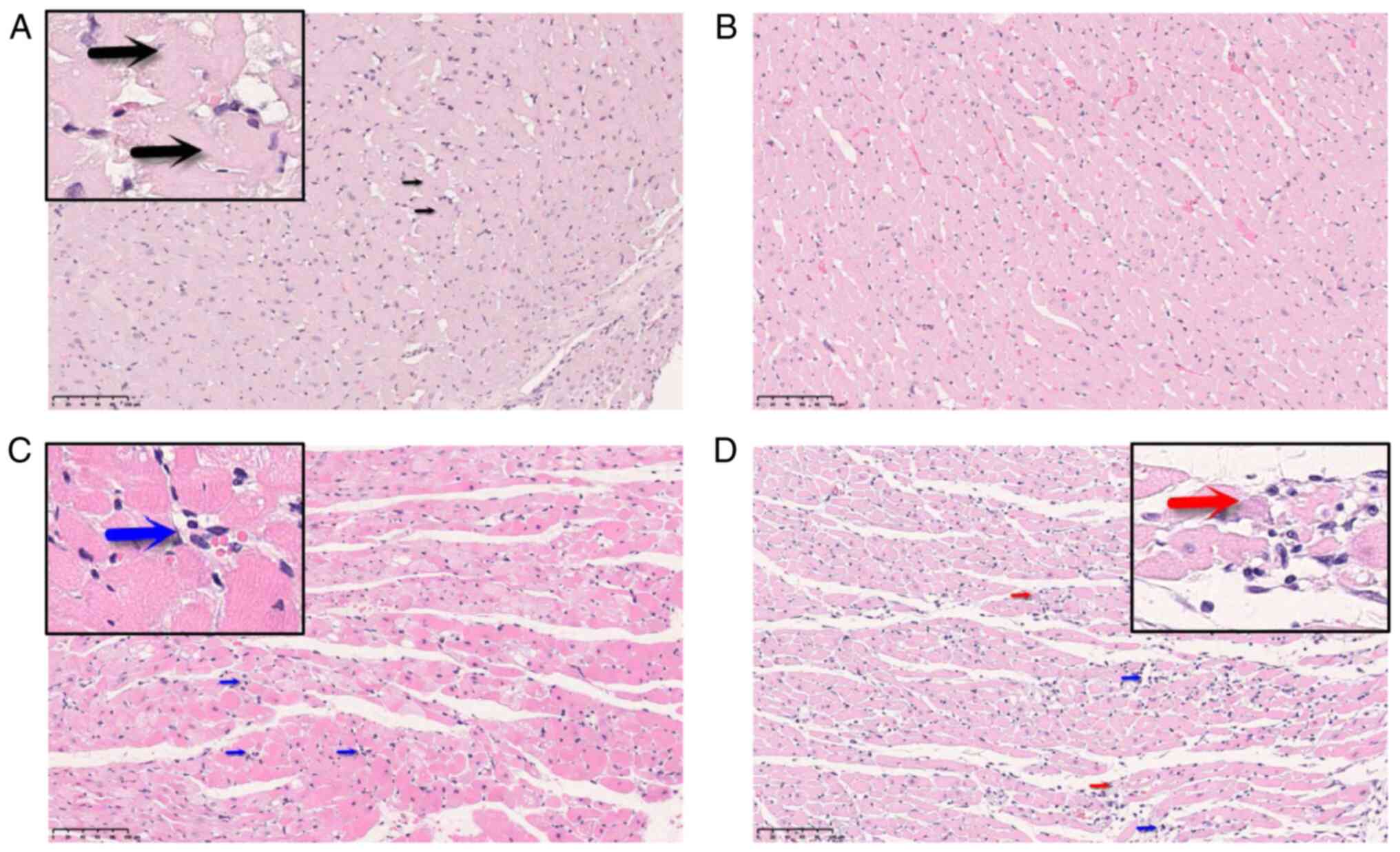
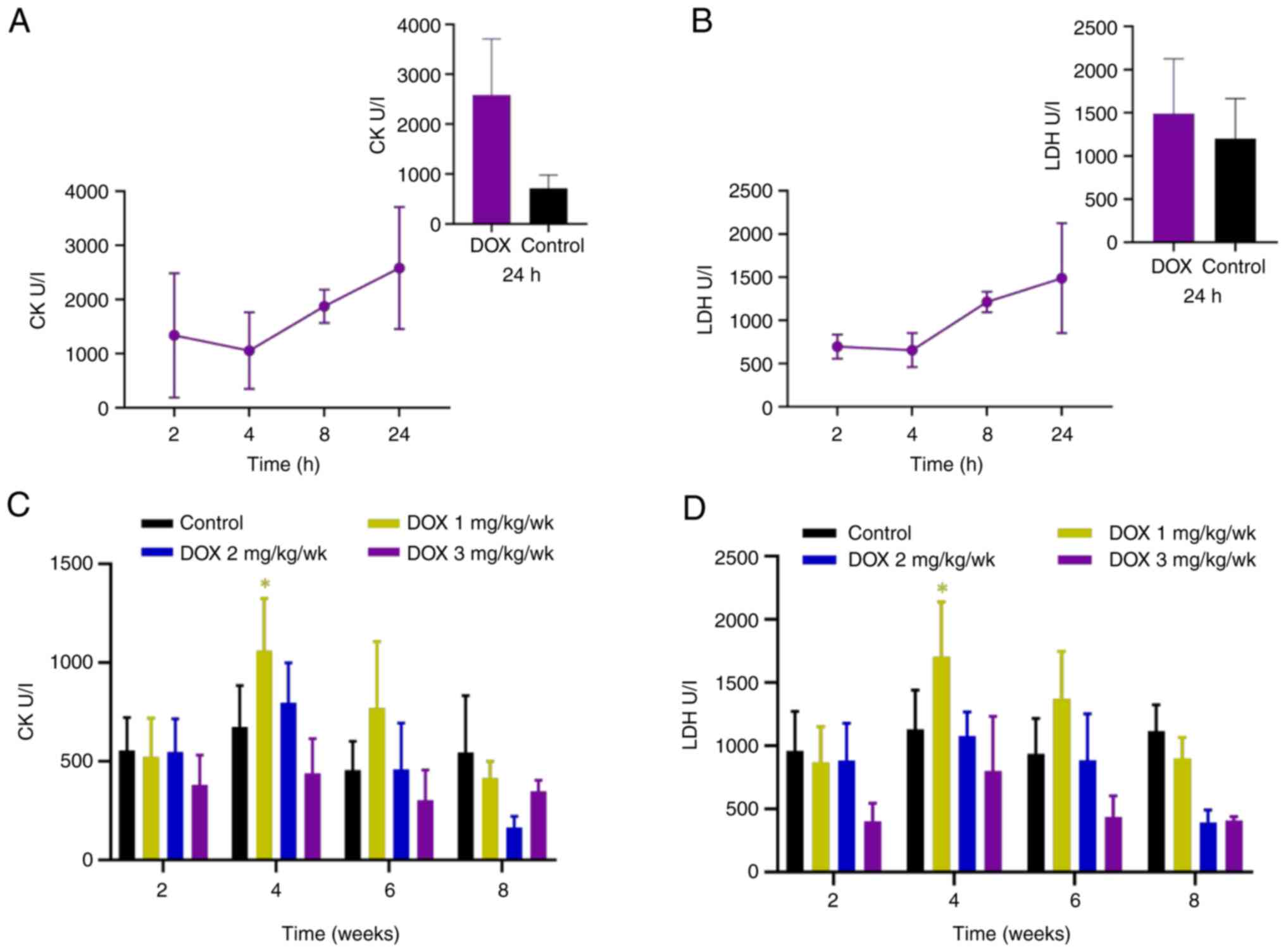
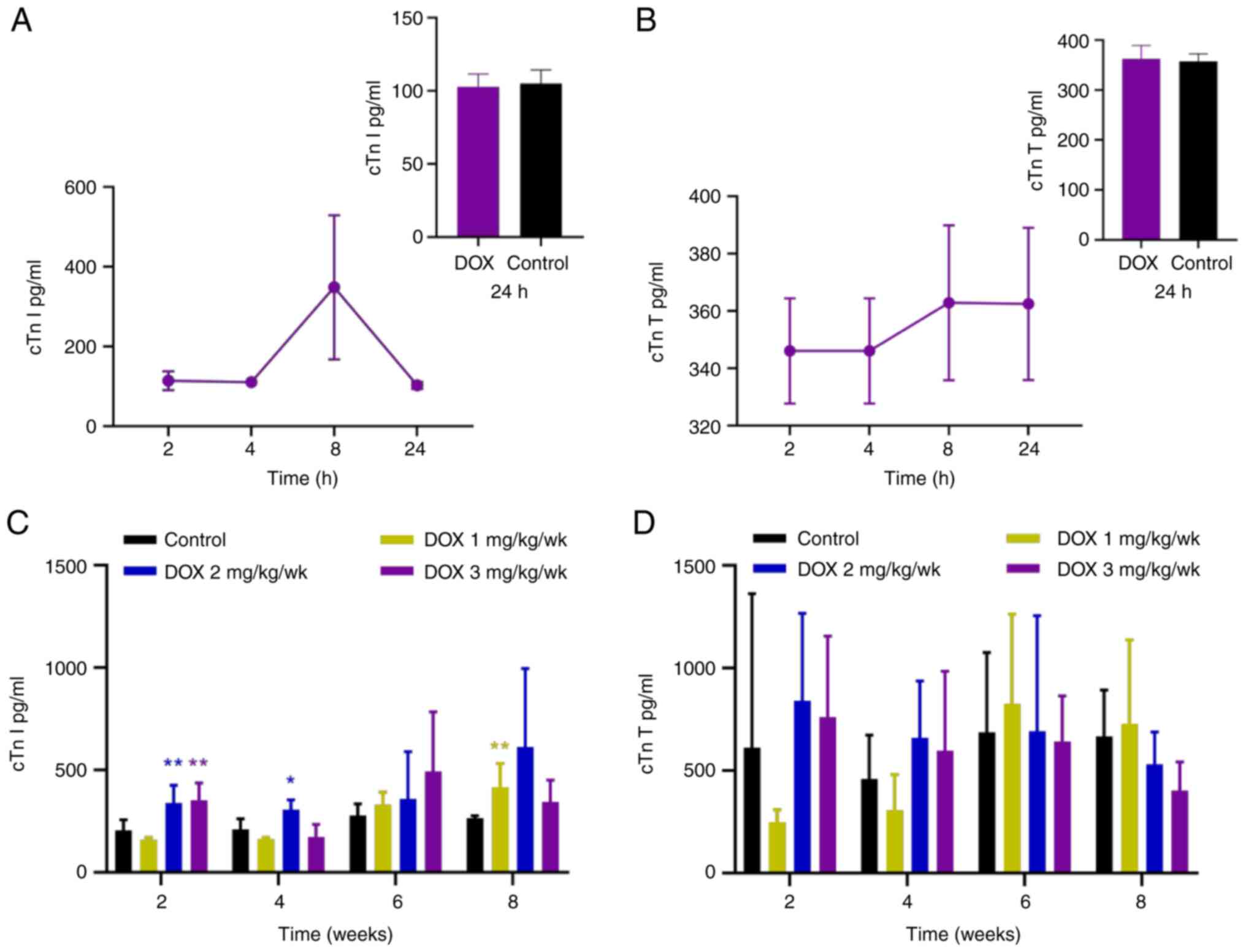
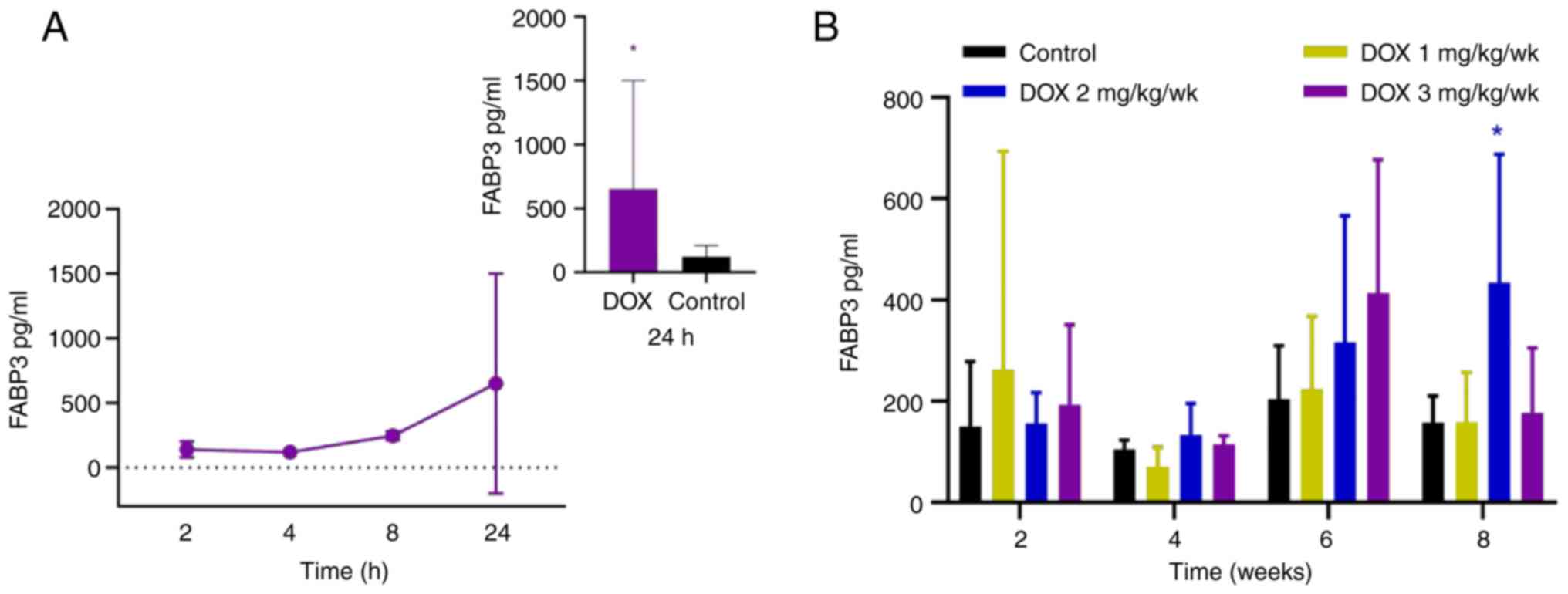
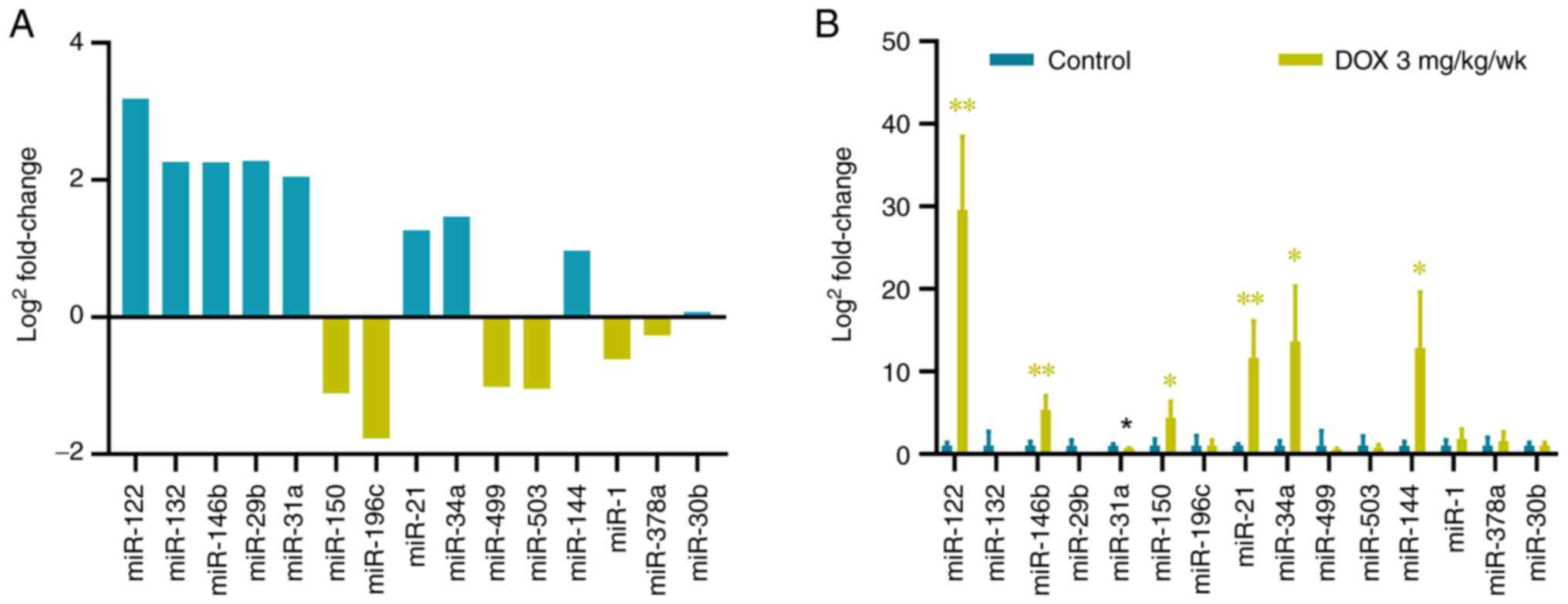
