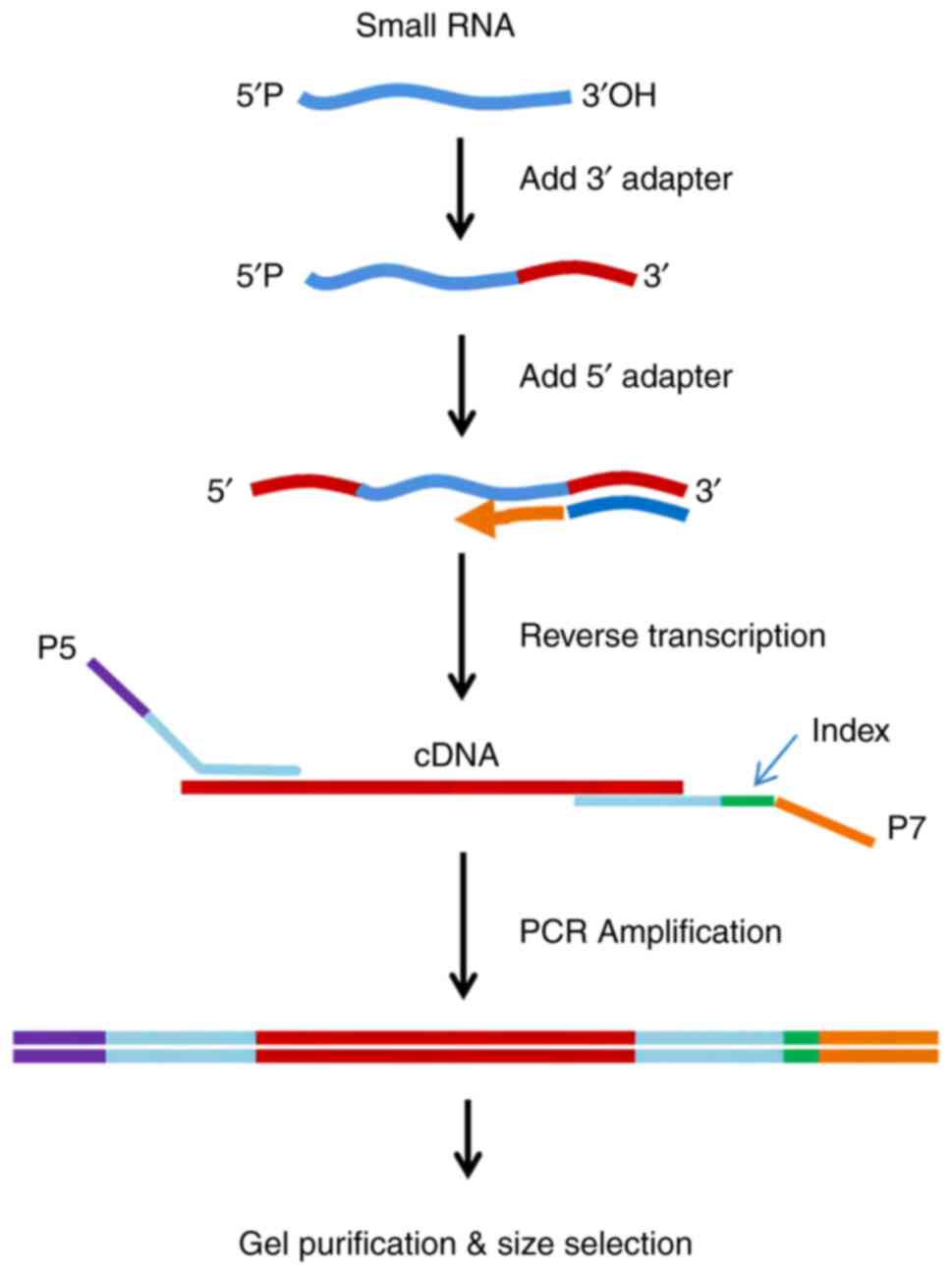
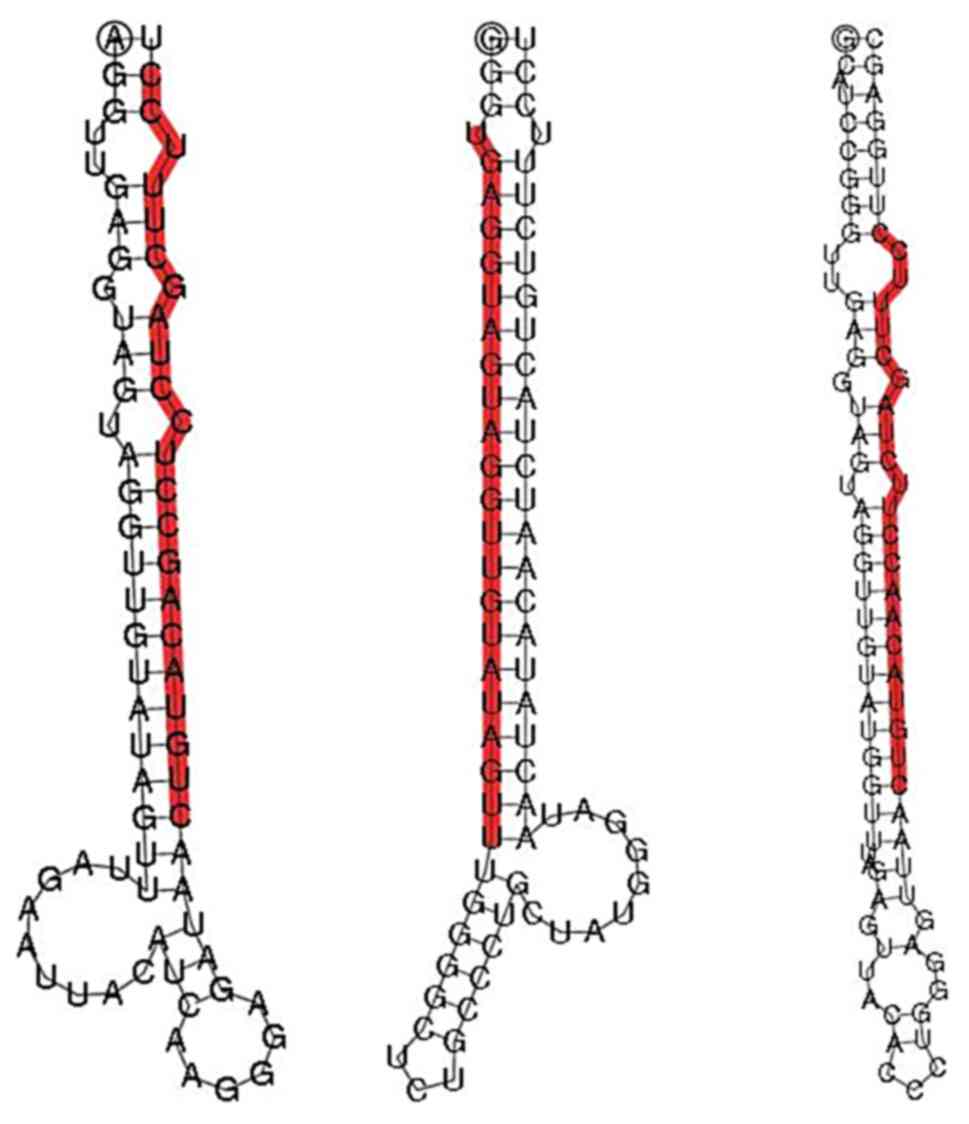
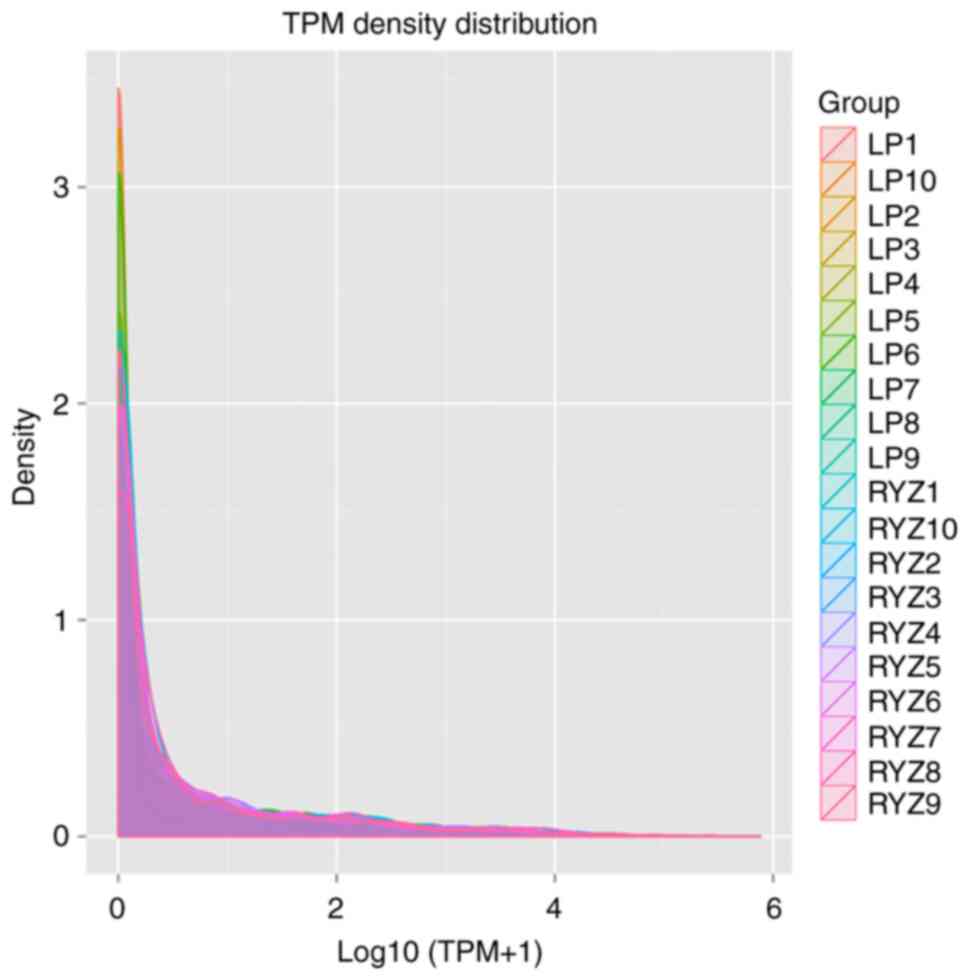
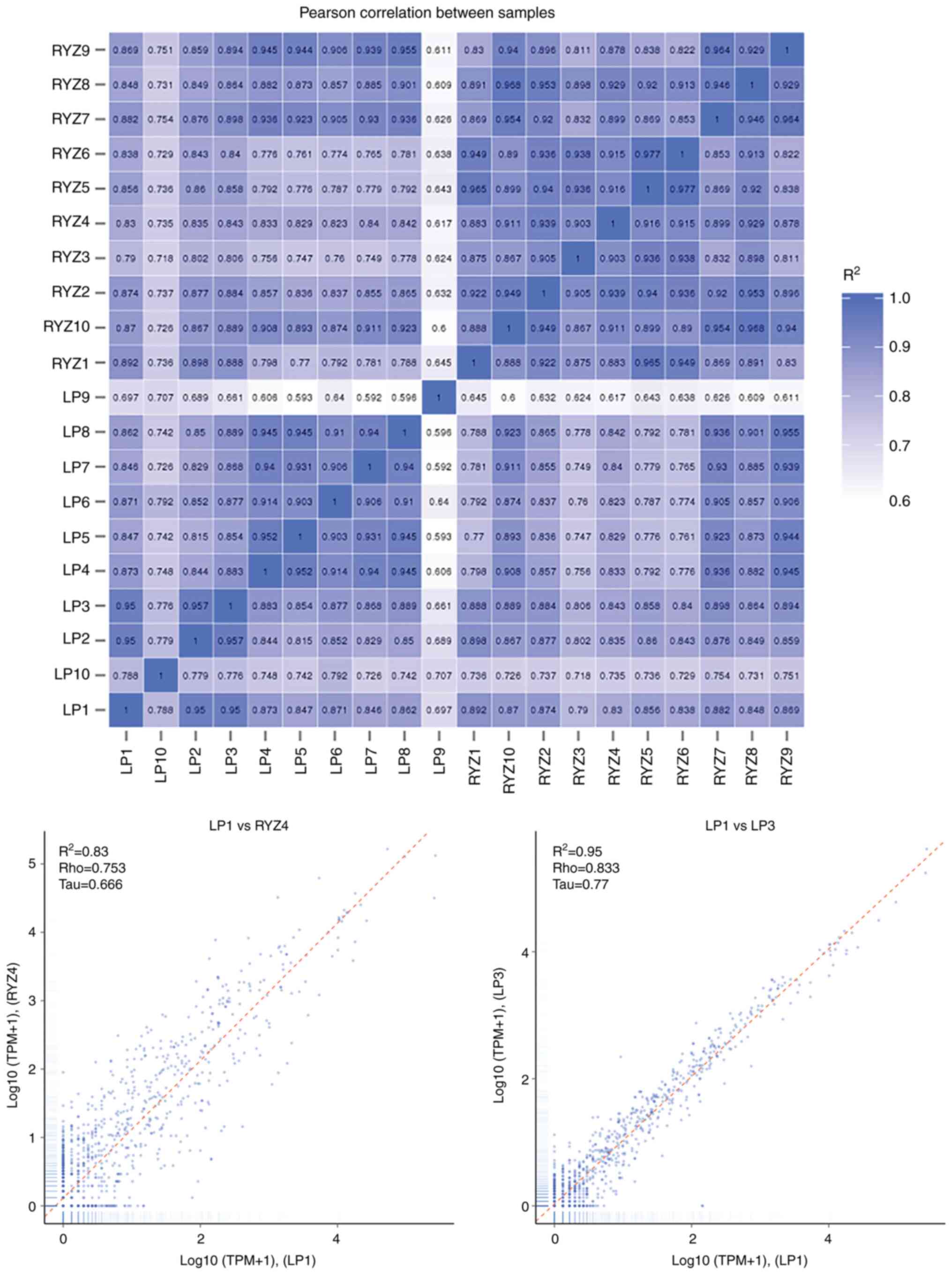
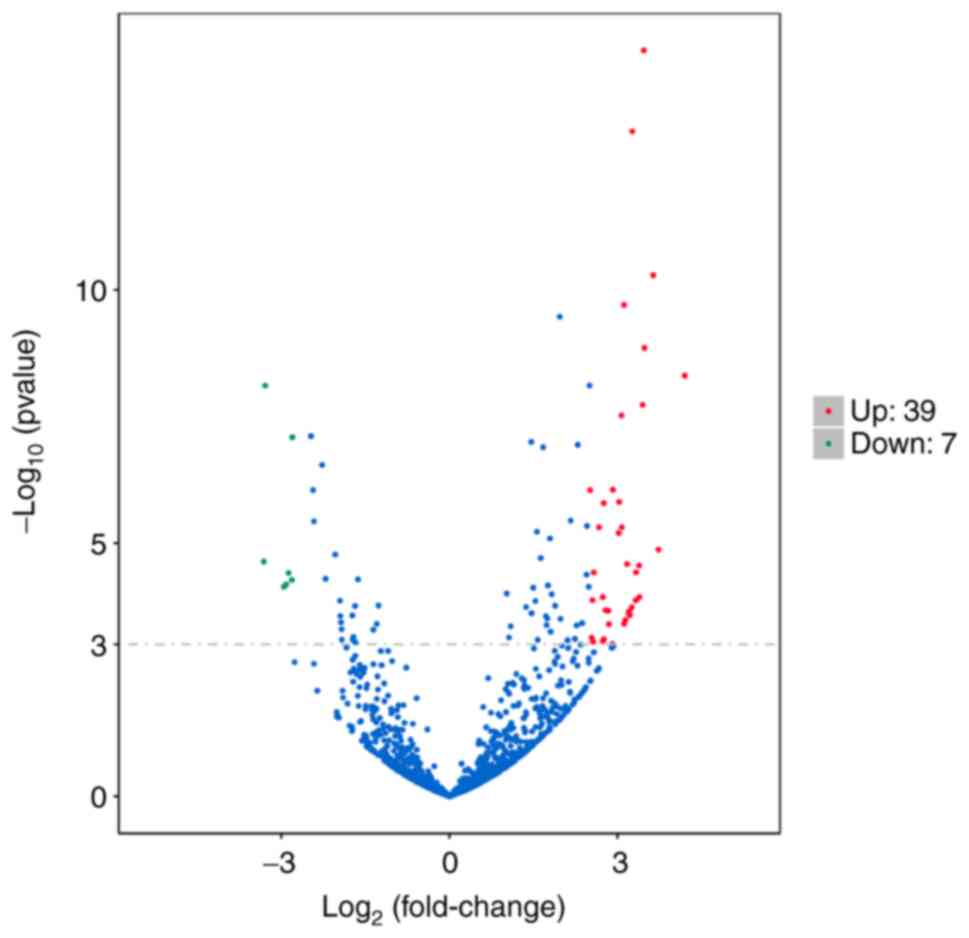
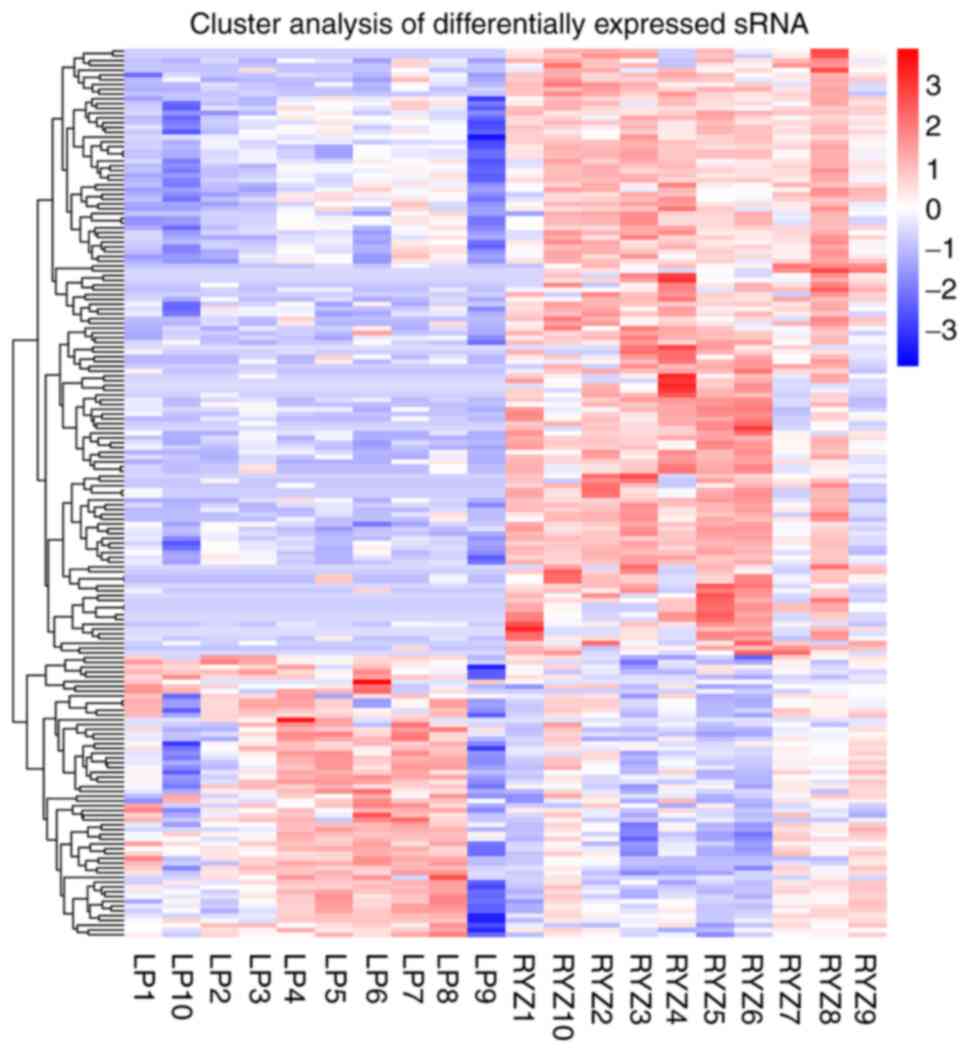
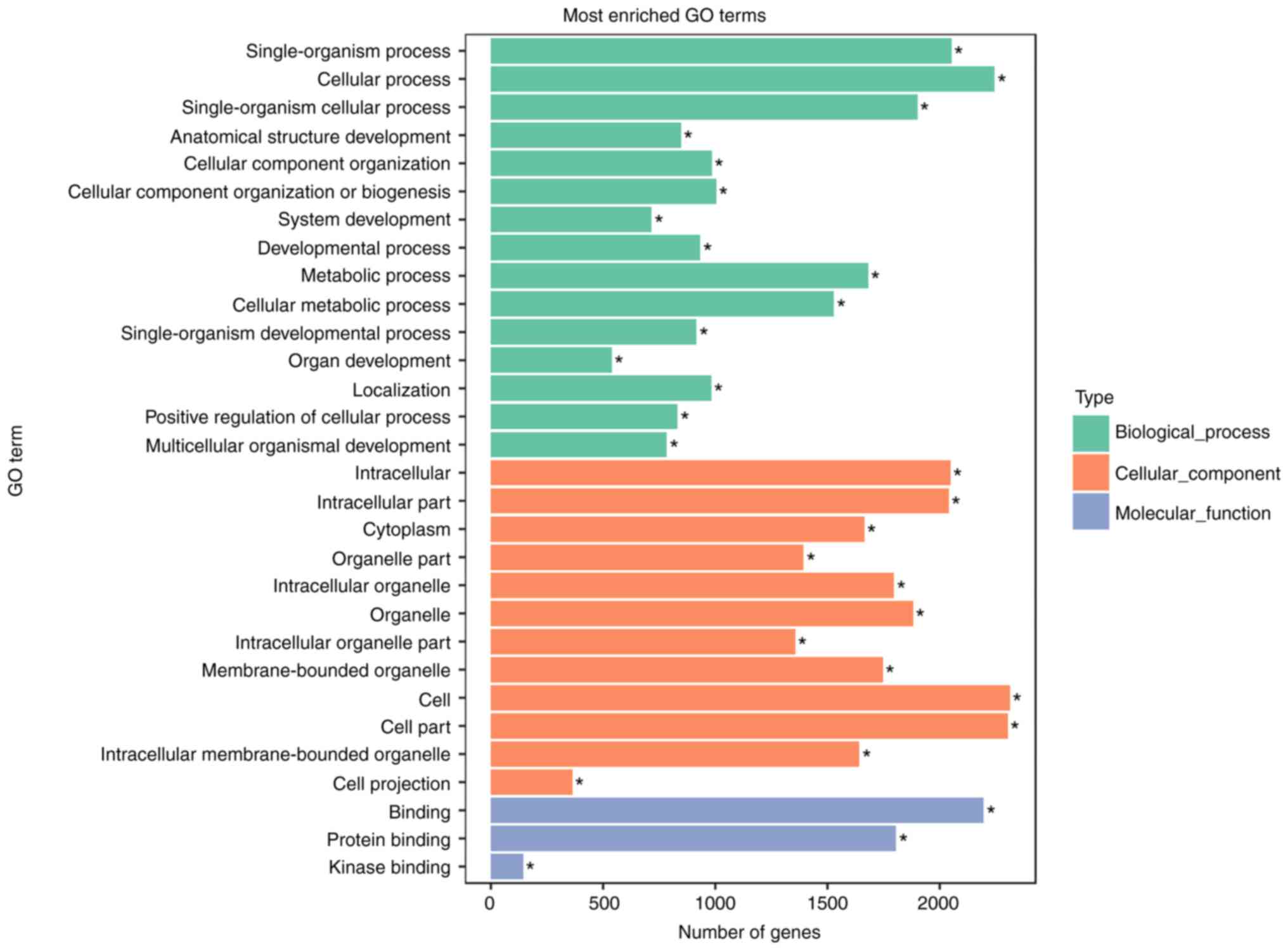
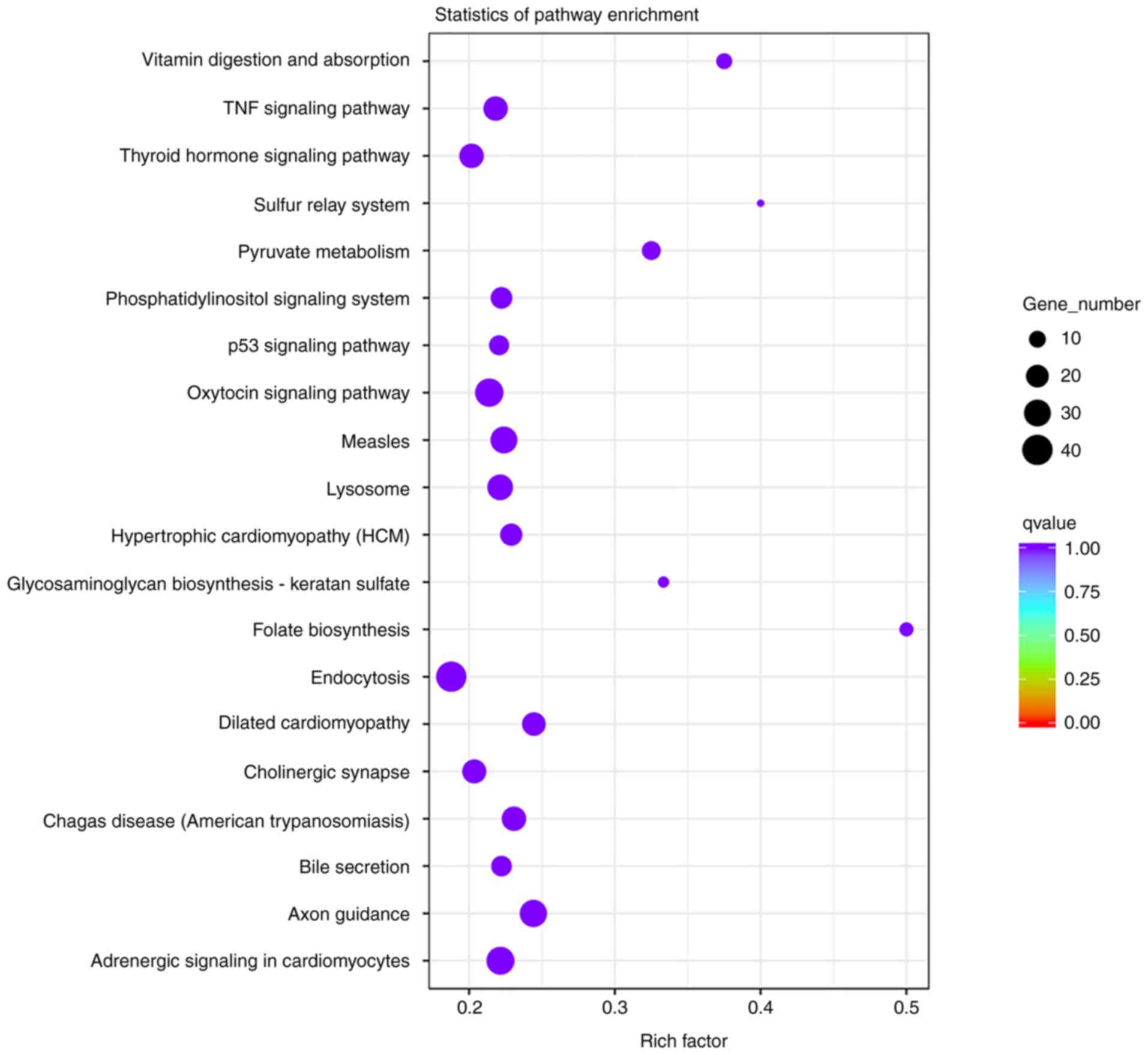
|
1
|
Li J: Diagnosis and treatment of 75
