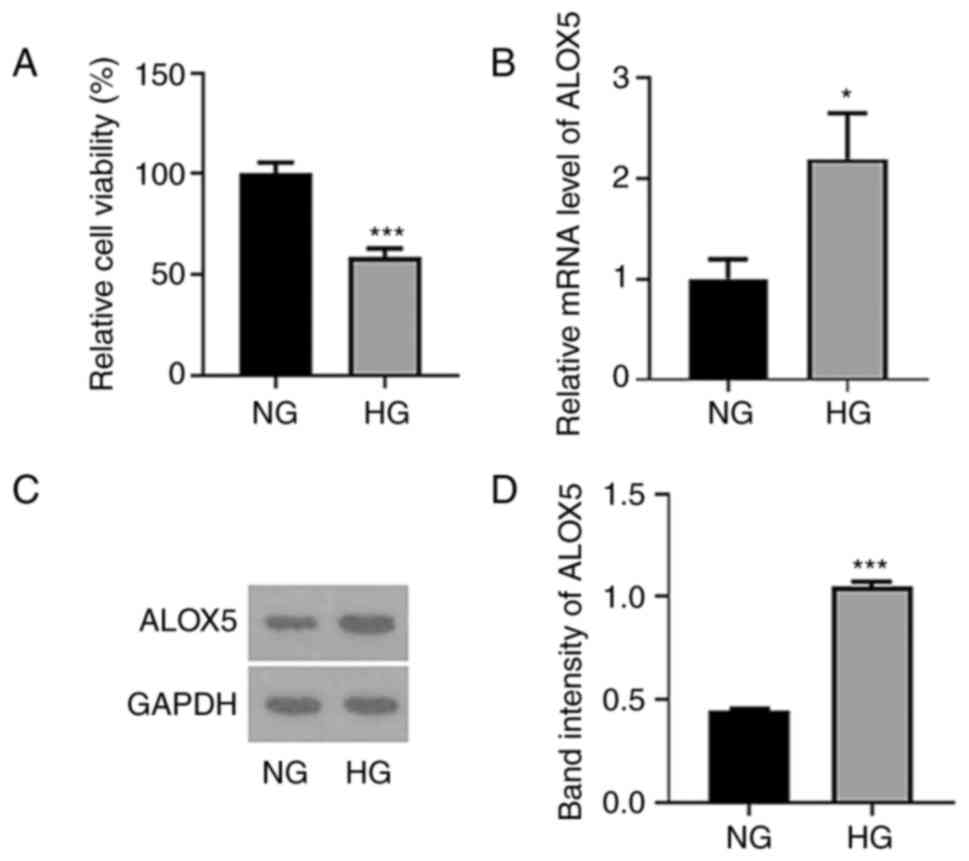
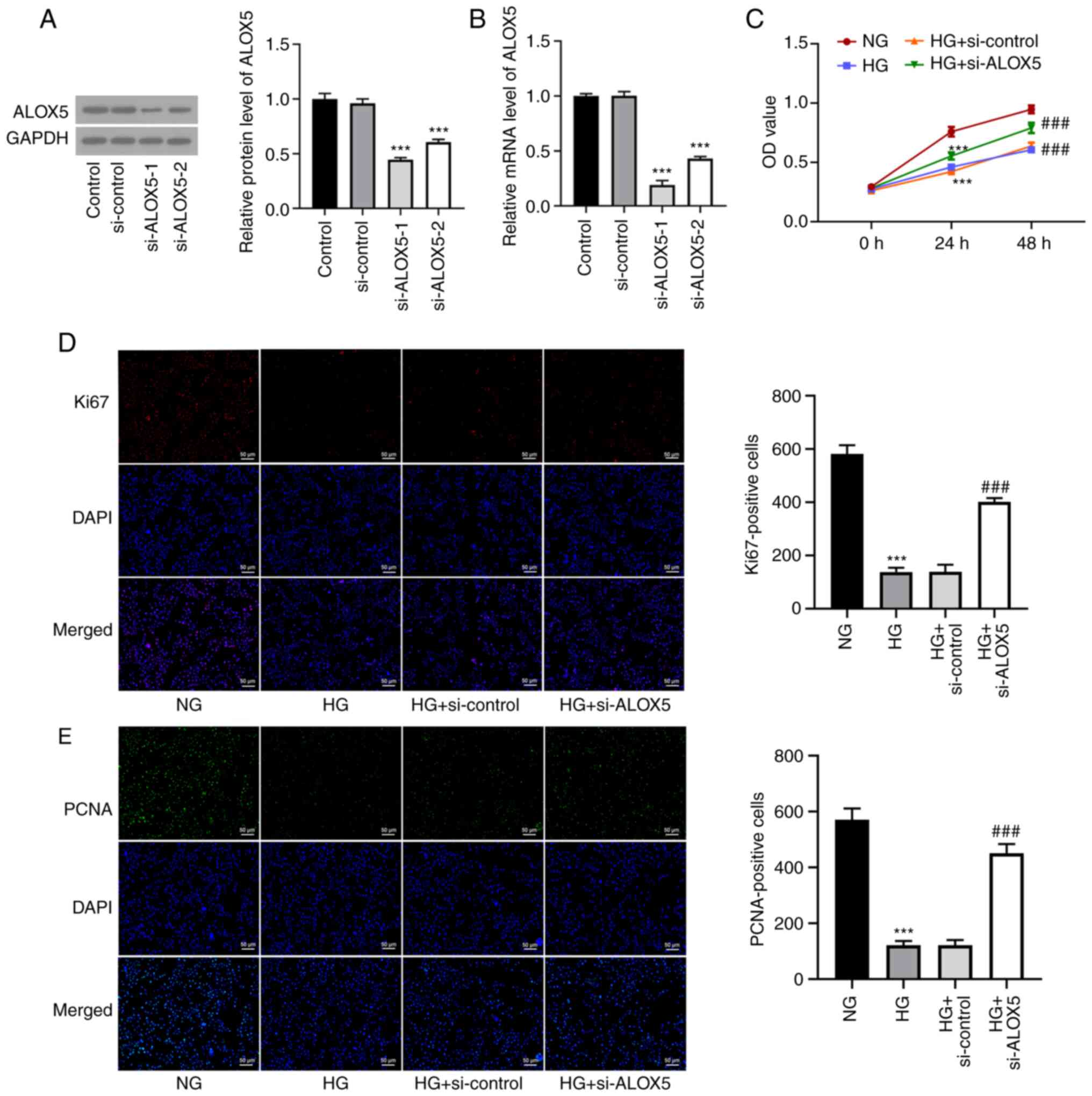
