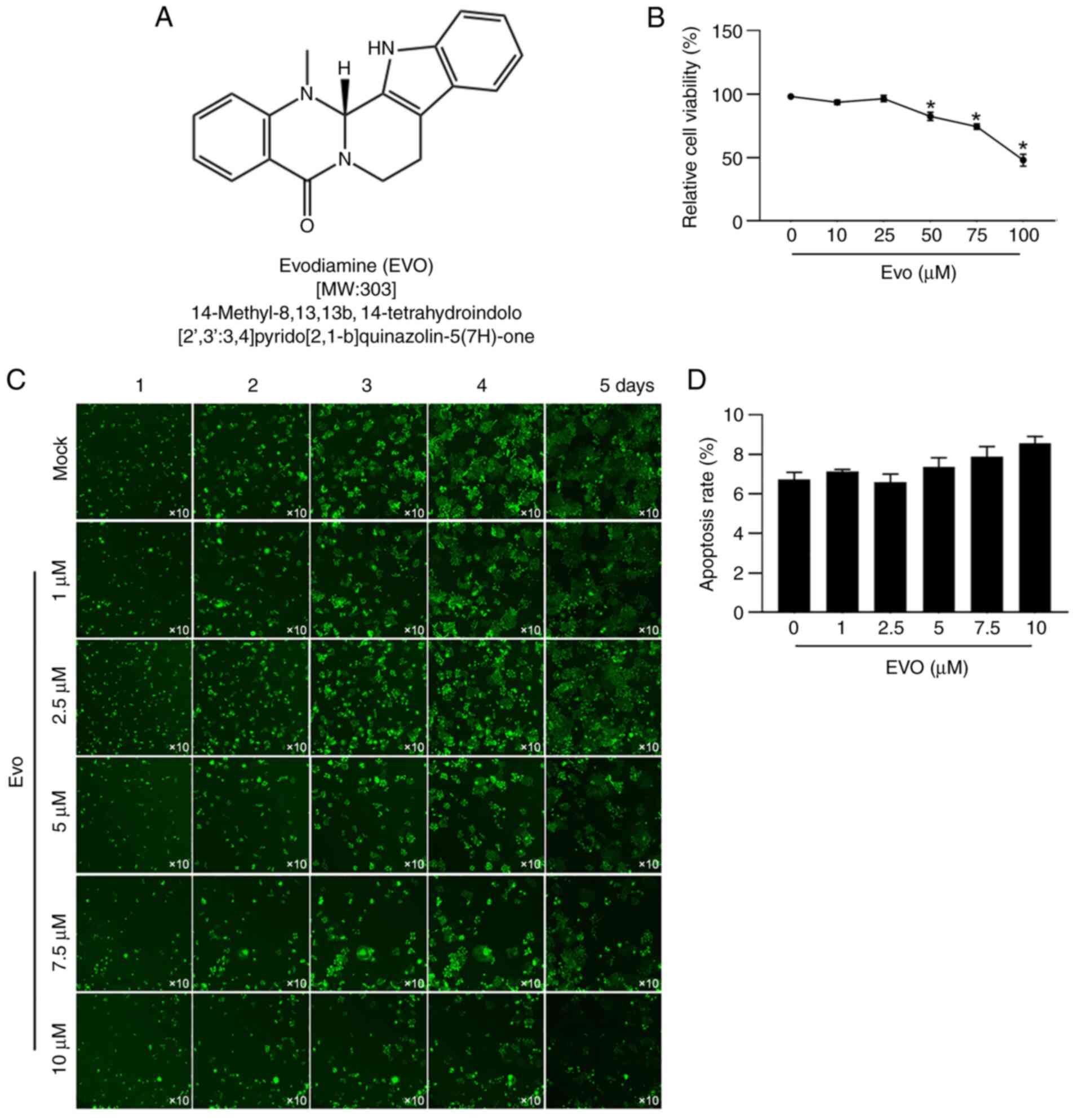
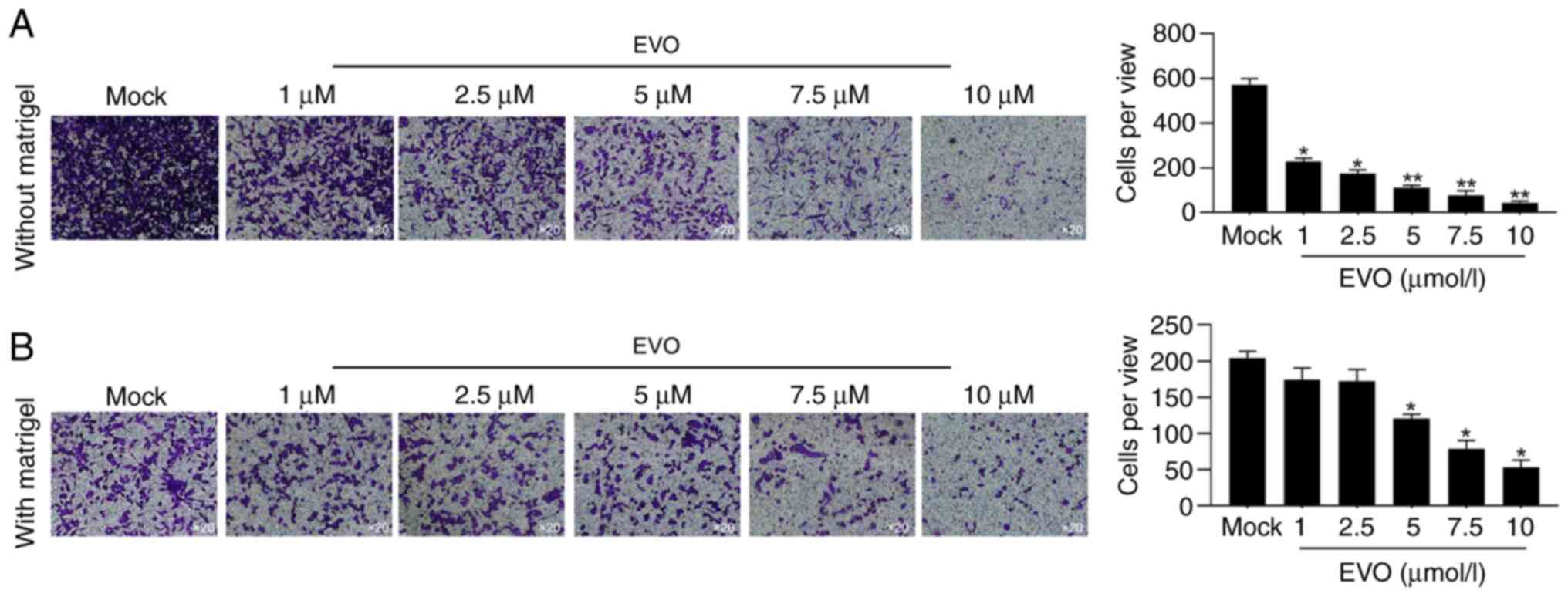
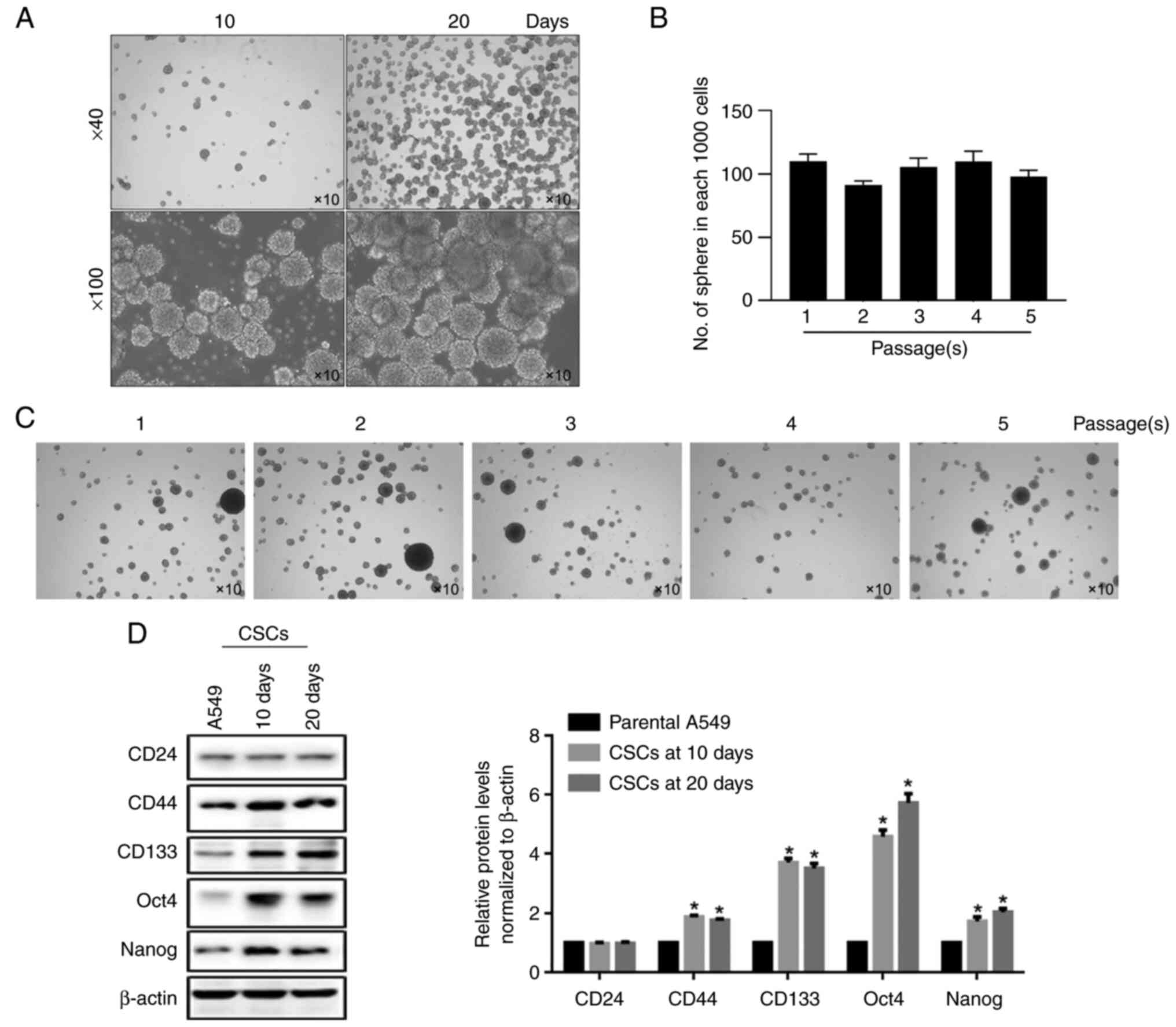
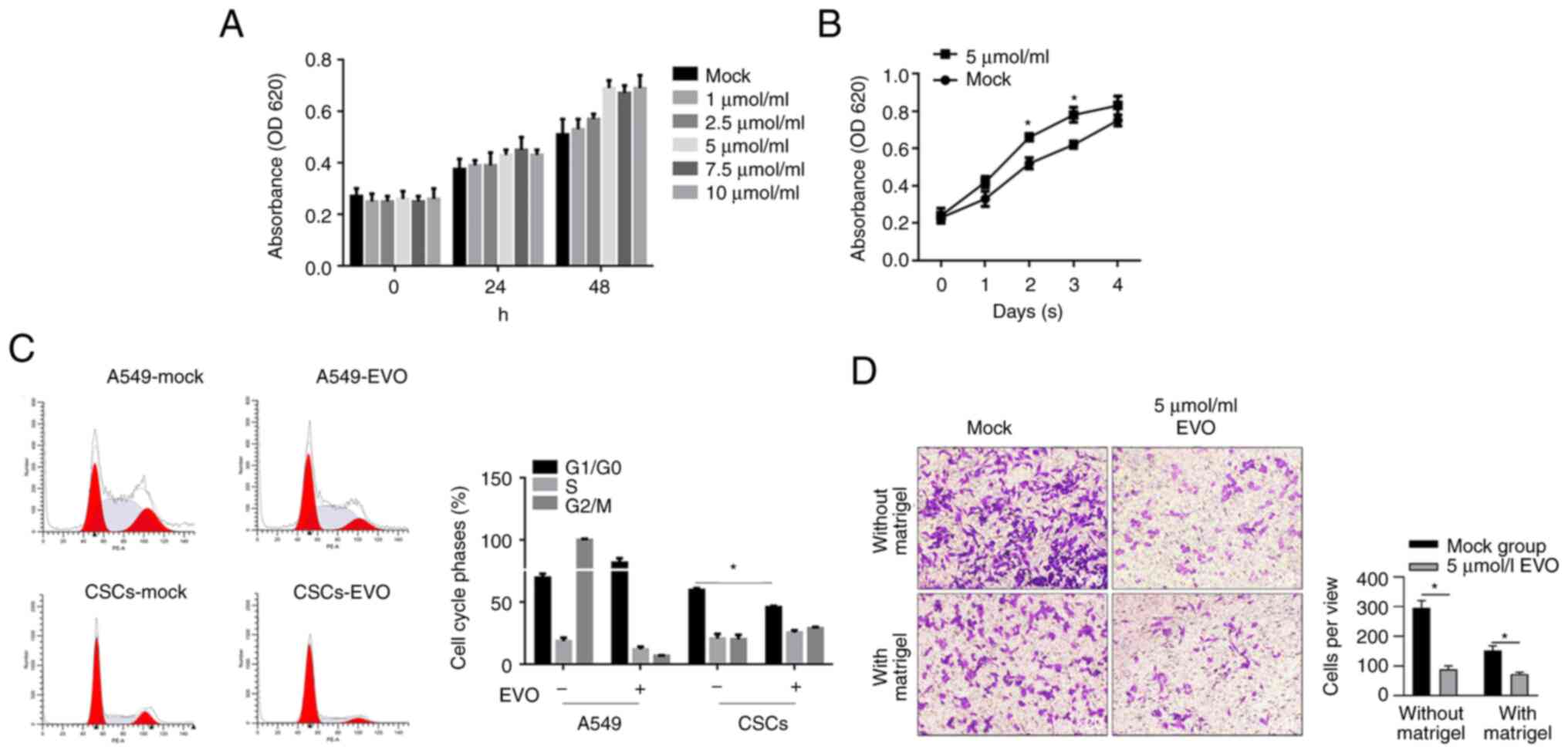
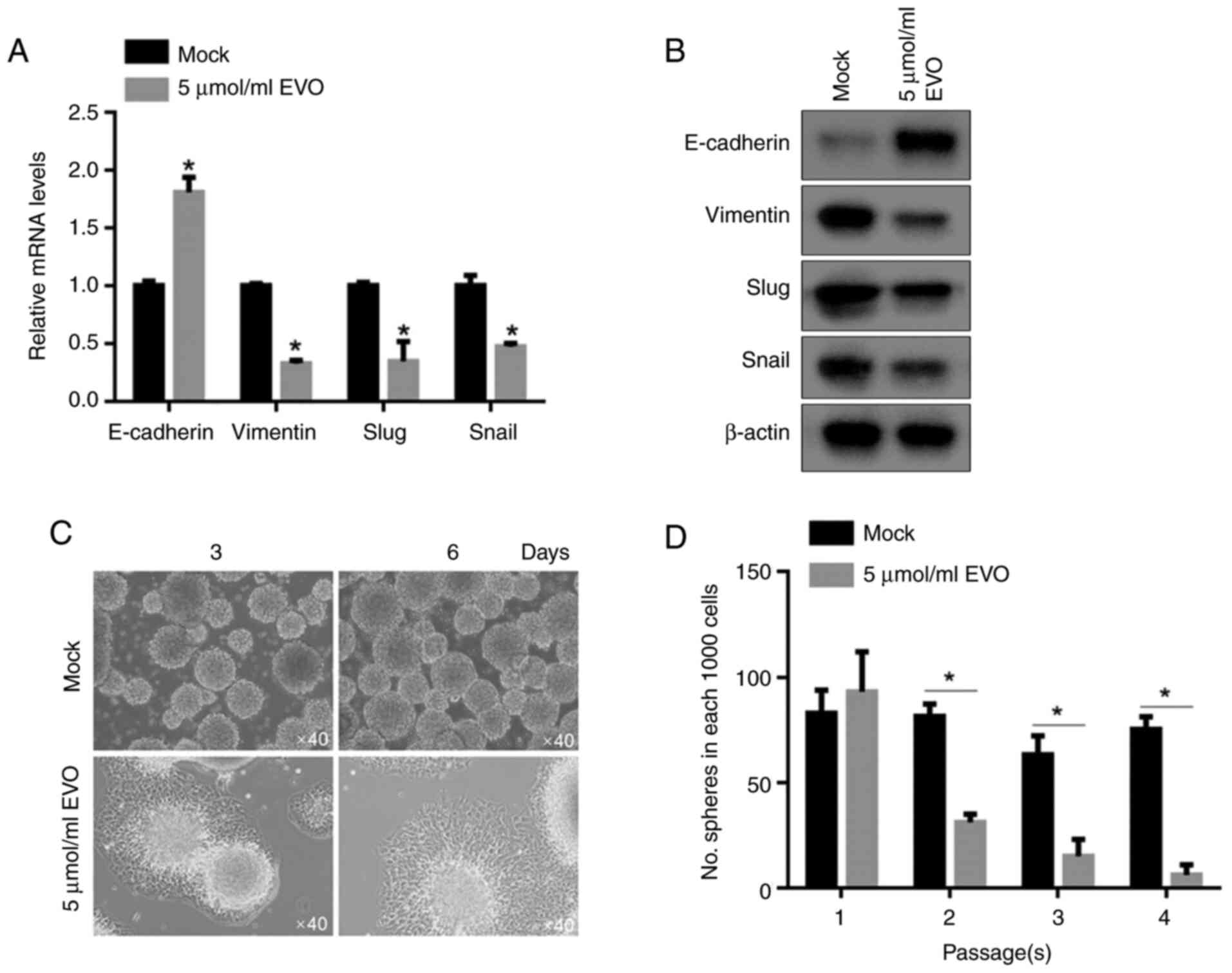
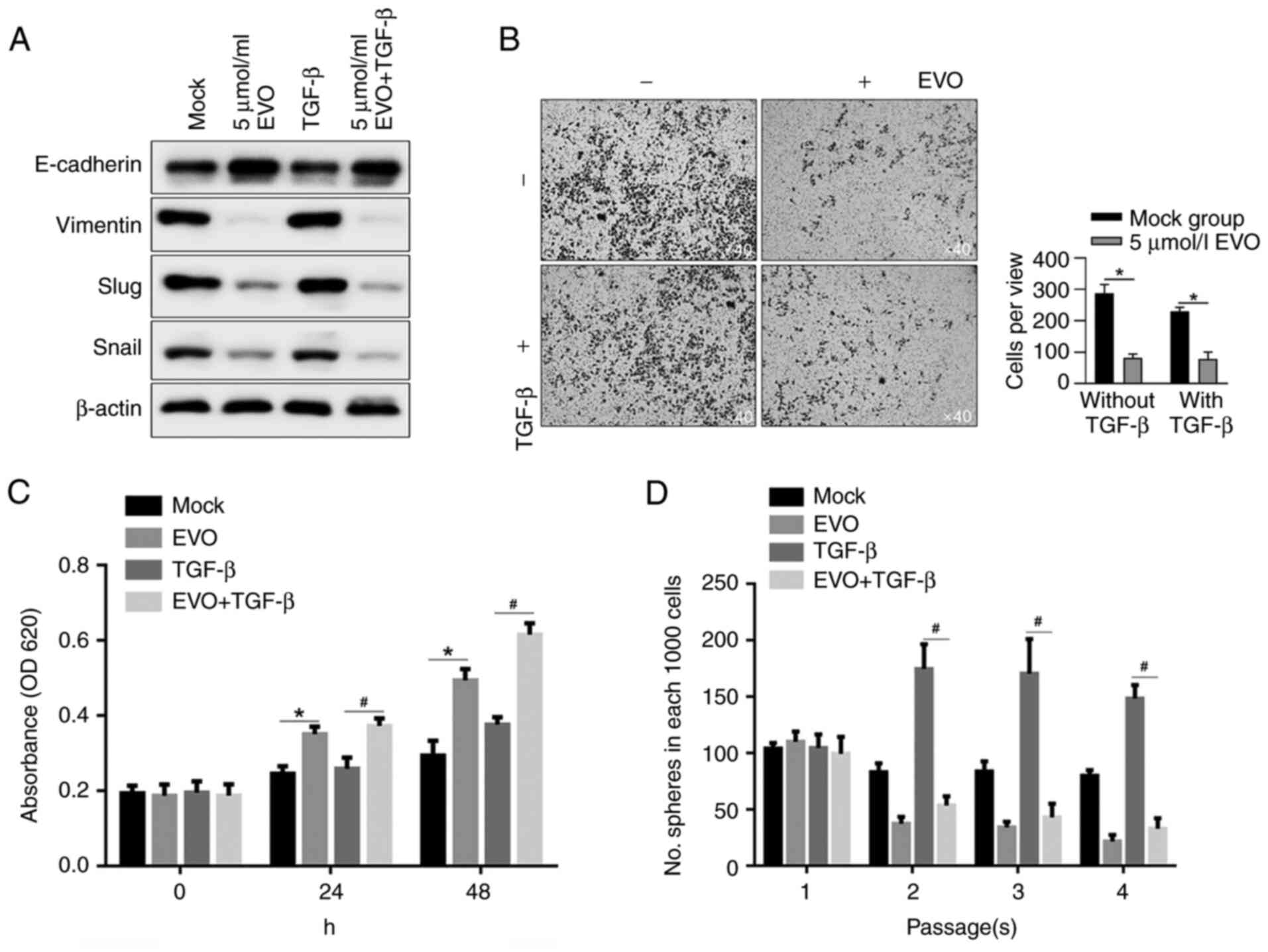
|
1
|
Yu H, Jin H, Gong W, Wang Z and Liang H:
Pharmacological actions of multi-target-directed evodiamine.
Molecules. 18:1826–1843. 2013.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
