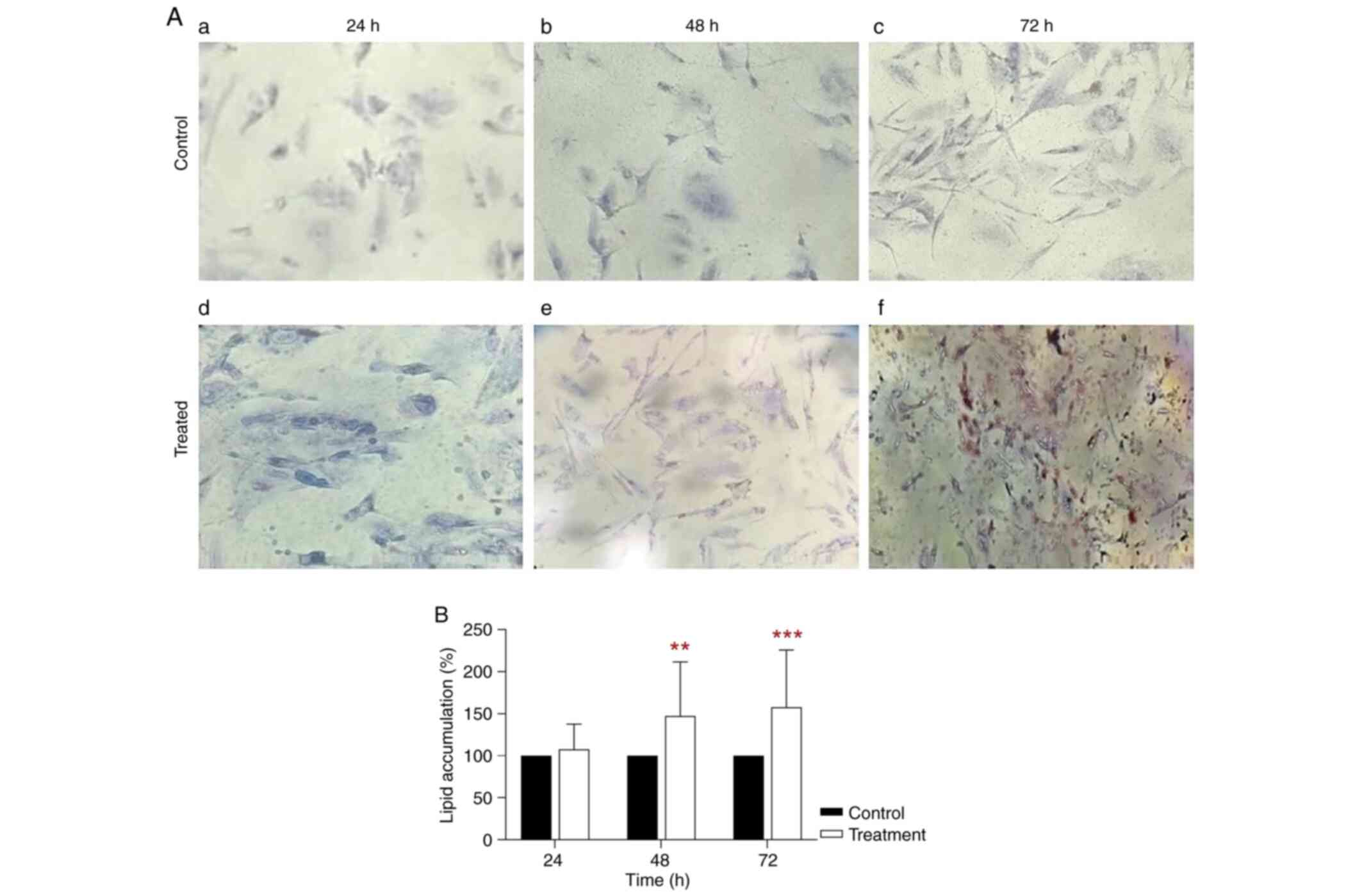
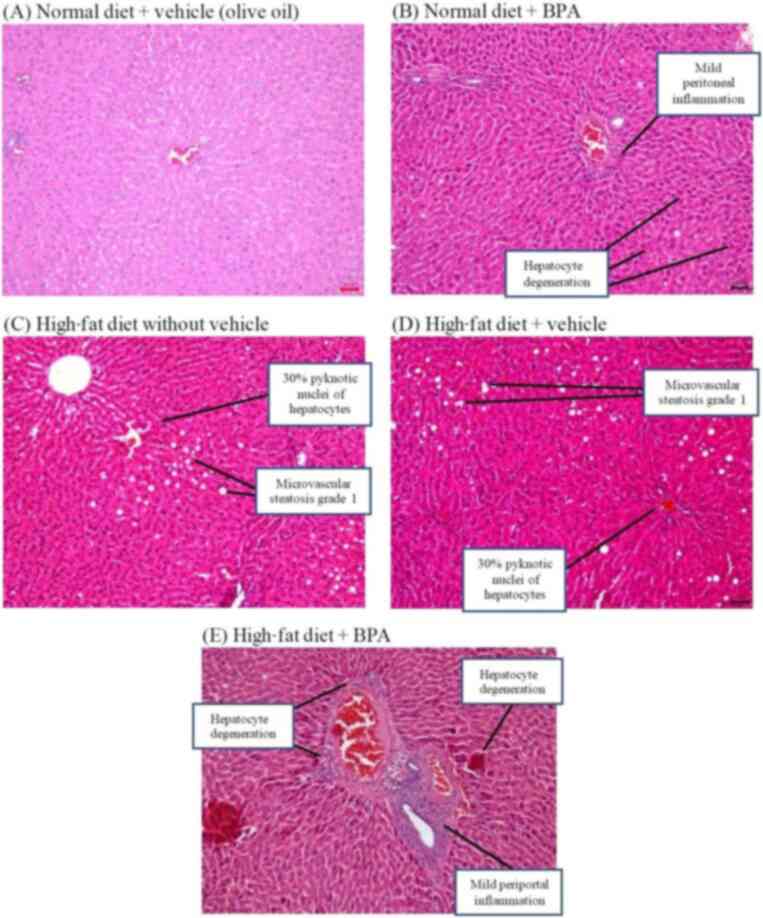
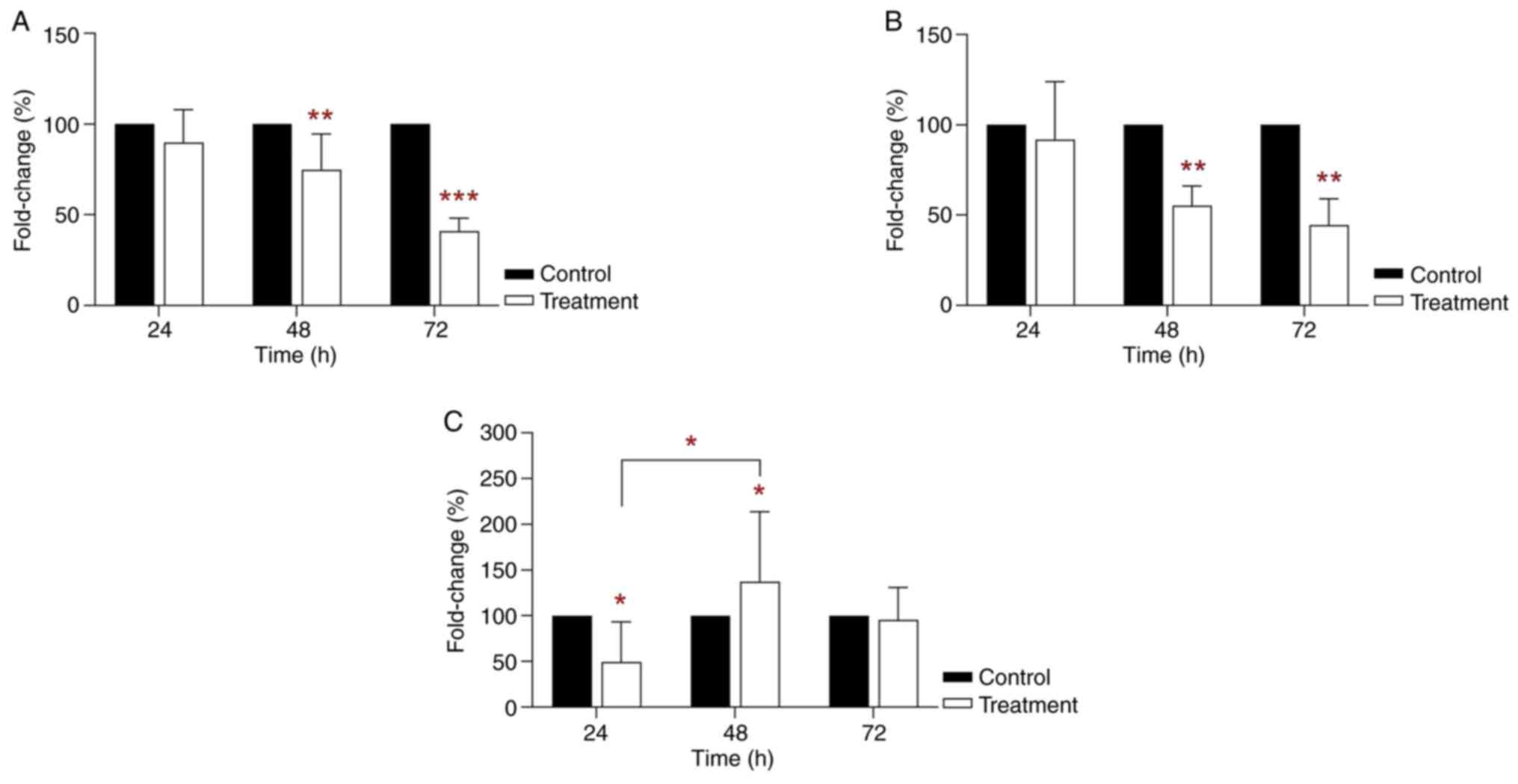
|
1
|
Rochester JR: Bisphenol A and human
health: A review of the literature. Reprod Toxicol. 42:132–155.