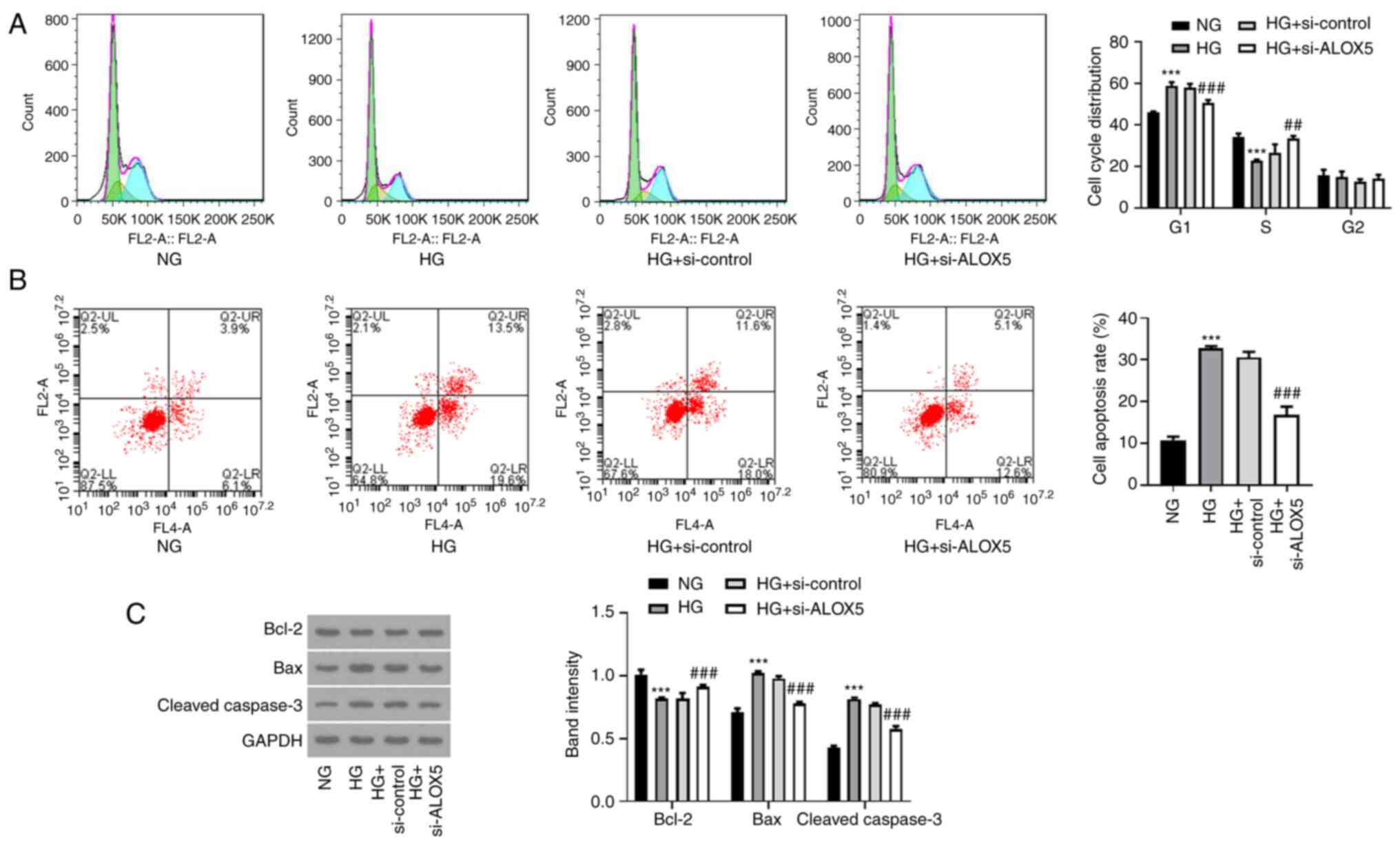
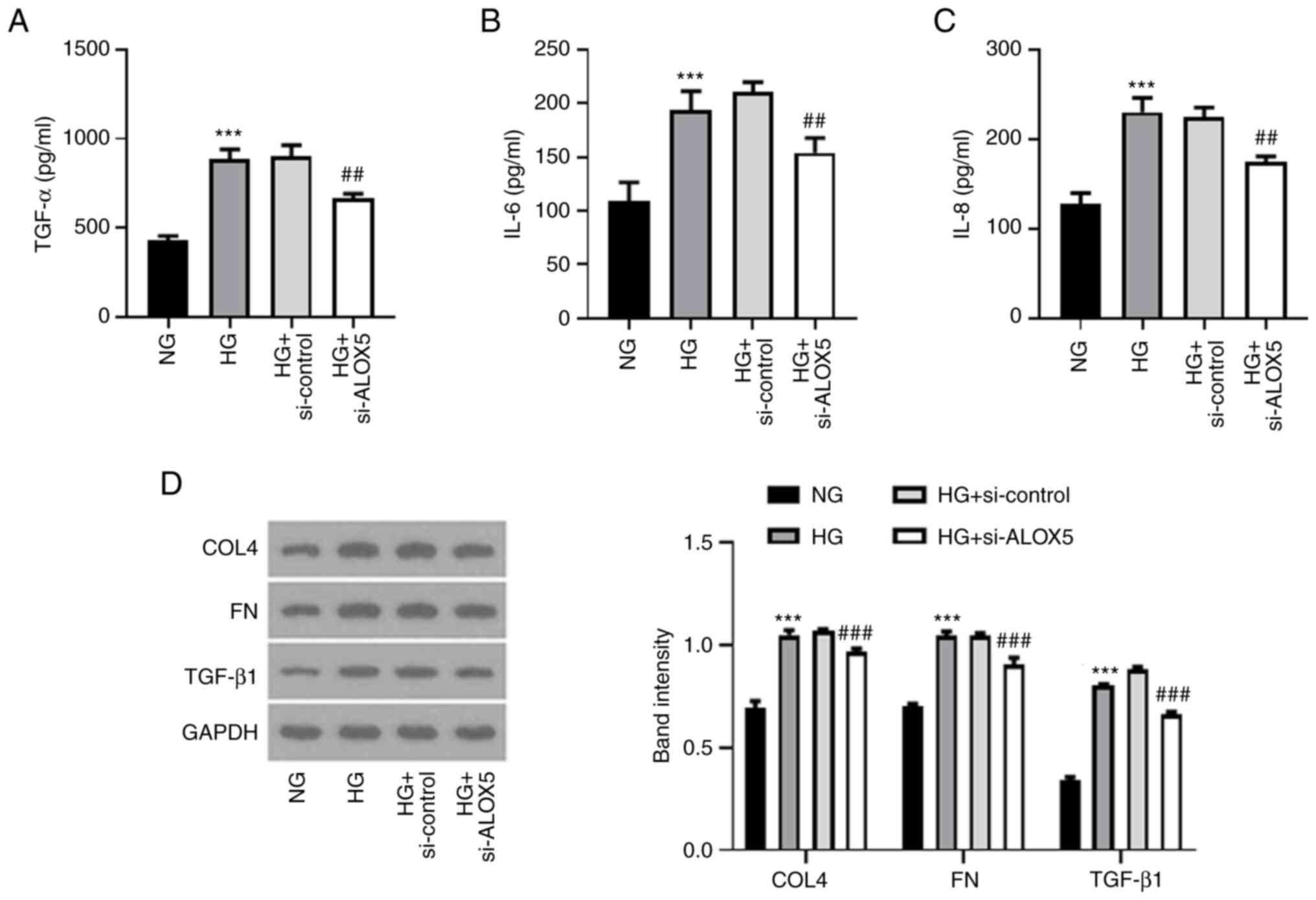
|
1
|
Sagoo MK and Gnudi L: Diabetic
nephropathy: An overview. Methods Mol Biol. 2067:3–7.
