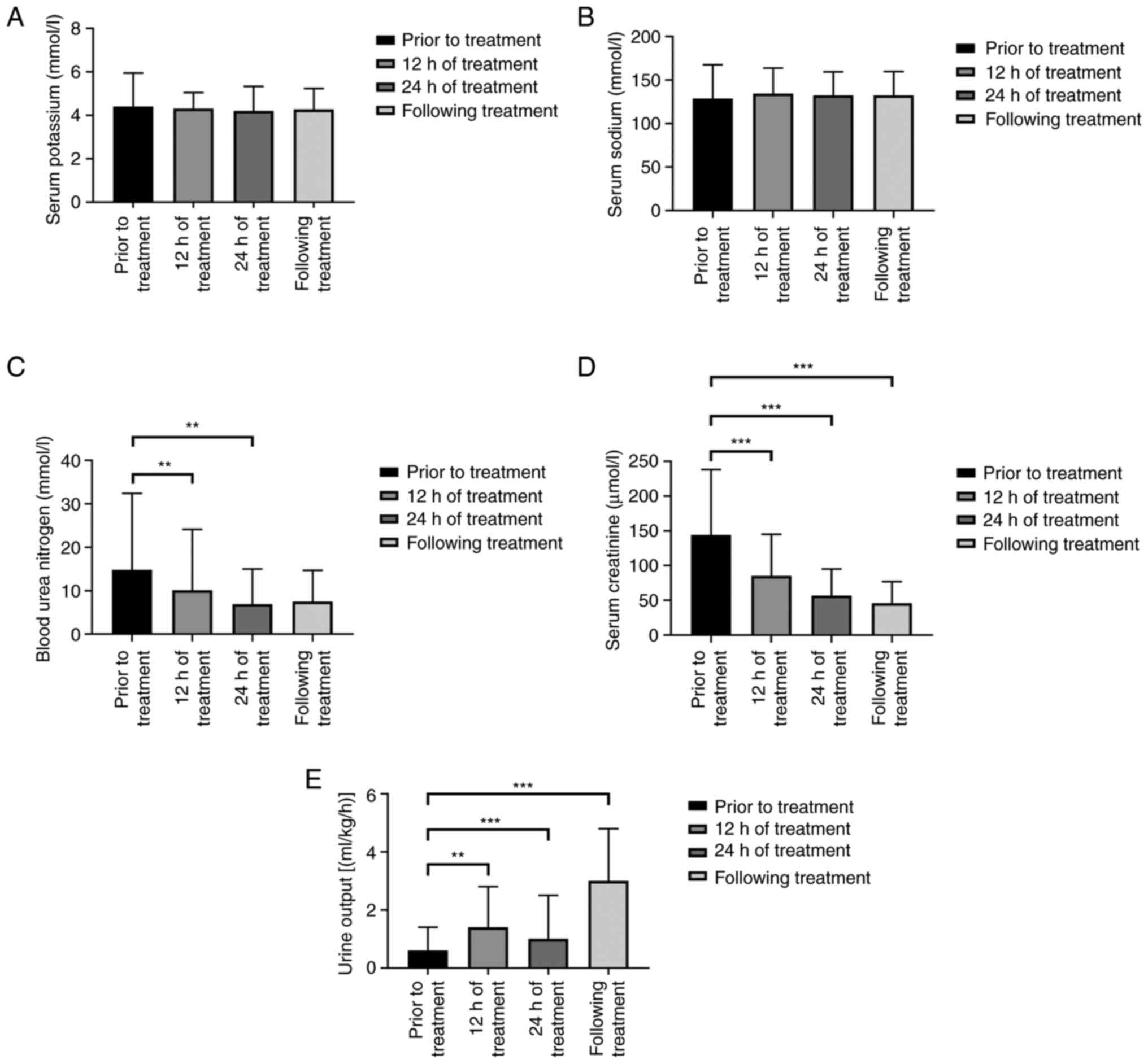
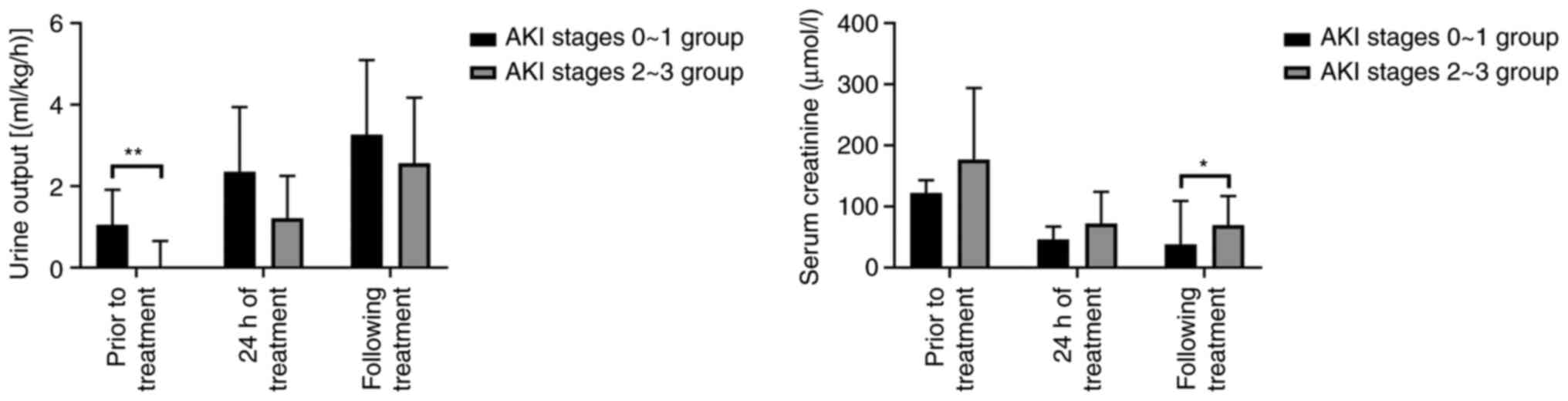
|
1
|
Kavanaugh KJ, Jetton JG and Kent AL:
Neonatal acute kidney injury: Understanding of the impact on the
smallest patients. Crit Care Clin. 37:349–363. 2021.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
2
|
Jetton JG, Boohaker LJ, Sethi SK, Wazir S,
Rohatgi S, Soranno DE, Chishti AS, Woroniecki R, Mammen C, Swanson
JR, et al: Incidence and outcomes of neonatal acute kidney injury
(AWAKEN): A multicentre, multinational, observational cohort study.
Lancet Child Adolesc Health. 1:184–194. 2017.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
3
|
Gallo D, de Bijl-Marcus KA, Alderliesten
T, Lilien M and Groenendaal F: Early acute kidney injury in preterm
and term neonates: Incidence, outcome, and associated clinical
features. Neonatology. 118:174–179. 2021.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
4
|
Diane Mok TY, Tseng MH, Chiang MC, Lin JL,
Chu SM, Hsu JF and Lien R: Renal replacement therapy in the
neonatal intensive care unit. Pediatr Neonatol. 59:474–480.
2018.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
5
|
Erkol Tuncer GH, Ekim M, Okulu E, Atasay B
and Kendirli T: Continuous renal replacement therapy in critically
ill children: single-center experience. Turk J Med Sci. 51:188–194.
2021.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
6
|
Khwaja A: KDIGO clinical practice
guidelines for acute kidney injury. Nephron Clin Pract.
120:c179–c184. 2012.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
7
|
SooHoo MM, Patel SS, Jaggers J, Faubel S
and Gist KM: Acute kidney injury defined by fluid corrected
