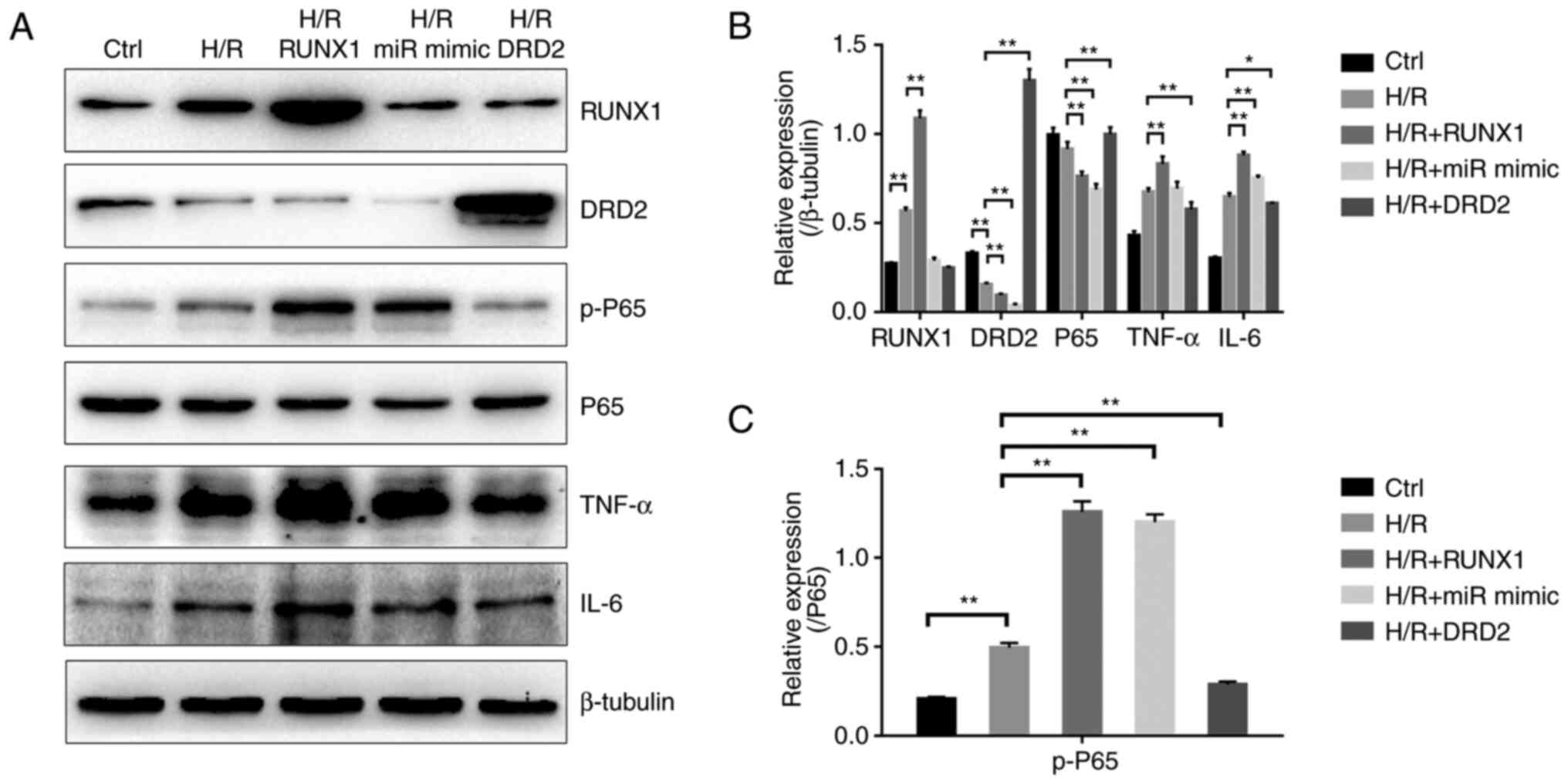
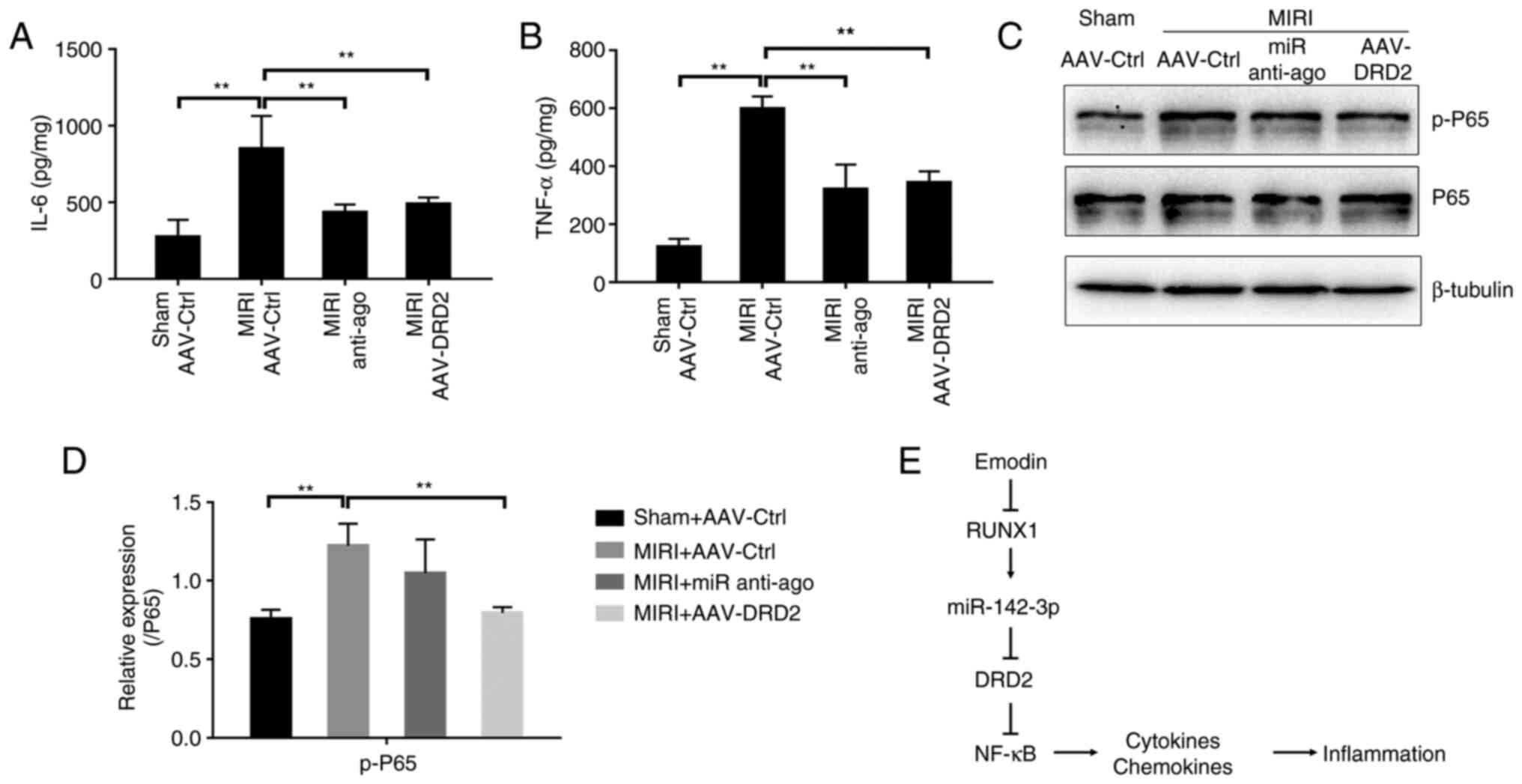
|
1
|
Edmondson D and von Känel R:
Post-traumatic stress disorder and cardiovascular disease. Lancet
Psychiatry. 4:320–329. 2017.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
2
|
Andersson C and Vasan RS: Epidemiology of
cardiovascular disease in young individuals. Nat Rev Cardiol.
15:230–240. 2018.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
3
|
Rout A, Tantry US, Novakovic M, Sukhi A
and Gurbel PA: Targeted pharmacotherapy for ischemia reperfusion
injury in acute myocardial infarction. Expert Opin Pharmacother.
21:1851–1865. 2020.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
4
|
Xiong YY, Gong ZT, Tang RJ and Yang YJ:
The pivotal roles of exosomes derived from endogenous immune cells
and exogenous stem cells in myocardial repair after acute
myocardial infarction. Theranostics. 11:1046–1058. 2021.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
5
|
Chen M, Li X, Yang H, Tang J and Zhou S:
Hype or hope: Vagus nerve stimulation against acute myocardial
ischemia-reperfusion injury. Trends Cardiovasc Med. 30:481–488.
