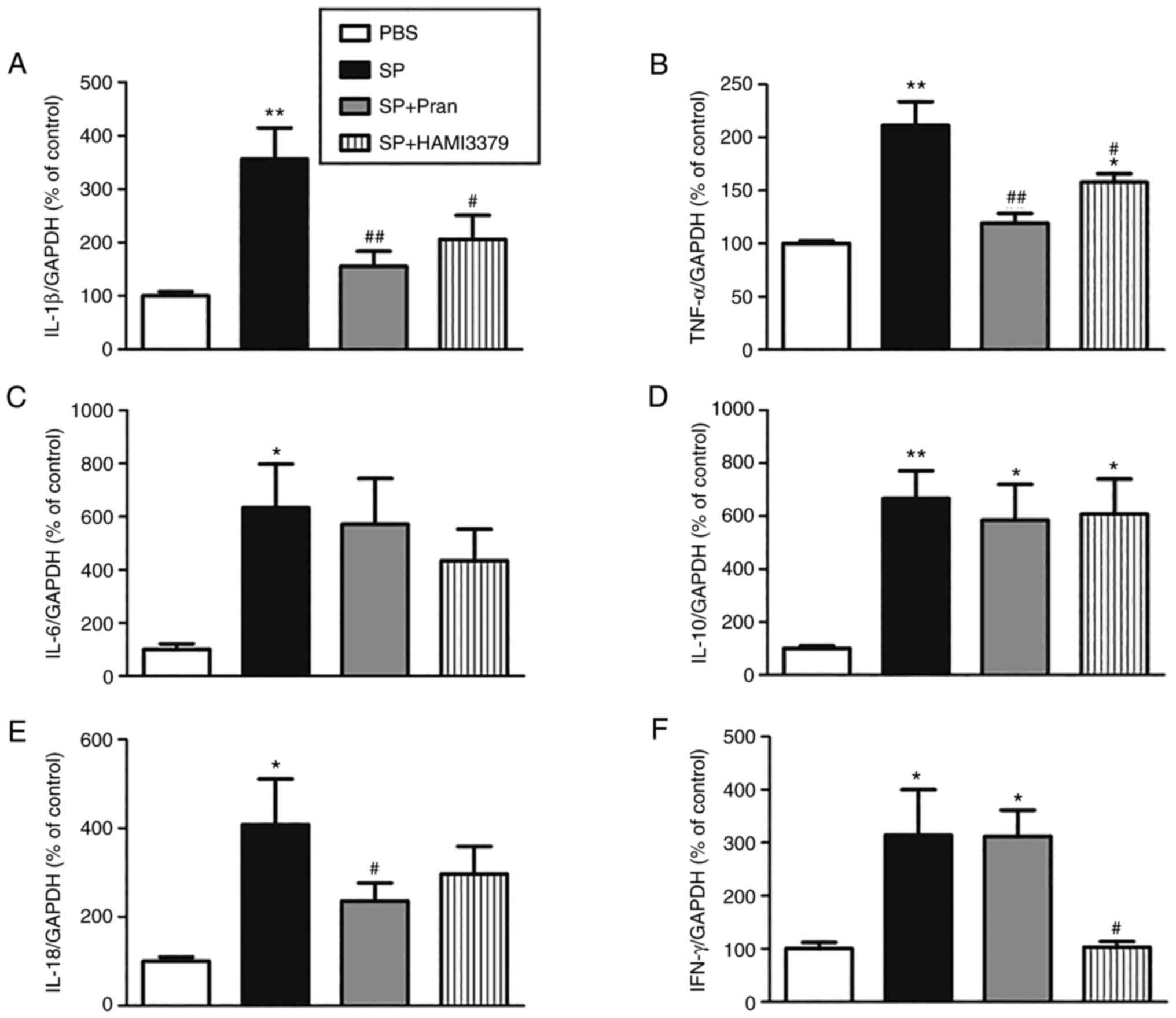
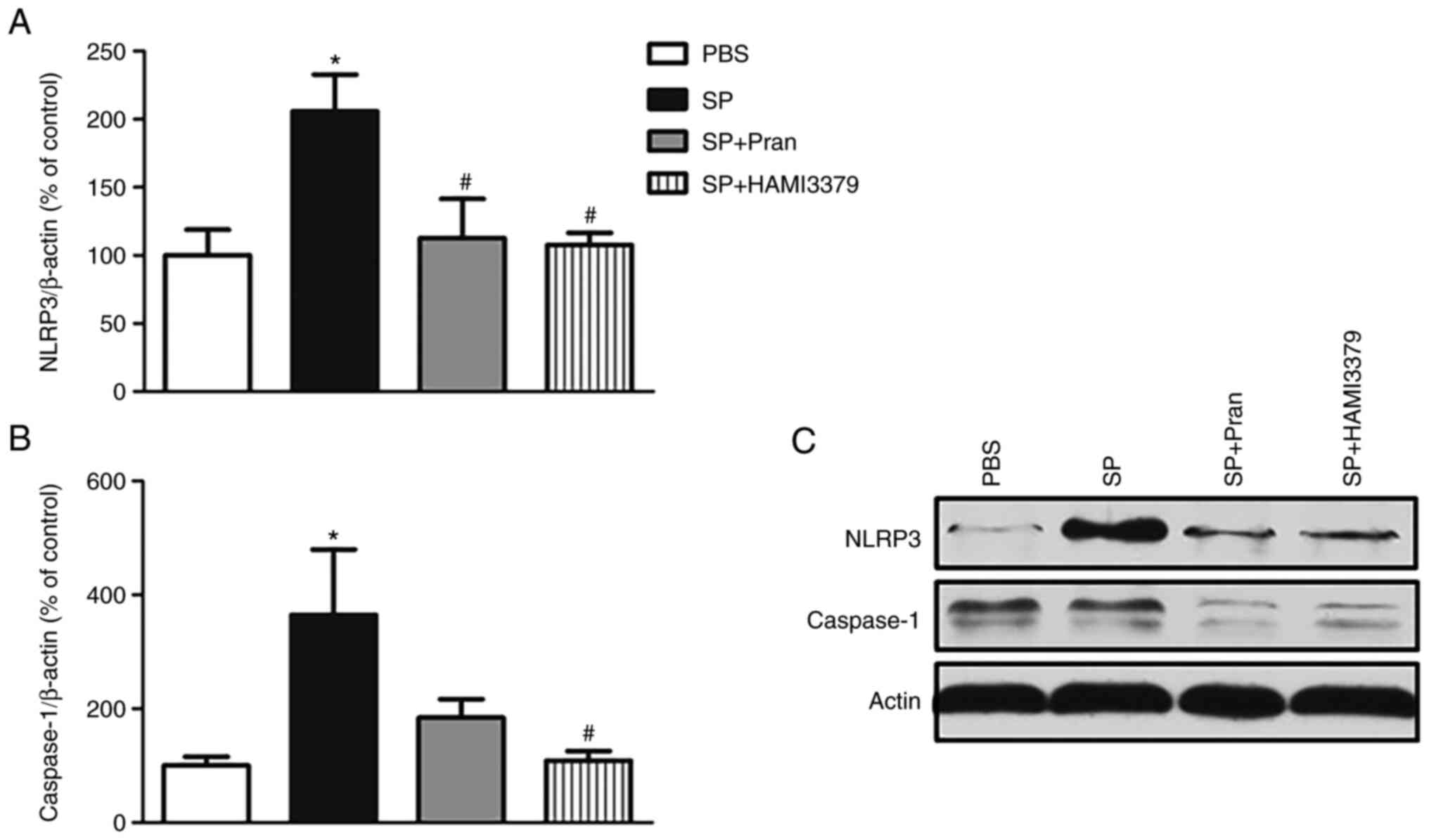
|
1
|
Li Y, Yin Z, Shao Z, Li M, Liang X, Sandhu
HS, Hadler SC, Li J, Sun Y, Li J, et al: Population-based
surveillance for bacterial meningitis in China, September
2006-December 2009. Emerg Infect Dis. 20:61–69. 2014.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
2
|
Brouwer MC and van de Beek D: Epidemiology
of community-acquired bacterial meningitis. Curr Opin Infect Dis.