2
|
Huang DM, Guh JH, Huang YT, Chueh SC,
Chiang PC and Teng CM: Induction of mitotic arrest and apoptosis in
human prostate cancer pc-3 cells by evodiamine. J Urol.
173:256–261. 2005.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
3
|
Zhao LC, Li J, Liao K, Luo N, Shi QQ, Feng
ZQ and Chen DL: Evodiamine induces apoptosis and inhibits migration
of HCT-116 human colorectal cancer cells. Int J Mol Sci.
16:27411–27421. 2015.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
4
|
Kan SF, Huang WJ, Lin LC and Wang PS:
Inhibitory effects of evodiamine on the growth of human prostate
cancer cell line LNCaP. Int J Cancer. 110:641–651. 2004.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
5
|
Wang KL, Hsia SM, Yeh JY, Cheng SC, Wang
PS and Wang SW: Anti-proliferative effects of evodiamine on human
breast cancer cells. PLoS One. 8(e67297)2013.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
6
|
Ogasawara M, Matsubara T and Suzuki H:
Inhibitory effects of evodiamine on in vitro invasion and
experimental lung metastasis of murine colon cancer cells. Biol
Pharm Bull. 24:917–920. 2001.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
7
|
Zhang C, Fan X, Xu X, Yang X, Wang X and
Liang HP: Evodiamine induces caspase-dependent apoptosis and S
phase arrest in human colon Lovo cells. Anticancer Drugs.
21:766–776. 2010.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
8
|
Ferlay J, Shin HR, Bray F, Forman D,
Mathers C and Parkin DM: Estimates of worldwide burden of cancer in
2008: GLOBOCAN 2008. Int J Cancer. 127:2893–2917. 2010.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
9
|
Lynch TJ, Adjei AA, Bunn PA Jr, Eisen TG,
Engelman J, Goss GD, Haber DA, Heymach JV, Jänne PA, Johnson BE, et
al: Summary statement: Novel agents in the treatment of lung
cancer: Advances in epidermal growth factor receptor-targeted
agents. Clin Cancer Res. 12 (14 Pt 2):4365s–4371s. 2006.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
10
|
Reya T, Morrison SJ, Clarke MF and
Weissman IL: Stem cells, cancer, and cancer stem cells. Nature.