2013.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
2
|
Ma Y, Liu H, Wu J, Yuan L, Wang Y, Du X,
Wang R, Marwa PW, Petlulu P, Chen X, et al: The adverse health
effects of Bisphenol A and related toxicity mechanisms. Environ
Res. 176(108575)2019.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
3
|
Quesnot N, Bucher S, Fromenty B and Robin
MA: Modulation of metabolizing enzymes by Bisphenol A in human and
animal models. Chem Res Toxicol. 27:1463–1473. 2014.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
4
|
Bertoli S, Leone A and Battezzati A: Human
Bisphenol A exposure and the diabesity phenotype. Dose Response.
13(1559325815599173)2015.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
5
|
Salehi A, Loganathan N and Belsham DD:
Bisphenol A induces Pomc gene expression through neuroinflammatory
and PPARγ nuclear receptor-mediated mechanisms in POMC-expressing
hypothalamic neuronal models. Mol Cell Endocrinol. 479:12–19.
2019.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
6
|
Peyre L, Rouimi P, de Sousa G,
Héliès-Toussaint C, Carré B, Barcellini S, Chagnon MC and Rahmani
R: Comparative study of Bisphenol A and its analogue bisphenol S on
human hepatic cells: A focus on their potential involvement in
non-alcoholic fatty liver disease. Food Chem Toxicol. 70:9–18.
2014.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
7
|
Eweda SM, Newairy ASA, Abdou HM and Gaber
AS: Bisphenol A-induced oxidative damage in the hepatic and cardiac
tissues of rats: The modulatory role of sesame lignans. Exp Ther
Med. 19:33–44. 2020.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
8
|
Jalal N, Surendranath AR, Pathak JL, Yu S
and Chung CY: Bisphenol a (BPA) the mighty and the mutagenic.
Toxicol Rep. 5:76–84. 2018.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
9
|
Ohore OE and Songhe Z: Endocrine
disrupting effects of Bisphenol A exposure and recent advances on
its removal by water treatment systems. A review. Sci Afr.
5(e00135)2019.
|
|
10
|
Kourouma A, Quan C, Duan P, Qi S, Yu T,
Wang Y and Yang K: Bisphenol A induces apoptosis in liver cells
through Induction of ROS. Adv Toxicol. 2015(901983)2015.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
11
|
Kang JH, Katayama Y and Kondo F:
Biodegradation or metabolism of Bisphenol A: From microorganisms to
mammals. Toxicology. 217:81–90. 2006.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
12
|
Chen ZJ, Yang XL, Liu H, Wei W, Zhang KS,
Huang HB, Giesy JP, Liu HL, Du J and Wang HS: Bisphenol A modulates
colorectal cancer protein profile and promotes the metastasis via
induction of epithelial to mesenchymal transitions. Arch Toxicol.