31:78–84. 2018.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
3
|
Edmond K, Scott S, Korczak V, Ward C,
Sanderson C, Theodoratou E, Clark A, Griffiths U, Rudan I and
Campbell H: Long term sequelae from childhood pneumonia; systematic
review and meta-analysis. PLoS One. 7(e31239)2012.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
4
|
Oldekamp S, Pscheidl S, Kress E, Soehnlein
O, Jansen S, Pufe T, Wang JM, Tauber SC and Brandenburg LO: Lack of
formyl peptide receptor 1 and 2 leads to more severe inflammation
and higher mortality in mice with of pneumococcal meningitis.
Immunology. 143:447–461. 2014.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
5
|
Geldhoff M, Mook-Kanamori BB, Brouwer MC,
Troost D, Leemans JC, Flavell RA, Van der Ende A, Van der Poll T
and Van de Beek D: Inflammasome activation mediates inflammation
and outcome in humans and mice with pneumococcal meningitis. BMC
Infect Dis. 13(358)2013.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
6
|
Wang G, Fu Y, Ma K, Liu J and Liu X: NOD2
regulates microglial inflammation through the TAK1-NF-κB pathway
and autophagy activation in murine pneumococcal meningitis. Brain
Res Bull. 158:20–30. 2020.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
7
|
Bäck M, Dahlén SE, Drazen JM, Evans JF,
Serhan CN, Shimizu T, Yokomizo T and Rovati GE: International union
of basic and clinical pharmacology. LXXXIV: Leukotriene receptor
nomenclature, distribution, and pathophysiological functions.
Pharmacol Rev. 63:539–584. 2011.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
8
|
Singh R, Gupta S, Dastidar S and Ray A:
Cysteinyl leukotrienes and their receptors: Molecular and
functional characteristics. Pharmacology. 85:336–349.
2010.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
9
|
Takahashi Y, Imai K, Ikeda H, Kubota Y,
Yamazaki E and Susa F: Open study of pranlukast add-on therapy in
intractable partial epilepsy. Brain Dev. 35:236–244.
2013.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
10
|
Zhu L, Maruvada R, Sapirstein A, Malik KU,
Peters-Golden M and Kim KS: Arachidonic acid metabolism regulates
Escherichia coli penetration of the blood-brain barrier. Infect
Immun. 78:4302–4310. 2010.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
11
|
Maruvada R, Zhu L, Pearce D, Zheng Y,
Perfect J, Kwon-Chung KJ and Kim KS: Cryptococcus neoformans
phospholipase B1 activates host cell Rac1 for traversal across the
blood-brain barrier. Cell Microbiol. 14:1544–1553. 2012.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
12
|
Zhu L, Maruvada R, Sapirstein A,
Peters-Golden M and Kim K: Cysteinyl leukotrienes as novel host
factors facilitating Cryptococcus neoformans penetration into the
brain. Cell Microbiol 19: 10.1111/cmi.12661, 2017.
|
|
13
|
Yu S, Yan J, Chen X, Zhu X, Li X and Liao
L: Expression of cysteinyl leukotriene receptor in brain tissues of
rats with Streptococcus pneumoniae meningitis. Int J Clin Exp
Pathol. 12:4242–4252. 2019.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
14
|
Zhang Y, Liu X, Bai X, Lin Y, Li Z, Fu J,
Li M, Zhao T, Yang H, Xu R, et al: Melatonin prevents endothelial
cell pyroptosis via regulation of long noncoding RNA
MEG3/miR-223/NLRP3 axis. J Pineal Res. 64:2018.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
15
|
Kim J, Paton J, Briles D, Rhee D and Pyo
S: Streptococcus pneumoniae induces pyroptosis through the
regulation of autophagy in murine microglia. Oncotarget.
6:44161–44178. 2015.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
16
|
Loeffler JM, Ringer R, Hablutzel M, Tauber
MG and Leib SL: The free radical scavenger alpha-phenyl-tert-butyl
nitrone aggravates hippocampal apoptosis and learning deficits in
experimental pneumococcal meningitis. J Infect Dis. 183:247–252.
