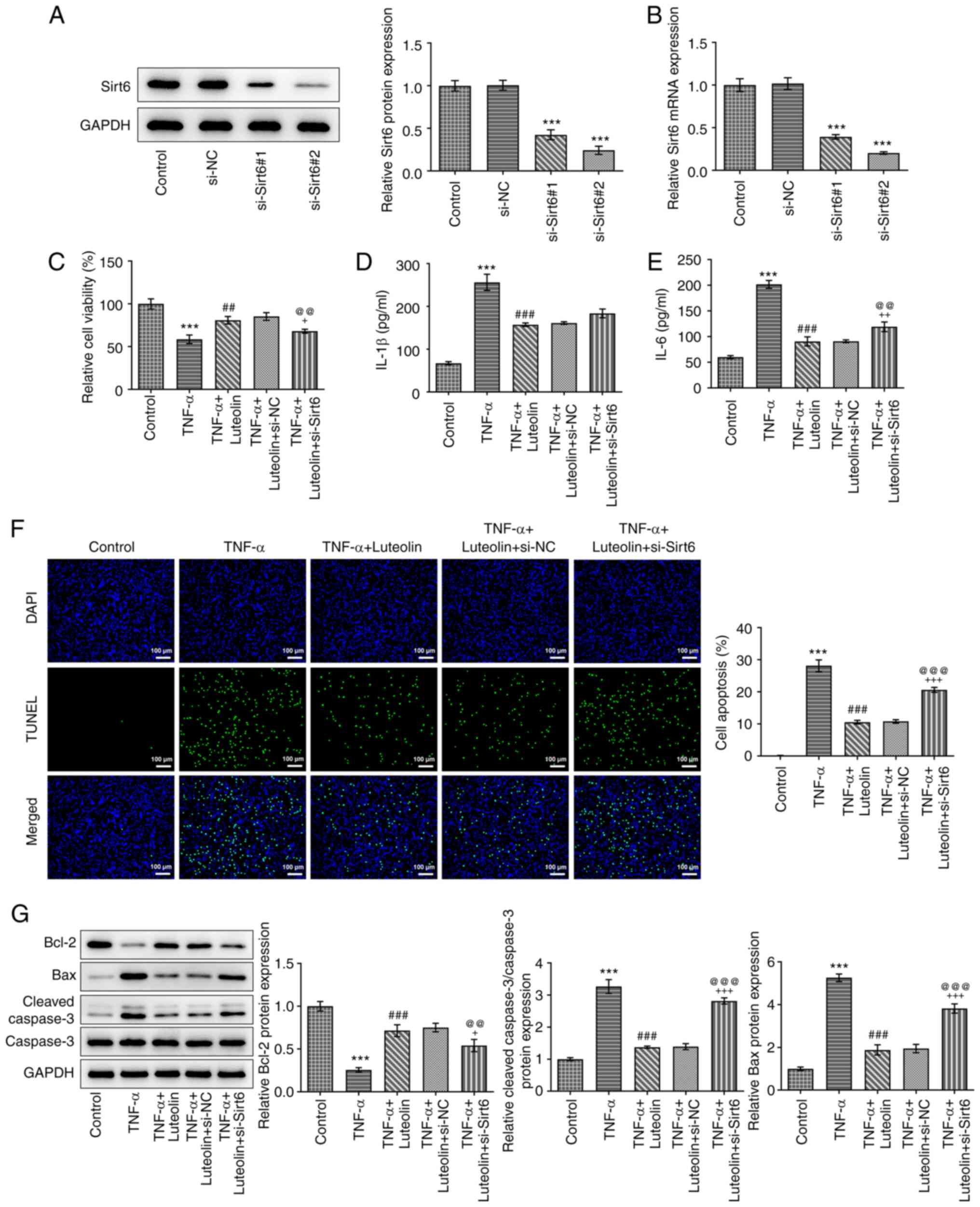
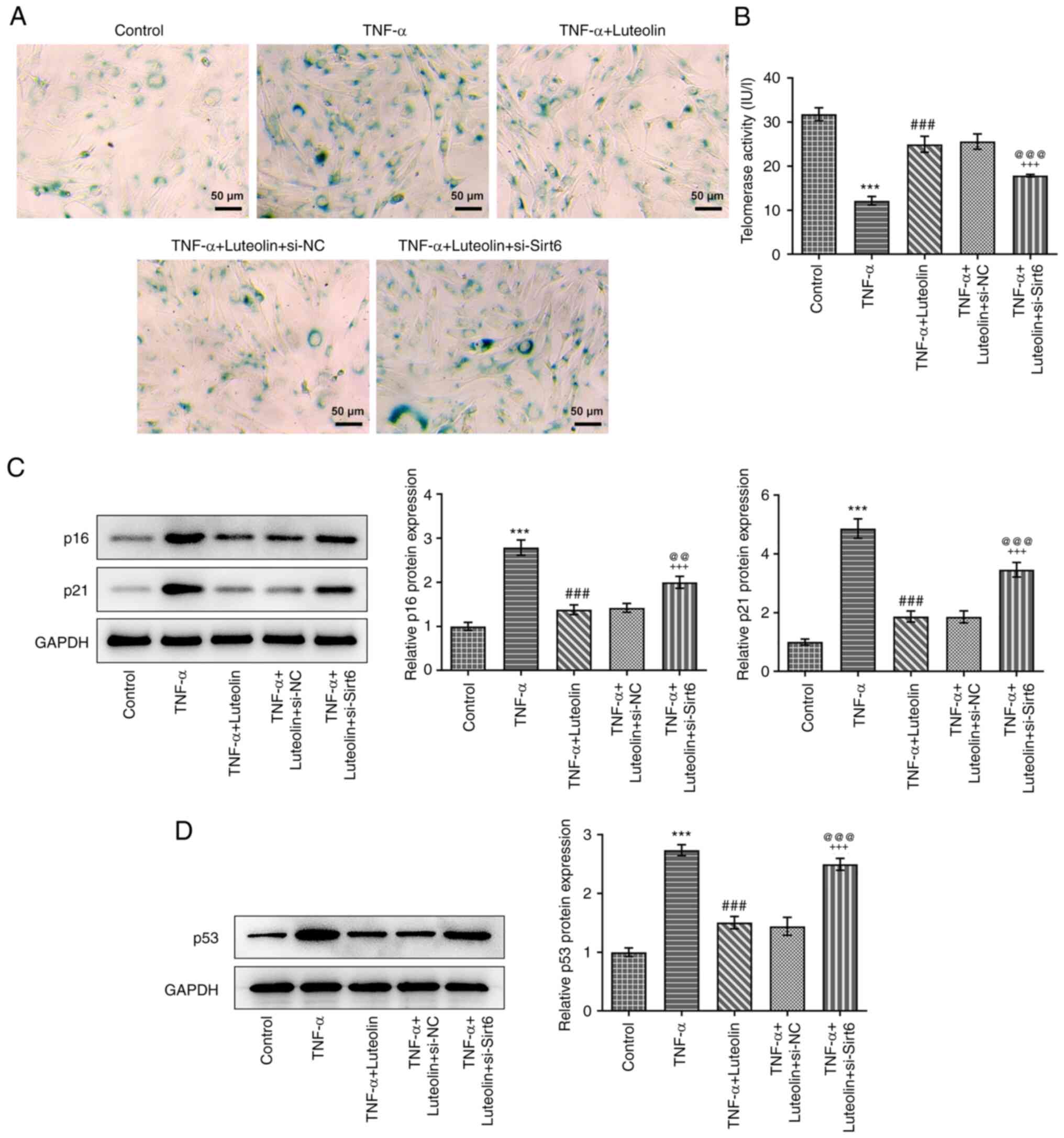
|
1
|
Luoma K, Riihimäki H, Luukkonen R,
Raininko R, Viikari-Juntura E and Lamminen A: Low back pain in
relation to lumbar disc degeneration. Spine (Phila Pa 1976).
25:487–492. 2000.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
2
|
Cazzanelli P and Wuertz-Kozak K: MicroRNAs
in intervertebral disc degeneration, apoptosis, inflammation, and
mechanobiology. Int J Mol Sci. 21(3601)2020.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
3
|
Wu PH, Kim HS and Jang IT: Intervertebral
disc diseases PART 2: A review of the current diagnostic and
treatment strategies for intervertebral disc disease. Int J Mol
Sci. 21(2135)2020.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
4
|
Vergroesen PP, Kingma I, Emanuel KS,
Hoogendoorn RJ, Welting TJ, van Royen BJ, van Dieën JH and Smit TH:
Mechanics and biology in intervertebral disc degeneration: A
vicious circle. Osteoarthritis Cartilage. 23:1057–1070.
