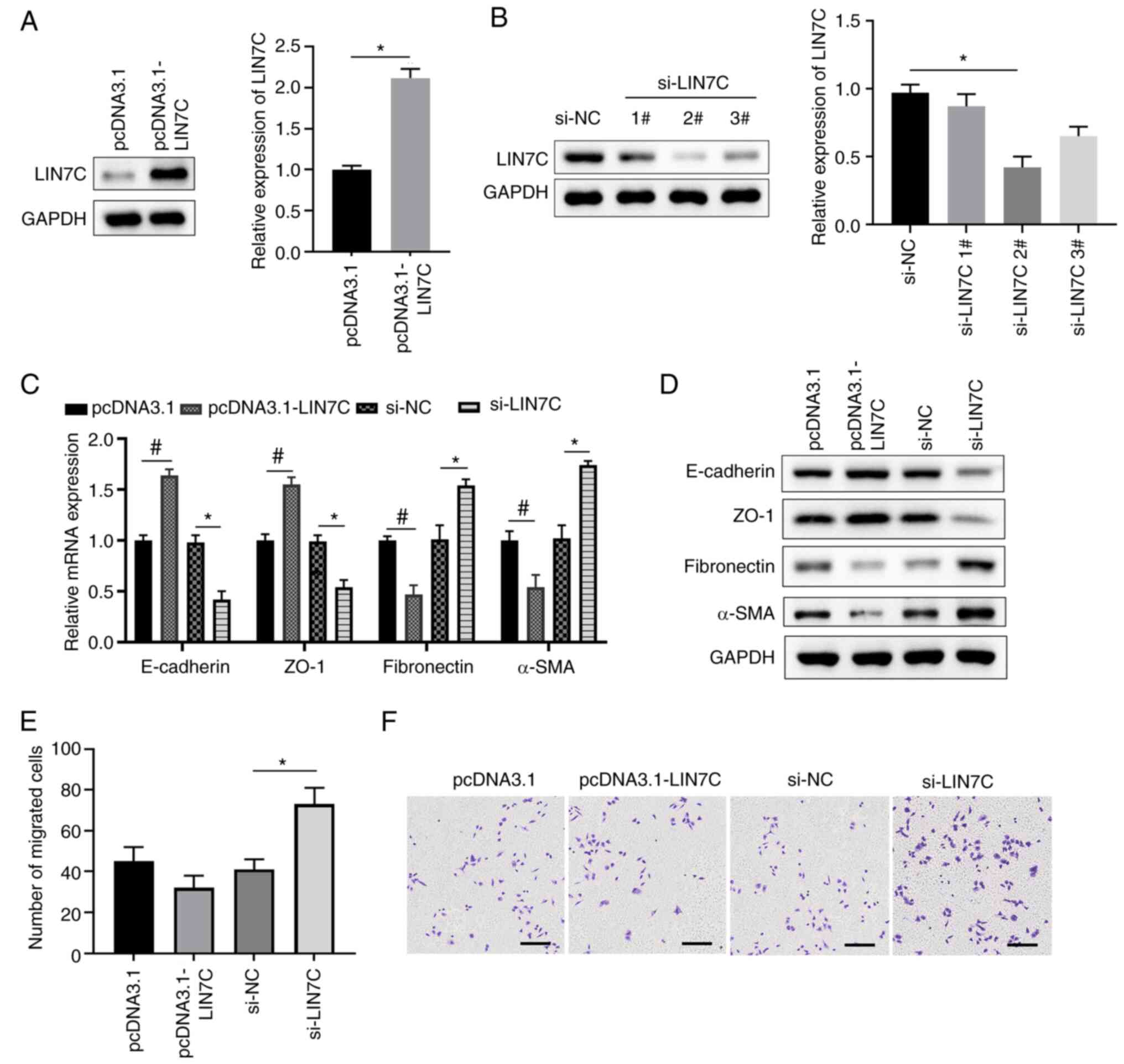
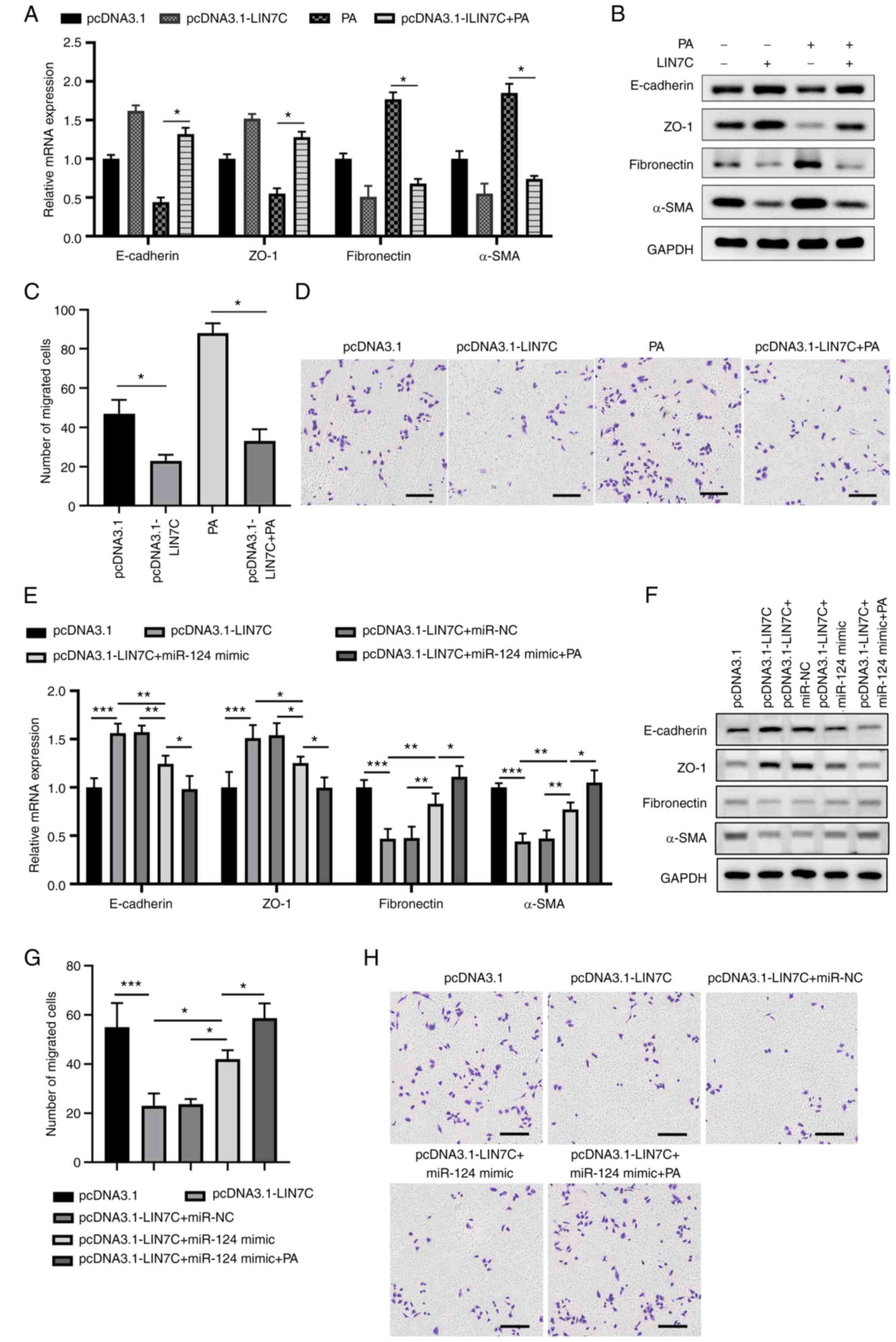
|
1
|
Pastor JC: Proliferative
vitreoretinopathy: An overview. Surv Ophthalmol. 43:3–18.
1998.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
2
|
Di Lauro S, Kadhim MR, Charteris DG and
Pastor JC: Classifications for proliferative vitreoretinopathy
(PVR): An analysis of their use in publications over the last 15
years. J Ophthalmol. 2016(7807596)2016.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
3
|
Coffee RE, Jiang L and Rahman SA:
Proliferative vitreoretinopathy: Advances in surgical management.