2020.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
6
|
Yellon DM and Hausenloy DJ: Myocardial
reperfusion injury. N Engl J Med. 357:1121–1135. 2007.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
7
|
Keeley EC, Boura JA and Grines CL: Primary
angioplasty versus intravenous thrombolytic therapy for acute
myocardial infarction: A quantitative review of 23 randomised
trials. Lancet. 361:13–20. 2003.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
8
|
Hausenloy DJ and Yellon DM: Myocardial
ischemia-reperfusion injury: A neglected therapeutic target. J Clin
Invest. 123:92–100. 2013.PubMed/NCBI View
Article : Google Scholar
|
|
9
|
Davidson SM, Ferdinandy P, Andreadou I,
Bøtker HE, Heusch G, Ibáñez B, Ovize M, Schulz R, Yellon DM,
Hausenloy DJ, et al: Multitarget strategies to reduce myocardial
ischemia/reperfusion injury: JACC review topic of the week. J Am
Coll Cardiol. 73:89–99. 2019.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
10
|
Chang JC, Lien CF, Lee WS, Chang HR, Hsu
YC, Luo YP, Jeng JR, Hsieh JC and Yang KT: Intermittent hypoxia
prevents myocardial mitochondrial Ca2+ overload and cell
death during ischemia/reperfusion: The role of reactive oxygen
species. Cells. 8(564)2019.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
11
|
Kawaguchi M, Takahashi M, Hata T, Kashima
Y, Usui F, Morimoto H, Izawa A, Takahashi Y, Masumoto J, Koyama J,
et al: Inflammasome activation of cardiac fibroblasts is essential
for myocardial ischemia/reperfusion injury. Circulation.
123:594–604. 2011.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
12
|
Wallert M, Ziegler M, Wang X, Maluenda A,
Xu X, Yap ML, Witt R, Giles C, Kluge S, Hortmann M, et al:
α-Tocopherol preserves cardiac function by reducing oxidative
stress and inflammation in ischemia/reperfusion injury. Redox Biol.
26(101292)2019.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
13
|
Sun X, Wei Z, Li Y, Wang J, Hu J, Yin Y,
Xie J and Xu B: Renal denervation restrains the inflammatory
response in myocardial ischemia-reperfusion injury. Basic Res
Cardiol. 115(15)2020.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
14
|
Ong SB, Hernández-Reséndiz S,
Crespo-Avilan GE, Mukhametshina RT, Kwek XY, Cabrera-Fuentes HA and
Hausenloy DJ: Inflammation following acute myocardial infarction:
Multiple players, dynamic roles, and novel therapeutic
opportunities. Pharmacol Ther. 186:73–87. 2018.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
15
|
Chen X, Li X, Zhang W, He J, Xu B, Lei B,
Wang Z, Cates C, Rousselle T and Li J: Activation of AMPK inhibits
inflammatory response during hypoxia and reoxygenation through
modulating JNK-mediated NF-κB pathway. Metabolism. 83:256–270.
2018.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
16
|
Chen J, Jiang Z, Zhou X, Sun X, Cao J, Liu
Y and Wang X: Dexmedetomidine preconditioning protects
cardiomyocytes against hypoxia/reoxygenation-induced necroptosis by
inhibiting HMGB1-mediated inflammation. Cardiovasc Drugs Ther.
33:45–54. 2019.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
17
|
Dong X, Fu J, Yin X, Cao S, Li X, Lin L
and Huyiligeqi and Ni J: Emodin: A review of its pharmacology,
toxicity and pharmacokinetics. Phytother Res. 30:1207–1218.
2016.PubMed/NCBI View
Article : Google Scholar
|
|
18
|
Dong X, Zeng Y, Liu Y, You L, Yin X, Fu J
and Ni J: Aloe-emodin: A review of its pharmacology, toxicity, and
pharmacokinetics. Phytother Res. 34:270–281. 2020.PubMed/NCBI View
Article : Google Scholar
|
|
19
|
Ye B, Chen X, Dai S, Han J, Liang X, Lin
S, Cai X, Huang Z and Huang W: Emodin alleviates myocardial
ischemia/reperfusion injury by inhibiting gasdermin D-mediated
pyroptosis in cardiomyocytes. Drug Des Devel Ther. 13:975–990.
