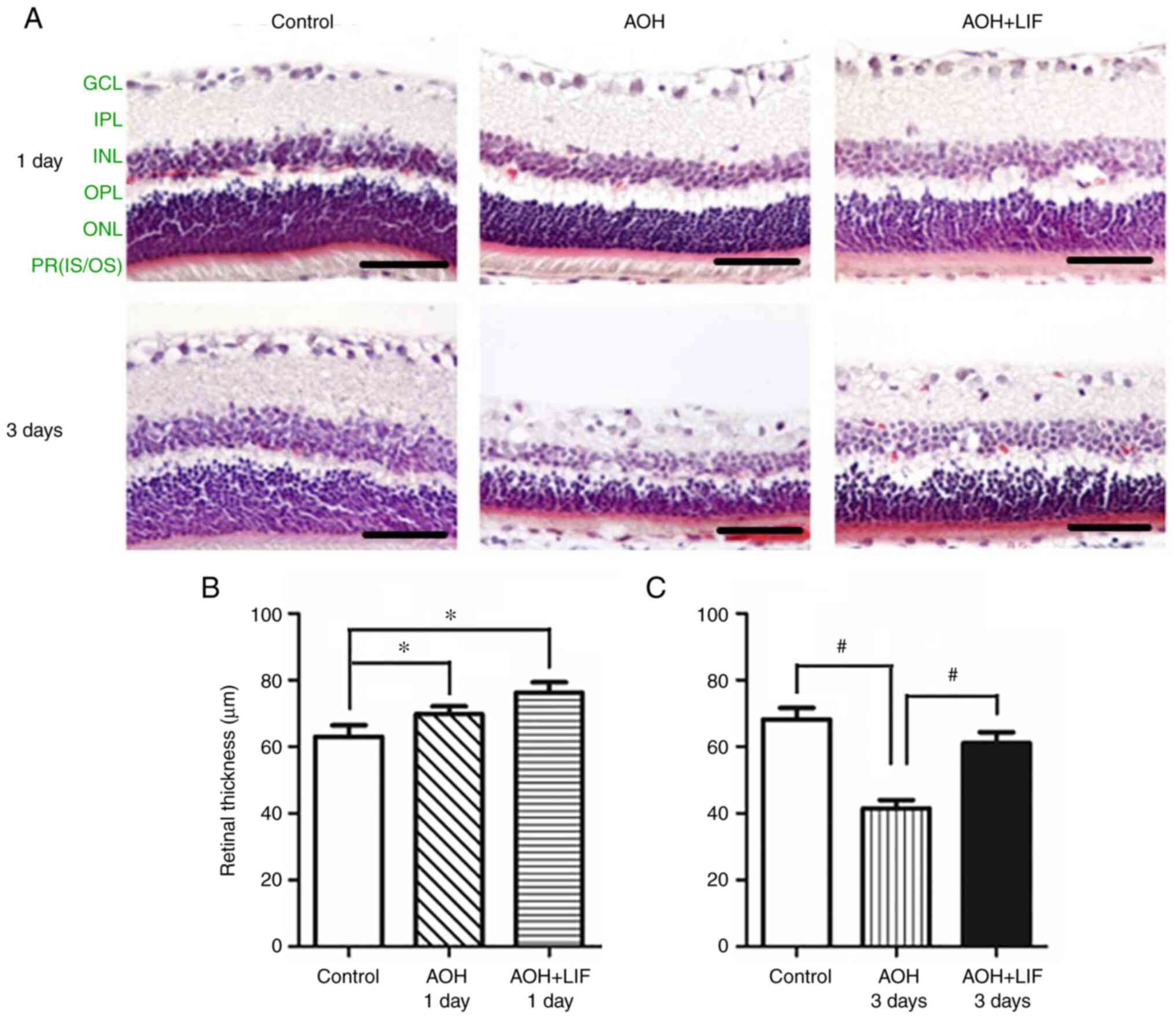
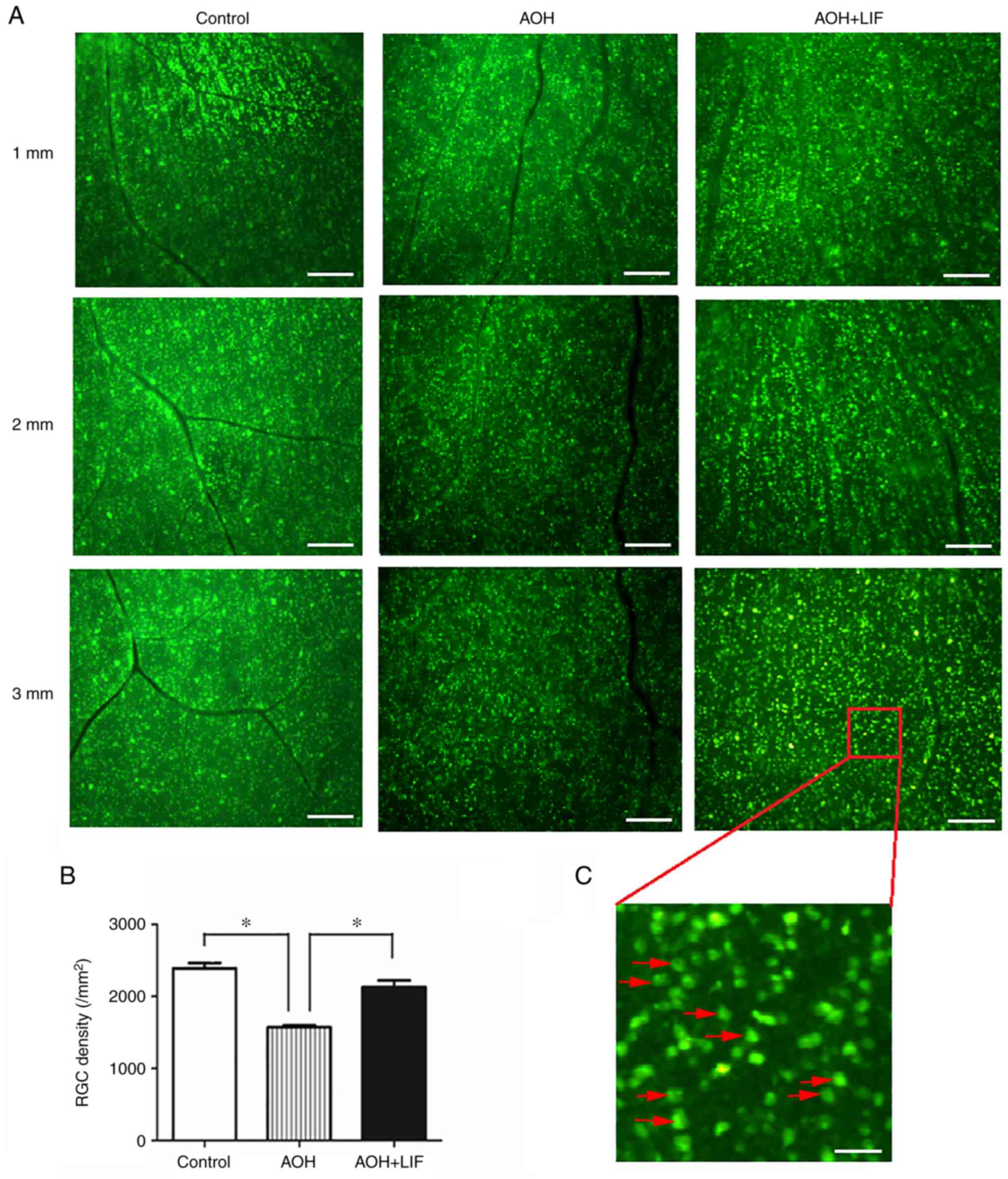
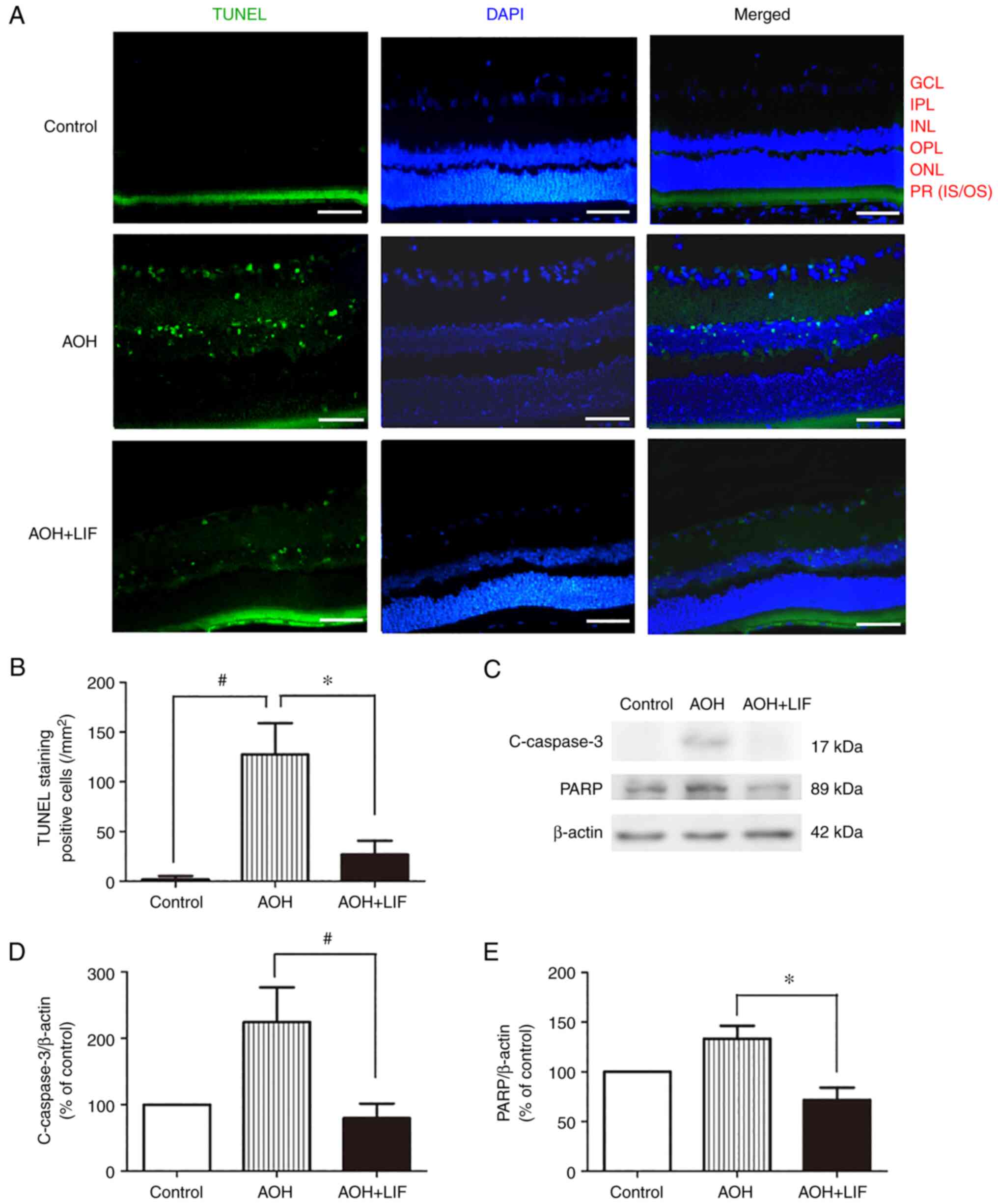