patients with idiopathic lobular granulomatous mastitis. J Invest
Surg. 32:414–420. 2019.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
2
|
Parperis K, Achilleos S, Costi E and
Vardas M: Granulomatous mastitis, erythema nodosum and arthritis
syndrome: Case-based review. Rheumatol Int. 41:1175–1181.
2021.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
3
|
Toprak N, Toktas O, Ince S, Gunduz AM,
Yokus A, Akdeniz H and Ozkacmaz S: Does ARFI elastography
complement B-mode ultrasonography in the radiological diagnosis of
idiopathic granulomatous mastitis and invasive ductal carcinoma.
Acta Radiol. 63:28–34. 2020.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
4
|
Emsen A, Köksal H, Özdemir H, Kadoglou N
and Artaç H: The alteration of lymphocyte subsets in idiopathic
granulomatous mastitis. Turk J Med Sci. 51:1905–1911.
2021.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
5
|
Ucaryilmaz H, Koksal H, Emsen A, Kadoglou
N, Dixon JM and Artac H: The role of regulatory T and B cells in
the etiopathogenesis of idiopathic granulomatous mastitis. Immunol
Invest. 51:357–367. 2022.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
6
|
Li XQ, Yuan JP, Fu AS, Wu HL, Liu R, Liu
TG, Sun SR and Chen C: New insights of Corynebacterium
kroppenstedtii in granulomatous lobular mastitis based on
nanopore sequencing. J Invest Surg. 35:639–646. 2022.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
7
|
Naik MA, Korlimarla A, Shetty ST,
Fernandes AM and Pai SA: Cystic neutrophilic granulomatous
mastitis: A clinicopathological study with 16s rRNA sequencing for
the detection of corynebacteria in formalin-fixed paraffin-embedded
tissue. Int J Surg Pathol. 28:371–381. 2020.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
8
|
Huang Y and Wu H: A retrospective analysis
of recurrence risk factors for granulomatous lobular mastitis in
130 patients: More attention should be paied to prolactin level.