2020.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
2
|
Gheith O, Farouk N, Nampoory N, Halim MA
and Al-Otaibi T: Diabetic kidney disease: World wide difference of
prevalence and risk factors. J Nephropharmacol. 5:49–56.
2016.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
3
|
Narres M, Claessen H, Droste S, Kvitkina
T, Koch M, Kuss O and Icks A: The incidence of end-stage renal
disease in the diabetic (compared to the non-diabetic) population:
A systematic review. PLoS One. 11(e0147329)2016.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
4
|
Si X, Li P, Zhang Y, Zhang Y, Lv W and Qi
D: Renoprotective effects of olmesartan medoxomil on diabetic
nephropathy in streptozotocin-induced diabetes in rats. Biomed Rep.
2:24–28. 2014.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
5
|
Shi Y and Hu FB: The global implications
of diabetes and cancer. Lancet. 383:1947–1948. 2014.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
6
|
Weir MA and Herzog CA: Beta blockers in
patients with end-stage renal disease-evidence-based
recommendations. Semin Dial. 31:219–225. 2018.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
7
|
Dobrian AD, Lieb DC, Cole BK,
Taylor-Fishwick DA, Chakrabarti SK and Nadler JL: Functional and
pathological roles of the 12- and 15-lipoxygenases. Prog Lipid Res.
50:115–131. 2011.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
8
|
Chen F, Ghosh A, Lin J, Zhang C, Pan Y,
Thakur A, Singh K, Hong H and Tang S: 5-lipoxygenase pathway and
its downstream cysteinyl leukotrienes as potential therapeutic
targets for Alzheimer's disease. Brain Behav Immun. 88:844–855.
2020.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
9
|
Wang Y, Skibbe JR, Hu C, Dong L, Ferchen
K, Su R, Li C, Huang H, Weng H, Huang H, et al: ALOX5 exhibits
anti-tumor and drug-sensitizing effects in MLL-rearranged leukemia.
Sci Rep. 7(1853)2017.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
10
|
Lisovyy OO, Dosenko VE, Nagibin VS,
Tumanovska LV, Korol MO, Surova OV and Moibenko OO:
Cardioprotective effect of 5-lipoxygenase gene (ALOX5) silencing in
ischemia-reperfusion. Acta Biochim Pol. 56:687–694. 2009.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
11
|
Wu Y, Sun H, Song F, Huang C and Wang J:
Deletion of Alox5 gene decreases osteogenic differentiation but
increases adipogenic differentiation of mouse induced pluripotent
stem cells. Cell Tissue Res. 358:135–147. 2014.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
12
|
Zhu L, Yang F, Wang L, Dong L, Huang Z,
Wang G, Chen G and Li Q: Identification the ferroptosis-related
gene signature in patients with esophageal adenocarcinoma. Cancer
Cell Int. 21(124)2021.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
13
|
Tang J, Zhang C, Lin J, Duan P, Long J and
Zhu H: ALOX5-5-HETE promotes gastric cancer growth and alleviates
chemotherapy toxicity via MEK/ERK activation. Cancer Med.