Int Ophthalmol Clin. 54:91–109. 2014.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
4
|
Idrees S, Sridhar J and Kuriya AE:
Proliferative vitreoretinopathy: A review. Int Ophthalmol Clin.
59:221–240. 2019.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
5
|
Charteris DG: Proliferative
vitreoretinopathy: Pathobiology, surgical management, and
adjunctive treatment. Br J Ophthalmol. 79:953–960. 1995.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
6
|
Lee SC, Kwon OW, Seong GJ, Kim SH, Ahn JE
and Kay ED: Epitheliomesenchymal transdifferentiation of cultured
RPE cells. Ophthalmic Res. 33:80–86. 2001.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
7
|
Mudhar HS: A brief review of the
histopathology of proliferative vitreoretinopathy (PVR). Eye
(Lond). 34:246–250. 2020.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
8
|
Zou H, Shan C, Ma L, Liu J, Yang N and
Zhao J: Polarity and epithelial-mesenchymal transition of retinal
pigment epithelial cells in proliferative vitreoretinopathy. Peer
J. 8(e10136)2020.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
9
|
He H, Kuriyan AE, Su CW, Mahabole M, Zhang
Y, Zhu YT, Flynn HW, Parel JM and Tseng SC: Inhibition of
proliferation and epithelial mesenchymal transition in retinal
pigment epithelial cells by heavy chain-hyaluronan/pentraxin 3. Sci
Rep. 7(43736)2017.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
10
|
Tamiya S, Liu L and Kaplan HJ:
Epithelial-mesenchymal transition and proliferation of retinal
pigment epithelial cells initiated upon loss of cell-cell contact.
Invest Ophthalmol Vis Sci. 51:2755–2763. 2010.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
11
|
Carta G, Murru E, Banni S and Manca C:
Palmitic acid: Physiological role, metabolism and nutritional
implications. Front Physiol. 8(902)2017.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
12
|
Mancini A, Imperlini E, Nigro E,
Montagnese C, Daniele A, Orrù S and Buono P: Biological and
nutritional properties of palm oil and palmitic acid: Effects on
health. Molecules. 20:17339–17361. 2015.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
13
|
Wang Y, Qian Y, Fang Q, Zhong P, Li W,
Wang L, Fu W, Zhang Y, Xu Z, Li X and Liang G: Saturated palmitic
acid induces myocardial inflammatory injuries through direct
binding to TLR4 accessory protein MD2. Nat Commun.
8(13997)2017.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
14
|
Fatima S, Hu X, Huang C, Zhang W, Cai J,
Huang M, Gong RH, Chen M, Ho AHM, Su T, et al: High-fat diet
feeding and palmitic acid increase CRC growth in β2AR-dependent
manner. Cell Death Dis. 10(711)2019.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
15
|
de Araujo Junior RF, Eich C, Jorquera C,
Schomann T, Baldazzi F, Chan AB and Cruz LJ: Ceramide and palmitic
acid inhibit macrophage-mediated epithelial-mesenchymal transition
in colorectal cancer. Mol Cell Biochem. 468:153–168.
2020.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
16
|
Gutierrez MA, Davis SS, Rosko A, Nguyen
SM, Mitchell KP, Mateen S, Neves J, Garcia TY, Mooney S, Perdew GH,
et al: A novel AhR ligand, 2AI, protects the retina from
environmental stress. Sci Rep. 6(29025)2016.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
17
|
Osada H and Takahashi T: MicroRNAs in
biological processes and carcinogenesis. Carcinogenesis. 28:2–12.
2007.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
18
|
Kaneko H and Terasaki H: Biological
involvement of microRNAs in proliferative vitreoretinopathy. Transl
Vis Sci Technol. 6(5)2017.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
19
|
Usui-Ouchi A, Ouchi Y, Kiyokawa M, Sakuma
T, Ito R and Ebihara N: Upregulation of Mir-21 levels in the
vitreous humor is associated with development of proliferative
vitreoretinal disease. PLoS One. 11(e0158043)2016.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
20
|
Wang L, Dong F, Reinach PS, He D, Zhao X,
Chen X, Hu DN and Yan D: MicroRNA-182 suppresses HGF/SF-induced
increases in retinal pigment epithelial cell proliferation and
migration through targeting c-Met. PLoS One.
