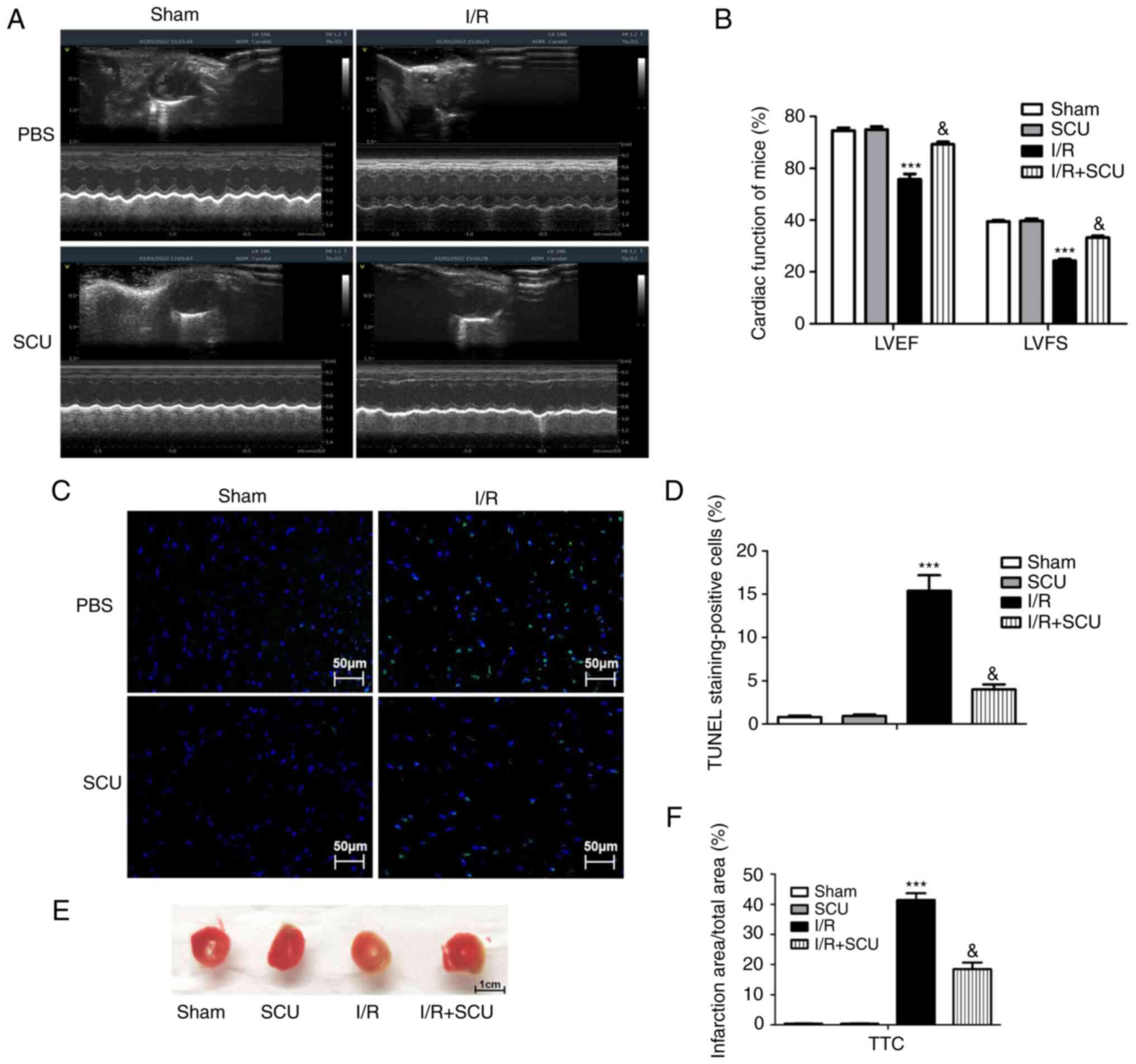
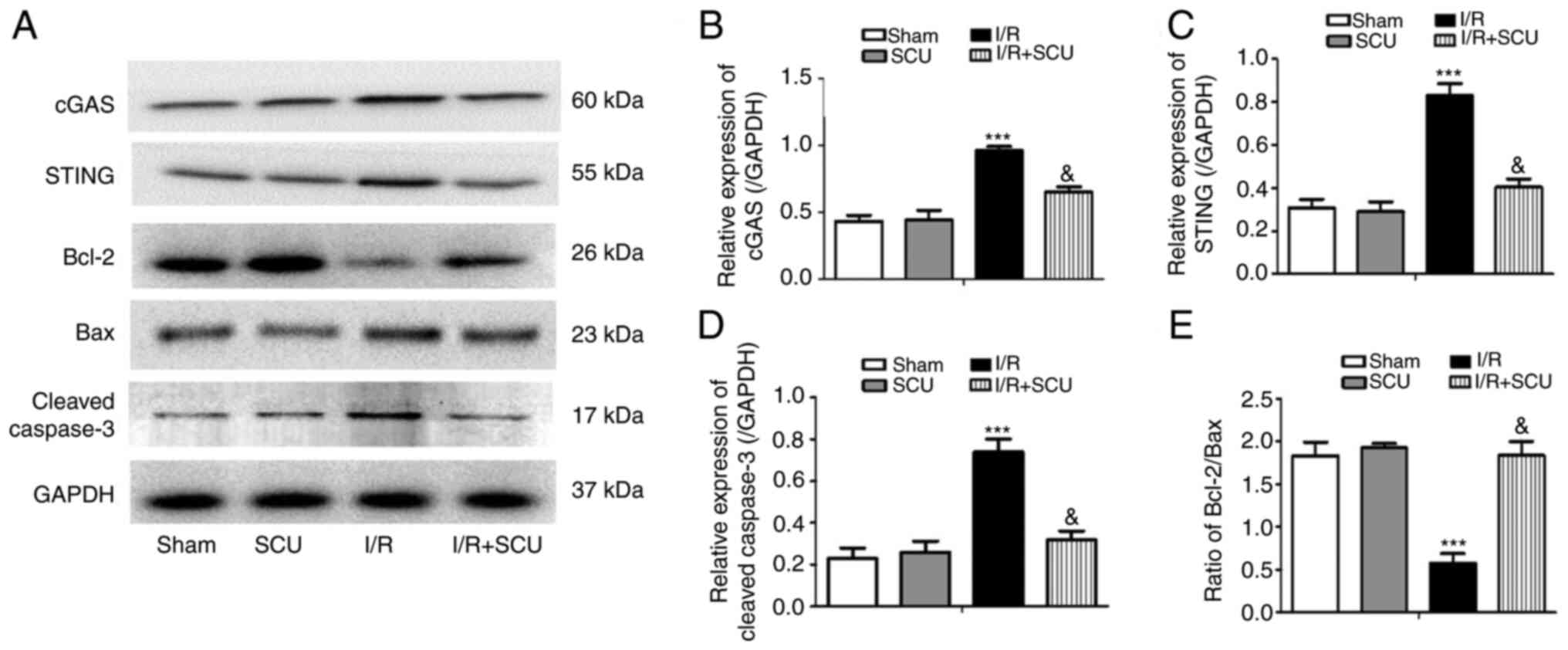
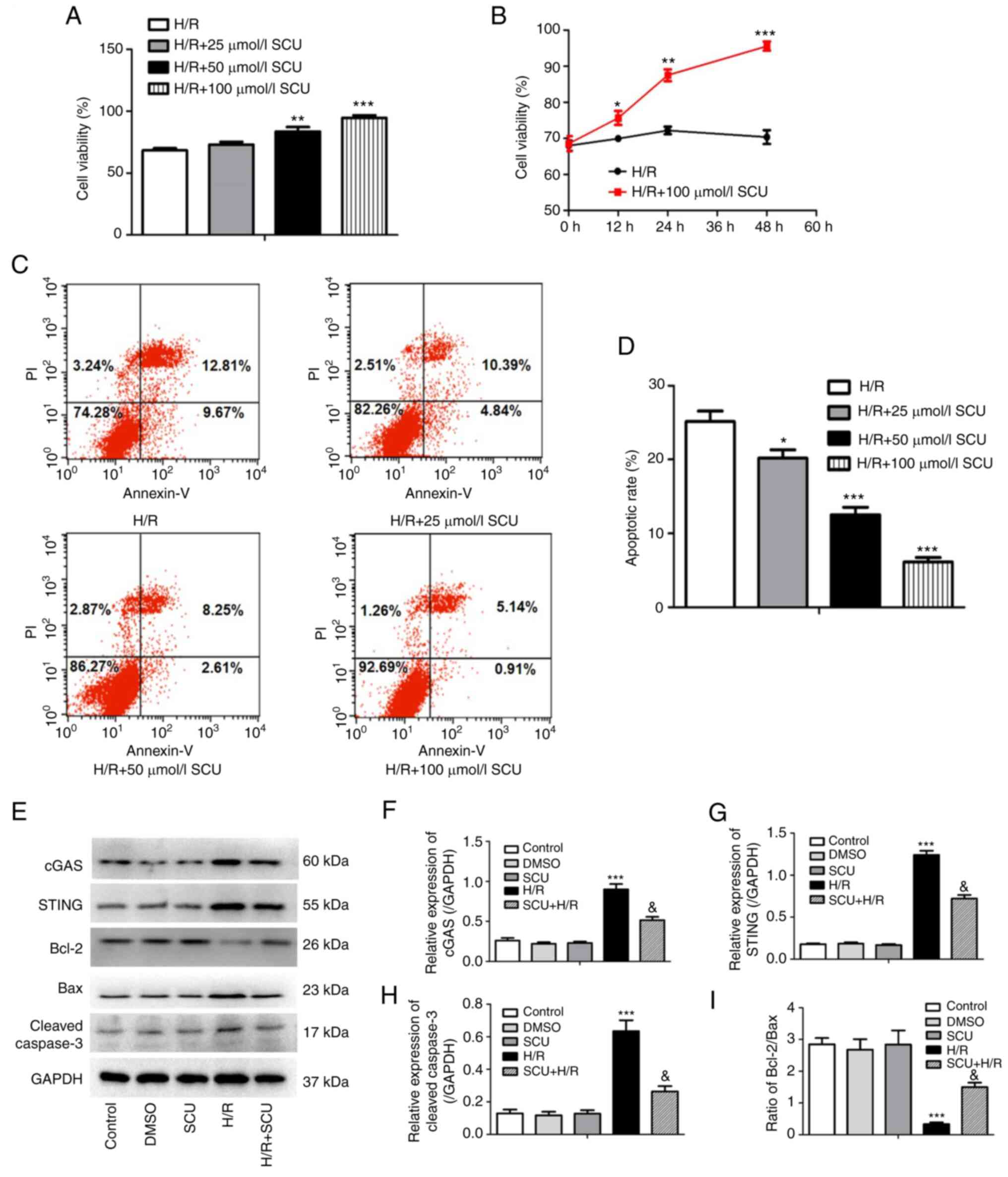
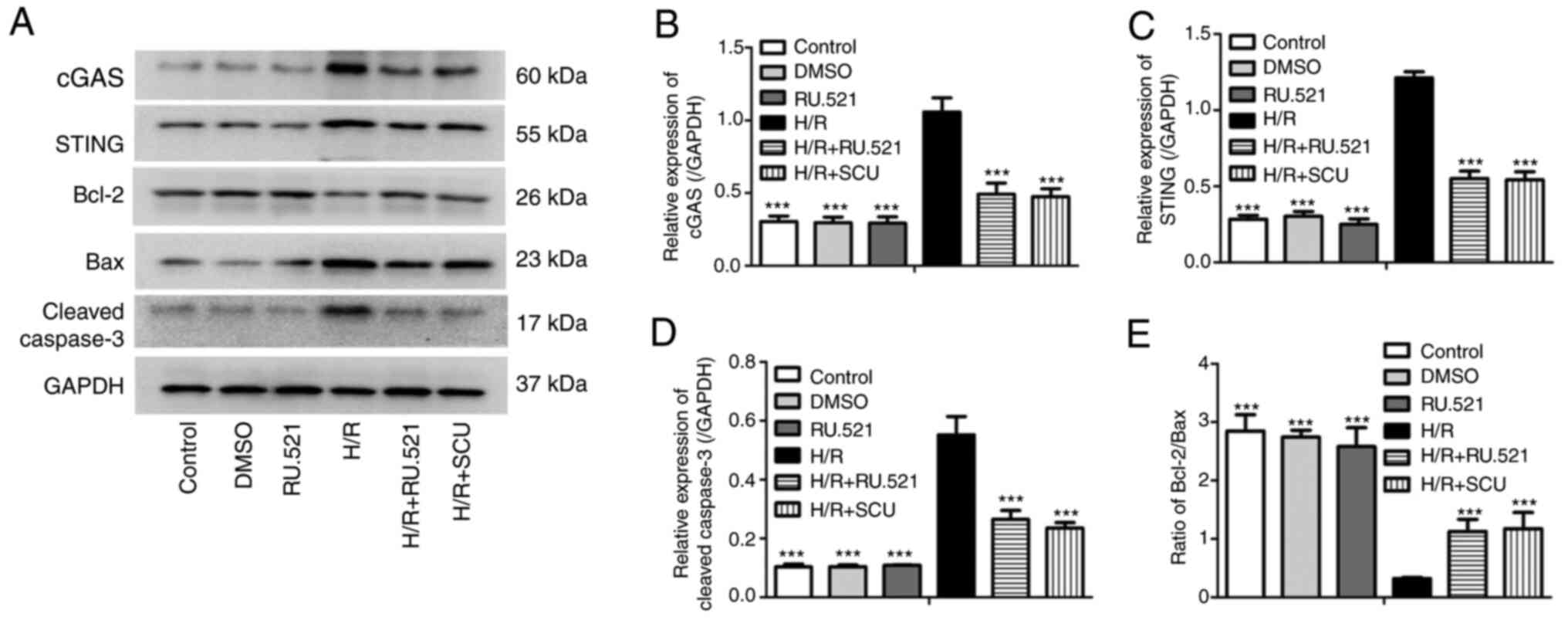
|
1
|
Wei D, Tang L, Su L, Zeng S, Telushi A,
Lang X, Zhang Y, Qin M, Qiu L, Zhong C and Yu J: Edgeworthia
gardneri (Wall.) Meisn. extract protects against myocardial
infarction by inhibiting NF-κB-and MAPK-mediated endothelial
inflammation. Front Cardiovasc Med. 9(1013013)2022.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
2
|
Writing Committee for the VISION Study
Investigators. Devereaux PJ, Biccard BM, Sigamani A, Xavier D, Chan