414:105–111. 2001.PubMed/NCBI View
Article : Google Scholar
|
|
11
|
Wang JC and Dick JE: Cancer stem cells:
Lessons from leukaemia. Trends Cell Biol. 15:494–501.
2005.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
12
|
Clarke MF, Dick JE, Dirks PB, Eaves CJ,
Jamieson CH, Jones DL, Visvader J, Weissman IL and Wahl GM: Cancer
stem cells-perspectives on current status and future directions:
AACR workshop on cancer stem cells. Cancer Res. 66:9339–9344.
2006.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
13
|
Tirino V, Camerlingo R, Franco R, Malanga
D, La Rocca A, Viglietto G, Rocco G and Pirozzi G: The role of
CD133 in the identification and characterisation of
tumour-initiating cells in non-small-cell lung cancer. Eur J
Cardiothorac Surg. 36:446–453. 2009.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
14
|
Chiou SH, Wang ML, Chou YT, Chen CJ, Hong
CF, Hsieh WJ, Chang HT, Chen YS, Lin TW, Hsu HS and Wu CW:
Coexpression of Oct4 and Nanog enhances malignancy in lung
adenocarcinoma by inducing cancer stem cell-like properties and
epithelial-mesenchymal transdifferentiation. Cancer Res.
70:10433–10444. 2010.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
15
|
Yuan P, Kadara H, Behrens C, Tang X, Woods
D, Solis LM, Huang J, Spinola M, Dong W, Yin G, et al: Sex
determining region Y-Box 2 (SOX2) is a potential cell-lineage gene
highly expressed in the pathogenesis of squamous cell carcinomas of
the lung. PLoS One. 5(e9112)2010.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
16
|
Eramo A, Lotti F, Sette G, Pilozzi E,
Biffoni M, Di Virgilio A, Conticello C, Ruco L, Peschle C and De
Maria R: Identification and expansion of the tumorigenic lung
cancer stem cell population. Cell Death Differ. 15:504–514.
2008.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
17
|
Justilien V, Regala RP, Tseng IC, Walsh
MP, Batra J, Radisky ES, Murray NR and Fields AP: A. Fields, Matrix
Metalloproteinase-10 is required for lung cancer stem cell
maintenance, tumor initation and metastatic potential. PLoS One.
7(e35040)2010.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
18
|
Zhang L, Wang D, Li Y, Liu Y, Xie X, Wu Y,
Zhou Y, Ren J, Zhang J, Zhu H and Su Z: CCL21/CCR7 axis contributed
to CD133+ pancreatic cancer stem-like cell metastasis via EMT and
Erk/NF-kB pathway. PLoS One. 11(e0158529)2016.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
19
|
Mani SA, Guo W, Liao MJ, Eaton EN, Ayyanan
A, Zhou AY, Brooks M, Reinhard F, Zhang CC, Shipitsin M, et al: The
epithelial-mesenchymal transition generates cells with properties
of stem cells. Cell. 133:704–715. 2008.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
20
|
Morel AP, Lièvre M, Thomas C, Hinkal G,
Ansieau S and Puisieux A: Generation of breast cancer stem cells
through epithelial-mesenchymal transition. PLoS One.
3(e2888)2008.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
21
|
Livak KJ and Schmittgen TD: Analysis of
relative gene expression data using real-time quantitative PCR and
the 2(-Delta Delta C(T)) Method. Methods. 25:402–408.
2001.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
22
|
Spaderna S, Schmalhofer O, Hlubek F, Berx
G, Eger A, Merkel S, Jung A, Kirchner T and Brabletz T: A
transient, EMT-linked loss of basement membranes indicates
metastasis and poor survival in colorectal cancer.
Gastroenterology. 131:830–840. 2006.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
23
|
Prall F: Tumour budding in colorectal
carcinoma. Histopathology. 50:151–162. 2007.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
24
|
Tiwari N, Gheldof A, Tatari M and
Christofori G: EMT as the ultimate survival mechanism of cancer
cells. Semin Cancer Biol. 22:194–207. 2012.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|