Ann Palliat Med. 10:2824–2831. 2021.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
9
|
O'Brien J, Hayder H, Zayed Y and Peng C:
Overview of MicroRNA biogenesis, mechanisms of actions, and
circulation. Front Endocrinol (Lausanne). 9(402)2018.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
10
|
Shi G, Li D, Zhang D, Xu Y, Pan Y, Lu L,
Li J, Xia X, Dou H and Hou Y: IRF-8/miR-451a regulates M-MDSC
differentiation via the AMPK/mTOR signal pathway during lupus
development. Cell Death Discov. 7(179)2021.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
11
|
Nakashima M, Ishikawa K, Fugiwara A, Shu
K, Fukushima Y, Okamoto M, Tsukamoto H, Kouwaki T and Oshiumi H:
miR-451a levels rather than human papillomavirus vaccine
administration is associated with the severity of murine
experimental autoimmune encephalomyelitis. Sci Rep.
11(9369)2021.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
12
|
Aksan H, Kundaktepe BP, Sayili U,
Velidedeoglu M, Simsek G, Koksal S, Gelisgen R, Yaylim I and Uzun
H: Circulating miR-155, let-7c, miR-21, and PTEN levels in
differential diagnosis and prognosis of idiopathic granulomatous
mastitis and breast cancer. Biofactors. 46:955–962. 2020.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
13
|
Enright AJ, John B, Gaul U, Tuschl T,
Sander C and Marks DS: MicroRNA targets in Drosophila. Genome Biol.
5(R1)2003.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
14
|
Krüger J and Rehmsmeier M: RNAhybrid:
microRNA target prediction easy, fast and flexible. Nucleic Acids
Res. 34 (Web Server Issue):W451–W454. 2006.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
15
|
Wen M, Shen Y, Shi S and Tang T: miREvo:
An integrative microRNA evolutionary analysis platform for
next-generation sequencing experiments. BMC Bioinformatics.
13(140)2012.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
16
|
Friedländer MR, Mackowiak SD, Li N, Chen W
and Rajewsky N: miRDeep2 accurately identifies known and hundreds
of novel microRNA genes in seven animal clades. Nucleic Acids Res.
40:37–52. 2012.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
17
|
Mao X, Cai T, Olyarchuk JG and Wei L:
Automated genome annotation and pathway identification using the
KEGG Orthology (KO) as a controlled vocabulary. Bioinformatics.
21:3787–3793. 2005.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
18
|
Schmittgen TD and Livak KJ: Analyzing
real-time PCR data by the comparative C(T) method. Nat Protoc.
3:1101–1108. 2008.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
19
|
Kanehisa M, Araki M, Goto S, Hattori M,
Hirakawa M, Itoh M, Katayama T, Kawashima S, Okuda S, Tokimatsu T
and Yamanishi Y: KEGG for linking genomes to life and the
environment. Nucleic Acids Res. 36 (Database Issue):D480–D484.
2008.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
20
|
Ertürk TF, Çakır Ö, Yaprak Bayrak B, Güneş
A, Aydemir S and Utkan NZ: Local steroid treatment: An effective
procedure for idiopathic granulomatous mastitis, including
complicated cases. J Invest Surg. 35:745–751. 2022.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
21
|
Ringsted S and Friedman M: A rheumatologic
approach to granulomatous mastitis: A case series and review of the
literature. Int J Rheum Dis. 24:526–532. 2021.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
22
|
Koksal H: What are the new findings with
regard to the mysterious disease idiopathic granulomatous mastitis?
Surg Today. 51:1158–1168. 2021.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
23
|
Ip KH, Koch K and Lamont D: Granulomatosis
with polyangiitis: A life-threatening cause of granulomatous
mastitis. ANZ J Surg. 91:E59–E60. 2021.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
24
|
Luo W, Xu B, Wang L, Xiang L, Lai M, Zhang
X and Liu X: Clinical characteristics and predictive factors of
erythema nodosum in granulomatous lobular mastitis. Australas J
Dermatol. 62:342–346. 2021.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
25
|
Yildirim E, Kayadibi Y, Bektas S, Ucar N,
Oymak A, Er AM, Senturk A and Demir IA: Comparison of the
efficiency of systemic therapy and intralesional steroid
administration in the treatment of idiopathic granulomatous
mastitis. The novel treatment for granulomatous mastitis. Ann Ital
Chir. 92:234–241. 2021.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
26
|
Toktas O, Konca C, Trabulus DC, Soyder A,
Koksal H, Karanlik H, Kamali Polat A, Ozbas S, Yormaz S, Isik A, et
al: A novel first-line treatment alternative for noncomplicated
idiopathic granulomatous mastitis: Combined intralesional steroid
injection with topical steroid administration. Breast Care (Basel).
16:181–187. 2021.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
27
|
Postolova A, Troxell ML, Wapnir IL and
Genovese MC: Methotrexate in the treatment of idiopathic
granulomatous mastitis. J Rheumatol. 47:924–927. 2020.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
28
|
Kafadar MT, Bahadır MV and Girgin S:
Low-dose methotrexate use in idiopathic granulomatous mastitis: An
alternative treatment method. Breast Care (Basel). 16:402–407.
2021.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
29
|
Chiu LW, Goodwin K, Vohra P and Amerson E:
Cystic neutrophilic granulomatous mastitis regression with the
tumor necrosis factor-α inhibitor, adalimumab. Eur J Breast Health.
18:94–101. 2021.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
30
|
Saydam M, Yilmaz KB, Sahin M, Yanik H,
Akinci M, Yilmaz I, Balas S, Azili C and Gulcelik MA: New findings
on autoimmune etiology of idiopathic granulomatous mastitis: Serum
IL-17, IL-22 and IL-23 levels of patients. J Invest Surg.