2015.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
5
|
Kos N, Gradisnik L and Velnar T: A brief
review of the degenerative intervertebral disc disease. Med Arch.
73:421–424. 2019.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
6
|
Zhang Y, He F, Chen Z, Su Q, Yan M, Zhang
Q, Tan J, Qian L and Han Y: Melatonin modulates IL-1β-induced
extracellular matrix remodeling in human nucleus pulposus cells and
attenuates rat intervertebral disc degeneration and inflammation.
Aging (Albany NY). 11:10499–10512. 2019.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
7
|
Guo Z, Gao WS, Wang YF, Gao F, Wang W and
Ding WY: MiR-502 suppresses TNF-α-induced nucleus pulposus cell
apoptosis by targeting TARF2. Biomed Res Int.
2021(5558369)2021.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
8
|
Purmessur D, Walter BA, Roughley PJ,
Laudier DM, Hecht AC and Iatridis J: A role for TNFα in
intervertebral disc degeneration: A non-recoverable catabolic
shift. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 433:151–156. 2013.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
9
|
Lin Y, Shi R, Wang X and Shen HM:
Luteolin, a flavonoid with potential for cancer prevention and
therapy. Curr Cancer Drug Targets. 8:634–646. 2008.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
10
|
Aziz N, Kim MY and Cho JY:
Anti-inflammatory effects of luteolin: A review of in vitro, in
vivo, and in silico studies. J Ethnopharmacol. 225:342–358.
2018.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
11
|
Imran M, Rauf A, Abu-Izneid T, Nadeem M,
Shariati MA, Khan IA, Imran A, Orhan IE, Rizwan M, Atif M, et al:
Luteolin, a flavonoid, as an anticancer agent: A review. Biomed
Pharmacother. 112(108612)2019.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
12
|
Zhu RZ, Li BS, Gao SS, Seo JH and Choi BM:
Luteolin inhibits H2O2-induced cellular
senescence via modulation of SIRT1 and p53. Korean J Physiol
Pharmacol. 25:297–305. 2021.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
13
|
Kempuraj D, Thangavel R, Kempuraj DD,
Ahmed ME, Selvakumar GP, Raikwar SP, Zaheer SA, Iyer SS,
Govindarajan R, Chandrasekaran PN and Zaheer A: Neuroprotective
effects of flavone luteolin in neuroinflammation and neurotrauma.
Biofactors. 47:190–197. 2021.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
14
|
Li L, Luo W, Qian Y, Zhu W, Qian J, Li J,
Jin Y, Xu X and Liang G: Luteolin protects against diabetic
cardiomyopathy by inhibiting NF-κB-mediated inflammation and
activating the Nrf2-mediated antioxidant responses. Phytomedicine.
59(152774)2019.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
15
|
Zhang L, Wang X, Zhang L, Virgous C and Si
H: Combination of curcumin and luteolin synergistically inhibits
TNF-α-induced vascular inflammation in human vascular cells and
mice. J Nutr Biochem. 73(108222)2019.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
16
|
Fei J, Liang B, Jiang C, Ni H and Wang L:
Luteolin inhibits IL-1β-induced inflammation in rat chondrocytes and
attenuates osteoarthritis progression in a rat model. Biomed
Pharmacother. 109:1586–1592. 2019.
|
|
17
|
Yang SC, Chen PJ, Chang SH, Weng YT, Chang
FR, Chang KY, Chen CY, Kao TI and Hwang TL: Luteolin attenuates
neutrophilic oxidative stress and inflammatory arthritis by
inhibiting Raf1 activity. Biochem Pharmacol. 154:384–396.