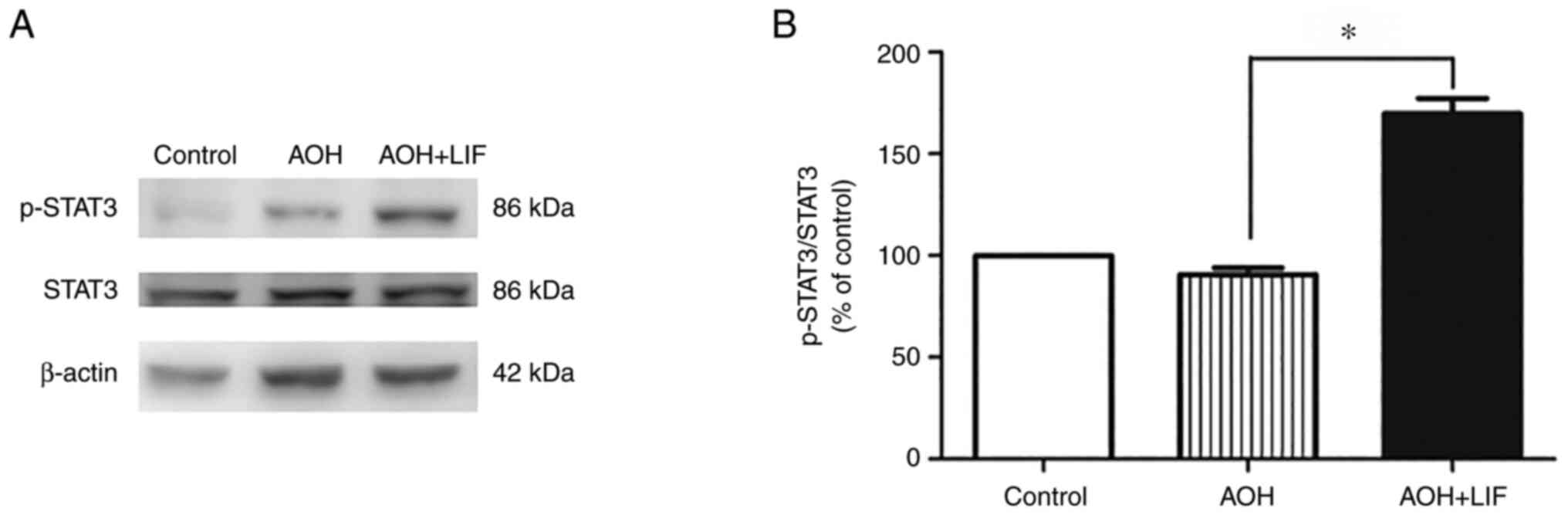
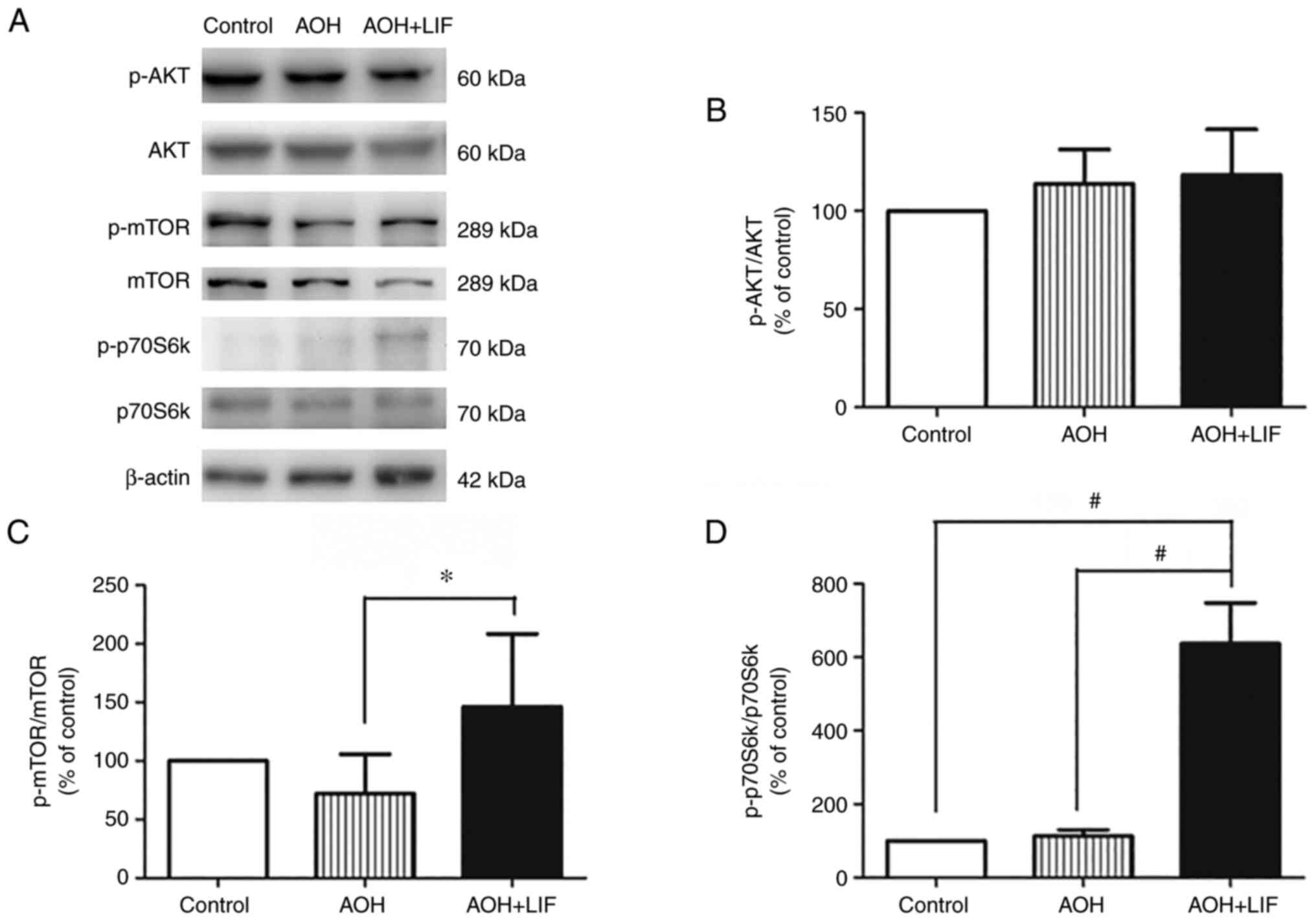
