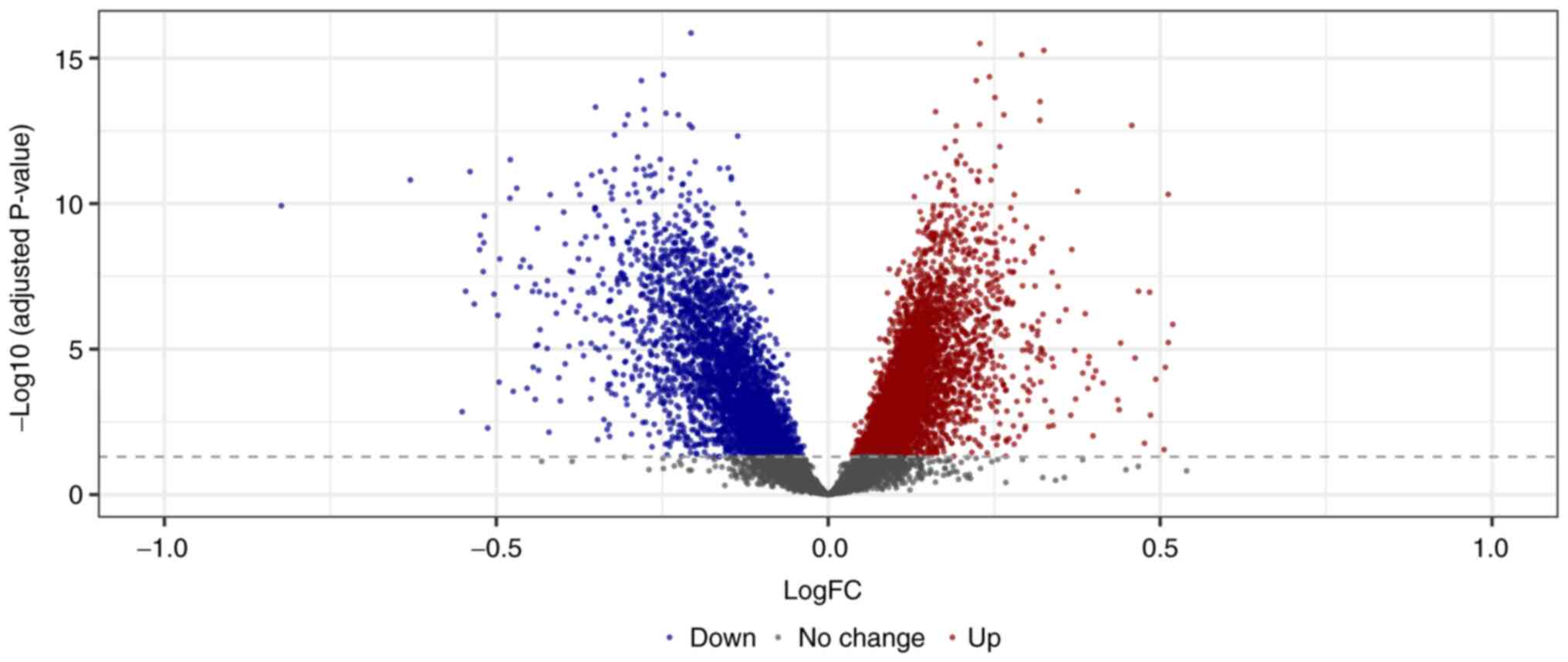
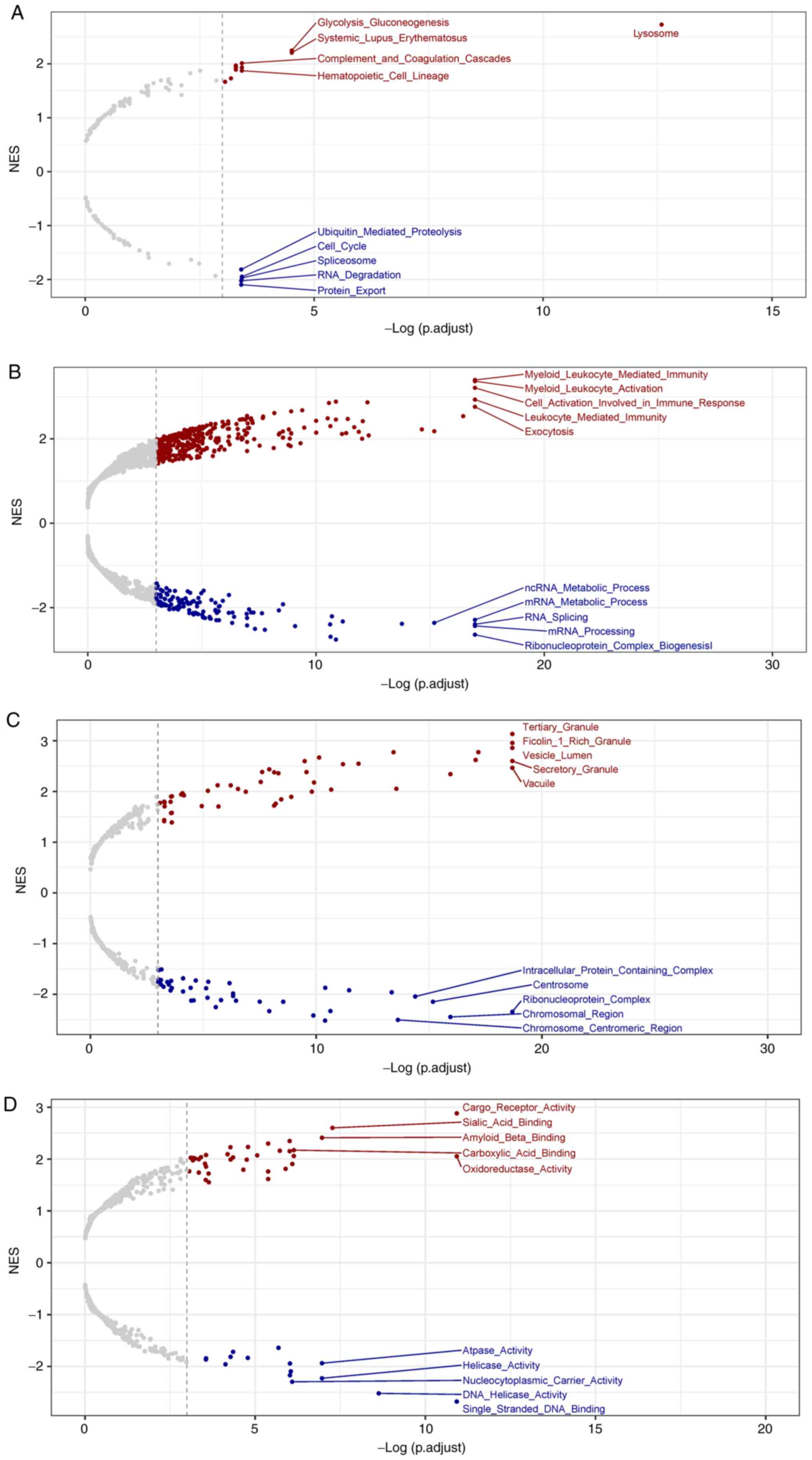
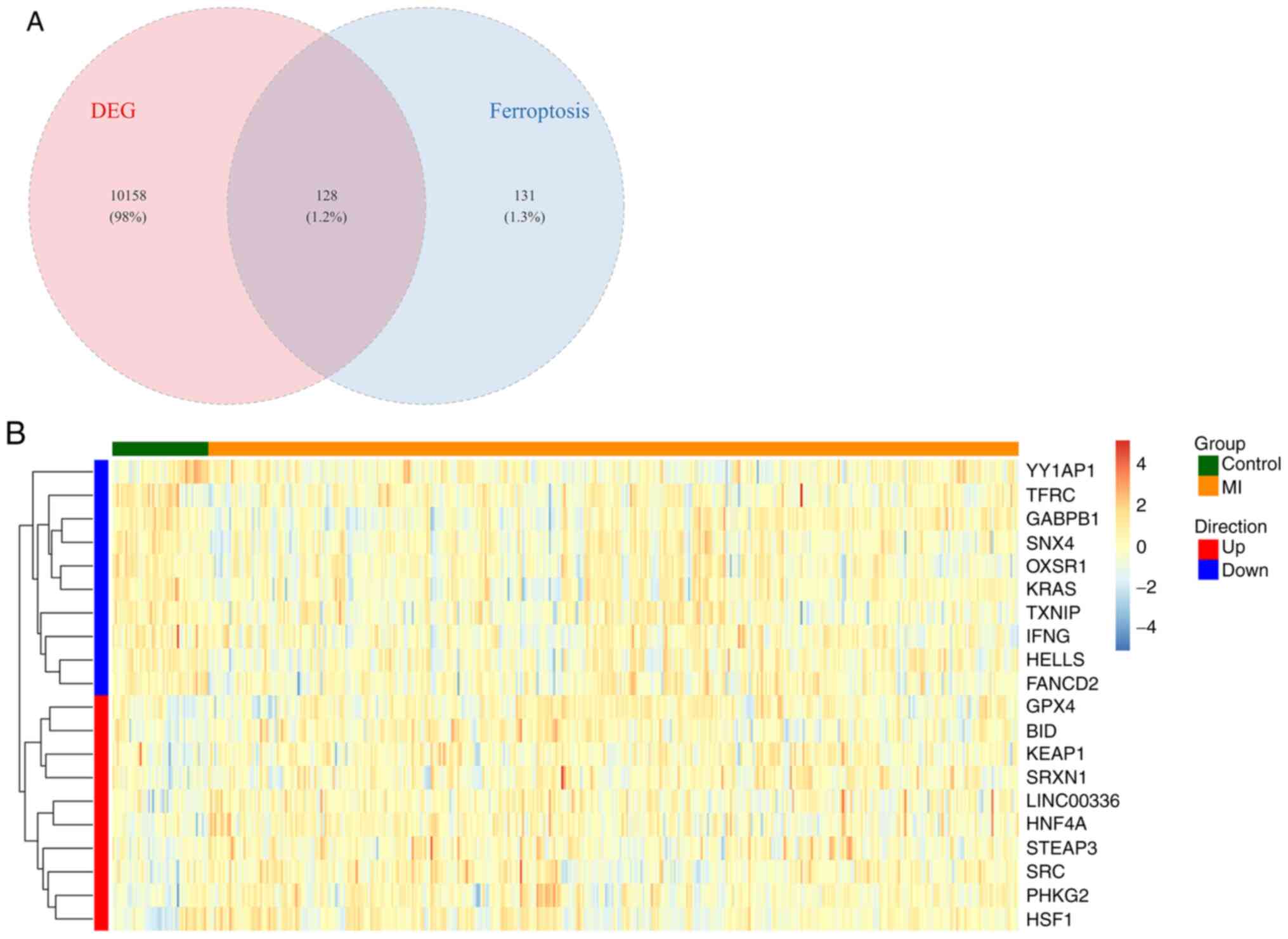
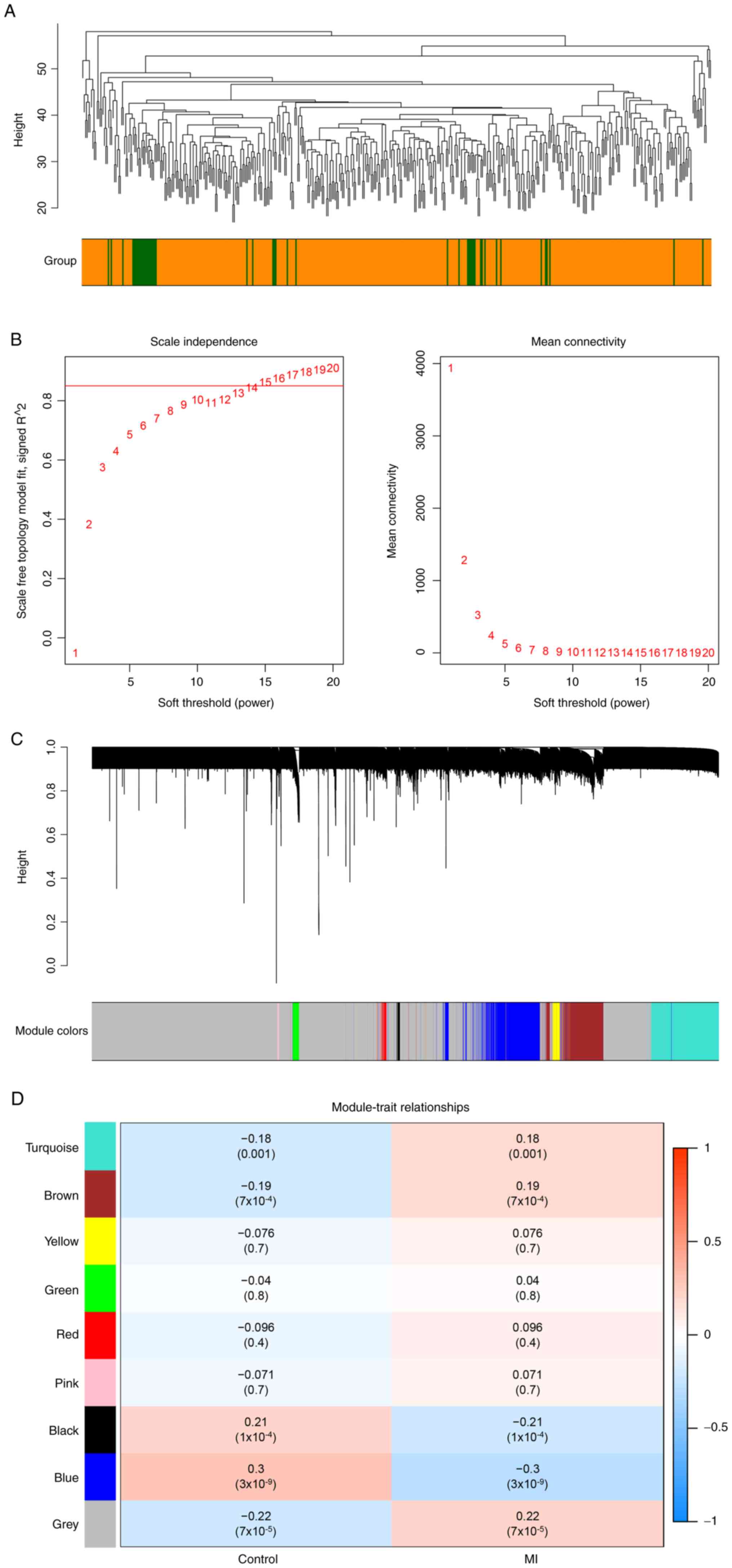
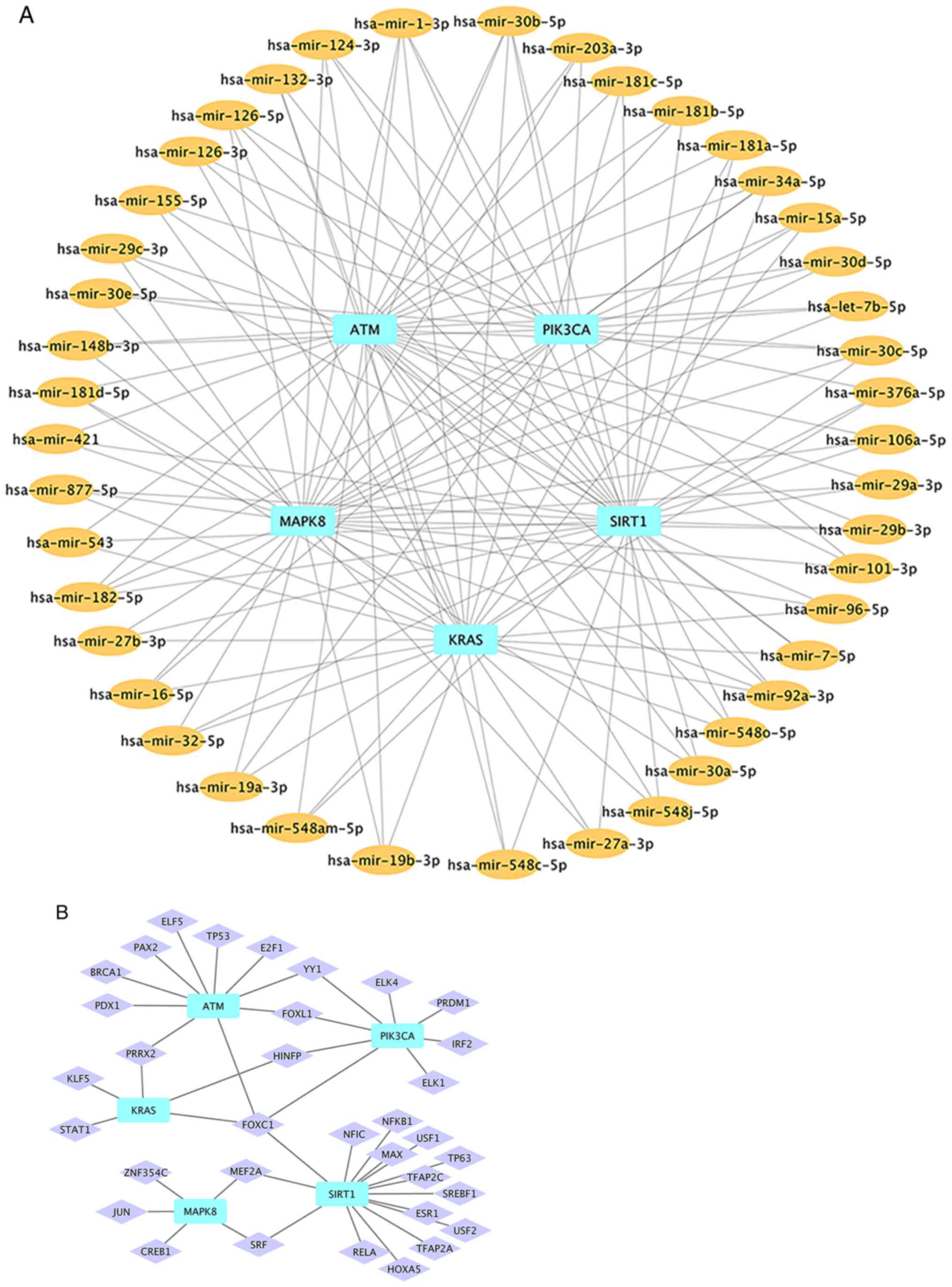
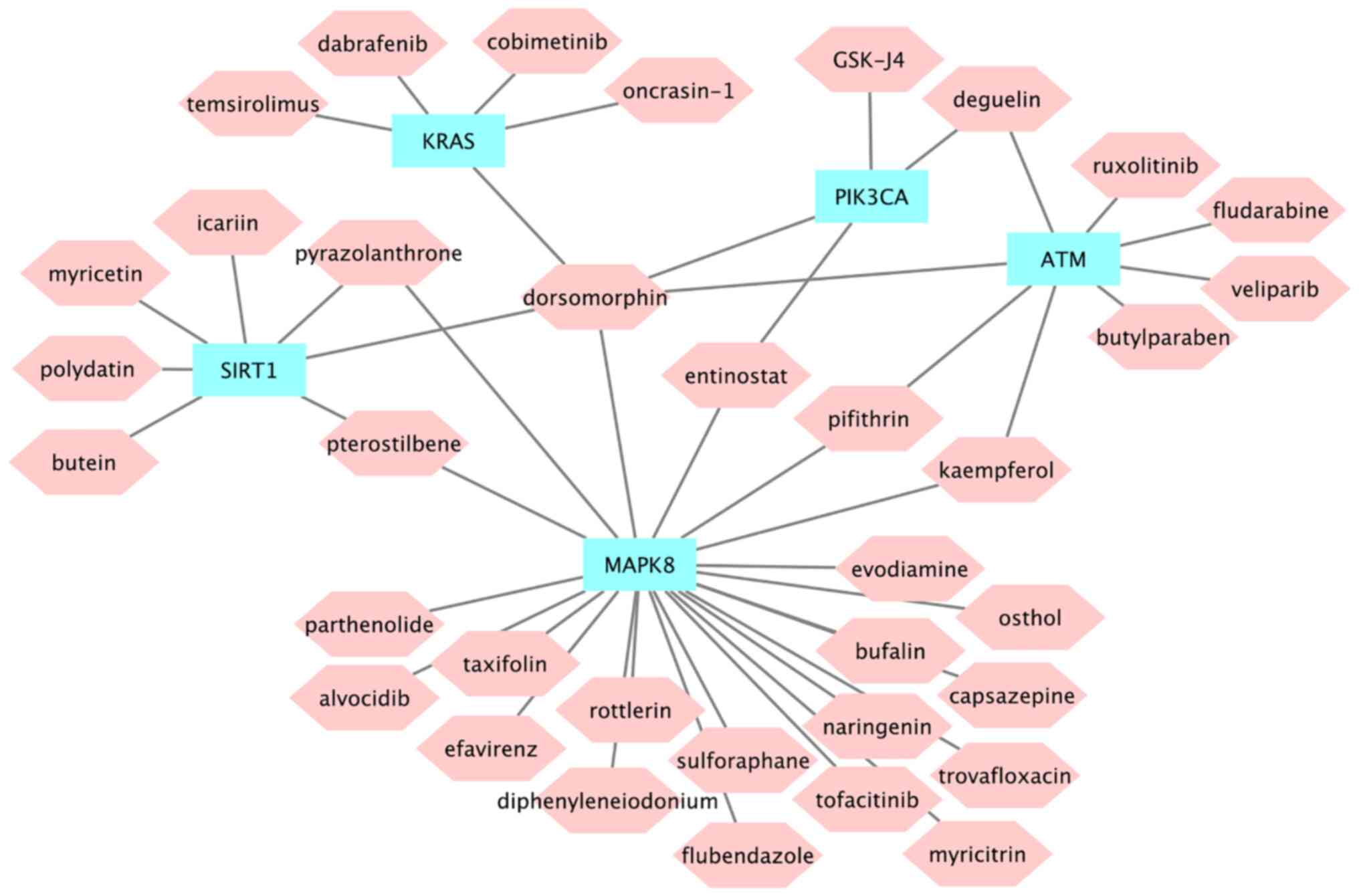
