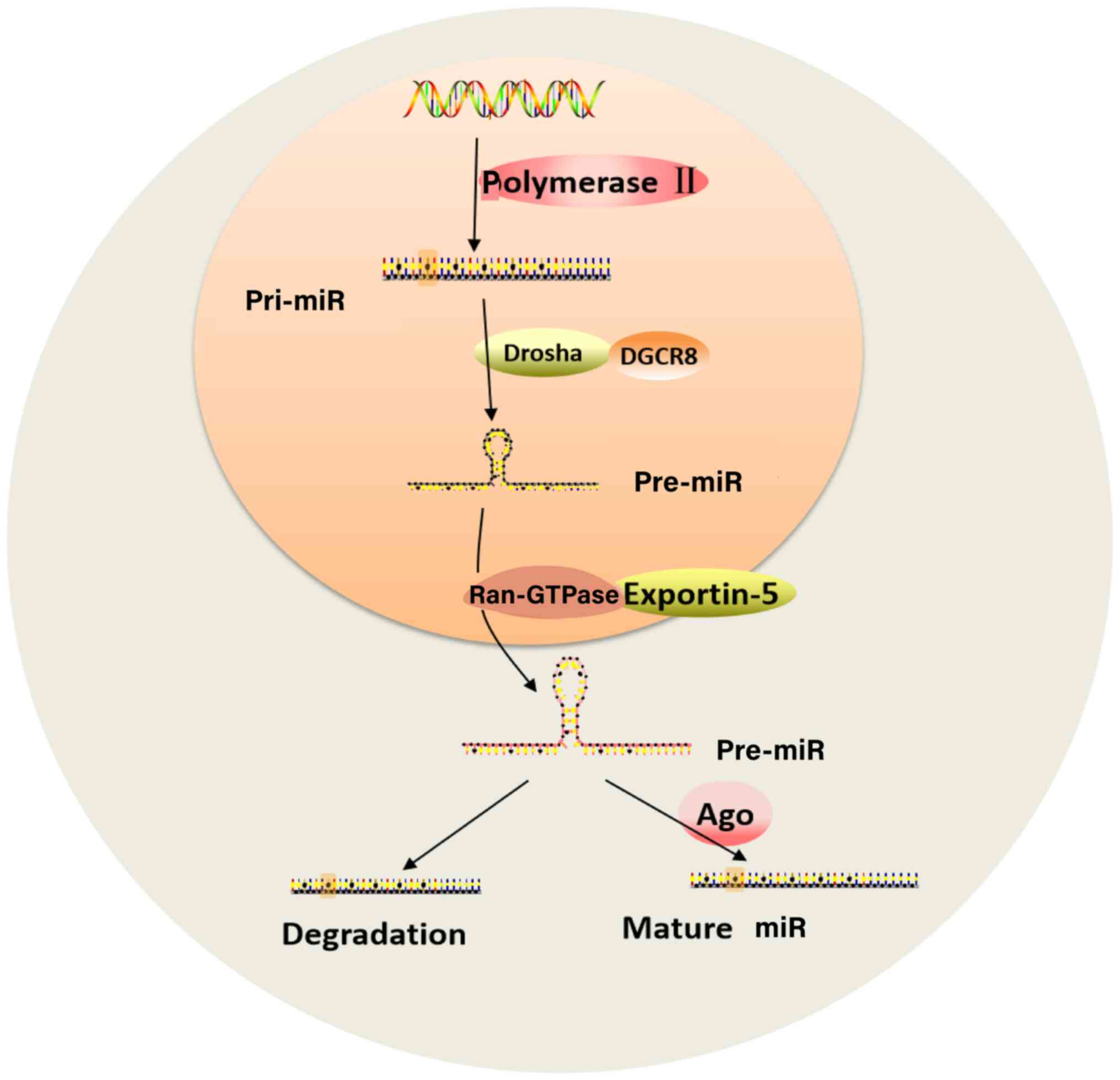
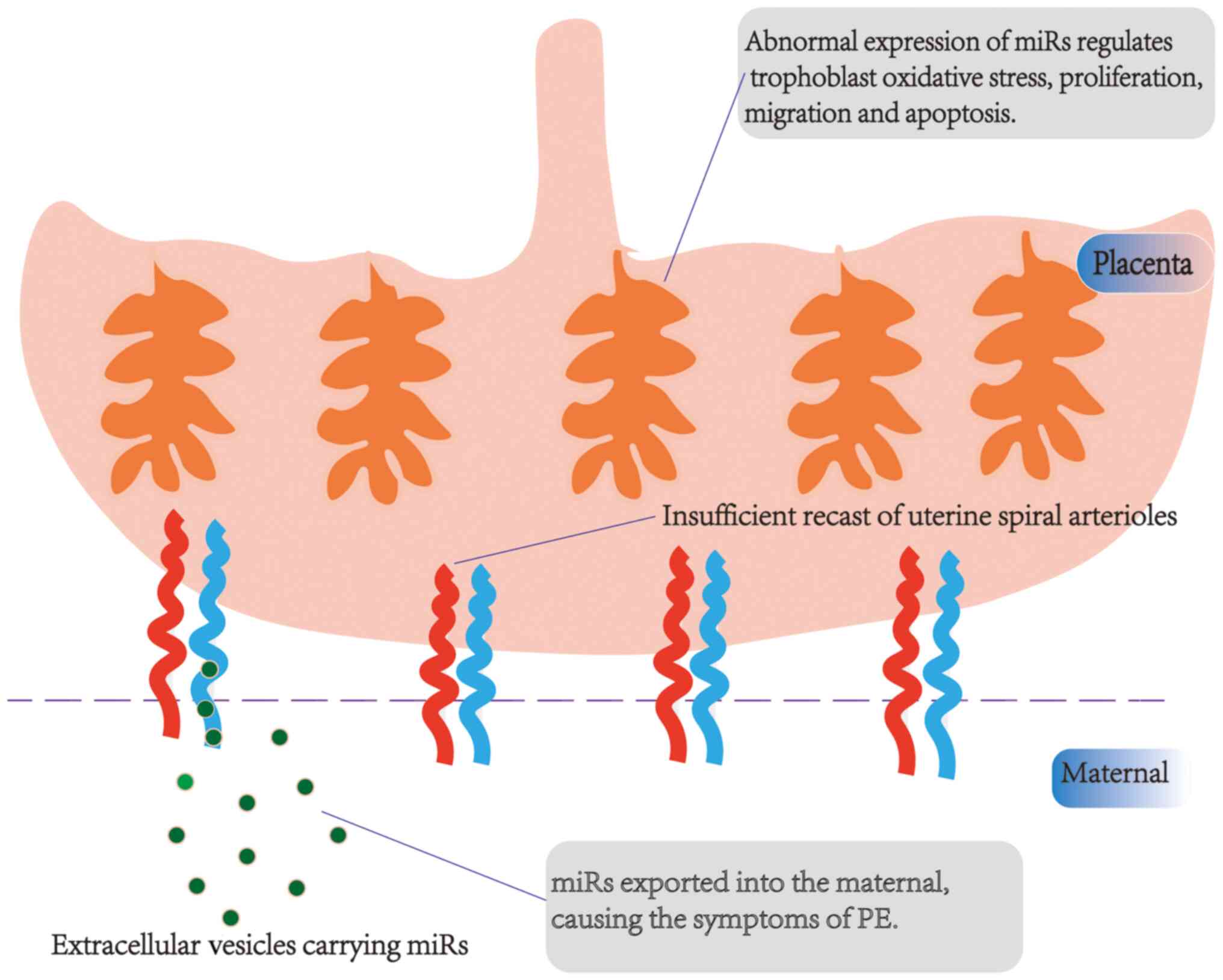
|
1
|
Lowe SA, Bowyer L, Lust K, McMahon LP,
Morton M, North RA, Paech M and Said JM: SOMANZ guidelines for the
management of hypertensive disorders of pregnancy 2014. Aust N Z J
Obstet Gynaecol. 55:e1–e29. 2015.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
2
|
Pankiewicz K, Fijałkowska A, Issat T and
Maciejewski TM: Insight into the key points of preeclampsia
pathophysiology: Uterine artery remodeling and the role of
MicroRNAs. Int J Mol Sci. 22(3132)2021.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
3
|
Redman CW and Sargent IL: Latest advances
in understanding preeclampsia. Science. 308:1592–1594.