MTV, Srinathan SK, Walsh M, Abraham V, Pearse R, et al: Association
of postoperative high-sensitivity troponin levels with myocardial
injury and 30-day mortality among patients undergoing noncardiac
surgery. JAMA. 317:1642–1651. 2017.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
3
|
Li F, Li J, Li S, Guo S and Li P:
Modulatory effects of Chinese herbal medicines on energy metabolism
in ischemic heart diseases. Front Pharmacol. 11(995)2020.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
4
|
Keller K, Sagoschen I, Schmitt VH, Münzel
T, Gori T and Hobohm L: Hypothermia and its role in patients with
ST-segment-elevation myocardial infarction and cardiac arrest.
Front Cardiovasc Med. 9(1051978)2022.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
5
|
Eltzschig HK and Eckle T: Ischemia and
reperfusion-from mechanism to translation. Nat Med. 17:1391–1401.
2011.PubMed/NCBI View
Article : Google Scholar
|
|
6
|
Khan SU, Rahman H, Arshad A, Khan MU,
Lekkala M, Yang TJ, Mishra A and Kaluski E: Percutaneous coronary
intervention versus surgery in left main stenosis-a meta-analysis
and systematic review of randomised controlled trials. Heart Lung
Circ. 27:138–146. 2018.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
7
|
Heusch G: Cardioprotection: Chances and
challenges of its translation to the clinic. Lancet. 381:166–175.
2013.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
8
|
Lv B, Zhou J, He S, Zheng Y, Yang W, Liu
S, Liu C, Wang B, Li D and Lin J: Induction of myocardial
infarction and myocardial ischemia-reperfusion injury in mice. J
Vis Exp, 2022.
|
|
9
|
Scarabelli T, Stephanou A, Rayment N,
Pasini E, Comini L, Curello S, Ferrari R, Knight R and Latchman D:
Apoptosis of endothelial cells precedes myocyte cell apoptosis in
ischemia/reperfusion injury. Circulation. 104:253–256.