2001.PubMed/NCBI View
Article : Google Scholar
|
|
17
|
Türeyen K, Vemuganti R, Sailor KA and
Dempsey RJ: Infarct volume quantification in mouse focal cerebral
ischemia: A comparison of triphenyltetrazolium chloride and cresyl
violet staining techniques. J Neurosci Methods. 139:203–207.
2004.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
18
|
Livak KJ and Schmittgen TD: Analysis of
relative gene expression data using real-time quantitative PCR and
the 2(-Delta Delta C(T)) method. Methods. 25:402–408.
2001.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
19
|
Mostowy R, Croucher NJ, Hanage WP, Harris
SR, Bentley S and Fraser C: Heterogeneity in the frequency and
characteristics of homologous recombination in pneumococcal
evolution. PLoS Genet. 10(e1004300)2014.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
20
|
Pfister LA, Tureen JH, Shaw S, Christen S,
Ferriero DM, Täuber MG and Leib SL: Endothelin inhibition improves
cerebral blood flow and is neuroprotective in pneumococcal
meningitis. Ann Neurol. 47:329–335. 2000.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
21
|
Förderreuther S, Tatsch K, Einhäupl KM and
Pfister HW: Abnormalities of cerebral blood flow in the acute phase
of bacterial meningitis in adults. J Neurol. 239:431–436.
1992.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
22
|
Tureen JH, Täuber MG and Sande MA: Effect
of hydration status on cerebral blood flow and cerebrospinal fluid
lactic acidosis in rabbits with experimental meningitis. J Clin
Invest. 89:947–953. 1992.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
23
|
Pschibul A, Janzarik WG, Franck P,
Hufnagel M, Beck C and Korinthenberg R: Cystic encephalomalacia
following vasculopathy and vasospasm of proximal intracranial
arteries due to pneumococcal meningitis in a infant.
Neuropediatrics. 49:213–216. 2018.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
24
|
Yu GL, Wei EQ, Wang ML, Zhang WP, Zhang
SH, Weng JQ, Chu LS, Fang SH, Zhou Y, Chen Z, et al: Pranlukast, a
cysteinyl leukotriene receptor-1 antagonist, protects against
chronic ischemic brain injury and inhibits the glial scar formation
in mice. Brain Res. 1053:116–125. 2005.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
25
|
Shi QJ, Wang H, Liu ZX, Fang SH, Song XM,
Lu YB, Zhang WP, Sa XY, Ying HZ and Wei EQ: HAMI 3379, a CysLT2R
antagonist, dose- and time-dependently attenuates brain injury and
inhibits microglial inflammation after focal cerebral ischemia in
rats. Neuroscience. 291:53–69. 2015.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
26
|
Leib SL, Kim YS, Chow LL, Sheldon RA and
Täuber MG: Reactive oxygen intermediates contribute to necrotic and
apoptotic neuronal injury in an infant rat model of bacterial
meningitis due to group B streptococci. J Clin Invest.
98:2632–2639. 1996.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
27
|
Wellmer A, Noeske C, Gerber J, Munzel U
and Nau R: Spatial memory and learning deficits after experimental
pneumococcal meningitis in mice. Neurosci Lett. 296:137–140.
2000.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
28
|
Zhu N, Liu W, Prakash A, Zhang C and Kim
KS: Targeting E. coli invasion of the blood-brain barrier for
investigating the pathogenesis and therapeutic development of E.
coli meningitis. Cell Microbiol. 22(e13231)2020.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
29
|
Zhang XY, Wang XR, Xu DM, Yu SY, Shi QJ,
Zhang LH, Chen L, Fang SH, Lu YB, Zhang WP and Wei EQ: HAMI 3379, a
CysLT2 receptor antagonist, attenuates ischemia-like neuronal
injury by inhibiting microglial activation. J Pharmacol Exp Ther.
346:328–341. 2013.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
30
|
Ramesh G, MacLean A and Philipp M:
Cytokines and chemokines at the crossroads of neuroinflammation,
neurodegeneration, and neuropathic pain. Mediators Inflamm.