2005.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
4
|
Wojczakowski W, Kimber-Trojnar Ż, Dziwisz
F, Słodzińska M, Słodziński H and Leszczyńska-Gorzelak B:
Preeclampsia and cardiovascular risk for offspring. J Clin Med.
10(3154)2021.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
5
|
Parada-Niño L, Castillo-León LF and Morel
A: Preeclampsia, natural history, genes and miRs associated with
the syndrome. J Pregnancy. 2022(3851225)2022.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
6
|
Huppertz B: Placental origins of
preeclampsia: Challenging the current hypothesis. Hypertension.
51:970–975. 2008.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
7
|
Ives CW, Sinkey R, Rajapreyar I, Tita ATN
and Oparil S: Preeclampsia-Pathophysiology and clinical
presentations: JACC State-of-the-Art Review. J Am Coll Cardiol.
76:1690–1702. 2020.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
8
|
Henderson JT, O'Connor E and Whitlock EP:
Low-dose aspirin for prevention of morbidity and mortality from
preeclampsia. Ann Intern Med. 161:613–614. 2014.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
9
|
Yang Y, Le Ray I, Zhu J, Zhang J, Hua J
and Reilly M: Preeclampsia prevalence, risk factors and pregnancy
outcomes in Sweden and China. JAMA Netw Open.
4(e218401)2021.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
10
|
Beermann J, Piccoli MT, Viereck J and Thum
T: Non-coding RNAs in development and disease: Background,
mechanisms and therapeutic approaches. Physiol Rev. 96:1297–1325.
2016.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
11
|
Sun N, Qin S, Zhang L and Liu S: Roles of
noncoding RNAs in preeclampsia. Reprod Biol Endocrinol.
19(100)2021.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
12
|
Ashraf UM, Hall DL, Rawls AZ and Alexander
BT: Epigenetic processes during preeclampsia and effects on fetal
development and chronic health. Clin Sci (Lond). 135:2307–2327.
2021.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
13
|
Kulcheski FR, Christoff AP and Margis R:
Circular RNAs are miRNA sponges and can be used as a new class of
biomarker. J Biotechnol. 238:42–51. 2016.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
14
|
Munjas J, Sopić M, Stefanović A, Košir R,
Ninić A, Joksić I, Antonić T, Spasojević-Kalimanovska V and Prosenc
Zmrzljak U: Non-Coding RNAs in preeclampsia-molecular mechanisms
and diagnostic potential. Int J Mol Sci. 22(10652)2021.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
15
|
Brodowski L, Schröder-Heurich B, von
Hardenberg S, Richter K, von Kaisenberg CS, Dittrich-Breiholz O,
Meyer N, Dörk T and von Versen-Höynck F: MicroRNA Profiles of
Maternal and Neonatal Endothelial Progenitor Cells in Preeclampsia.
Int J Mol Sci. 22(5320)2021.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
16
|
Bao S, Zhou T, Yan C, Bao J, Yang F, Chao
S, Zhou M and Xu Z: A blood-based miRNA signature for early
non-invasive diagnosis of preeclampsia. BMC Med.
20(303)2022.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
17
|
Laganà AS and Naem A: The Pathogenesis of
Endometriosis: Are Endometrial Stem/Progenitor Cells Involved? Stem
Cells in Reproductive Tissues and Organs. Virant-Klun I (ed). Stem
Cell Biology and Regenerative Medicine, Humana. 70:193–216.