10:5246–5255. 2021.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
14
|
Heemskerk MM, Giera M, Bouazzaoui FE, Lips
MA, Pijl H, van Dijk KW and van Harmelen V: Increased PUFA content
and 5-Lipoxygenase pathway expression are associated with
subcutaneous adipose tissue inflammation in obese women with type 2
diabetes. Nutrients. 7:7676–7690. 2015.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
15
|
ul Ain Q, Greig NH, Nawaz MS, Rashid S and
Kamal MA: Exploring N(1)-p-fluorobenzyl-cymserine as an inhibitor
of 5-lipoxygenase as a candidate for type 2 diabetes and
neurodegenerative disorder treatment. CNS Neurol Disord Drug
Targets. 13:197–202. 2014.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
16
|
Ramalho T, Filgueiras L, Silva-Jr IA,
Pessoa AFM and Jancar S: Impaired wound healing in type 1 diabetes
is dependent on 5-lipoxygenase products. Sci Rep.
8(14164)2018.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
17
|
Schwartzman ML, Iserovich P, Gotlinger K,
Bellner L, Dunn MW, Sartore M, Grazia Pertile M, Leonardi A, Sathe
S, Beaton A, et al: Profile of lipid and protein autacoids in
diabetic vitreous correlates with the progression of diabetic
retinopathy. Diabetes. 59:1780–1788. 2010.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
18
|
Gubitosi-Klug RA, Talahalli R, Du Y,
Nadler JL and Kern TS: 5-Lipoxygenase, but not 12/15-lipoxygenase,
contributes to degeneration of retinal capillaries in a mouse model
of diabetic retinopathy. Diabetes. 57:1387–1393. 2008.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
19
|
Landgraf SS, Silva LS, Peruchetti DB,
Sirtoli GM, Moraes-Santos F, Portella VG, Silva-Filho JL, Pinheiro
CS, Abreu TP, Takiya CM, et al: 5-Lypoxygenase products are
involved in renal tubulointerstitial injury induced by albumin
overload in proximal tubules in mice. PLoS One.
9(e107549)2014.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
20
|
Reinhold SW, Vitzthum H, Filbeck T, Wolf
K, Lattas C, Riegger GA, Kurtz A and Krämer BK: Gene expression of
5-, 12-, and 15-lipoxygenases and leukotriene receptors along the
rat nephron. Am J Physiol Renal Physiol. 290:F864–F872.
2006.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
21
|
Qi H, Yao L and Liu Q: NORAD affects the
progression of diabetic nephropathy through targeting miR-520h to
upregulate TLR4. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 521:190–195.
2020.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
22
|
Du Y, Yang YT, Tang G, Jia JS, Zhu N and
Yuan WJ: Butyrate alleviates diabetic kidney disease by mediating
the miR-7a-5p/P311/TGF-beta1 pathway. FASEB J. 34:10462–10475.
2020.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
23
|
Yang X, Luo W, Li L, Hu X, Xu M, Wang Y,
Feng J, Qian J, Guan X, Zhao Y and Liang G: CDK9 inhibition
improves diabetic nephropathy by reducing inflammation in the
kidneys. Toxicol Appl Pharmacol. 416(115465)2021.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
24
|
Xu J, Xiang P, Liu L, Sun J and Ye S:
Metformin inhibits extracellular matrix accumulation, inflammation
and proliferation of mesangial cells in diabetic nephropathy by
regulating H19/miR-143-3p/TGF-β1 axis. J Pharm Pharmacol.
72:1101–1109. 2020.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
25
|
Livak KJ and Schmittgen TD: Analysis of
relative gene expression data using real-time quantitative PCR and
the 2(-Delta Delta C(T)) method. Methods. 25:402–408.
2001.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
26
|
Jurikova M, Danihel L, Polak S and Varga
I: Ki67, PCNA, and MCM proteins: Markers of proliferation in the
diagnosis of breast cancer. Acta Histochem. 118:544–552.
2016.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
27
|
Liu T, Zhang L, Joo D and Sun SC: NF-κB
signaling in inflammation. Signal Transduct Target Ther.
2(17023)2017.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
28
|
Donate-Correa J, Martín-Núñez E,
Muros-de-Fuentes M, Mora-Fernández C and Navarro-González JF:
Inflammatory cytokines in diabetic nephropathy. J Diabetes Res.
2015(948417)2015.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
29
|
Samsu N: Diabetic nephropathy: Challenges
in pathogenesis, diagnosis, and treatment. Biomed Res Int.
2021(1497449)2021.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
30
|
Moreno JA, Gomez-Guerrero C, Mas S, Sanz
AB, Lorenzo O, Ruiz-Ortega M, Opazo L, Mezzano S and Egido J:
Targeting inflammation in diabetic nephropathy: A tale of hope.