89:1371–1381. 2015.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
13
|
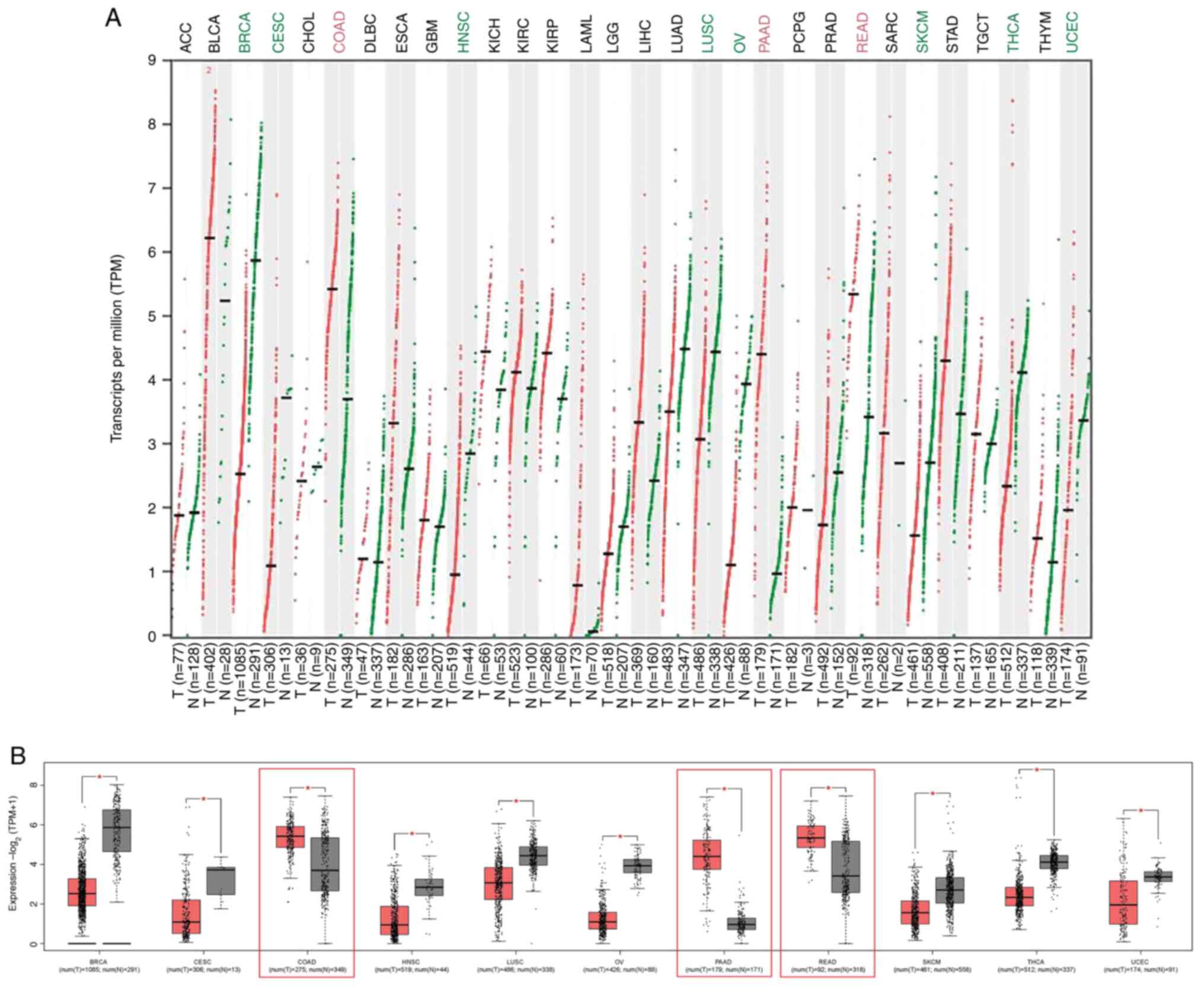
Tang Z, Li C, Kang B, Gao G, Li C and
Zhang Z: GEPIA: A web server for cancer and normal gene expression
profiling and interactive analyses. Nucleic Acids Res. 45:W98–W102.
2017.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
14
|
Abdalkareem EA, Ong CY, Lim BH and Khoo
BY: Neutralizing FGF4 protein in conditioned medium of
IL-21-silenced HCT116 cells restores the migratory activity of the
colorectal cancer cells. Cytotechnology. 70:1363–1374.