2022.
|
|
18
|
Lv Y, Lu C, Ji X, Miao Z, Long W, Ding H
and Lv M: Roles of microRNAs in preeclampsia. J Cell Physiol.
234:1052–1061. 2019.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
19
|
Baek D, Villén J, Shin C, Camargo FD, Gygi
SP and Bartel DP: The impact of microRNAs on protein output.
Nature. 455:64–71. 2008.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
20
|
Gantier MP, McCoy CE, Rusinova I, Saulep
D, Wang D, Xu D, Irving AT, Behlke MA, Hertzog PJ, Mackay F and
Williams BR: Analysis of microRNA turnover in mammalian cells
following Dicer1 ablation. Nucleic Acids Res. 39:5692–5703.
2011.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
21
|
Borchert GM, Lanier W and Davidson BL: RNA
polymerase III transcribes human microRNAs. Nat Struct Mol Biol.
13:1097–1101. 2006.PubMed/NCBI View
Article : Google Scholar
|
|
22
|
Bohnsack MT, Czaplinski K and Gorlich D:
Exportin 5 is a RanGTP-dependent dsRNA-binding protein that
mediates nuclear export of pre-miRs. RNA. 10:185–191.
2004.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
23
|
Bernstein E, Caudy AA, Hannon GJ and
Hammond SM: Role for a bidentate ribonuclease in the initiation
step of RNA interference. Nature. 409:363–366. 2001.PubMed/NCBI View
Article : Google Scholar
|
|
24
|
Golden RJ, Chen B, Li T, Braun J,
Manjunath H, Chen X, Wu J, Schmid V, Chang TC, Kopp F, et al: An
Argonaute phosphorylation cycle promotes microRNA-mediated
silencing. Nature. 542:197–202. 2017.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
25
|
Robertson SA, Zhang B, Chan H, Sharkey DJ,
Barry SC, Fullston T and Schjenken JE: MicroRNA regulation of
immune events at conception. Mol Reprod Dev. 84:914–925.
2017.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
26
|
Lykke-Andersen K, Gilchrist MJ, Grabarek
JB, Das P, Miska E and Zernicka-Goetz M: Maternal Argonaute 2 is
essential for early mouse development at the maternal-zygotic
transition. Mol Biol Cell. 19:4383–4392. 2008.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
27
|
Morales-Prieto DM, Chaiwangyen W,
Ospina-Prieto S, Schneider U, Herrmann J, Gruhn B and Markert UR:
MicroRNA expression profiles of trophoblastic cells. Placenta.
33:725–734. 2012.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
28
|
Hromadnikova I, Kotlabova K, Ondrackova M,
Pirkova P, Kestlerova A, Novotna V, Hympanova L and Krofta L:
Expression profile of C19MC microRNAs in placental tissue in
pregnancy-related complications. DNA Cell Biol. 34:437–457.
2015.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
29
|
Hromadnikova I, Kotlabova K, Ivankova K
and Krofta L: First trimester screening of circulating C19MC
microRNAs and the evaluation of their potential to predict the
onset of preeclampsia and IUGR. PLoS One.
12(e0171756)2017.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
30
|
Luo L, Ye G, Nadeem L, Fu G, Yang BB,
Honarparvar E, Dunk C, Lye S and Peng C: MicroRNA-378a-5p promotes
trophoblast cell survival, migration and invasion by targeting
Nodal. J Cell Sci. 125(Pt 13):3124–3132. 2012.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
31
|
Hassan SS, Romero R, Pineles B, Tarca AL,
Montenegro D, Erez O, Mittal P, Kusanovic JP, Mazaki-Tovi S,
Espinoza J, et al: MicroRNA expression profiling of the human
uterine cervix after term labor and delivery. Am J Obstet Gynecol.
202:80.e1–e8. 2010.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
32
|
Gu Y, Sun J, Groome LJ and Wang Y:
Differential miRNA expression profiles between the first and third
trimester human placentas. Am J Physiol Endocrinol Metab.