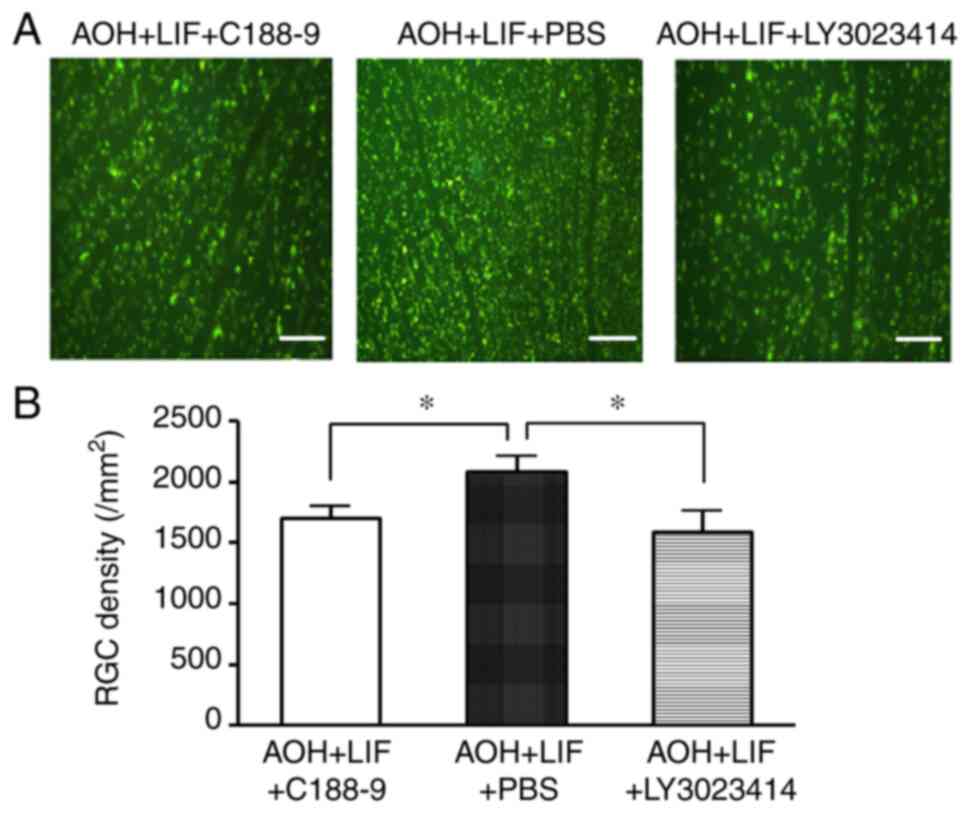
|
1
|
Tham YC, Li X, Wong TY, Quigley HA, Aung T
and Cheng CY: Global prevalence of glaucoma and projections of
glaucoma burden through 2040: A systematic review and
meta-analysis. Ophthalmology. 121:2081–2090. 2014.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
2
|
Quigley HA: Glaucoma. Lancet.