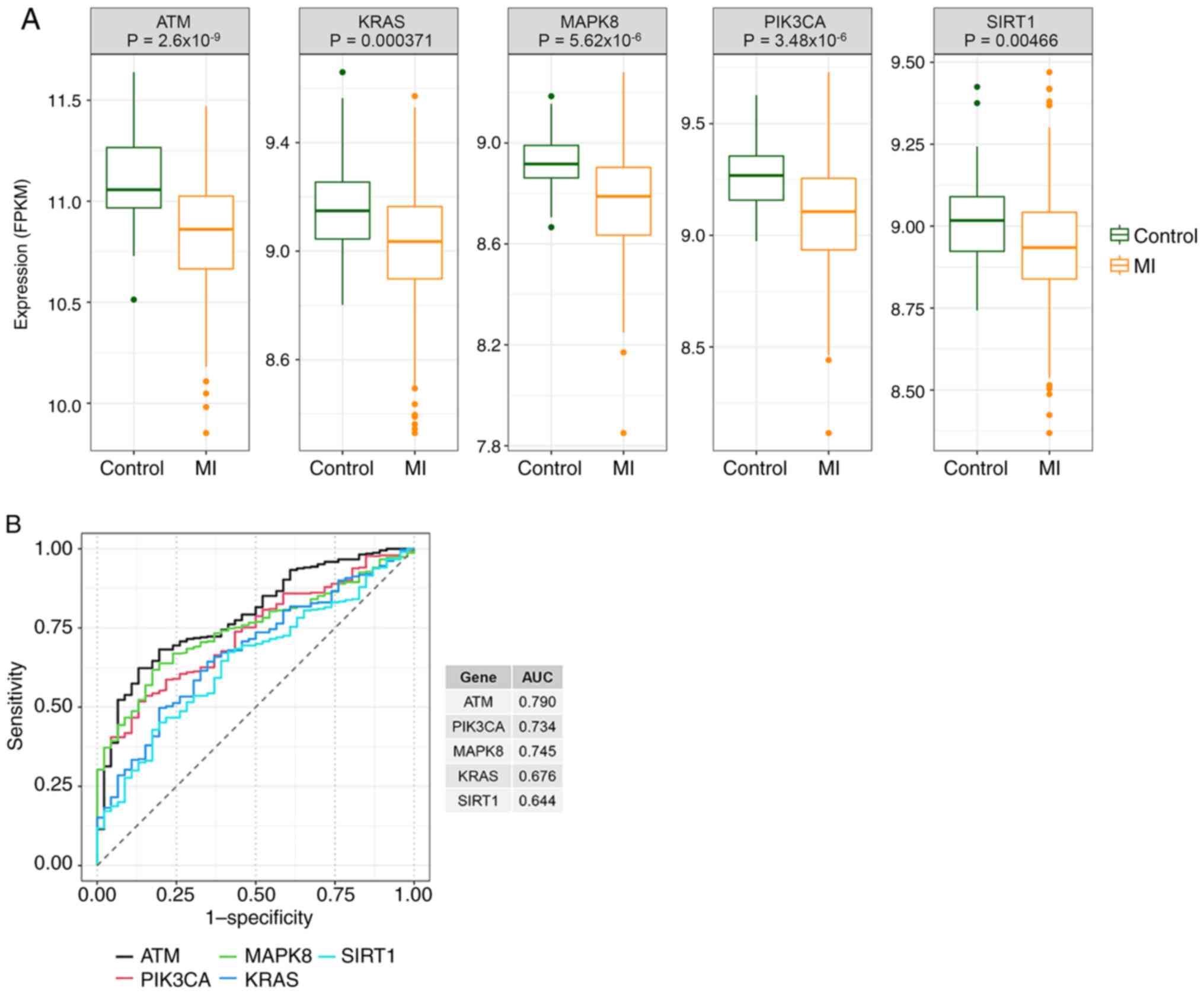
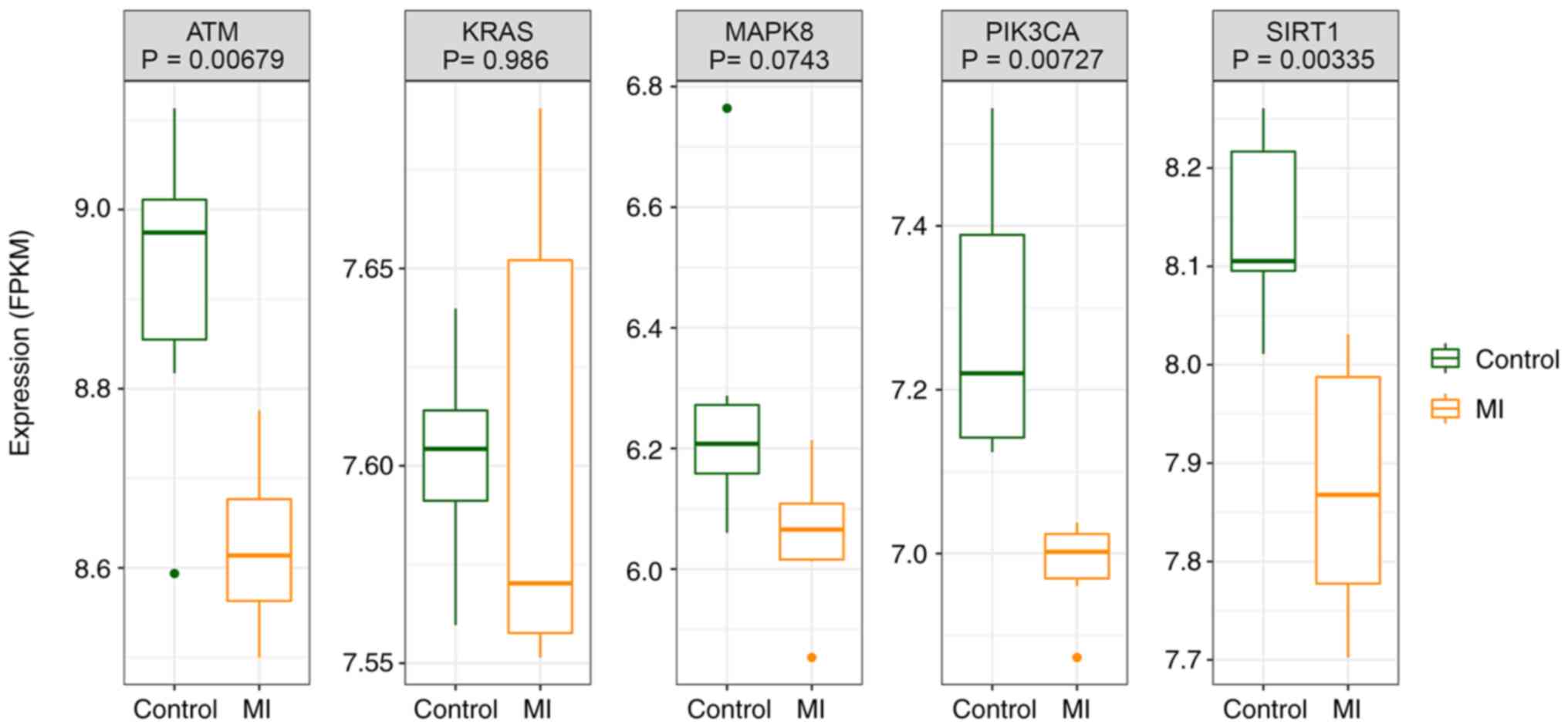
|
1
|
Camacho X, Nedkoff L, Wright FL, Nghiem N,
Buajitti E, Goldacre R, Rosella LC, Seminog O, Tan EJ, Hayes A, et
al: Relative contribution of trends in myocardial infarction event
rates and case fatality to declines in mortality: An international
comparative study of 1·95 million events in 80·4 million people in
four countries. Lancet Public Health. 7:e229–e239. 2022.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
2
|
Thygesen K, Alpert JS, Jaffe AS, Simoons
ML, Chaitman BR, White HD, Thygesen K, Alpert JS, White HD, Jaffe
AS, et al: Third universal definition of myocardial infarction. J
Am Coll Cardiol. 60:1581–1598. 2012.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
3
|
Thygesen K, Alpert JS, Jaffe AS, Chaitman
BR, Bax JJ, Morrow DA and White HD: Fourth universal definition of
myocardial infarction (2018). J Am Coll Cardiol. 72:2231–2264.