2018.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
18
|
Shahgaldi S and Kahmini FR: A
comprehensive review of Sirtuins: With a major focus on redox
homeostasis and metabolism. Life Sci. 282(119803)2021.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
19
|
O'Callaghan C and Vassilopoulos A:
Sirtuins at the crossroads of stemness, aging, and cancer. Aging
Cell. 16:1208–1218. 2017.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
20
|
Mendes KL, Lelis DF and Santos SHS:
Nuclear sirtuins and inflammatory signaling pathways. Cytokine
Growth Factor Rev. 38:98–105. 2017.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
21
|
Chang HC and Guarente L: SIRT1 and other
sirtuins in metabolism. Trends Endocrinol Metab. 25:138–145.
2014.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
22
|
Kang L, Hu J, Weng Y, Jia J and Zhang Y:
Sirtuin 6 prevents matrix degradation through inhibition of the
NF-κB pathway in intervertebral disc degeneration. Exp Cell Res.
352:322–332. 2017.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
23
|
Chen J, Xie JJ, Jin MY, Gu YT, Wu CC, Guo
WJ, Yan YZ, Zhang ZJ, Wang JL, Zhang XL, et al: Sirt6
overexpression suppresses senescence and apoptosis of nucleus
pulposus cells by inducing autophagy in a model of intervertebral
disc degeneration. Cell Death Dis. 9(56)2018.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
24
|
Akter R, Afrose A, Rahman MR, Chowdhury R,
Nirzhor SSR, Khan RI and Kabir MT: A comprehensive analysis into
the therapeutic application of natural products as SIRT6 modulators
in Alzheimer's disease, aging, cancer, inflammation, and diabetes.
Int J Mol Sci. 22(4180)2021.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
25
|
Livak KJ and Schmittgen TD: Analysis of
relative gene expression data using real-time quantitative PCR and
the 2(-Delta Delta C(T)) method. Methods. 25:402–408.
2001.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
26
|
Su L, Dong Y, Wang Y, Wang Y, Guan B, Lu
Y, Wu J, Wang X, Li D, Meng A and Fan F: Potential role of
senescent macrophages in radiation-induced pulmonary fibrosis. Cell
Death Dis. 12(527)2021.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
27
|
Bernardes de Jesus B and Blasco MA:
Telomerase at the intersection of cancer and aging. Trends Genet.
29:513–520. 2013.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
28
|
Zhao CQ, Jiang LS and Dai LY: Programmed
cell death in intervertebral disc degeneration. Apoptosis.
11:2079–2088. 2006.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
29
|
Zhu L, Yu C, Zhang X, Yu Z, Zhan F, Yu X,
Wang S, He F, Han Y and Zhao H: The treatment of intervertebral
disc degeneration using traditional Chinese medicine. J
Ethnopharmacol. 263(113117)2020.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
30
|
Gendrisch F, Esser PR, Schempp CM and
Wölfle U: Luteolin as a modulator of skin aging and inflammation.
Biofactors. 47:170–180. 2021.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
31
|
Zhao CQ, Wang LM, Jiang LS and Dai LY: The
cell biology of intervertebral disc aging and degeneration. Ageing
Res Rev. 6:247–261. 2007.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
32
|
Wang B, Ke W, Wang K, Li G, Ma L, Lu S,
Xiang Q, Liao Z, Luo R, Song Y, et al: Mechanosensitive ion channel
piezo1 activated by matrix stiffness regulates oxidative
stress-induced senescence and apoptosis in human intervertebral
disc degeneration. Oxid Med Cell Longev.
2021(8884922)2021.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
33
|
Horiuchi T, Mitoma H, Harashima S,
Tsukamoto H and Shimoda T: Transmembrane TNF-alpha: Structure,
function and interaction with anti-TNF agents. Rheumatology
(Oxford). 49:1215–1228. 2010.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
34
|
Hong J, Yan J, Chen J, Li S, Huang Y,
Huang Z, Chen W, Liang A and Ye W: Identification of key potential
targets for TNF-α/TNFR1-related intervertebral disc degeneration by
bioinformatics analysis. Connect Tissue Res. 62:531–541.
2021.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
35
|
Kang R, Li H, Rickers K, Ringgaard S, Xie
L and Bünger C: Intervertebral disc degenerative changes after
intradiscal injection of TNF-α in a porcine model. Eur Spine J.