2013(480739)2013.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
31
|
Liu X, Chauhan VS, Young AB and Marriott
I: NOD2 mediates inflammatory responses of primary murine glia to
Streptococcus pneumoniae. Glia. 58:839–847. 2010.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
32
|
Giridharan VV, Collodel A, Generoso JS,
Scaini G, Wassather R, Selvaraj S, Hasbun R, Dal-Pizzol F,
Petronilho F and Barichello T: Neuroinflammation trajectories
precede cognitive impairment after experimental meningitis-evidence
from an in vivo PET study. J Neuroinflammation.
17(5)2020.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
33
|
Zhang D, Hu X, Qian L, O'Callaghan JP and
Hong JS: Astrogliosis in CNS pathologies: Is there a role for
microglia? Mol Neurobiol. 41:232–241. 2010.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
34
|
Rohl C, Lucius R and Sievers J: The effect
of activated microglia on astrogliosis parameters in astrocyte
cultures. Brain Res. 1129:43–52. 2007.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
35
|
Fang SH, Wei EQ, Zhou Y, Wang ML, Zhang
WP, Yu GL, Chu LS and Chen Z: Increased expression of cysteinyl
leukotriene receptor-1 in the brain mediates neuronal damage and
astrogliosis after focal cerebral ischemia in rats. Neuroscience.
140:969–979. 2006.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
36
|
Fang SH, Zhou Y, Chu LS, Zhang WP, Wang
ML, Yu GL, Peng F and Wei EQ: Spatio-temporal expression of
cysteinyl leukotriene receptor-2 mRNA in rat brain after focal
cerebral ischemia. Neurosci Lett. 412:78–83. 2007.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
37
|
Zhao CZ, Zhao B, Zhang XY, Huang XQ, Shi
WZ, Liu HL, Fang SH, Lu YB, Zhang WP, Tang FD and Wei EQ: Cysteinyl
leukotriene receptor 2 is spatiotemporally involved in neuron
injury, astrocytosis and microgliosis after focal cerebral ischemia
in rats. Neuroscience. 189:1–11. 2011.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
38
|
Mitchell AJ, Yau B, McQuillan JA, Ball HJ,
Too LK, Abtin A, Hertzog P, Leib SL, Jones CA, Gerega SK, et al:
Inflammasome-dependent IFN-γ drives pathogenesis in Streptococcus
pneumoniae meningitis. J Immunol. 189:4970–4980. 2012.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
39
|
Matsuse H, Kondo Y, Machida I, Kawano T,
Saeki S, Tomari S, Obase Y, Fukushima C, Mizuta Y and Kohno S:
Effects of anti-inflammatory therapies on recurrent and low-grade
respiratory syncytial virus infections in a murine model of asthma.
Ann Allergy Asthma Immunol. 97:55–60. 2006.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
40
|
Fujii M, Tanaka H and Abe S:
Interferon-gamma up-regulates expression of cysteinyl leukotriene
type 2 receptors on eosinophils in asthmatic patients. Chest.
128:3148–3155. 2005.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
41
|
Liu Y, Duan C, Chen H, Wang C, Liu X, Qiu
M, Tang H, Zhang F, Zhou X and Yang J: Inhibition of COX-2/mPGES-1
and 5-LOX in macrophages by leonurine ameliorates monosodium urate
crystal-induced inflammation. Toxicol Appl Pharmacol. 351:1–11.
2018.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
42
|
Amaral FA, Costa VV, Tavares LD, Sachs D,
Coelho FM, Fagundes CT, Soriani FM, Silveira TN, Cunha LD, Zamboni
DS, et al: NLRP3 inflammasome-mediated neutrophil recruitment and
hypernociception depend on leukotriene B(4) in a murine model of
gout. Arthritis Rheum. 64:474–484. 2012.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
43
|
Zhang W, Ba G, Tang R, Li M and Lin H:
Ameliorative effect of selective NLRP3 inflammasome inhibitor
MCC950 in an ovalbumin-induced allergic rhinitis murine model. Int
Immunopharmacol. 83(106394)2020.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|