2018.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
4
|
Collet JP, Thiele H, Barbato E, Barthélémy
O, Bauersachs J, Bhatt DL, Dendale P, Dorobantu M, Edvardsen T,
Folliguet T, et al: 2020 ESC guidelines for the management of acute
coronary syndromes in patients presenting without persistent
ST-segment elevation. Eur Heart J. 42:1289–1367. 2021.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
5
|
Ibanez B, James S, Agewall S, Antunes MJ,
Bucciarelli-Ducci C, Bueno H, Caforio A, Crea F, Goudevenos JA,
Halvorsen S, et al: 2017 ESC guidelines for the management of acute
myocardial infarction in patients presenting with ST-segment
elevation: The task force for the management of acute myocardial
infarction in patients presenting with ST-segment elevation of the
European society of cardiology (ESC). Eur Heart J. 39:119–177.
2018.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
6
|
Spione F, Arevalos V, Gabani R, Sabaté M
and Brugaletta S: Coronary microvascular angina: A state-of-the-art
review. Front Cardiovasc Med. 9(800918)2022.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
7
|
Jiang X, Stockwell BR and Conrad M:
Ferroptosis: Mechanisms, biology and role in disease. Nat Rev Mol
Cell Biol. 22:266–282. 2021.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
8
|
Wang J, Liu Y, Wang Y and Sun L: The
cross-link between ferroptosis and kidney diseases. Oxid Med Cell
Longev. 2021(6654887)2021.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
9
|
Chen C, Wang D, Yu Y, Zhao T, Min N, Wu Y,
Kang L, Zhao Y, Du L, Zhang M, et al: Legumain promotes tubular
ferroptosis by facilitating chaperone-mediated autophagy of GPX4 in
AKI. Cell Death Dis. 12(65)2021.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
10
|
Zhao L, Zhou X, Xie F and Zhang L, Yan H,
Huang J, Zhang C, Zhou F, Chen J and Zhang L: Ferroptosis in cancer
and cancer immunotherapy. Cancer Commun (Lond). 42:88–116.
2022.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
11
|
Wu X, Li Y, Zhang S and Zhou X:
Ferroptosis as a novel therapeutic target for cardiovascular
disease. Theranostics. 11:3052–3059. 2021.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
12
|
Li W, Li W, Leng Y, Xiong Y and Xia Z:
Ferroptosis is involved in diabetes myocardial ischemia/reperfusion
injury through endoplasmic reticulum stress. DNA Cell Biol.
39:210–225. 2020.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
13
|
Ma S, Sun L, Wu W, Wu J, Sun Z and Ren J:
USP22 protects against myocardial ischemia-reperfusion injury via
the SIRT1-p53/SLC7A11-dependent inhibition of ferroptosis-induced
cardiomyocyte death. Front Physiol. 11(551318)2020.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
14
|
Jelinek A, Heyder L, Daude M, Plessner M,
Krippner S, Grosse R, Diederich WE and Culmsee C: Mitochondrial
rescue prevents glutathione peroxidase-dependent ferroptosis. Free
Radic Biol Med. 117:45–57. 2018.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
15
|
Chen HY, Xiao ZZ, Ling X, Xu RN, Zhu P and
Zheng SY: ELAVL1 is transcriptionally activated by FOXC1 and
promotes ferroptosis in myocardial ischemia/reperfusion injury by
regulating autophagy. Mol Med. 27(14)2021.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
16
|
Fang X, Wang H, Han D, Xie E, Yang X, Wei
J, Gu S, Gao F, Zhu N, Yin X, et al: Ferroptosis as a target for
protection against cardiomyopathy. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA.
116:2672–2680. 2019.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
17
|
Fan Z, Cai L, Wang S, Wang J and Chen B:
Baicalin prevents myocardial ischemia/reperfusion injury through
inhibiting ACSL4 mediated ferroptosis. Front Pharmacol.
12(628988)2021.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
18
|
Eling N, Reuter L, Hazin J, Hamacher-Brady
A and Brady NR: Identification of artesunate as a specific
activator of ferroptosis in pancreatic cancer cells. Oncoscience.
2:517–532. 2015.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
19
|
Linkermann A, Skouta R, Himmerkus N, Mulay
SR, Dewitz C, De Zen F, Prokai A, Zuchtriegel G, Krombach F, Welz
PS, et al: Synchronized renal tubular cell death involves
ferroptosis. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 111:16836–16841.