304:E836–E843. 2013.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
33
|
Skalis G, Katsi V, Miliou A, Georgiopoulos
G, Papazachou O, Vamvakou G, Nihoyannopoulos P, Tousoulis D and
Makris T: MicroRNAs in Preeclampsia. Microrna. 8:28–35.
2019.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
34
|
Qiu C, Chen G and Cui Q: Towards the
understanding of microRNA and environmental factor interactions and
their relationships to human diseases. Sci Rep.
2(318)2012.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
35
|
Hromadnikova I, Kotlabova K, Doucha J,
Dlouha K and Krofta L: Absolute and relative quantification of
placenta-specific micrornas in maternal circulation with placental
insufficiency-related complications. J Mol Diagn. 14:160–167.
2012.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
36
|
Ali A, Hadlich F, Abbas MW, Iqbal MA,
Tesfaye D, Bouma GJ, Winger QA and Ponsuksili S: MicroRNA-mRNA
networks in pregnancy complications: A comprehensive downstream
analysis of potential biomarkers. Int J Mol Sci.
22(2313)2021.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
37
|
Wang W, Feng L, Zhang H, Hachy S, Satohisa
S, Laurent LC, Parast M, Zheng J and Chen DB: Preeclampsia
up-regulates angiogenesis-associated microRNA (i.e., miR-17, -20a,
and -20b) that target ephrin-B2 and EPHB4 in human placenta. J Clin
Endocrinol Metab. 97:E1051–E1059. 2012.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
38
|
Li Q, Long A, Jiang L, Cai L, Xie LI, Gu
J, Chen X and Tan L: Quantification of preeclampsia-related
microRNAs in maternal serum. Biomed Rep. 3:792–796. 2015.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
39
|
Jing J, Wang Y, Quan Y, Wang Z, Liu Y and
Ding Z: Maternal obesity alters C19MC microRNAs expression profile
in fetal umbilical cord blood. Nutr Metab (Lond).
17(52)2020.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
40
|
Ali A, Bouma GJ, Anthony RV and Winger QA:
The Role of LIN28-let-7-ARID3B pathway in placental development.
Int J Mol Sci. 21(3637)2020.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
41
|
Lu J, Sun Y, Cao Y and Zhang Y: Small RNA
sequencing reveals placenta-derived exosomal microRNAs associated
with preeclampsia. J Hypertens. 40:1030–1041. 2022.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
42
|
Zang J, Yan M, Zhang Y, Peng W, Zuo J,
Zhou H, Gao G, Li M, Chu Y and Ye Y: MiR-326 inhibits trophoblast
growth, migration and invasion by targeting PAX8 via Hippo pathway.
Reprod Biol Endocrinol. 20(38)2022.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
43
|
Gao Y, Zhang X and Meng T: Overexpression
of let-7b exerts beneficial effects on the functions of human
placental trophoblasts by activating the ERK1/2 signaling pathway.
Mol Reprod Dev. 89:39–53. 2022.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
44
|
Zou AX, Chen B, Li QX and Liang YC:
MiR-134 inhibits infiltration of trophoblast cells in placenta of
patients with preeclampsia by decreasing ITGB1 expression. Eur Rev
Med Pharmacol Sci. 22:2199–2206. 2018.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
45
|
Ojeda-Casares H and Paradisi I: The
regulatory network played by miRANs during normal pregnancy and
preeclampsia: A comparative study. Microrna. 10:263–275.
2021.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
46
|
Yang L, Liu C, Zhang C, Shang R, Zhang Y,
Wu S and Long Y: LncRNA small nucleolar RNA host gene 5 inhibits
trophoblast autophagy in preeclampsia by targeting microRNA-31-5p
and promoting the transcription of secreted protein acidic and rich
in cysteine. Bioengineered. 13:7221–7237. 2022.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
47
|
Yuan Y, Wang X, Sun Q, Dai X and Cai Y:
MicroRNA-16 is involved in the pathogenesis of pre-eclampsia via
regulation of Notch2. J Cell Physiol. 235:4530–4544.