Expert Opin Investig Drugs. 27:917–930. 2018.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
31
|
Chow FY, Nikolic-Paterson DJ, Ozols E,
Atkins RC and Tesch GH: Intercellular adhesion molecule-1
deficiency is protective against nephropathy in type 2 diabetic
db/db mice. J Am Soc Nephrol. 16:1711–1722. 2005.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
32
|
Zheng H, Li X, Yang X, Yan F, Wang C and
Liu J: miR-217/Mafb axis involve in high glucose-induced β-TC-tet
cell damage via regulating NF-κB signaling pathway. Biochem Genet.
58:901–913. 2020.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
33
|
Dong J, Li H, Bai Y and Wu C: Muscone
ameliorates diabetic peripheral neuropathy through activating
AKT/mTOR signalling pathway. J Pharm Pharmacol. 71:1706–1713.
2019.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
34
|
Rane MJ, Song Y, Jin S, Barati MT, Wu R,
Kausar H, Tan Y, Wang Y, Zhou G, Klein JB, et al: Interplay between
Akt and p38 MAPK pathways in the regulation of renal tubular cell
apoptosis associated with diabetic nephropathy. Am J Physiol Renal
Physiol. 298:F49–F61. 2010.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
35
|
Yu Q, Zhang M, Qian L, Wen D and Wu G:
Luteolin attenuates high glucose-induced podocyte injury via
suppressing NLRP3 inflammasome pathway. Life Sci. 225:1–7.
2019.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
36
|
Ma J, Zhao N, Du L and Wang Y:
Downregulation of lncRNA NEAT1 inhibits mouse mesangial cell
proliferation, fibrosis, and inflammation but promotes apoptosis in
diabetic nephropathy. Int J Clin Exp Pathol. 12:1174–1183.
2019.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
37
|
Liu G, Shea CM, Jones JE, Price GM, Warren
W, Lonie E, Yan S, Currie MG, Profy AT, Masferrer JL and Zimmer DP:
Praliciguat inhibits progression of diabetic nephropathy in ZSF1
rats and suppresses inflammation and apoptosis in human renal
proximal tubular cells. Am J Physiol Renal Physiol. 319:F697–F711.
2020.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
38
|
Oguiza A, Recio C, Lazaro I, Mallavia B,
Blanco J, Egido J and Gomez-Guerrero C: Peptide-based inhibition of
IκB kinase/nuclear factor-κB pathway protects against
diabetes-associated nephropathy and atherosclerosis in a mouse
model of type 1 diabetes. Diabetologia. 58:1656–1667.
2015.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
39
|
Schröfelbauer B, Polley S, Behar M, Ghosh
G and Hoffmann A: NEMO ensures signaling specificity of the
pleiotropic IKKβ by directing its kinase activity toward IκBα. Mol
Cell. 47:111–121. 2012.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
40
|
Manna K, Mishra S, Saha M, Mahapatra S,
Saha C, Yenge G, Gaikwad N, Pal R, Oulkar D, Banerjee K and Das
Saha K: Amelioration of diabetic nephropathy using pomegranate peel
extract-stabilized gold nanoparticles: Assessment of NF-κB and Nrf2
signaling system. Int J Nanomedicine. 14:1753–1777. 2019.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
41
|
Zhang Y, Ren S, Ji Y and Liang Y:
Pterostilbene ameliorates nephropathy injury in
streptozotocin-induced diabetic rats. Pharmacology. 104:71–80.
2019.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
42
|
Kolati SR, Kasala ER, Bodduluru LN,
Mahareddy JR, Uppulapu SK, Gogoi R, Barua CC and Lahkar M: BAY
11-7082 ameliorates diabetic nephropathy by attenuating
hyperglycemia-mediated oxidative stress and renal inflammation via
NF-κB pathway. Environ Toxicol Pharmacol. 39:690–699.
2015.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
43
|
Zhao Y, Wang W, Wang Q, Zhang X and Ye L:
Lipid metabolism enzyme 5-LOX and its metabolite LTB4 are capable
of activating transcription factor NF-κB in hepatoma cells. Biochem
Biophys Res Commun. 418:647–651. 2012.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
44
|
Cheng JH, Zhang WJ, Zhu JF, Cui D, Song
KD, Qiang P, Mei CZ, Nie ZC, Ding BS, Han Z, et al: CaMKIIγ
regulates the viability and self-renewal of acute myeloid leukaemia
stem-like cells by the Alox5/NF-κB pathway. Int J Lab Hematol.
43:699–706. 2021.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|