2019.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
20
|
Li Q, Gao J, Pang X, Chen A and Wang Y:
Molecular mechanisms of action of emodin: As an anti-cardiovascular
disease drug. Front Pharmacol. 11(559607)2020.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
21
|
Bartel DP: MicroRNAs: Genomics,
biogenesis, mechanism, and function. Cell. 116:281–297.
2004.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
22
|
Hu F, Zhang S, Chen X, Fu X, Guo S, Jiang
Z and Chen K: MiR-219a-2 relieves myocardial ischemia-reperfusion
injury by reducing calcium overload and cell apoptosis through
HIF1α/NMDAR pathway. Exp Cell Res. 395(112172)2020.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
23
|
Zhang C, Liang R, Gan X, Yang X, Chen L
and Jian J: MicroRNA-384-5p/beclin-1 as potential indicators for
epigallocatechin gallate against cardiomyocytes ischemia
reperfusion injury by inhibiting autophagy via PI3K/Akt pathway.
Drug Des Devel Ther. 13:3607–3623. 2019.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
24
|
Chen Z, Su X, Shen Y, Jin Y, Luo T, Kim
IM, Weintraub NL and Tang Y: MiR322 mediates cardioprotection
against ischemia/reperfusion injury via FBXW7/notch pathway. J Mol
Cell Cardiol. 133:67–74. 2019.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
25
|
Yu SY, Dong B, Fang ZF, Hu XQ, Tang L and
Zhou SH: Knockdown of lncRNA AK139328 alleviates myocardial
ischaemia/reperfusion injury in diabetic mice via modulating
miR-204-3p and inhibiting autophagy. J Cell Mol Med. 22:4886–4898.
2018.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
26
|
Livak KJ and Schmittgen TD: Analysis of
relative gene expression data using real-time quantitative PCR and
the 2(-Delta Delta C(T)) method. Methods. 25:402–408.
2001.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
27
|
Tong Z, Cui Q, Wang J and Zhou Y: TransmiR
v2.0: An updated transcription factor-microRNA regulation database.
Nucleic Acids Res. 47 (D1):D253–D258. 2019.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
28
|
Wang LJ, Qiu BQ, Yuan MM, Zou HX, Gong CW,
Huang H, Lai SQ and Liu JC: Identification and validation of
dilated cardiomyopathy-related genes via bioinformatics analysis.
Int J Gen Med. 15:3663–3676. 2022.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
29
|
Ogier-Denis E, Fasseu M, Vandewalle A and
Laburthe M: MicroRNAs and intestinal pathophysiology. Med Sci
(Paris). 23:509–514. 2007.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
30
|
Yu LM, Dong X, Xue XD, Xu S, Zhang X, Xu
YL, Wang ZS, Wang Y, Gao H, Liang YX, et al: Melatonin attenuates
diabetic cardiomyopathy and reduces myocardial vulnerability to
ischemia-reperfusion injury by improving mitochondrial quality
control: Role of SIRT6. J Pineal Res. 70(e12698)2021.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
31
|
Ekshyyan O and Aw TY: Apoptosis in acute
and chronic neurological disorders. Front Biosci. 9:1567–1576.
2004.PubMed/NCBI View
Article : Google Scholar
|
|
32
|
Atreya I, Atreya R and Neurath MF:
NF-kappaB in inflammatory bowel disease. J Intern Med. 263:591–596.
2008.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
33
|
Huang Q, Lu G, Shen HM, Chung MC and Ong
CN: Anti-cancer properties of anthraquinones from rhubarb. Med Res
Rev. 27:609–630. 2007.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
34
|
Zhu T, Zhang W, Feng SJ and Yu HP: Emodin
suppresses LPS-induced inflammation in RAW264.7 cells through a
PPARγ-dependent pathway. Int Immunopharmacol. 34:16–24.
2016.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
35
|
Zhu X, Zeng K, Qiu Y, Yan F and Lin C:
Therapeutic effect of emodin on collagen-induced arthritis in mice.
Inflammation. 36:1253–1259. 2013.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
36
|
Ding QH, Ye CY, Chen EM, Zhang W and Wang
XH: Emodin ameliorates cartilage degradation in osteoarthritis by
inhibiting NF-κB and Wnt/β-catenin signaling in-vitro and in-vivo.