2020.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
48
|
Wang R, Liu W, Liu X, Liu X, Tao H, Wu D,
Zhao Y and Zou L: MicroRNA-210 regulates human trophoblast cell
line HTR-8/SVneo function by attenuating Notch1 expression:
Implications for the role of microRNA-210 in pre-eclampsia. Mol
Reprod Dev. 86:896–907. 2019.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
49
|
Zhang Y, Fei M, Xue G, Zhou Q, Jia Y, Li
L, Xin H and Sun S: Elevated levels of hypoxia-inducible
microRNA-210 in pre-eclampsia: New insights into molecular
mechanisms for the disease. J Cell Mol Med. 16:249–259.
2012.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
50
|
Xiaobo Z, Qizhi H, Zhiping W and Tao D:
Down-regulated miR-149-5p contributes to preeclampsia via
modulating endoglin expression. Pregnancy Hypertens. 15:201–208.
2019.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
51
|
Liu B, Liu L, Cui S, Qi Y and Wang T:
Expression and significance of microRNA-126 and VCAM-1 in placental
tissues of women with early-onset preeclampsia. J Obstet Gynaecol
Res. 47:2042–2050. 2021.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
52
|
Ali Z, Zafar U, Zaki S, Ahmad S, Khaliq S
and Lone KP: Expression levels of MiRNA-16, SURVIVIN and TP53 in
Preeclamptic and Normotensive women. J Pak Med Assoc. 71:2208–2213.
2021.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
53
|
Shi Z, She K, Li H, Yuan X, Han X and Wang
Y: MicroRNA-454 contributes to sustaining the proliferation and
invasion of trophoblast cells through inhibiting Nodal/ALK7
signaling in pre-eclampsia. Chem Biol Interact. 298:8–14.
2019.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
54
|
Lai W and Yu L: Elevated MicroRNA 183
impairs trophoblast migration and invasiveness by downregulating
FOXP1 expression and elevating GNG7 Expression during Preeclampsia.
Mol Cell Biol. 41(e00236)2020.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
55
|
Wang YP, Zhao P, Liu JY, Liu SM and Wang
YX: MicroRNA-132 stimulates the growth and invasiveness of
trophoblasts by targeting DAPK-1. Eur Rev Med Pharmacol Sci.
24:9837–9843. 2020.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
56
|
Wang CY, Tsai PY, Chen TY, Tsai HL, Kuo PL
and Su MT: Elevated miR-200a and miR-141 inhibit endocrine
gland-derived vascular endothelial growth factor expression and
ciliogenesis in preeclampsia. J Physiol. 597:3069–3083.
2019.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
57
|
Yang X and Meng T: miR-215-5p decreases
migration and invasion of trophoblast cells through regulating CDC6
in preeclampsia. Cell Biochem Funct. 38:472–479. 2020.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
58
|
Ni H, Wang X, Qu H, Gao X and Yu X:
MiR-95-5p involves in the migration and invasion of trophoblast
cells by targeting low density lipoprotein receptor-related protein
6. J Obstet Gynaecol Res. 47:184–197. 2021.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
59
|
Umapathy A, Chamley LW and James JL:
Reconciling the distinct roles of angiogenic/anti-angiogenic
factors in the placenta and maternal circulation of normal and
pathological pregnancies. Angiogenesis. 23:105–117. 2020.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
60
|
Cornelius DC: Preeclampsia: From
inflammation to immunoregulation. Clin Med Insights Blood Disord.
11(1179545X17752325)2018.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
61
|
Schoots MH, Gordijn SJ, Scherjon SA, van
Goor H and Hillebrands JL: Oxidative stress in placental pathology.