11(e0167684)2016.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
21
|
Takayama K, Kaneko H, Hwang SJ, Ye F,
Higuchi A, Tsunekawa T, Matsuura T, Iwase T, Asami T, Ito Y, et al:
Increased ocular levels of microRNA-148a in cases of retinal
detachment promote epithelial-mesenchymal transition. Invest
Ophthalmol Vis Sci. 57:2699–2705. 2016.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
22
|
Hou Q, Zhou L, Tang J, Ma N, Xu A, Tang J,
Zheng D, Chen X, Chen F, Dong XD and Tu L: LGR4 is a direct target
of microRNA-34a and modulates the proliferation and migration of
retinal pigment epithelial ARPE-19 cells. PLoS One.
11(e0168320)2016.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
23
|
Livak KJ and Schmittgen TD: Analysis of
relative gene expression data using real-time quantitative PCR and
the 2(-Delta Delta C(T)) method. Methods. 25:402–408.
2001.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
24
|
Li X, Zhao M and He S: RPE
epithelial-mesenchymal transition plays a critical role in the
pathogenesis of proliferative vitreoretinopathy. Ann Transl Med.
8(263)2020.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
25
|
Tamiya S and Kaplan HJ: Role of
epithelial-mesenchymal transition in proliferative
vitreoretinopathy. Exp Eye Res. 142:26–31. 2016.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
26
|
Nagasaka Y, Kaneko H, Ye F, Kachi S, Asami
T, Kato S, Takayama K, Hwang SJ, Kataoka K, Shimizu H, et al: Role
of Caveolin-1 for blocking the epithelial-mesenchymal transition in
proliferative vitreoretinopathy. Invest Ophthalmol Vis Sci.
58:221–229. 2017.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
27
|
Huang F, Chen J, Wang J, Zhu P and Lin W:
Palmitic acid induces microRNA-221 expression to decrease glucose
uptake in HepG2 cells via the PI3K/AKT/GLUT4 pathway. Biomed Res
Int. 2019(8171989)2019.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
28
|
Gu X, Wang XQ, Lin MJ, Liang H, Fan SY,
Wang L, Yan X, Liu W and Shen FX: Molecular interplay between
microRNA-130a and PTEN in palmitic acid-mediated impaired function
of endothelial progenitor cells: Effects of metformin. Int J Mol
Med. 43:2187–2198. 2019.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
29
|
Chu-Tan JA, Rutar M, Saxena K, Aggio-Bruce
R, Essex RW, Valter K, Jiao H, Fernando N, Wooff Y, Madigan MC, et
al: MicroRNA-124 dysregulation is associated with retinal
inflammation and photoreceptor death in the degenerating retina.
Invest Ophthalmol Vis Sci. 59:4094–4105. 2018.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
30
|
Ji H, Sang M, Liu F, Ai N and Geng C:
miR-124 regulates EMT based on ZEB2 target to inhibit invasion and
metastasis in triple-negative breast cancer. Pathol Res Pract.
215:697–704. 2019.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
31
|
Shi B, Wang Y and Yin F:
MALAT1/miR-124/Capn4 axis regulates proliferation, invasion and EMT
in nasopharyngeal carcinoma cells. Cancer Biol Ther. 18:792–800.
2017.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
32
|
Chen J, Zhong Y and Li L: miR-124 and
miR-203 synergistically inactivate EMT pathway via coregulation of
ZEB2 in clear cell renal cell carcinoma (ccRCC). J Transl Med.
18(69)2020.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
33
|
Wu J, Weng Y, He F, Liang D and Cai L:
LncRNA MALAT-1 competitively regulates miR-124 to promote EMT and
development of non-small-cell lung cancer. Anticancer Drugs.
29:628–636. 2018.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
34
|
Li Y, Yan J, Wang Y, Wang C, Zhang C and
Li G: LINC00240 promotes gastric cancer cell proliferation,
migration and EMT via the miR-124-3p / DNMT3B axis. Cell Biochem
Funct. 38:1079–1088. 2020.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
35
|
Luz M and Knust E: Fluorescently tagged
Lin7c is a dynamic marker for polarity maturation in the zebrafish
retinal epithelium. Biol Open. 2:867–871. 2013.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|