2018.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
15
|
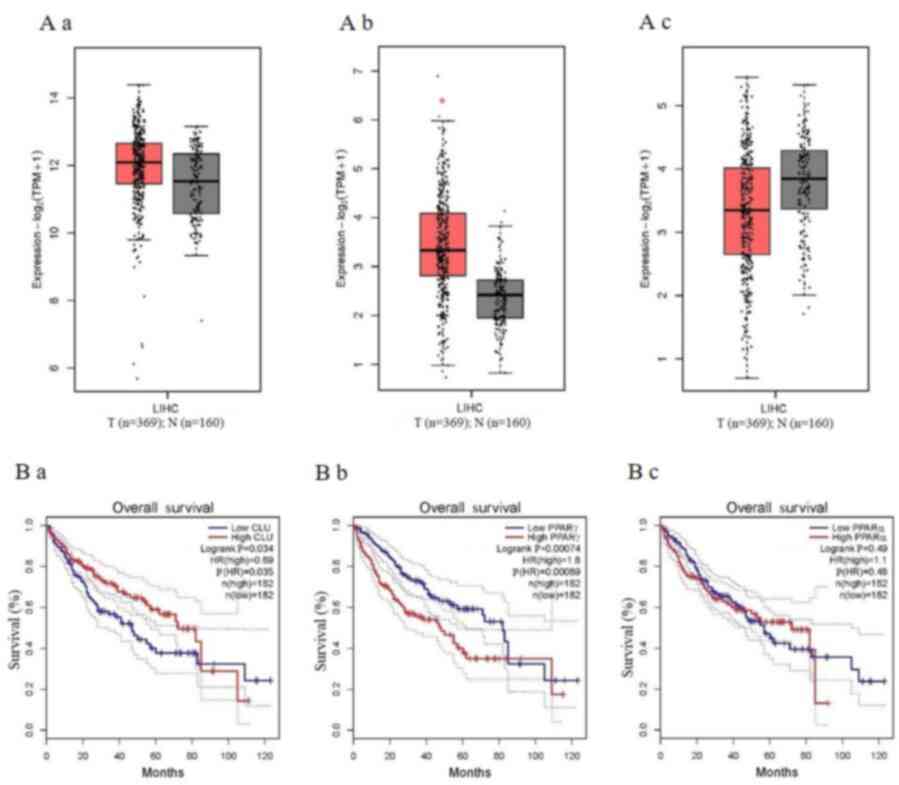
Livak KJ and Schmittgen TD: Analysis of
relative gene expression data using real-time quantitative PCR and
the 2(-Delta Delta C(T)) method. Methods. 25:402–408.
2001.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
16
|
Li H, Han D, Hou Y, Chen H and Chen Z:
Statistical inference methods for two crossing survival curves: A
comparison of methods. PLoS One. 10(e0116774)2015.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
17
|
Institutional Animal Care and Use
Committee (IACUC): Universiti Putra Malaysia Code of Practice for
the Care and Use of Animals for Scientific Purposes. University
Putra Malaysia, Seri Kembangan, 2020. http://www.tncpi.upm.edu.my/upload/dokumen/20180522092738IACUC_-_UPM_Code_of_Practice.pdf.
|
|
18
|
Jucá MJ, Bandeira BC, Carvalho DS and Leal
AT: Comparative study of 1,2-dimethylhydrazine and azoxymethane on
the induction of colorectal cancer in rats. J Coloproctology.
34:167–173. 2014.
|
|
19
|
Wee Y, Liu Y, Lu J, Li X and Zhao M:
Identification of novel prognosis-related genes associated with
cancer using integrative network analysis. Sci Rep.
8(3233)2018.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
20
|
Esteves F, Rueff J and Kranendonk M: The
central role of cytochrome P450 in xenobiotic metabolism-a brief
review on a fascinating enzyme family. J Xenobiot. 11:94–114.
2021.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
21
|
Hafezi SA and Abdel-Rahman WM: The
Endocrine disruptor Bisphenol A (BPA) exerts a wide range of
effects in carcinogenesis and response to therapy. Curr Mol
Pharmacol. 12:230–238. 2019.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
22
|
Pazienza V, Vinciguerra M and Mazzoccoli
G: PPARs Signaling and cancer in the gastrointestinal system. PPAR
Res. 2012(560846)2012.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
23
|
Eibl G: The role of PPAR-gamma and its
interaction with COX-2 in pancreatic cancer. PPAR Res.
2008(326915)2008.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
24
|
Burstein HJ, Demetri GD, Mueller E, Sarraf
P, Spiegelman BM and Winer EP: Use of the peroxisome
proliferator-activated receptor (PPAR) gamma ligand troglitazone as
treatment for refractory breast cancer: A phase II study. Br Cancer
Res Treat. 79:391–397. 2003.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
25
|
Augimeri G, Giordano C, Gelsomino L,
Plastina P, Barone I, Catalano S, Andò S and Bonofiglio D: The role
of PPARγ ligands in breast cancer: From basic research to clinical
studies. Cancers (Basel). 12(2623)2020.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
26
|
Robbins GT and Nie D: PPAR gamma,
bioactive lipids and cancer progression. Front Biosci (Landmark
Ed). 17:1816–1834. 2012.PubMed/NCBI View
Article : Google Scholar
|
|
27
|
Dai Y, Qiao L, Chan KW, Yang M, Ye J, Ma
J, Zou B, Gu Q, Wang J, Pang R, et al: Peroxisome
proliferator-activated receptor-gamma contributes to the inhibitory
effects of Embelin on colon carcinogenesis. Cancer Res.