377:1367–1377. 2011.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
3
|
Heijl A, Leske MC, Bengtsson B, Hyman L,
Bengtsson B and Hussein M: Reduction of intraocular pressure and
glaucoma progression: Results from the early manifest glaucoma
trial. Arch Ophthalmol. 120:1268–1279. 2002.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
4
|
Lichter PR, Musch DC, Gillespie BW, Guire
KE, Janz NK, Wren PA and Mills RP: CIGTS Study Group. Interim
clinical outcomes in the Collaborative Initial Glaucoma Treatment
Study comparing initial treatment randomized to medications or
surgery. Ophthalmology. 108:1943–1953. 2001.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
5
|
Leske MC, Heijl A, Hyman L, Bengtsson B
and Komaroff E: Factors for progression and glaucoma treatment: The
Early Manifest Glaucoma Trial. Curr Opin Ophthalmol. 15:102–106.
2004.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
6
|
Comparison of glaucomatous progression
between untreated patients with normal-tension glaucoma and
patients with therapeutically reduced intraocular pressures.
Collaborative Normal-Tension Glaucoma Study Group. Am J Ophthalmol.
126:487–497. 1998.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
7
|
Diekmann H and Fischer D: Glaucoma and
optic nerve repair. Cell Tissue Res. 353:327–337. 2013.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
8
|
Gauthier AC and Liu J: Neurodegeneration
and neuroprotection in glaucoma. Yale J Biol Med. 89:73–79.
2016.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
9
|
He S, Stankowska DL, Ellis DZ,
Krishnamoorthy RR and Yorio T: Targets of neuroprotection in
glaucoma. J Ocul Pharmacol Ther. 34:85–106. 2018.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
10
|
Wang Y, Lv J, Huang C, Li X, Chen Y, Wu W
and Wu R: Human Umbilical Cord-mesenchymal stem cells survive and
migrate within the vitreous cavity and ameliorate retinal damage in
a novel rat model of chronic glaucoma. Stem Cells Int.
2021(8852517)2021.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
11
|
Büchi ER: Cell death in rat retina after
pressure-induced ischaemia-reperfusion insult: Electron microscopic
study. II. Outer nuclear layer. Jpn J Ophthalmol. 36:62–68.
1992.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
12
|
Büchi ER: Cell death in the rat retina
after a pressure-induced ischaemia-reperfusion insult: An electron
microscopic study. I. Ganglion cell layer and inner nuclear layer.
Exp Eye Res. 55:605–613. 1992.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
13
|
Burgoyne CF, Downs JC, Bellezza AJ, Suh JK
and Hart RT: The optic nerve head as a biomechanical structure: A
new paradigm for understanding the role of IOP-related stress and
strain in the pathophysiology of glaucomatous optic nerve head
damage. Prog Retin Eye Res. 24:39–73. 2005.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
14
|
Fechtner RD and Weinreb RN: Mechanisms of
optic nerve damage in primary open angle glaucoma. Surv Ophthalmol.
39:23–42. 1994.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
15
|
Fahy ET, Chrysostomou V and Crowston JG:
Mini-review: Impaired axonal transport and glaucoma. Curr Eye Res.