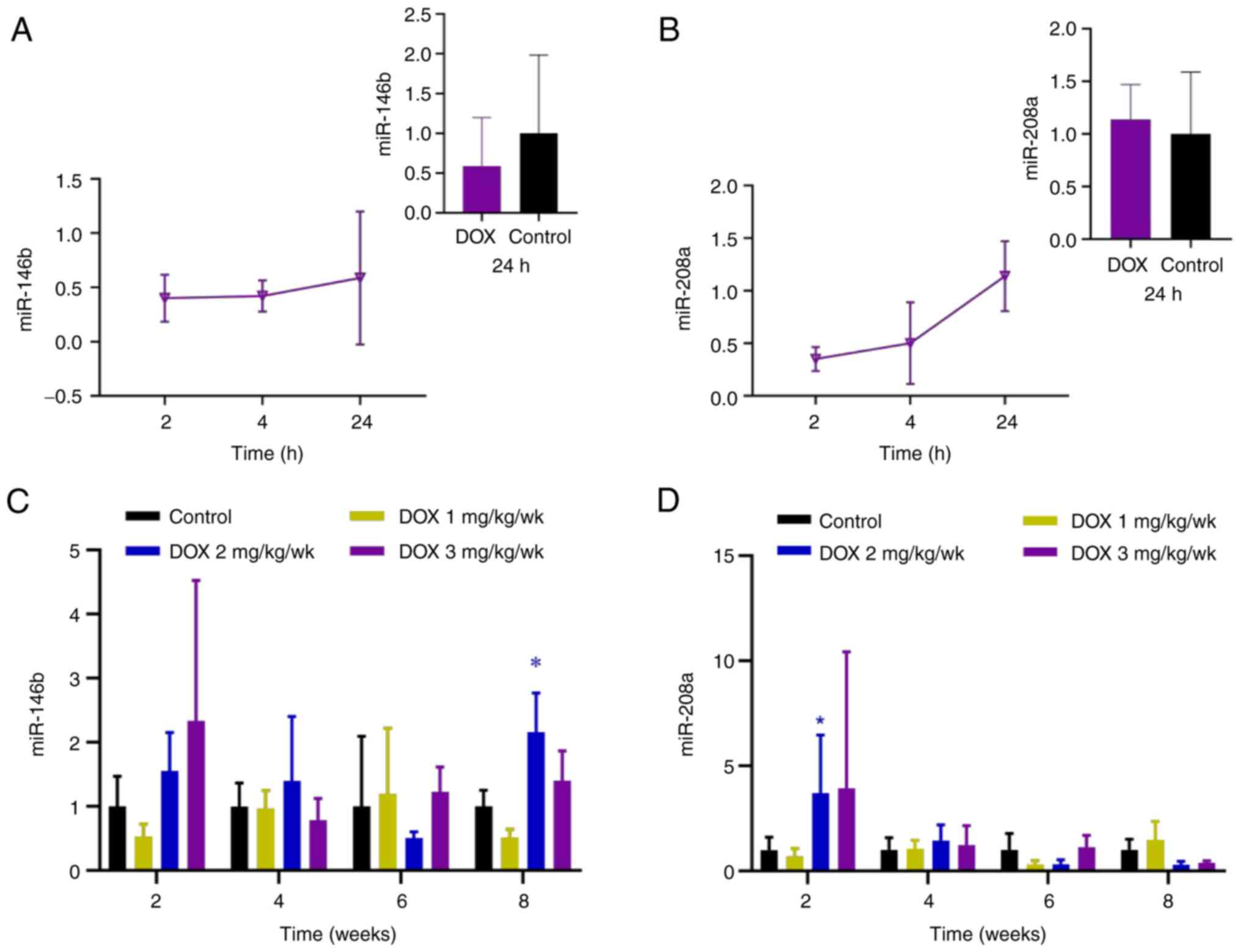
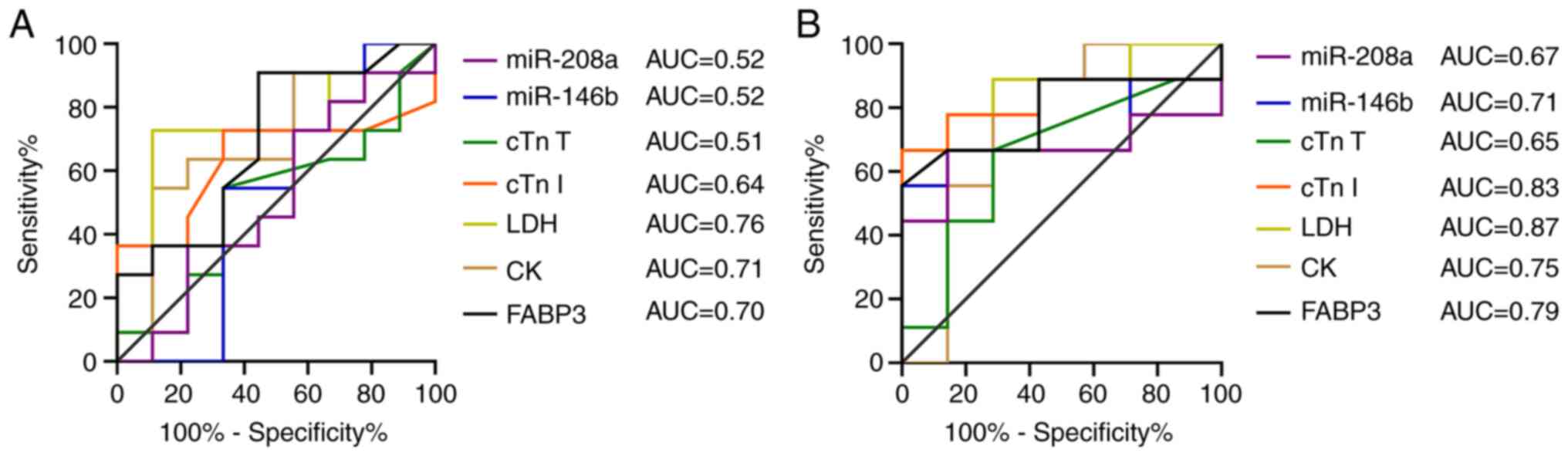
|
1
|
Laverty H, Benson C, Cartwright E, Cross
M, Garland C, Hammond T, Holloway C, McMahon N, Milligan J, Park B,
et al: How can we improve our understanding of cardiovascular
safety liabilities to develop safer medicines? Br J Pharmacol.
163:675–693. 2011.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
2
|
Sharma A, McKeithan WL, Serrano R, Kitani
T, Burridge PW, Del Álamo JC, Mercola M and Wu JC: Use of human
induced pluripotent stem cell-derived cardiomyocytes to assess drug
cardiotoxicity. Nat Protoc. 13:3018–3041. 2018.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
3
|
Chaudhari U, Nemade H, Gaspar JA,
Hescheler J, Hengstler JG and Sachinidis A: MicroRNAs as early
toxicity signatures of doxorubicin in human-induced pluripotent
stem cell-derived cardiomyocytes. Arch Toxicol. 90:3087–3098.
