follow-up of neonatal sepsis in premature infants. J Perinatol.
29:225–231. 2008.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
79
|
Kim KE and Han JY: Evaluation of the
clinical performance of an automated procalcitonin assay for the
quantitative detection of bloodstream infection. Korean J Lab Med.
30:153–159. 2010.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
80
|
Ugarte H, Silva E, Mercan D, De Mendonca A
and Vincent JL: Procalcitonin used as a marker of infection in the
intensive care unit. Crit Care Med. 27:498–504. 1999.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
81
|
Deis JN, Creech CB, Estrada CM and Abramo
TJ: Procalcitonin as a marker of severe bacterial infection in
children in the emergency department. Pediatr Emerg Care. 26:51–60.
2010.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
82
|
Schneider CP, Yilmaz Y, Kleespies A, Jauch
KW and Hartl WH: Accuracy of procalcitonin for outcome prediction
in unselected postoperative critically ill patients. Shock.
31:568–573. 2009.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
83
|
Amaral A, Opal SM and Vincent JL:
Coagulation in sepsis. Intensive Care Med. 30:1032–1040.
2004.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
84
|
Fu Y, Jiang H, Li LX, Chen J, Niu Q and Li
RX: Correlation of coagulation indicators with inflammatory markers
for sepsis in the patients with hematological malignancies.
Zhongguo Shi Yan Xue Ye Xue Za Zhi. 22:1381–1385. 2014.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar : (In Chinese).
|
|
85
|
Zhan ZG and Li CS: Prognostic value of
D-dimer in patients with sepsis in emergency department: A
prospective study. Zhongguo Wei Zhong Bing Ji Jiu Yi Xue.
24:135–139. 2012.PubMed/NCBI(In Chinese).
|
|
86
|
Rodelo JR, De la Rosa G, Valencia ML,
Ospina S, Arango CM, Gómez CI, García A, Nuñez E and Jaimes FA:
d-dimer is a significant prognostic factor in patients with
suspected infection and sepsis. Am J Emerg Med. 30:1991–1999.
2012.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
87
|
Kono H, Asakawa M, Fujii H, Maki A,
Amemiya H, Yamamoto M, Matsuda M and Matsumoto Y: Edaravone, a
novel free radical scavenger, prevents liver injury and mortality
in rats administered endotoxin. J Pharmacol Exp Ther. 307:74–82.
2003.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
88
|
Nagi MN, Alam K, Badary OA, al-Shabanah
OA, al-Sawaf HA and al-Bekairi AM: Thymoquinone protects against
carbon tetrachloride hepatotoxicity in mice via an antioxidant
mechanism. Biochem Mol Biol Int. 47:153–159. 1999.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|