41:273–283. 2016.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
16
|
Hartsock MJ, Cho H, Wu L, Chen WJ, Gong J
and Duh EJ: A Mouse model of retinal ischemia-reperfusion injury
through elevation of intraocular pressure. J Vis Exp.
54065:2016.PubMed/NCBI View
Article : Google Scholar : doi:
10.3791/54065.
|
|
17
|
Osborne NN, Ugarte M, Chao M, Chidlow G,
Bae JH, Wood JP and Nash MS: Neuroprotection in relation to retinal
ischemia and relevance to glaucoma. Surv Ophthalmol. 43 (Suppl
1):S102–S128. 1999.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
18
|
Faiq MA, Wollstein G, Schuman JS and Chan
KC: Cholinergic nervous system and glaucoma: From basic science to
clinical applications. Prog Retin Eye Res.
72(100767)2019.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
19
|
Adornetto A, Russo R and Parisi V:
Neuroinflammation as a target for glaucoma therapy. Neural Regen
Res. 14:391–394. 2019.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
20
|
Joly S, Lange C, Thiersch M, Samardzija M
and Grimm C: Leukemia inhibitory factor extends the lifespan of
injured photoreceptors in vivo. J Neurosci. 28:13765–13774.
2008.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
21
|
Leibinger M, Müller A, Andreadaki A, Hauk
TG, Kirsch M and Fischer D: Neuroprotective and axon
growth-promoting effects following inflammatory stimulation on
mature retinal ganglion cells in mice depend on ciliary
neurotrophic factor and leukemia inhibitory factor. J Neurosci.
29:14334–14341. 2009.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
22
|
Burdon T, Smith A and Savatier P:
Signalling, cell cycle and pluripotency in embryonic stem cells.
Trends Cell Biol. 12:432–438. 2002.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
23
|
Mathieu ME, Saucourt C, Mournetas V,
Gauthereau X, Thézé N, Praloran V, Thiébaud P and Bœuf H:
LIF-dependent signaling: New pieces in the Lego. Stem Cell Rev Rep.
8:1–15. 2012.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
24
|
Peñuelas S, Anido J, Prieto-Sánchez RM,
Folch G, Barba I, Cuartas I, García-Dorado D, Poca MA, Sahuquillo
J, Baselga J and Seoane J: TGF-beta increases glioma-initiating
cell self-renewal through the induction of LIF in human
glioblastoma. Cancer Cell. 15:315–327. 2009.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
25
|
Pera MF and Tam PP: Extrinsic regulation
of pluripotent stem cells. Nature. 465:713–720. 2010.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
26
|
Zeng X, Huang Z, Mao X, Wang J, Wu G and
Qiao S: N-carbamylglutamate enhances pregnancy outcome in rats
through activation of the PI3K/PKB/mTOR signaling pathway. PLoS
One. 7(e41192)2012.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
27
|
Zouein FA, Kurdi M and Booz GW: LIF and
the heart: Just another brick in the wall? Eur Cytokine Netw.
24:11–19. 2013.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
28
|
Rattner A and Nathans J: The genomic
response to retinal disease and injury: Evidence for endothelin
signaling from photoreceptors to glia. J Neurosci. 25:4540–4549.
2005.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
29
|
Samardzija M, Wariwoda H, Imsand C, Huber
P, Heynen SR, Gubler A and Grimm C: Activation of survival pathways
in the degenerating retina of rd10 mice. Exp Eye Res. 99:17–26.
2012.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
30
|
Samardzija M, Wenzel A, Aufenberg S,
Thiersch M, Remé C and Grimm C: Differential role of Jak-STAT
signaling in retinal degenerations. Faseb J. 20:2411–2413.
2006.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
31
|
Schaeferhoff K, Michalakis S, Tanimoto N,
Fischer MD, Becirovic E, Beck SC, Huber G, Rieger N, Riess O,
Wissinger B, et al: Induction of STAT3-related genes in fast
degenerating cone photoreceptors of cpfl1 mice. Cell Mol Life Sci.