2016.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
4
|
Onakpoya IJ, Heneghan CJ and Aronson JK:
Post-marketing withdrawal of 462 medicinal products because of
adverse drug reactions: A systematic review of the world
literature. BMC Med. 14(10)2016.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
5
|
Volkova M and Russell R III: Anthracycline
cardiotoxicity: Prevalence, pathogenesis and treatment. Curr
Cardiol Rev. 7:214–220. 2011.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
6
|
Jin SA, Lim BK, Seo HJ, Kim SK, Ahn KT,
Jeon BH and Jeong JO: Elevation of serum APE1/Ref-1 in experimental
murine myocarditis. Int J Mol Sci. 18(2664)2017.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
7
|
Ferdinandy P, Baczkó I, Bencsik P, Giricz
Z, Görbe A, Pacher P, Varga ZV, Varró A and Schulz R: Definition of
hidden drug cardiotoxicity: Paradigm change in cardiac safety
testing and its clinical implications. Eur Heart J. 40:1771–1777.
2019.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
8
|
Koh E, Nakamura T and Takahashi H:
Troponin-T and brain natriuretic peptide as predictors for
adriamycin-induced cardiomyopathy in rats. Circ J. 68:163–167.
2004.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
9
|
Gallay-Lepoutre J, Bélanger MC and Nadeau
ME: Prospective evaluation of Doppler echocardiography, tissue
Doppler imaging and biomarkers measurement for the detection of
doxorubicin-induced cardiotoxicity in dogs: A pilot study. Res Vet
Sci. 105:153–159. 2016.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
10
|
Sandhu H and Maddock H: Molecular basis of
cancer-therapy-induced cardiotoxicity: Introducing microRNA
biomarkers for early assessment of subclinical myocardial injury.
Clin Sci (Lond). 126:377–400. 2014.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
11
|
Boyd JW: The mechanisms relating to
increases in plasma enzymes and isoenzymes in diseases of animals.
Vet Clin Pathol. 12:9–24. 1983.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
12
|
Bertinchant JP, Robert E, Polge A,
Marty-Double C, Fabbro-Peray P, Poirey S, Aya G, Juan JM, Ledermann
B, de la Coussaye JE and Dauzat M: Comparison of the diagnostic
value of cardiac troponin I and T determinations for detecting
early myocardial damage and the relationship with histological
findings after isoprenaline-induced cardiac injury in rats. Clin
Chim Acta Int J Clin Chem. 298:13–28. 2000.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
13
|
Apple FS, Murakami MM, Ler R, Walker D and
York M: HESI Technical Committee of Biomarkers Working Group on
Cardiac Troponins. Analytical characteristics of commercial cardiac
troponin I and T immunoassays in serum from rats, dogs, and monkeys
with induced acute myocardial injury. Clin Chem. 54:1982–1989.
2008.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
14
|
Tonomura Y, Matsushima S, Kashiwagi E,
Fujisawa K, Takagi S, Nishimura Y, Fukushima R, Torii M and
Matsubara M: Biomarker panel of cardiac and skeletal muscle
troponins, fatty acid binding protein 3 and myosin light chain 3
for the accurate diagnosis of cardiotoxicity and musculoskeletal
toxicity in rats. Toxicology. 302:179–189. 2012.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
15
|
Katrukha IA: Human cardiac troponin
complex. Structure and functions. Biochemistry (Mosc).
78:1447–1465. 2013.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
16
|
Christenson RH and Azzazy HME: Biomarkers
of myocardial necrosis-past, present, and future. In: Morrow DA,
ed. Cardiovascular Biomarkers: Pathophysiology and Disease
Management. Morrow DA (ed.) Humana Press: pp. 3-25, 2006.
|
|
17
|
Zhuang L, Li C, Chen Q, Jin Q, Wu L, Lu L,
Yan X and Chen K: Fatty acid-binding protein 3 contributes to
ischemic heart injury by regulating cardiac myocyte apoptosis and
MAPK pathways. Am J Physiol Heart Circ Physiol. 316:H971–H984.
2019.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
18
|
Kim K, Chini N, Fairchild DG, Engle SK,
Reagan WJ, Summers SD and Mirsalis JC: Evaluation of cardiac
toxicity biomarkers in rats from different laboratories. Toxicol
Pathol. 44:1072–1083. 2016.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
19
|
Songbo M, Lang H, Xinyong C, Bin X, Ping Z
and Liang S: Oxidative stress injury in doxorubicin-induced
cardiotoxicity. Toxicol Lett. 307:41–48. 2019.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
20
|
Abdel-Daim MM, Kilany OE, Khalifa HA and
Ahmed AAM: Allicin ameliorates doxorubicin-induced cardiotoxicity
in rats via suppression of oxidative stress, inflammation and
apoptosis. Cancer Chemother Pharmacol. 80:745–753. 2017.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
21
|
Rababa'h AM, Guillory AN, Mustafa R and
Hijjawi T: Oxidative stress and cardiac remodeling: An updated
edge. Curr Cardiol Rev. 14:53–59. 2018.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
22
|
Vacchi-Suzzi C, Hahne F, Scheubel P,
Marcellin M, Dubost V, Westphal M, Boeglen C, Büchmann-Møller S,
Cheung MS, Cordier A, et al: Heart structure-specific
transcriptomic atlas reveals conserved microRNA-mRNA interactions.