2001.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
10
|
Chen X, Li X, Zhang W, He J, Xu B, Lei B,
Wang Z, Cates C, Rousselle T and Li J: Activation of AMPK inhibits
inflammatory response during hypoxia and reoxygenation through
modulating JNK-mediated NF-κB pathway. Metabolism. 83:256–270.
2018.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
11
|
Neri M, Fineschi V, Di Paolo M, Pomara C,
Riezzo I, Turillazzi E and Cerretani D: Cardiac oxidative stress
and inflammatory cytokines response after myocardial infarction.
Curr Vasc Pharmacol. 13:26–36. 2015.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
12
|
Arslan F, Keogh B, McGuirk P and Parker
AE: TLR2 and TLR4 in ischemia reperfusion injury. Mediators
Inflamm. 2010(704202)2010.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
13
|
Ebrahimi H, Badalzadeh R, Mohammadi M and
Yousefi B: Diosgenin attenuates inflammatory response induced by
myocardial reperfusion injury: Role of mitochondrial ATP-sensitive
potassium channels. J Physiol Biochem. 70:425–432. 2014.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
14
|
Civril F, Deimling T, de Oliveira Mann CC,
Ablasser A, Moldt M, Witte G, Witte G, Hornung V and Hopfner KP:
Structural mechanism of cytosolic DNA sensing by cGAS. Nature.
498:332–337. 2013.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
15
|
Gulen MF, Koch U, Haag SM, Schuler F,
Apetoh L, Villunger A, Radtke F and Ablasser A: Signalling strength
determines proapoptotic functions of STING. Nat Commun.
8(427)2017.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
16
|
Heidegger S, Haas T and Poeck H: Cutting
edge in IFN regulation: Inflammatory caspases cleave cGAS.
Immunity. 46:333–335. 2017.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
17
|
Liao Y, Cheng J, Kong X, Li S, Li X, Zhang
M, Zhang H, Yang T, Dong Y, Li J, et al: HDAC3 inhibition
ameliorates ischemia/reperfusion-induced brain injury by regulating
the microglial cGAS-STING pathway. Theranostics. 10:9644–9662.
2020.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
18
|
Shi X, Chen G and Liu X, Qiu Y, Yang S,
Zhang Y, Fang X, Zhang C and Liu X: Scutellarein inhibits cancer
cell metastasis in vitro and attenuates the development of
fibrosarcoma in vivo. Int J Mol Med. 35:31–38.
2015.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
19
|
Hong H and Liu GQ: Protection against
hydrogen peroxide-induced cytotoxicity in PC12 cells by
scutellarin. Life Sci. 74:2959–2973. 2004.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
20
|
Yang N, Zhao Y, Wang Z, Liu Y and Zhang Y:
Scutellarin suppresses growth and causes apoptosis of human
colorectal cancer cells by regulating the p53 pathway. Mol Med Rep.
15:929–935. 2017.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
21
|
Guo H, Hu LM, Wang SX, Wang YL, Shi F, Li
H, Liu Y, Kang LY and Gao XM: Neuroprotective effects of
scutellarin against hypoxic-ischemic-induced cerebral injury via
augmentation of antioxidant defense capacity. Chin J Physiol.
54:399–405. 2011.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
22
|
Zhang HF, Hu XM, Wang LX, Xu SQ and Zeng
FD: Protective effects of scutellarin against cerebral ischemia in
rats: Evidence for inhibition of the apoptosis-inducing factor
pathway. Planta Med. 75:121–126. 2009.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
23
|
Wang Z, Yu J, Wu J, Qi F, Wang H, Wang Z
and Xu Z: Scutellarin protects cardiomyocyte ischemia-reperfusion
injury by reducing apoptosis and oxidative stress. Life Sci.
157:200–207. 2016.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
24
|
Xu LJ, Chen RC, Ma XY, Zhu Y, Sun GB and
Sun XB: Scutellarin protects against myocardial
ischemia-reperfusion injury by suppressing NLRP3 inflammasome
activation. Phytomedicine. 68(153169)2020.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
25
|
Hu XM, Zhou MM, Hu XM and Zeng FD:
Neuroprotective effects of scutellarin on rat neuronal damage
induced by cerebral ischemia/reperfusion. Acta Pharmacol Sin.