69:4776–4783. 2009.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
28
|
Vandenberg LN, Hauser R, Marcus M, Olea N
and Welshons WV: Human exposure to Bisphenol A (BPA). Reprod
Toxicol. 24:139–177. 2007.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
29
|
Vom Saal FS, Nagel SC, Coe BL, Angle BM
and Taylor JA: The estrogenic endocrine disrupting chemical
Bisphenol A (BPA) and obesity. Mol Cell Endocrinol. 354:74–84.
2012.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
30
|
Mahamuni D and Shrinithivihahshini ND:
Need for regulatory policies in India, on the use of Bisphenol A in
food contact plastic containers. Curr Sci. 113:861–868. 2017.
|
|
31
|
Bhandari R, Xiao J and Shankar A: Urinary
Bisphenol A and obesity in U.S. children. Am J Epidemiol.
177:1263–1270. 2013.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
32
|
Pereira-Fernandes A, Demaegdt H,
Vandermeiren K, Hectors TL, Jorens PG, Blust R and Vanparys C:
Evaluation of a screening system for obesogenic compounds:
Screening of endocrine disrupting compounds and evaluation of the
PPAR dependency of the effect. PLoS One. 8(e77481)2013.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
33
|
Moreno-Gómez-Toledano R, Arenas MI,
Sánchez-Esteban S, Cook A, Saura M and Bosch RJ: Critical analysis
of human exposure to Bisphenol A and its novel implications on
renal, cardiovascular and hypertensive diseases. In: Hot Topics in
Endocrinology and Metabolism [Internet]. Heshmati HM (ed).
IntechOpen, London, 2021.
|
|
34
|
Filardi T, Panimolle F, Lenzi A and Morano
S: Bisphenol A and phthalates in diet: An emerging link with
pregnancy complications. Nutrients. 12(525)2020.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
35
|
Ahmed S and Atlas E: Bisphenol S- and
Bisphenol A-induced adipogenesis of murine preadipocytes occurs
through direct peroxisome proliferator-activated receptor gamma
activation. Int J Obes (Lond). 40:1566–1573. 2016.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
36
|
Rogers JA, Metz L and Yong VW: Review:
Endocrine disrupting chemicals and immune responses: A focus on
bisphenol-A and its potential mechanisms. Mol Immunol. 53:421–430.
2013.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
37
|
MacKay H and Abizaid A: A plurality of
molecular targets: The receptor ecosystem for bisph++enol-A (BPA).
Horm Behav. 101:59–67. 2018.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
38
|
Gao P, Wang L, Yang N, Wen J, Zhao M, Su
G, Zhang J and Weng D: Peroxisome proliferator-activated receptor
gamma (PPARγ) activation and metabolism disturbance induced by
Bisphenol A and its replacement analog bisphenol S using in vitro
macrophages and in vivo mouse models. Environ Int.
134(105328)2020.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
39
|
Li CH, Zhang DH, Jiang LD, Qi Y and Guo
LH: Binding and activity of Bisphenol Analogues to human peroxisome
proliferator-activated receptor β/δ. Ecotoxicol Environ Saf.
226(112849)2021.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
40
|
Cimmino I, Fiory F, Perruolo G, Miele C,
Beguinot F, Formisano P and Oriente F: Potential mechanisms of
Bisphenol A (BPA) contributing to human disease. Int J Mol Sci.
21(5761)2020.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
41
|
Oliviero F, Marmugi A, Viguié C, Gayrard
V, Picard-Hagen N and Mselli-Lakhal L: Are BPA substitutes as
obesogenic as BPA? Int J Mol Sci. 23(4238)2022.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
42
|
Alves-Bezerra M and Cohen DE: Triglyceride
metabolism in the liver. Compr Physiol. 8:1–8. 2017.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
43
|
Ribeiro E, Ladeira C and Viegas S:
Occupational exposure to Bisphenol A (BPA): A reality that still
needs to be unveiled. Toxics. 5(22)2017.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
44
|
Geens T, Aerts D, Berthot C, Bourguignon
JP, Goeyens L, Lecomte P, Maghuin-Rogister G, Pironnet AM,
Pussemier L, Scippo ML, et al: A review of dietary and non-dietary
exposure to bisphenol-A. Food Chem Toxicol. 50:3725–3740.