Placenta. 69:153–161. 2018.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
62
|
Wang H, Zhang L, Guo X, Bai Y, Li YX, Sha
J, Peng C, Wang YL and Liu M: MiR-195 modulates oxidative
stress-induced apoptosis and mitochondrial energy production in
human trophoblasts via flavin adenine dinucleotide-dependent
oxidoreductase domain-containing protein 1 and pyruvate
dehydrogenase phosphatase regulatory subunit. J Hypertens.
36:306–318. 2018.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
63
|
Wu P, van Den Berg C, Alfirevic Z, O'Brien
S, Röthlisberger M, Baker PN, Kenny LC, Kublickiene K and Duvekot
JJ: Early pregnancy biomarkers in pre-eclampsia: A systematic
review and meta-analysis. Int J Mol Sci. 16:23035–23056.
2015.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
64
|
Zhao G, Miao H, Li X, Chen S, Hu Y, Wang Z
and Hou Y: TGF-β3-induced miR-494 inhibits macrophage polarization
via suppressing PGE2 secretion in mesenchymal stem cells. FEBS
Lett. 590:1602–1613. 2016.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
65
|
Muralimanoharan S, Maloyan A, Mele J, Guo
C, Myatt LG and Myatt L: MIR-210 modulates mitochondrial
respiration in placenta with preeclampsia. Placenta. 33:816–823.
2012.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
66
|
Abdelazim SA, Shaker OG, Aly YAH and
Senousy MA: Uncovering serum placental-related non-coding RNAs as
possible biomarkers of preeclampsia risk, onset and severity
revealed MALAT-1, miR-363 and miR-17. Sci Rep.
12(1249)2022.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
67
|
Gan L, Liu Z, Wei M, Chen Y, Yang X, Chen
L and Xiao X: MiR-210 and miR-155 as potential diagnostic markers
for pre-eclampsia pregnancies. Medicine (Baltimore).
96(e7515)2017.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
68
|
Luque A, Farwati A, Crovetto F, Crispi F,
Figueras F, Gratacos E and Aran JM: Usefulness of circulating
microRNAs for the prediction of early preeclampsia at
first-trimester of pregnancy. Sci Rep. 4(4882)2014.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
69
|
Winger EE, Reed JL and Ji X: First
trimester PBMC microRNA predicts adverse pregnancy outcome. Am J
Reprod Immunol. 72:515–526. 2014.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
70
|
Yu P, Fan S, Huang L, Yang L and Du Y:
MIR210 as a potential molecular target to block invasion and
metastasis of gastric cancer. Med Hypotheses. 84:209–212.
2015.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
71
|
Jaszczuk I, Koczkodaj D, Kondracka A,
Kwaśniewska A, Winkler I and Filip A: The role of miRNA-210 in
pre-eclampsia development. Ann Med. 54:1350–1356. 2022.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
72
|
Wang Z, Zhao G, Zeng M, Feng W and Liu J:
Overview of extracellular vesicles in the pathogenesis of
preeclampsia†. Biol Reprod. 105:32–39. 2021.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
73
|
Cui J, Chen X, Lin S, Li L, Fan J, Hou H
and Li P: MiR-101-containing extracellular vesicles bind to BRD4
and enhance proliferation and migration of trophoblasts in
preeclampsia. Stem Cell Res Ther. 11(231)2020.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
74
|
Bendifallah S, Dabi Y, Suisse S, Jornea L,
Bouteiller D, Touboul C, Puchar A and Daraï E: MicroRNome analysis
generates a blood-based signature for endometriosis. Sci Rep.
12(4051)2022.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
75
|
Hemmatzadeh M, Shomali N, Yousefzadeh Y,
Mohammadi H, Ghasemzadeh A and Yousefi M: MicroRNAs: Small
molecules with a large impact on pre-eclampsia. J Cell Physiol.
235:3235–3248. 2020.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
76
|
Chaemsaithong P, Sahota DS and Poon LC:
First trimester preeclampsia screening and prediction. Am J Obstet
Gynecol. 226 (2S):S1071–S1097.e2. 2022.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|