67:3173–3186. 2010.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
32
|
Agca C and Grimm C: Leukemia inhibitory
factor signaling in degenerating retinas. Adv Exp Med Biol.
801:389–394. 2014.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
33
|
Liu SC, Tsang NM, Chiang WC, Chang KP,
Hsueh C, Liang Y, Juang JL, Chow KP and Chang YS: Leukemia
inhibitory factor promotes nasopharyngeal carcinoma progression and
radioresistance. J Clin Invest. 123:5269–5283. 2013.PubMed/NCBI View
Article : Google Scholar
|
|
34
|
Chen H, Qu Y, Tang B, Xiong T and Mu D:
Role of mammalian target of rapamycin in hypoxic or ischemic brain
injury: Potential neuroprotection and limitations. Rev Neurosci.
23:279–287. 2012.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
35
|
Hu Q, Huang C, Wang Y and Wu R: Expression
of leukemia inhibitory factor in the rat retina following acute
ocular hypertension. Mol Med Rep. 12:6577–6583. 2015.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
36
|
Xu J, Li Y, Song S, Cepurna W, Morrison J
and Wang RK: Evaluating changes of blood flow in retina, choroid,
and outer choroid in rats in response to elevated intraocular
pressure by 1300 nm swept-source OCT. Microvasc Res. 121:37–45.
2019.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
37
|
Lafuente MP, Villegas-Pérez MP,
Sellés-Navarro I, Mayor-Torroglosa S, Miralles de Imperial J and
Vidal-Sanz M: Retinal ganglion cell death after acute retinal
ischemia is an ongoing process whose severity and duration depends
on the duration of the insult. Neuroscience. 109:157–168.
2002.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
38
|
Liao XX, Chen D, Shi J, Sun YQ, Sun SJ, So
KF and Fu QL: The expression patterns of Nogo-A, myelin associated
glycoprotein and oligodendrocyte myelin glycoprotein in the retina
after ocular hypertension: The expression of myelin proteins in the
retina in glaucoma. Neurochem Res. 36:1955–1961. 2011.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
39
|
Ueki Y, Wang J, Chollangi S and Ash JD:
STAT3 activation in photoreceptors by leukemia inhibitory factor is
associated with protection from light damage. J Neurochem.
105:784–796. 2008.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
40
|
Majumder A, Banerjee S, Harrill JA,
Machacek DW, Mohamad O, Bacanamwo M, Mundy WR, Wei L, Dhara SK and
Stice SL: Neurotrophic effects of leukemia inhibitory factor on
neural cells derived from human embryonic stem cells. Stem Cells.
30:2387–2399. 2012.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
41
|
Crowley LC and Waterhouse NJ: Detecting
cleaved Caspase-3 in apoptotic cells by flow cytometry. Cold Spring
Harb Protoc. (2016)2016.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
42
|
Soldani C and Scovassi AI:
Poly(ADP-ribose) polymerase-1 cleavage during apoptosis: An update.
Apoptosis. 7:321–328. 2002.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
43
|
Seki M and Lipton SA: Targeting
excitotoxic/free radical signaling pathways for therapeutic
intervention in glaucoma. Prog Brain Res. 173:495–510.
2008.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
44
|
Lee HJ, Lee JO, Lee YW, Kim SA, Seo IH,
Han JA, Kang MJ, Kim SJ, Cho YH, Park JJ, et al: LIF, a novel
myokine, protects against amyloid-beta-induced neurotoxicity via
akt-mediated autophagy signaling in hippocampal cells. Int J
Neuropsychopharmacol. 22:402–414. 2019.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
45
|
Bürgi S, Samardzija M and Grimm C:
Endogenous leukemia inhibitory factor protects photoreceptor cells
against light-induced degeneration. Mol Vis. 15:1631–1637.
2009.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
46
|
Morgan-Warren PJ, Berry M, Ahmed Z, Scott
RA and Logan A: Exploiting mTOR signaling: A novel translatable
treatment strategy for traumatic optic neuropathy? Invest
Ophthalmol Vis Sci. 54:6903–6916. 2013.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|