creatinine in neonates after the norwood procedure. World J Pediatr
Congenit Heart Surg. 9:513–521. 2018.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
8
|
Yoon BR, Leem AY, Park MS, Kim YS and
Chung KS: Optimal timing of initiating continuous renal replacement
therapy in septic shock patients with acute kidney injury. Sci Rep.
9(11981)2019.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
9
|
Suzuki J, Ohnuma T, Sanayama H, Ito K,
Fujiwara T, Yamada H, Lefor AK and Sanui M: The optimal timing of
continuous renal replacement therapy according to the modified
RIFLE classification in critically ill patients with acute kidney
injury: A retrospective observational study. Renal Replacement
Therapy. 3(30)2017.
|
|
10
|
Roman-Filip C, Catană MG, Bereanu A,
Lăzăroae A, Gligor F and Sava M: Therapeutic plasma exchange and
double filtration plasmapheresis in severe neuroimmune disorders.
Acta Clin Croat. 58:621–626. 2019.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
11
|
Uber AM and Sutherland SM: Acute kidney
injury in hospitalized children: Consequences and outcomes. Pediatr
Nephrol. 35:213–220. 2020.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
12
|
Mian AN, Askenazi DJ and Mhanna MJ:
Therapeutic options for neonatal acute kidney injury (AKI). Curr
Treat Opt Pediatrics. 2:1–13. 2016.
|
|
13
|
Selewski DT, Charlton JR, Jetton JG,
Guillet R, Mhanna MJ, Askenazi DJ and Kent AL: Neonatal Acute
kidney injury. Pediatrics. 136:e463–e473. 2015.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
14
|
Perico N, Askenazi D, Cortinovis M and
Remuzzi G: Maternal and environmental risk factors for neonatal AKI
and its long-term consequences. Nat Rev Nephrol. 14:688–703.