2014.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
20
|
Maciejak A, Kiliszek M, Michalak M, Tulacz
D, Opolski G, Matlak K, Dobrzycki S, Segiet A, Gora M and Burzynska
B: Gene expression profiling reveals potential prognostic
biomarkers associated with the progression of heart failure. Genome
Med. 7(26)2015.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
21
|
Osmak G, Baulina N, Koshkin P and Favorova
O: Collapsing the list of myocardial infarction-related
differentially expressed genes into a diagnostic signature. J
Transl Med. 18(231)2020.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
22
|
Barrett T, Wilhite SE, Ledoux P,
Evangelista C, Kim IF, Tomashevsky M, Marshall KA, Phillippy KH,
Sherman PM, Holko M, et al: NCBI GEO: Archive for functional
genomics data sets-update. Nucleic Acids Res. 41:D991–D995.
2013.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
23
|
Tian Q, Zhou Y, Zhu L, Gao H and Yang J:
Development and validation of a ferroptosis-related gene signature
for overall survival prediction in lung adenocarcinoma. Front Cell
Dev Biol. 9(684259)2021.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
24
|
Chan B: Data analysis using R programming.
Adv Exp Med Biol. 1082:47–122. 2018.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
25
|
Love MI, Huber W and Anders S: Moderated
estimation of fold change and dispersion for RNA-seq data with
DESeq2. Genome Biol. 15(550)2014.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
26
|
Qian L, Xia Z, Zhang M, Han Q, Hu D, Qi S,
Xing D, Chen Y and Zhao X: Integrated bioinformatics-based
identification of potential diagnostic biomarkers associated with
diabetic foot ulcer development. J Diabetes Res.
2021(5445349)2021.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
27
|
Langfelder P and Horvath S: WGCNA: An R
package for weighted correlation network analysis. BMC
Bioinformatics. 9(559)2008.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
28
|
The Gene Ontology Consortium. Expansion of
the gene ontology knowledgebase and resources. Nucleic Acids Res.
45:D331–D338. 2017.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
29
|
Kanehisa M and Goto S: KEGG: Kyoto
encyclopedia of genes and genomes. Nucleic Acids Res. 28:27–30.
2000.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
30
|
Szklarczyk D, Franceschini A, Wyder S,
Forslund K, Heller D, Huerta-Cepas J, Simonovic M, Roth A, Santos
A, Tsafou KP, et al: STRING v10: Protein-protein interaction
networks, integrated over the tree of life. Nucleic Acids Res.
43:D447–D452. 2015.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
31
|
Shannon P, Markiel A, Ozier O, Baliga NS,
Wang JT, Ramage D, Amin N, Schwikowski B and Ideker T: Cytoscape: A
software environment for integrated models of biomolecular
interaction networks. Genome Res. 13:2498–2504. 2003.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
32
|
Robin X, Turck N, Hainard A, Tiberti N,
Lisacek F, Sanchez JC and Müller M: pROC: An open-source package
for R and S+ to analyze and compare ROC curves. BMC Bioinformatics.
12(77)2011.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
33
|
Zhang Y, Shen B, Zhuge L and Xie Y:
Identification of differentially expressed genes between the colon
and ileum of patients with inflammatory bowel disease by gene
co-expression analysis. J Int Med Res.
48(300060519887268)2020.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
34
|
Han Y, Yu G, Sarioglu H,
Caballero-Martinez A, Schlott F, Ueffing M, Haase H, Peschel C and
Krackhardt AM: Proteomic investigation of the interactome of FMNL1
in hematopoietic cells unveils a role in calcium-dependent membrane
plasticity. J Proteomics. 78:72–82. 2013.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
35
|
Davis AP, Grondin CJ, Johnson RJ, Sciaky
D, Wiegers J, Wiegers TC and Mattingly CJ: Comparative
toxicogenomics database (CTD): Update 2021. Nucleic Acids Res.
49:D1138–D1143. 2021.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
36
|
Chang L, Zhou G, Soufan O and Xia J:
miRNet 2.0: Network-based visual analytics for miRNA functional
analysis and systems biology. Nucleic Acids Res. 48:W244–W251.
2020.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
37
|
Diamond GA: A clinically relevant
classification of chest discomfort. J Am Coll Cardiol. 1:574–575.
1983.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
38
|
Montalescot G, Sechtem U, Achenbach S,
Andreotti F, Arden C, Budaj A, Bugiardini R, Crea F, Cuisset T, Di
Mario C, et al: 2013 ESC guidelines on the management of stable
coronary artery disease: The task force on the management of stable
coronary artery disease of the European society of cardiology. Eur
Heart J. 34:2949–3003. 2013.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
39
|
Fihn SD, Gardin JM, Abrams J, Berra K,
Blankenship JC, Dallas AP, Douglas PS, Foody JM, Gerber TC,
Hinderliter AL, et al: 2012 ACCF/AHA/ACP/AATS/PCNA/SCAI/STS
guideline for the diagnosis and management of patients with stable
ischemic heart disease: A report of the American college of
cardiology foundation/American heart association task force on
practice guidelines, and the American college of physicians,
American association for thoracic surgery, preventive
cardiovascular nurses association, society for cardiovascular
angiography and interventions, and society of thoracic surgeons.
Circulation. 126:e354–e471. 2012.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
40
|
Livak KJ and Schmittgen TD: Analysis of
relative gene expression data using real-time quantitative PCR and
the 2(-Delta Delta C(T)) method. Methods. 25:402–408.
2001.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
41
|
Lamb J, Crawford ED, Peck D, Modell JW,
Blat IC, Wrobel MJ, Lerner J, Brunet JP, Subramanian A, Ross KN, et
al: The connectivity map: Using gene-expression signatures to
connect small molecules, genes, and disease. Science.
313:1929–1935. 2006.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
42
|
Wen W, Wu P, Zhang Y, Chen Z, Sun J and
Chen H: Comprehensive analysis of NAFLD and the therapeutic target
identified. Front Cell Dev Biol. 9(704704)2021.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
43
|
Contessotto P and Pandit A: Therapies to
prevent post-infarction remodelling: From repair to regeneration.
