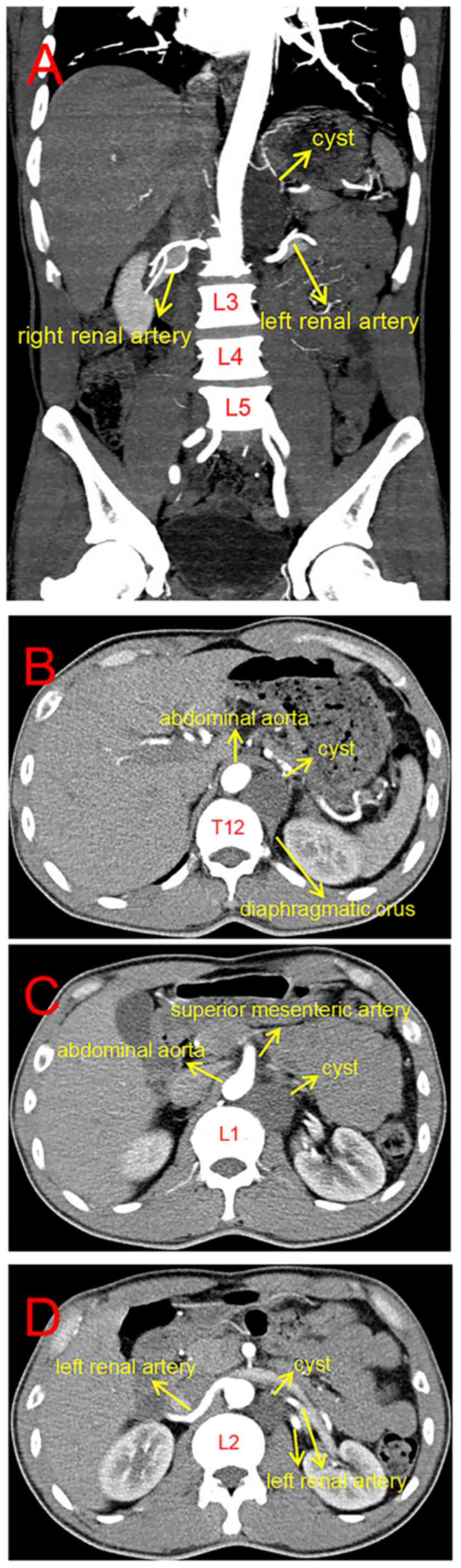
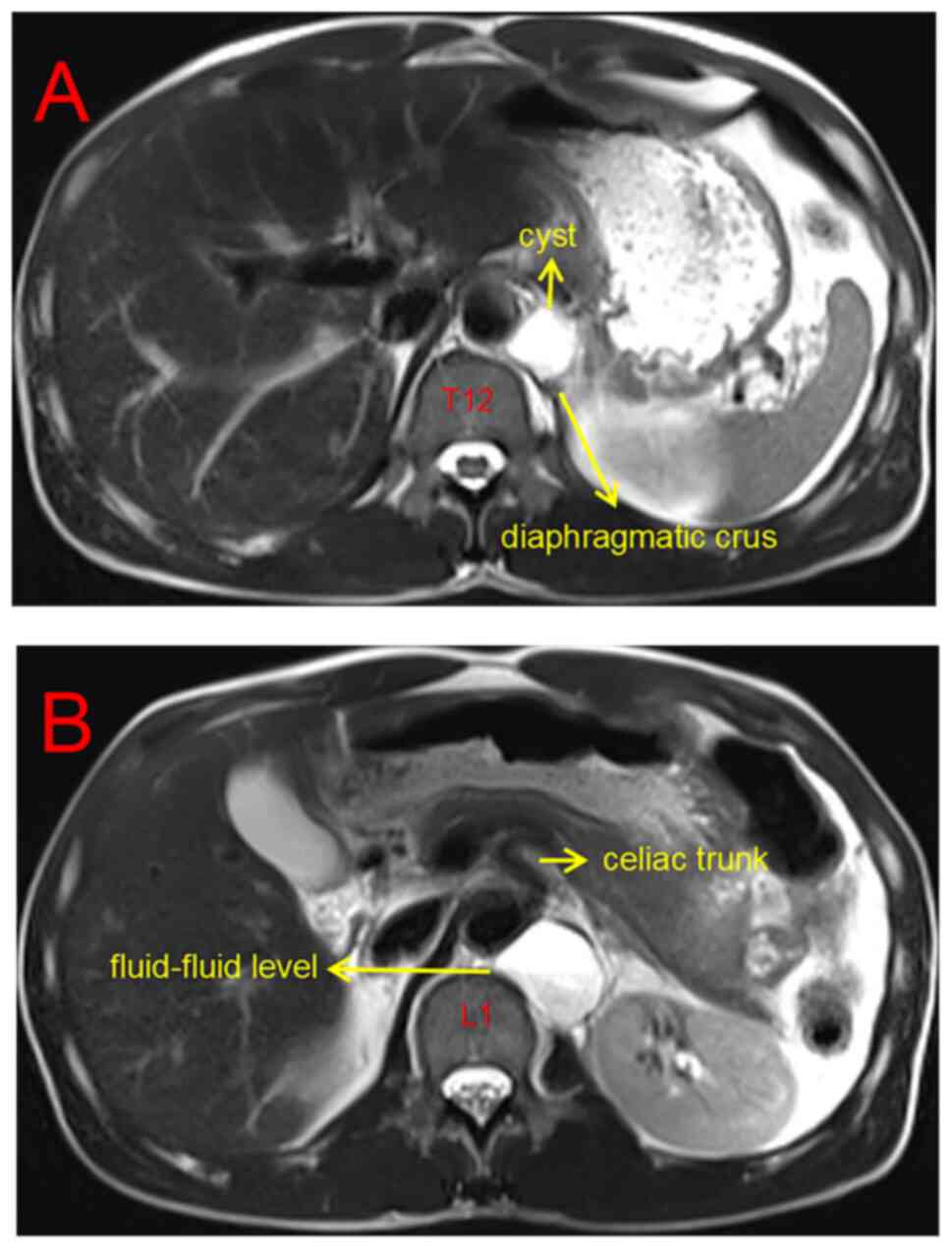
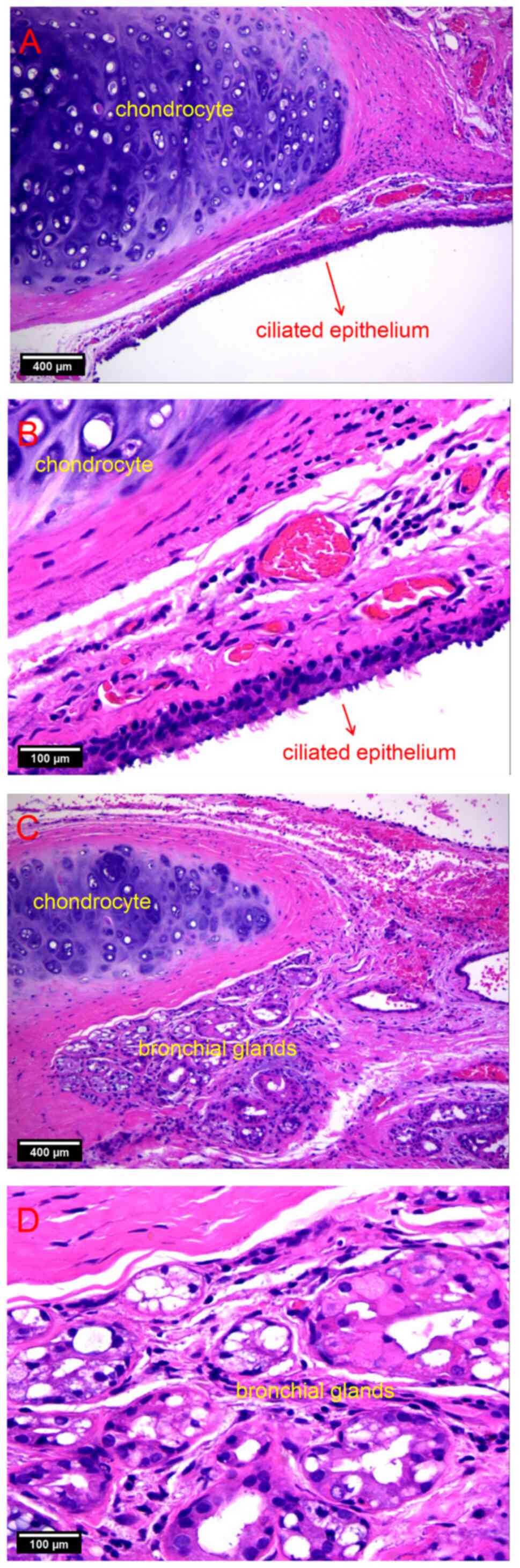
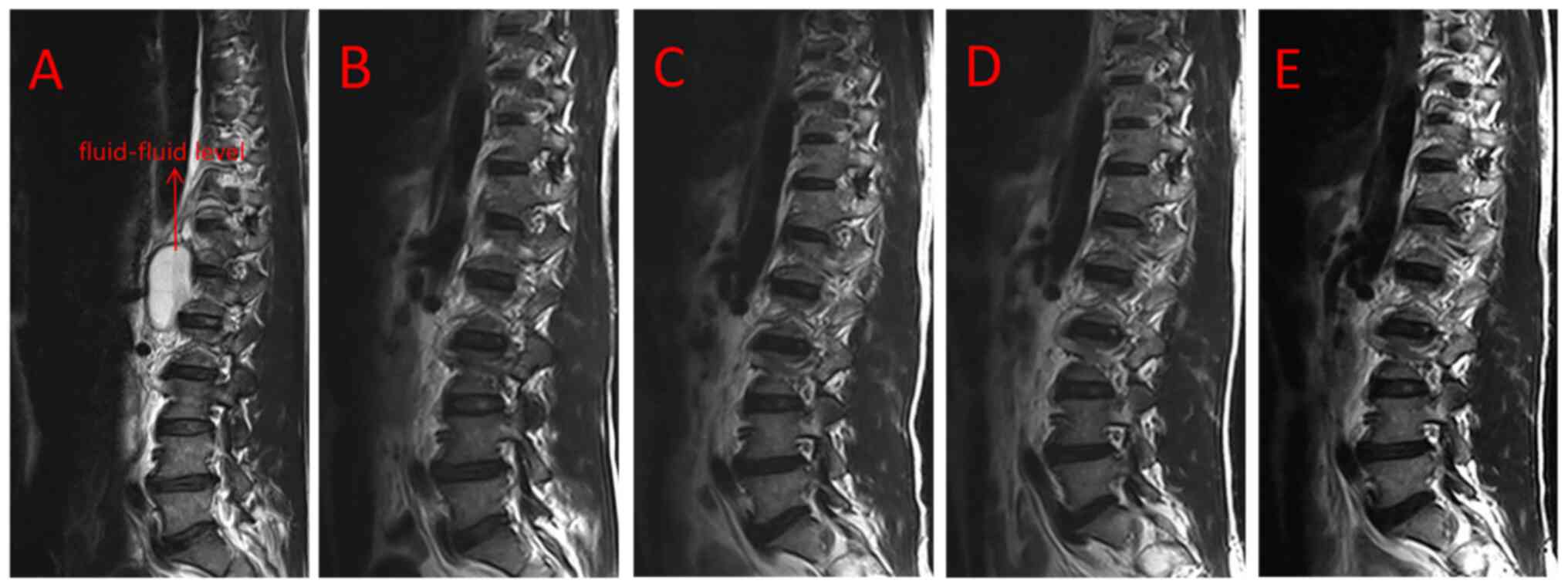
|
1
|
Yang DM, Jung DH, Kim H, Kang JH, Kim SH,
Kim JH and Hwang HY: Retroperitoneal cystic masses: CT, clinical,
and pathologic findings and literature review. Radiographics.
24:1353–1365. 2004.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
2
|
Tang J, Zeng Z, Deng S and Lin F: Ectopic
bronchogenic cyst arising from the diaphragm: A rare case report
and literature review. BMC Surg. 21(321)2021.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
3
|
Hamad AM, Rea F and Haroon S: Bronchial
atresia and bronchogenic cyst with saprophytic aspergilloma. Am J
Respir Crit Care Med. 203:e33–e34. 2021.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
4
|
Liang MK, Yee HT, Song JW and Marks JL:
Subdiaphragmatic bronchogenic cysts: A comprehensive review of the
literature. Am Surg. 71:1034–1041. 2005.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
5
|
Tu C, Zhu J, Shao C, Mao W, Zhou X, Lin Q,
Li Z, Zhang J, Zhou Q and Chen W: Gastric bronchogenic cysts: A
case report and literature review. Exp Ther Med. 11:1265–1270.
2016.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
6
|
Syred K and Weissferdt A: Non-neoplastic
mediastinal cysts. Adv Anat Pathol. 27:294–302. 2020.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
7
|
McAdams HP, Kirejczyk WM,
Rosado-de-Christenson ML and Matsumoto S: Bronchogenic cyst:
Imaging features with clinical and histopathologic correlation.