24:2010–2016. 2015.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
36
|
Sprung CN, Ivashkevich A, Forrester HB,
Redon CE, Georgakilas A and Martin OA: Oxidative DNA damage caused
by inflammation may link to stress-induced non-targeted effects.
Cancer Lett. 356:72–81. 2015.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
37
|
Chen F, Jiang G, Liu H, Li Z, Pei Y, Wang
H, Pan H, Cui H, Long J, Wang J and Zheng Z: Melatonin alleviates
intervertebral disc degeneration by disrupting the
IL-1β/NF-κB-NLRP3 inflammasome positive feedback loop. Bone Res.
8(10)2020.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
38
|
Xia F, Wang C, Jin Y, Liu Q, Meng Q, Liu K
and Sun H: Luteolin protects HUVECs from TNF-α-induced oxidative
stress and inflammation via its effects on the Nox4/ROS-NF-κB and
MAPK pathways. J Atheroscler Thromb. 21:768–783. 2014.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
39
|
Ali F and Siddique YH: Bioavailability and
pharmaco-therapeutic potential of luteolin in overcoming
Alzheimer's disease. CNS Neurol Disord Drug Targets. 18:352–365.
2019.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
40
|
Ng F and Tang BL: Sirtuins' modulation of
autophagy. J Cell Physiol. 228:2262–2270. 2013.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
41
|
Lee OH, Woo YM, Moon S, Lee J, Park H,
Jang H, Park YY, Bae SK, Park KH, Heo JH and Choi Y: Sirtuin 6
deficiency induces endothelial cell senescence via downregulation
of forkhead box M1 expression. Aging (Albany NY). 12:20946–20967.
2020.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
42
|
Grootaert MOJ, Finigan A, Figg NL, Uryga
AK and Bennett MR: SIRT6 protects smooth muscle cells from
senescence and reduces atherosclerosis. Circ Res. 128:474–491.
2021.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
43
|
Wang J, Zheng B, Yang S, Wang F, Wang Z
and Wang J: The protective effects of Agomelatine against Aβ1-42
oligomers-induced cellular senescence mediated by SIRT6 and
Agomelatine's potential in AD treatment. Hum Cell. 34:1734–1743.
2021.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
44
|
Kim A, Lee W and Yun JM: Luteolin and
fisetin suppress oxidative stress by modulating sirtuins and
forkhead box O3a expression under in vitro diabetic conditions.
Nutr Res Pract. 11:430–434. 2017.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
45
|
Baker RG, Hayden MS and Ghosh S: NF-κB,
inflammation, and metabolic disease. Cell Metab. 13:11–22.
2011.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
46
|
Kawahara TL, Michishita E, Adler AS,
Damian M, Berber E, Lin M, McCord RA, Ongaigui KC, Boxer LD, Chang
HY and Chua KF: SIRT6 links histone H3 lysine 9 deacetylation to
NF-kappaB-dependent gene expression and organismal life span. Cell.
136:62–74. 2009.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
47
|
Zhang GZ, Liu MQ, Chen HW, Wu ZL, Gao YC,
Ma ZJ, He XG and Kang XW: NF-κB signalling pathways in nucleus
pulposus cell function and intervertebral disc degeneration. Cell
Prolif. 54(e13057)2021.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
48
|
Li P, Jin Y, Qi F, Wu F, Luo S, Cheng Y,
Montgomery RR and Qian F: SIRT6 acts as a negative regulator in
dengue virus-induced inflammatory response by targeting the DNA
binding domain of NF-κB p65. Front Cell Infect Microbiol.
8(113)2018.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
49
|
Chen J, Yan J, Li S, Zhu J, Zhou J, Li J,
Zhang Y, Huang Z, Yuan L, Xu K, et al: Atorvastatin inhibited TNF-α
induced matrix degradation in rat nucleus pulposus cells by
suppressing NLRP3 inflammasome activity and inducing autophagy
through NF-κB signaling. Cell Cycle. 20:2160–2173. 2021.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
50
|
Yang Y, Tan X, Xu J, Wang T, Liang T, Xu
X, Ma C, Xu Z, Wang W, Li H, et al: Luteolin alleviates
neuroinflammation via downregulating the TLR4/TRAF6/NF-κB pathway
after intracerebral hemorrhage. Biomed Pharmacother.
126(110044)2020.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|