34:993–997. 2021.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
31
|
Ozel L, Unal A, Unal E, Kara M, Erdoğdu E,
Krand O, Güneş P, Karagül H, Demiral S and Titiz MI: Granulomatous
mastitis: Is it an autoimmune disease? Diagnostic and therapeutic
dilemmas. Surg Today. 42:729–733. 2012.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
32
|
Huang YM, Lo C, Cheng CF, Lu CH, Hsieh SC
and Li KJ: Serum C-reactive protein and interleukin-6 levels as
biomarkers for disease severity and clinical outcomes in patients
with idiopathic granulomatous mastitis. J Clin Med.
10(2077)2021.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
33
|
Jiang L, Li X, Sun B, Ma T, Kong X and
Yang Q: Clinicopathological features of granulomatous lobular
mastitis and mammary duct ectasia. Oncol Lett. 19:840–848.
2020.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
34
|
Schelfout K, Tjalma WA, Cooremans ID,
Coeman DC, Colpaert CG and Buytaert PM: Observations of an
idiopathic granulomatous mastitis. Eur J Obstet Gynecol Reprod
Biol. 97:260–262. 2001.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
35
|
Li SB, Xiong Y, Han XR, Liu ZY, Lv XL and
Ning P: Pregnancy associated granulomatous mastitis: Clinical
characteristics, management, and outcome. Breastfeed Med.
16:759–764. 2021.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
36
|
Çetinkaya G, Kozan R, Emral AC and Tezel
E: Granulomatous mastitis, watch and wait is a good option. Ir J
Med Sci. 190:1117–1122. 2021.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
37
|
Hurley K, Lacey N, O'Dwyer CA, Bergin DA,
McElvaney OJ, O'Brien ME, McElvaney OF, Reeves EP and McElvaney NG:
Alpha-1 antitrypsin augmentation therapy corrects accelerated
neutrophil apoptosis in deficient individuals. J Immunol.
193:3978–3991. 2014.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
38
|
Williams MS, McClintock AH, Bourassa L and
Laya MB: Treatment of granulomatous mastitis: Is there a role for
antibiotics? Eur J Breast Health. 17:239–246. 2021.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
39
|
Co M, Cheng VCC, Wei J, Wong SCY, Chan
SMS, Shek T and Kwong A: Idiopathic granulomatous mastitis: A
10-year study from a multicentre clinical database. Pathology.
50:742–747. 2018.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
40
|
Uysal E, Soran A and Sezgin E:
Granulomatous Mastitis Study Group. Factors related to recurrence
of idiopathic granulomatous mastitis: What do we learn from a
multicentre study? ANZ J Surg. 88:635–639. 2018.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
41
|
Tang ELS, Ho CSB, Chan PMY, Chen JJC, Goh
MH and Tan EY: The therapeutic dilemma of idiopathic granulomatous
mastitis. Ann Acad Med Singap. 50:598–605. 2021.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
42
|
Hu X, Fan Y, Li H, Zhou R, Zhao X, Sun Y
and Zhang S: Impacts of cigarette smoking status on metabolomic and
gut microbiota profile in male patients with coronary artery
disease: A multi-omics study. Front Cardiovasc Med.
8(766739)2021.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
43
|
Kim SW, Kim HJ, Min K, Lee H, Lee SH, Kim
S, Kim JS and Oh B: The relationship between smoking cigarettes and
metabolic syndrome: A cross-sectional study with non-single
residents of Seoul under 40 years old. PLoS One.
16(e0256257)2021.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
44
|
Chen X, Zhang W, Yuan Q, Hu X, Xia T, Cao
T, Jia H and Zhang L: A novel therapy for granulomatous lobular
mastitis: Local heat therapy. Exp Ther Med. 22(1156)2021.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
45
|
Taylor GB, Paviour SD, Musaad S, Jones WO
and Holland DJ: A clinicopathological review of 34 cases of
inflammatory breast disease showing an association between
corynebacteria infection and granulomatous mastitis. Pathology.
35:109–119. 2003.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
46
|
Yu HJ, Deng H, Ma J, Huang SJ, Yang JM,
Huang YF, Mu XP, Zhang L and Wang Q: Clinical metagenomic analysis
of bacterial communities in breast abscesses of granulomatous
mastitis. Int J Infect Dis. 53:30–33. 2016.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
47
|
Bauer A, Hofmeyer S, Gere M, Nilsson K and
Tot T: Granulomatous mastitis caused by Rickettsia species.
Virchows Arch. 479:1091–1094. 2021.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
48
|
Zhang X, Cong L, Xu D, Leng Q, Shi M and
Zhou Y: AC092127.1-miR-451a-AE binding protein 2 signaling
facilitates malignant properties of breast cancer. J Breast Cancer.
24:389–401. 2021.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
49
|
Liu C, Pan A, Chen X, Tu J, Xia X and Sun
L: MiR-5571-3p and miR-135b-5p, derived from analyses of microRNA
profile sequencing, correlate with increased disease risk and
activity of rheumatoid arthritis. Clin Rheumatol. 38:1753–1765.
2019.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|