Radiology. 217:441–446. 2000.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
8
|
Xu Q, Feng Y, Ye K, Zhou Y and Zhan R:
Bronchogenic cyst in left anterior cranial fossa. Neurology.
84:1181–1182. 2015.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
9
|
Yilmaz C, Gulsen S, Sonmez E, Ozger O,
Unlukaplan M and Caner H: Intramedullary bronchogenic cyst of the
conus medullaris. J Neurosurg Spine. 11(477)2009.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
10
|
Jiang C, Wang H, Chen G, Jiang G and Zhang
P: Intradiaphragmatic bronchogenic cyst. Ann Thoracic Surg.
96:681–683. 2013.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
11
|
Sun B, Wang A, Chen H, Qian B, Yi X, Jiang
Y, Li Q, Fu W and Li J: Bronchogenic cyst of the stomach: A case
report and literature review. Exp Ther Med. 20(166)2020.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
12
|
Sanli A, Onen A, Ceylan E, Yilmaz E,
Silistreli E and Açikel U: A case of a bronchogenic cyst in a rare
location. Ann Thoracic Surg. 77:1093–1094. 2004.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
13
|
Lyon RD and Mcadams HP: Mediastinal
bronchogenic cyst: Demonstration of a fluid-fluid level at MR
imaging. Radiology. 186:427–428. 1993.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
14
|
Bargallo J, Luburich P, Garcia-Barrionuevo
J and Sanchez-Gonzalez M: Fluid-fluid level in bronchogenic cysts.
Radiology. 188:881–882. 1993.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
15
|
Aydingöz U, Ariyürek M, Selçuk ZT,
Demirkazik FB and Bariş YI: Calcium within a bronchogenic cyst with
a fluid level. Brit J Radiol. 70:761–763. 1997.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
16
|
Han SE, Kwon WJ, Cha HJ, Lee YJ, Lee T,
Seo KW, Jegal Y, Ahn J and Ra SW: Mediastinal bronchogenic cysts:
Demonstration of fluid-fluid level in bronchoscopic US imaging. J
Bronchology Interv Pulmonol. 24:153–155. 2017.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
17
|
Park JW, Jeong WG, Lee JE, Lee HJ, Ki SY,
Lee BC, Kim HO, Kim SK, Heo SH, Lim HS, et al: Pictorial review of
mediastinal masses with an emphasis on magnetic resonance imaging.
Korean J Radiol. 22:139–154. 2021.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
18
|
Jo W, Shin JS and Lee IS:
Supradiaphragmatic bronchogenic cyst extending into the
retroperitoneum. Ann Thoracic Surg. 81:369–370. 2006.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
19
|
Kunisaki SM: Narrative review of
congenital lung lesions. Transl Pediatr. 10:1418–1431.
2021.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
20
|
Sumiyoshi K, Shimizu S, Enjoji M, Iwashita
A and Kawakami K: Bronchogenic cyst in the abdomen. Virchows Arch A
Pathol Anat Histopathol. 408:93–98. 1985.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
21
|
Díaz Nieto R, Naranjo Torres A, Gómez
Alvarez M, Ruiz Rabelo JF, Pérez Manrique MC, Ciria Bru R, Valverde
Martínez A, Roldán de la Rúa J, Alonso Gómez J and Rufián Peña S:
Intraabdominal bronchogenic cyst. J Gastrointest Surg. 14:756–758.
2010.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
22
|
Anderson MI, O'Reilly KJ and Costabile RA:
Retroperitoneal bronchogenic cyst mimicking a pheochromocytoma. J
Urol. 166:1379–1380. 2001.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
23
|
Kawaguchi Y, Hanaoka J, Asakura S and
Fujita T: Infected bronchogenic cyst treated with drainage followed
by resection. Ann Thoracic Surg. 98:332–334. 2014.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
24
|
Altieri MS, Zheng R, Pryor AD, Heimann A,
Ahn S and Telem DA: Esophageal bronchogenic cyst and review of the
literature. Surg Endosc. 29:3010–3015. 2015.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
25
|
Kirmani B, Kirmani B and Sogliani F:
Should asymptomatic bronchogenic cysts in adults be treated
conservatively or with surgery? Interact Cardiovasc Thorac Surg.
11:649–659. 2010.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|