PLoS One. 8(e52442)2013.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
23
|
Williams Z, Ben-Dov IZ, Elias R,
Mihailovic A, Brown M, Rosenwaks Z and Tuschl T: Comprehensive
profiling of circulating microRNA via small RNA sequencing of cDNA
libraries reveals biomarker potential and limitations. Proc Natl
Acad Sci U S A. 110:4255–4260. 2013.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
24
|
Chen Y, Xu Y, Deng Z, Wang Y, Zheng Y,
Jiang W and Jiang L: MicroRNA expression profiling involved in
doxorubicin-induced cardiotoxicity using high-throughput
deep-sequencing analysis. Oncol Lett. 22(560)2021.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
25
|
Guo L, Zheng X, Wang E, Jia X, Wang G and
Wen J: Irigenin treatment alleviates doxorubicin (DOX)-induced
cardiotoxicity by suppressing apoptosis, inflammation and oxidative
stress via the increase of miR-425. Biomed Pharmacother.
125(109784)2020.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
26
|
Stepicheva NA and Song JL: Function and
regulation of microRNA-31 in development and disease. Mol Reprod
Dev. 83:654–674. 2016.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
27
|
Yang Y, Yu T, Jiang S, Zhang Y, Li M, Tang
N, Ponnusamy M, Wang JX and Li PF: miRNAs as potential therapeutic
targets and diagnostic biomarkers for cardiovascular disease with a
particular focus on WO2010091204. Expert Opin Ther Pat.
27:1021–1029. 2017.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
28
|
Zhao L, Qi Y, Xu L, Tao X, Han X, Yin L
and Peng J: MicroRNA-140-5p aggravates doxorubicin-induced
cardiotoxicity by promoting myocardial oxidative stress via
targeting Nrf2 and Sirt2. Redox Biol. 15:284–296. 2018.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
29
|
Nishimura Y, Kondo C, Morikawa Y, Tonomura
Y, Torii M, Yamate J and Uehara T: Plasma miR-208 as a useful
biomarker for drug-induced cardiotoxicity in rats. J Appl Toxicol.
35:173–180. 2015.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
30
|
Tony H, Yu K and Qiutang Z: MicroRNA-208a
silencing attenuates doxorubicin induced myocyte apoptosis and
cardiac dysfunction. Oxid Med Cell Longev.
2015(597032)2015.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
31
|
Desai VG, Kwekel JC, Vijay V, Moland CL,
Herman EH, Lee T, Han T, Lewis SM, Davis KJ, Muskhelishvili L, et
al: Early biomarkers of doxorubicin-induced heart injury in a mouse
model. Toxicol Appl Pharmacol. 281:221–229. 2014.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
32
|
Reagan WJ, York M, Berridge B, Schultze E,
Walker D and Pettit S: Comparison of cardiac troponin I and T,
including the evaluation of an ultrasensitive assay, as indicators
of doxorubicin-induced cardiotoxicity. Toxicol Pathol.
41:1146–1158. 2013.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
33
|
Livak KJ and Schmittgen TD: Analysis of
relative gene expression data using real-time quantitative PCR and
the 2(-Delta Delta C(T)) method. Methods. 25:402–408.
2001.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
34
|
Horie T, Ono K, Nishi H, Nagao K,
Kinoshita M, Watanabe S, Kuwabara Y, Nakashima Y, Takanabe-Mori R,
Nishi E, et al: Acute doxorubicin cardiotoxicity is associated with
miR-146a-induced inhibition of the neuregulin-ErbB pathway.
Cardiovasc Res. 87:656–664. 2010.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
35
|
Yin J, Xie J, Guo X, Ju L, Li Y and Zhang
Y: Plasma metabolic profiling analysis of cyclophosphamide-induced
cardiotoxicity using metabolomics coupled with UPLC/Q-TOF-MS and
ROC curve. J Chromatogr B Analyt Technol Biomed Life Sci.
1033-1034:428–435. 2016.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
36
|
Sullivan GM and Feinn R: Using effect
size-or why the P value is not enough. J Grad Med Educ. 4:279–282.
2012.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
37
|
Liao DH, Zhang C, Liu N, Cao LZ, Wang CS,
Feng QY, Yao DW, Long MH and Jiang P: Involvement of neurotrophic
signaling in doxorubicin-induced cardiotoxicity. Exp Ther Med.
19:1129–1135. 2020.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
38
|
Boshra S: Resveratrol modulates miR-34a in
cardiotoxicity induced by isoproterenol. J Med Food. 23:593–599.
2020.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
39
|
Prasanna PL, Renu K and Gopalakrishnan AV:
New molecular and biochemical insights of doxorubicin-induced
hepatotoxicity. Life Sci. 250(117599)2020.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
40
|
Bredahl EC, Najdawi W, Pass C, Siedlik J,
Eckerson J and Drescher K: Use of creatine and creatinine to
minimize doxorubicin-induced cytotoxicity in cardiac and skeletal
muscle myoblasts. Nutr Cancer. 73:2597–2604. 2021.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
41
|
Mihm MJ, Yu FS, Weinstein DM, Reiser PJ
and Bauer JA: Intracellular distribution of peroxynitrite during
doxorubicin cardiomyopathy: Evidence for selective impairment of
myofibrillar creatine kinase. Br J Pharmacol. 135:581–588.