Biomaterials. 275(120906)2021.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
44
|
Zhou T, Chuang CC and Zuo L: Molecular
characterization of reactive oxygen species in myocardial
ischemia-reperfusion injury. Biomed Res Int.
2015(864946)2015.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
45
|
Khosravi M, Poursaleh A, Ghasempour G,
Farhad S and Najafi M: The effects of oxidative stress on the
development of atherosclerosis. Biol Chem. 400:711–732.
2019.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
46
|
Ravingerová T, Kindernay L, Barteková M,
Ferko M, Adameová A, Zohdi V, Bernátová I, Ferenczyová K and Lazou
A: The molecular mechanisms of iron metabolism and its role in
cardiac dysfunction and cardioprotection. Int J Mol Sci.
21(7889)2020.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
47
|
Kura B, Bacova BS, Kalocayova B, Sykora M
and Slezak J: Oxidative stress-responsive MicroRNAs in heart
injury. Int J Mol Sci. 21(358)2020.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
48
|
Su LJ, Zhang JH, Gomez H, Murugan R, Hong
X, Xu D, Jiang F and Peng ZY: Reactive oxygen species-induced lipid
peroxidation in apoptosis, autophagy, and ferroptosis. Oxid Med
Cell Longev. 2019(5080843)2019.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
49
|
Liu Y, Wang Y, Liu J, Kang R and Tang D:
Interplay between MTOR and GPX4 signaling modulates
autophagy-dependent ferroptotic cancer cell death. Cancer Gene
Ther. 28:55–63. 2021.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
50
|
Baba Y, Higa JK, Shimada BK, Horiuchi KM,
Suhara T, Kobayashi M, Woo JD, Aoyagi H, Marh KS, Kitaoka H and
Matsui T: Protective effects of the mechanistic target of rapamycin
against excess iron and ferroptosis in cardiomyocytes. Am J Physiol
Heart Circ Physiol. 314:H659–H668. 2018.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
51
|
Shen Y, Chen X, Chi C, Wang H, Xue J, Su
D, Wang H, Li M, Liu B and Dong Q: Smooth muscle cell-specific
knockout of FBW7 exacerbates intracranial atherosclerotic stenosis.
Neurobiol Dis. 132(104584)2019.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
52
|
Ji Y, Luo J, Zeng J, Fang Y, Liu R, Luan F
and Zeng N: Xiaoyao pills ameliorate depression-like behaviors and
oxidative stress induced by olfactory bulbectomy in rats via the
activation of the PIK3CA-AKT1-NFE2L2/BDNF signaling pathway. Front
Pharmacol. 12(643456)2021.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
53
|
Park S, Shin J, Bae J, Han D, Park SR,
Shin J, Lee SK and Park HW: SIRT1 alleviates LPS-induced IL-1β
production by suppressing NLRP3 inflammasome activation and ROS
production in trophoblasts. Cells. 9(728)2020.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
54
|
Chen PH, Wu J, Ding CC, Lin CC, Pan S,
Bossa N, Xu Y, Yang WH, Mathey-Prevot B and Chi JT: Kinome screen
of ferroptosis reveals a novel role of ATM in regulating iron
metabolism. Cell Death Differ. 27:1008–1022. 2020.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
55
|
Shimada K, Skouta R, Kaplan A, Yang WS,
Hayano M, Dixon SJ, Brown LM, Valenzuela CA, Wolpaw AJ and
Stockwell BR: Global survey of cell death mechanisms reveals
metabolic regulation of ferroptosis. Nat Chem Biol. 12:497–503.
2016.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
56
|
Smith J, Tho LM, Xu N and Gillespie DA:
The ATM-Chk2 and ATR-Chk1 pathways in DNA damage signaling and
cancer. Adv Cancer Res. 108:73–112. 2010.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
57
|
Garikipati V, Verma SK, Jolardarashi D,
Cheng Z, Ibetti J, Cimini M, Tang Y, Khan M, Yue Y, Benedict C, et
al: Therapeutic inhibition of miR-375 attenuates post-myocardial
infarction inflammatory response and left ventricular dysfunction
via PDK-1-AKT signalling axis. Cardiovasc Res. 113:938–949.
2017.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
58
|
Baulina N, Osmak G, Kiselev I, Matveeva N,
Kukava N, Shakhnovich R, Kulakova O and Favorova O: NGS-identified
circulating miR-375 as a potential regulating component of
myocardial infarction associated network. J Mol Cell Cardiol.
121:173–179. 2018.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
59
|
Liao J, Chen Z, He Q, Liu Y and Wang J:
Differential gene expression analysis and network construction of
recurrent cardiovascular events. Mol Med Rep. 13:1746–1764.
2016.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
60
|
Tang D, Kroemer G and Kang R: Oncogenic
KRAS blockade therapy: Renewed enthusiasm and persistent
challenges. Mol Cancer. 20(128)2021.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
61
|
Wang X, Wang J, Chen F, Zhong Z and Qi L:
Detection of K-ras gene mutations in feces by magnetic nanoprobe in
patients with pancreatic cancer: A preliminary study. Exp Ther Med.
15:527–531. 2018.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
62
|
Huang L, Guo Z, Wang F and Fu L: KRAS
mutation: From undruggable to druggable in cancer. Signal Transduct
Target Ther. 6(386)2021.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
63
|
Dai E, Han L, Liu J, Xie Y, Kroemer G,
Klionsky DJ, Zeh HJ, Kang R, Wang J and Tang D: Autophagy-dependent
ferroptosis drives tumor-associated macrophage polarization via
release and uptake of oncogenic KRAS protein. Autophagy.
16:2069–2083. 2020.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
64
|
Jaschke N, Kleymann A, Hofbauer LC, Göbel
A and Rachner TD: Dorsomorphin: A novel inhibitor of Dickkopf-1 in
breast cancer. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 524:360–365.
2020.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|