Int Immunopharmacol. 61:222–230. 2018.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
37
|
Chen GL, Zhang JJ, Kao X, Wei LW and Liu
ZY: Emodin ameliorates lipopolysaccharides-induced corneal
inflammation in rats. Int J Ophthalmol. 8:665–669. 2015.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
38
|
Kitano A, Saika S, Yamanaka O, Ikeda K,
Okada Y, Shirai K and Reinach PS: Emodin suppression of ocular
surface inflammatory reaction. Invest Ophthalmol Vis Sci.
48:5013–5022. 2007.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
39
|
Wu Y, Tu X, Lin G, Xia H, Huang H, Wan J,
Cheng Z, Liu M, Chen G, Zhang H, et al: Emodin-mediated protection
from acute myocardial infarction via inhibition of inflammation and
apoptosis in local ischemic myocardium. Life Sci. 81:1332–1338.
2007.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
40
|
McCarroll CS, He W, Foote K, Bradley A,
McGlynn K, Vidler F, Nixon C, Nather K, Fattah C, Riddell A, et al:
Runx1 deficiency protects against adverse cardiac remodeling after
myocardial infarction. Circulation. 137:57–70. 2018.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
41
|
Li X, Zhang S, Wa M, Liu Z and Hu S:
MicroRNA-101 protects against cardiac remodeling following
myocardial infarction via downregulation of runt-related
transcription factor 1. J Am Heart Assoc. 8(e013112)2019.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
42
|
Cui Y, Chen LJ, Huang T, Ying JQ and Li J:
The pharmacology, toxicology and therapeutic potential of
anthraquinone derivative emodin. Chin J Nat Med. 18:425–435.
2020.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
43
|
Oshida K, Hirakata M, Maeda A, Miyoshi T
and Miyamoto Y: Toxicological effect of emodin in mouse testicular
gene expression profile. J Appl Toxicol. 31:790–800.
2011.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
44
|
Ghafouri-Fard S, Shoorei H and Taheri M:
Non-coding RNAs participate in the ischemia-reperfusion injury.
Biomed Pharmacother. 129(110419)2020.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
45
|
Suzuki HI and Miyazono K: Emerging
complexity of microRNA generation cascades. J Biochem. 149:15–25.
2011.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
46
|
Fan ZX and Yang J: The role of microRNAs
in regulating myocardial ischemia reperfusion injury. Saudi Med J.
36:787–793. 2015.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
47
|
Ong SB, Katwadi K, Kwek XY, Ismail NI,
Chinda K, Ong SG and Hausenloy DJ: Non-coding RNAs as therapeutic
targets for preventing myocardial ischemia-reperfusion injury.
Expert Opin Ther Targets. 22:247–261. 2018.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
48
|
Xing X, Guo S, Zhang G, Liu Y, Bi S, Wang
X and Lu Q: miR-26a-5p protects against myocardial
ischemia/reperfusion injury by regulating the PTEN/PI3K/AKT
signaling pathway. Braz J Med Biol Res. 53(e9106)2020.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
49
|
Wang JX, Zhang XJ, Li Q, Wang K, Wang Y,
Jiao JQ, Feng C, Teng S, Zhou LY, Gong Y, et al: MicroRNA-103/107
regulate programmed necrosis and myocardial ischemia/reperfusion
injury through targeting FADD. Circ Res. 117:352–363.
2015.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
50
|
Zhao J, Li X, Hu J, Chen F, Qiao S, Sun X,
Gao L, Xie J and Xu B: Mesenchymal stromal cell-derived exosomes
attenuate myocardial ischaemia-reperfusion injury through
miR-182-regulated macrophage polarization. Cardiovasc Res.
115:1205–1216. 2019.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
51
|
Hullinger TG, Montgomery RL, Seto AG,
Dickinson BA, Semus HM, Lynch JM, Dalby CM, Robinson K, Stack C,
Latimer PA, et al: Inhibition of miR-15 protects against cardiac
ischemic injury. Circ Res. 110:71–81. 2012.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
52
|
Chaudhuri AD, Choi DC, Kabaria S, Tran A
and Junn E: MicroRNA-7 regulates the function of mitochondrial
permeability transition pore by targeting VDAC1 expression. J Biol
Chem. 291:6483–6493. 2016.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
53
|
Shao W, Zhang SZ, Tang M, Zhang XH, Zhou
Z, Yin YQ, Zhou QB, Huang YY, Liu YJ, Wawrousek E, et al:
Suppression of neuroinflammation by astrocytic dopamine D2
receptors via αB-crystallin. Nature. 494:90–94. 2013.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|