2002.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
42
|
Fredericks S, Merton GK, Lerena MJ,
Heining P, Carter ND and Holt DW: Cardiac troponins and creatine
kinase content of striated muscle in common laboratory animals.
Clin Chim Acta. 304:65–74. 2001.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
43
|
Wang CC, Fang CC, Lee YH, Yang MT and Chan
KH: Effects of 4-week creatine supplementation combined with
complex training on muscle damage and sport performance. Nutrients.
10(1640)2018.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
44
|
Fonseca LB, Brito CJ, Silva RJ,
Silva-Grigoletto ME, da Silva WMJ and Franchini E: Use of
cold-water immersion to reduce muscle damage and delayed-onset
muscle soreness and preserve muscle power in jiu-jitsu athletes. J
Athl Train. 51:540–549. 2016.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
45
|
Glineur SF, De Ron P, Hanon E, Valentin
JP, Dremier S and Nogueira da Costa A: Paving the route to plasma
miR-208a-3p as an acute cardiac injury biomarker: Preclinical rat
data supports its use in drug safety assessment. Toxicol Sci.
149:89–97. 2016.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
46
|
Jasim ST, Al-Kuraishy HM and Al-Gareeb AI:
Gingko Biloba protects cardiomyocytes against acute doxorubicin
induced cardiotoxicity by suppressing oxidative stress. JPMA J Pak
Med Assoc. 69 (Suppl 3):S103–S107. 2019.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
47
|
Maynard SJ, Menown IB and Adgey AA:
Troponin T or troponin I as cardiac markers in ischaemic heart
disease. Heart. 83:371–373. 2000.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
48
|
Park KC, Gaze DC, Collinson PO and Marber
MS: Cardiac troponins: From myocardial infarction to chronic
disease. Cardiovasc Res. 113:1708–1718. 2017.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
49
|
Wu AH and Feng YJ: Biochemical differences
between cTnT and cTnI and their significance for diagnosis of acute
coronary syndromes. Eur Heart J. 19 (Suppl N):N25–N29.
1998.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
50
|
Herman EH, Lipshultz SE, Rifai N, Zhang J,
Papoian T, Yu ZX, Takeda K and Ferrans VJ: Use of cardiac troponin
T levels as an indicator of doxorubicin-induced cardiotoxicity.
Cancer Res. 58:195–197. 1998.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
51
|
Goel H, Melot J, Krinock MD, Kumar A,
Nadar SK and Lip GYH: Heart-type fatty acid-binding protein: An
overlooked cardiac biomarker. Ann Med. 52:444–461. 2020.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
52
|
Pan JA, Tang Y, Yu JY, Zhang H, Zhang JF,
Wang CQ and Gu J: miR-146a attenuates apoptosis and modulates
autophagy by targeting TAF9b/P53 pathway in doxorubicin-induced
cardiotoxicity. Cell Death Dis. 10(668)2019.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
53
|
Tavakoli Dargani Z and Singla DK:
Embryonic stem cell-derived exosomes inhibit doxorubicin-induced
TLR4-NLRP3-mediated cell death-pyroptosis. Am J Physiol Heart Circ
Physiol. 317:H460–H471. 2019.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
54
|
Perry MM, Williams AE, Tsitsiou E,
Larner-Svensson HM and Lindsay MA: Divergent intracellular pathways
regulate interleukin-1beta-induced miR-146a and miR-146b expression
and chemokine release in human alveolar epithelial cells. FEBS
Lett. 583:3349–3355. 2009.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
55
|
Taganov KD, Boldin MP, Chang KJ and
Baltimore D: NF-kappaB-dependent induction of microRNA miR-146, an
inhibitor targeted to signaling proteins of innate immune
responses. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA. 103:12481–12486. 2006.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
56
|
Callis TE, Pandya K, Seok HY, Tang RH,
Tatsuguchi M, Huang ZP, Chen JF, Deng Z, Gunn B, Shumate J, et al:
MicroRNA-208a is a regulator of cardiac hypertrophy and conduction
in mice. J Clin Invest. 119:2772–2786. 2009.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
57
|
Sadek KM, Mahmoud SFE, Zeweil MF and
Abouzed TK: Proanthocyanidin alleviates doxorubicin-induced cardiac
injury by inhibiting NF-kB pathway and modulating oxidative stress,
cell cycle, and fibrogenesis. J Biochem Mol Toxicol.
35(e22716)2021.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
58
|
Shyu KG, Wang BW, Wu GJ, Lin CM and Chang
H: Mechanical stretch via transforming growth factor-β1 activates
microRNA208a to regulate endoglin expression in cultured rat
cardiac myoblasts. Eur J Heart Fail. 15:36–45. 2013.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|