2012.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
45
|
Valentino R, D'Esposito V, Ariemma F,
Cimmino I, Beguinot F and Formisano P: Bisphenol A environmental
exposure and the detrimental effects on human metabolic health: Is
it necessary to revise the risk assessment in vulnerable
population? J Endocrinol Invest. 39:259–263. 2016.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
46
|
Ribeiro E, Delgadinho M and Brito M:
Environmentally relevant concentrations of Bisphenol A interact
with doxorubicin transcriptional effects in human cell lines.
Toxics. 7(43)2019.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
47
|
Liu Q, Shao W, Weng Z, Zhang X, Ding G, Xu
C, Xu J, Jiang Z and Gu A: In vitro evaluation of the hepatic lipid
accumulation of Bisphenol Analogs: A high-content screening assay.
Toxicol In Vitro. 68(104959)2020.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
48
|
Ke ZH, Pan JX, Jin LY, Xu HY, Yu TT, Ullah
K, Rahman TU, Ren J, Cheng Y, Dong XY, et al: Bisphenol A exposure
may induce hepatic lipid accumulation via reprogramming the DNA
methylation patterns of genes involved in lipid metabolism. Sci
Rep. 6(31331)2016.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
49
|
Wang J, Sun B, Hou M, Pan X and Li X: The
environmental obesogen Bisphenol A promotes adipogenesis by
increasing the amount of 11β-hydroxysteroid dehydrogenase type 1 in
the adipose tissue of children. Int J Obes (Lond). 37:999–1005.
2013.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
50
|
Xia W, Jiang Y, Li Y, Wan Y, Liu J, Ma Y,
Mao Z, Chang H, Li G, Xu B, et al: Early-life exposure to Bisphenol
A induces liver injury in rats involvement of mitochondria-mediated
apoptosis. PLoS One. 9(e90443)2014.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
51
|
Hussein RM and Eid JI: Pathological
mechanisms of liver injury caused by oral administration of
Bisphenol A. Life Sci J. 10:663–673. 2013.
|
|
52
|
Thoene M, Rytel L, Dzika E, Włodarczyk A,
Kruminis-Kaszkiel E, Konrad P and Wojtkiewicz J: Bisphenol A causes
liver damage and selectively alters the neurochemical coding of
intrahepatic parasympathetic nerves in juvenile porcine models
under physiological conditions. Int J Mol Sci.
18(2726)2017.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
53
|
Abdel-Wahab WM: Thymoquinone attenuates
toxicity and oxidative stress induced by Bisphenol A in liver of
male rats. Pak J Biol Sci. 17:1152–1160. 2014.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
54
|
Hassani FV, Abnous K, Mehri S, Jafarian A,
Birner-Gruenberger R, Yazdian Robati R and Hosseinzadeh H:
Proteomics and phosphoproteomics analysis of liver in male rats
exposed to Bisphenol A: Mechanism of hepatotoxicity and biomarker
discovery. Food Chem Toxicol. 112:26–38. 2018.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
55
|
Ke C, Liu X, Zuo H, Zhao J, Yang X and
Yuan J: The oxidative damage of Bisphenol A on the organs of the
mice. Sci Res. 5:1190–1194. 2013.
|
|
56
|
Lin Y, Ding D, Huang Q, Liu Q, Lu H, Lu Y,
Chi Y, Sun X, Ye G, Zhu H, et al: Downregulation of miR-192 causes
hepatic steatosis and lipid accumulation by inducing SREBF1: Novel
mechanism for Bisphenol A-triggered non-alcoholic fatty liver
disease. Biochim Biophys Acta Mol Cell Biol Lipids. 1862:869–882.