2018.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
15
|
Safina AI, Daminova MA and Abdullina GA:
Acute kidney injury in neonatal intensive care: Medicines involved.
Int J Risk Saf Med. 27 (Suppl 1):S9–S10. 2015.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
16
|
Askenazi DJ: AWAKEN-Ing a new frontier in
neonatal nephrology. Front Pediatr. 8(21)2020.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
17
|
Goldstein SL: Pediatric continuous renal
replacement therapy for ‘40 years of continuous renal replacement
therapy’. Contrib Nephrol. 194:146–154. 2018.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
18
|
Cho AY, Yoon HJ, Lee KY and Sun IO:
Clinical characteristics of sepsis-induced acute kidney injury in
patients undergoing continuous renal replacement therapy. Ren Fail.
40:403–409. 2018.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
19
|
Continuous renal replacement therapies,
international conference. San Diego, California, November 8-10,
1995. Abstracts. Blood Purif. 13:385–402. 1995.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
20
|
Ricci Z and Goldstein SL: Pediatric
continuous renal replacement therapy. Contrib Nephrol. 187:121–30.
2016.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
21
|
Ronco C, Ricci Z and Goldstein SL:
(R)evolution in the management of acute kidney injury in newborns.
Am J Kidney Dis. 66:206–211. 2015.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
22
|
Kes P and Basić Jukić N: Acute kidney
injury in the intensive care unit. Bosn J Basic Med Sci 10 Suppl. 1
(Suppl 1):S8–S12. 2010.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
23
|
Gorga SM, Sahay RD, Askenazi DJ, Bridges
BC, Cooper DS, Paden ML, Zappitelli M, Gist KM, Gien J, Basu RK, et
al: Fluid overload and fluid removal in pediatric patients on
extracorporeal membrane oxygenation requiring continuous renal
replacement therapy: A multicenter retrospective cohort study.
Pediatr Nephrol. 35:871–882. 2020.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
24
|
Ronco C, Garzotto F, Brendolan A, Zanella
M, Bellettato M, Vedovato S, Chiarenza F, Ricci Z and Goldstein SL:
Continuous renal replacement therapy in neonates and small infants:
Development and first-in-human use of a miniaturised machine
(CARPEDIEM). Lancet. 383:1807–1813. 2014.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
25
|
Noh ES, Kim HH, Kim HS, Han YS, Yang M,
Ahn SY, Sung SI, Chang YS and Park WS: Continuous renal replacement
therapy in preterm infants. Yonsei Med J. 60:984–991.
2019.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
26
|
Garzotto F, Vidal E, Ricci Z, Paglialonga
F, Giordano M, Laforgia N, Peruzzi L, Bellettato M, Murer L and
Ronco C: Continuous kidney replacement therapy in critically ill
neonates and infants: A retrospective analysis of clinical results
with a dedicated device. Pediatr Nephrol. 35:1699–1705.
2020.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
27
|
Hu Y, Peng XM and Xiao ZH: Application of
continuous renal replacement therapy in the treatment of neonates
with inherited metabolic diseases. Zhongguo Dang Dai Er Ke Za Zhi.
23:488–493. 2021.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar : (In Chinese).
|
|
28
|
Pedersen O, Jepsen SB and Toft P:
Continuous renal replacement therapy for critically ill infants and
children. Dan Med J. 59(A4385)2012.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
29
|
Lee ST and Cho H: Fluid overload and
outcomes in neonates receiving continuous renal replacement
therapy. Pediatr Nephrol. 31:2145–2152. 2016.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
30
|
Kellum JA and Ronco C: The 17th acute
disease quality initiative international consensus conference:
Introducing precision renal replacement therapy. Blood Purif.
42:221–223. 2016.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
31
|
Riley AA, Watson M, Smith C, Guffey D,
Minard CG, Currier H and Akcan Arikan A: Pediatric continuous renal
replacement therapy: Have practice changes changed outcomes? A
large single-center ten-year retrospective evaluation. BMC Nephrol.
19(268)2018.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
32
|
Symons JM, Brophy PD, Gregory MJ, McAfee
N, Somers MJ, Bunchman TE and Goldstein SL: Continuous renal
replacement therapy in children up to 10 kg. Am J Kidney Dis.
41:984–989. 2003.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|