2017.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
57
|
Marmugi A, Ducheix S, Lasserre F, Polizzi
A, Paris A, Priymenko N, Bertrand-Michel J, Pineau T, Guillou H,
Martin PG, et al: Low doses of Bisphenol A induce gene expression
related to lipid synthesis and trigger triglyceride accumulation in
adult mouse liver. Hepatology. 55:395–407. 2012.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
58
|
Periasamy S, Chien SP, Chang PC, Hsu DZ
and Liu MY: Sesame oil mitigates nutritional steatohepatitis via
attenuation of oxidative stress and inflammation: A tale of two-hit
hypothesis. J Nutr Biochem. 25:232–240. 2014.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
59
|
Rönn M, Kullberg J, Karlsson H, Berglund
J, Malmberg F, Orberg J, Lind L, Ahlström H and Lind PM: Bisphenol
A exposure increases liver fat in juvenile fructose-fed Fischer 344
rats. Toxicology. 303:125–132. 2013.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
60
|
Nicolucci C, Errico S, Federico A, Dallio
M, Loguercio C and Diano N: Human exposure to Bisphenol A and liver
health status: Quantification of urinary and circulating levels by
LC-MS/MS. J Pharm Biomed Anal. 140:105–112. 2017.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
61
|
Nishizawa H, Imanishi S and Manabe N:
Effects of exposure in utero to Bisphenol A on the expression of
aryl hydrocarbon receptor, related factors and xenobiotic
metabolizing enzymes in murine embryos. J Reprod Dev. 51:593–605.
2005.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
62
|
Jeong HG, Kimand JY and Choi CY:
Down-regulation of murine Cyp1a-1 in mouse hepatoma Hepa-1c1c7
cells by Bisphenol A. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 277:594–598.
2000.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
63
|
Nahar MS, Kim JH, Sartor MA and Dolinoy
DC: Bisphenol A-associated alterations in the expression and
epigenetic regulation of genes encoding xenobiotic metabolizing
enzymes in human fetal liver. Environ Mol Mutagen. 55:184–195.
2014.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
64
|
Meli R, Monnolo A, Annunziata C, Pirozzi C
and Ferrante MC: Oxidative stress and BPA toxicity: An antioxidant
approach for male and female reproductive dysfunction. Antioxidants
(Basel). 9(405)2020.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
65
|
Mahemuti L, Chen Q, Coughlan MC, Qiao C,
Chepelev NL, Florian M, Dong D, Woodworth RG, Yan J, Cao XL, et al:
Bisphenol A induces DSB-ATM-p53 signaling leading to cell cycle
arrest, senescence, autophagy, stress response and estrogen release
in human fetal lung fibroblasts. Arch Toxicol. 92:1453–1469.
2018.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
66
|
Khor CY and Khoo BY: PPARα plays an
important role in the migration activity and the expression of
CYP2S1 and CYP1B1 in Chrysin-treated HCT116 cells. Biotechnol Lett.
42:1581–1595. 2020.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
67
|
Hoffman SMG, Nelson DR and Keeney DS:
Organization, structure and evolution of the CYP2 gene cluster on
human chromosome 19. Pharmacogenetics. 11:687–698. 2001.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
68
|
Rylander T, Neve EP, Ingelman-Sundberg M
and Oscarson M: Identification and tissue distribution of the novel
human cytochrome P450 2S1 (CYP2S1). Biochem Biophys Res Commun.
281:529–535. 2001.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
69
|
Rivera SP, Saarikoski ST and Hankinson O:
Identification of a novel dioxin-inducible cytochrome P450. Mol
Pharmacol. 61:255–259. 2002.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
70
|
Choudhary D, Jansson I, Schenkman JB,
Sarfarazi M and Stoilov I: Comparative expression profiling of 40
mouse cytochrome P450 genes in embryonic and adult tissues. Arch
Biochem Biophys. 414:91–100. 2003.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
71
|
Smith G, Wolf CR, Deeni YY, Dawe RS, Evans
AT, Comrie MM, Ferguson J and Ibbotson SH: Cutaneous expression of
cytochrome P450 CYP2S1: Individuality in regulation by therapeutic
agents for psoriasis and other skin diseases. Lancet.
361:1336–1343. 2003.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
72
|
Saarikoski ST, Rivera SP, Hankinson O and
Husgafvel-Pursiainen K: CYP2S1: A short review. Toxicol Appl
Pharmacol. 207 (Suppl 2):S62–S69. 2005.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
73
|
Saarikoski ST, Wikman HA, Smith G, Wolff
CH and Husgafvel-Pursiainen K: Localization of cytochrome P450
CYP2S1 expression in human tissues by in situ hybridization and
immunohistochemistry. J Histochem Cytochem. 53:549–556.
2005.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
74
|
Yang C, Zhou Q, Li M, Tong X, Sun J, Qing
Y, Sun L, Yang X, Hu X, Jiang J, et al: Upregulation of CYP2S1 by
oxaliplatin is associated with p53 status in colorectal cancer cell
lines. Sci Rep. 6(33078)2016.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
75
|
Peters JM, Shah YM and Gonzalez FJ: The
role of peroxisome proliferator-activated receptors in
carcinogenesis and chemoprevention. Nat Rev Cancer. 12:181–195.
2012.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|