26:1454–1459. 2005.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
26
|
Gao J, Chen G, He H, Liu C, Xiong X, Li J
and Wang J: Therapeutic effects of breviscapine in cardiovascular
diseases: A review. Front Pharmacol. 8(289)2017.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
27
|
Li Y, Lu Y, Hu J, Gong Z, Yang W, Wang A,
Zheng J, Liu T, Chen T, Hu J, et al: Pharmacokinetic comparison of
scutellarin and paeoniflorin in sham-operated and middle cerebral
artery occlusion ischemia and reperfusion injury rats after
intravenous administration of Xin-Shao formula. Molecules.
21(1191)2016.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
28
|
Wu H and Jia L: Scutellarin attenuates
hypoxia/reoxygenation injury in hepatocytes by inhibiting apoptosis
and oxidative stress through regulating Keap1/Nrf2/ARE signaling.
Biosci Rep. 39(BSR20192501)2019.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
29
|
Lin LL, Liu AJ, Liu JG, Yu XH, Qin LP and
Su DF: Protective effects of scutellarin and breviscapine on brain
and heart ischemia in rats. J Cardiovasc Pharmacol. 50:327–332.
2007.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
30
|
Deng F, Zhao BC, Yang X, Lin ZB, Sun QS,
Wang YF, Yan ZZ, Liu WF, Li C, Hu JJ and Liu KX: The gut microbiota
metabolite capsiate promotes Gpx4 expression by activating TRPV1 to
inhibit intestinal ischemia reperfusion-induced ferroptosis. Gut
Microbes. 13:1–21. 2021.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
31
|
Huang KY, Que JQ, Hu ZS, Yu YW, Zhou YY,
Wang L, Xue YJ, Ji KT and Zhang XM: Metformin suppresses
inflammation and apoptosis of myocardiocytes by inhibiting
autophagy in a model of ischemia-reperfusion injury. Int J Biol
Sci. 16:2559–2579. 2020.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
32
|
Thompson CB: Apoptosis in the pathogenesis
and treatment of disease. Science. 267:1456–1462. 1995.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
33
|
Gross A, McDonnell JM and Korsmeyer SJ:
BCL-2 family members and the mitochondria in apoptosis. Genes Dev.
13:1899–1911. 1999.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
34
|
Youle RJ and Strasser A: The BCL-2 protein
family: Opposing activities that mediate cell death. Nat Rev Mol
Cell Bio. 9:47–59. 2008.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
35
|
Vaux DL, Cory S and Adams JM: Bcl-2 gene
promotes haemopoietic cell survival and cooperates with c-myc to
immortalize pre-B cells. Nature. 335:440–442. 1988.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
36
|
Lee R, Kim DW, Lee WY and Park HJ:
Zearalenone induces apoptosis and autophagy in a spermatogonia cell
line. Toxins (Basel). 14(148)2022.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
37
|
Siddiqui WA, Ahad A and Ahsan H: The
mystery of BCL2 family: Bcl-2 proteins and apoptosis: An update.
Arch Toxicol. 89:289–317. 2015.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
38
|
Liu LS, Bai XQ, Gao Y, Wu Q, Ren Z, Li Q,
Pan LH, He NY, Peng J and Tang ZH: PCSK9 promotes oxLDL-induced
PC12 cell apoptosis through the Bcl-2/Bax-caspase 9/3 signaling
pathway. J Alzheimers Dis. 57:723–734. 2017.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
39
|
Yao L, Chen H, Wu Q and Xie K:
Hydrogen-rich saline alleviates inflammation and apoptosis in
myocardial I/R injury via PINK-mediated autophagy. Int J Mol Med.
44:1048–1062. 2019.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
40
|
Wu J, Sun L, Chen X, Du F, Shi H, Chen C
and Chen ZJ: Cyclic GMP-AMP is an endogenous second messenger in
innate immune signaling by cytosolic DNA. Science. 339:826–830.
2013.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
41
|
Ishikawa H and Barber GN: STING is an
endoplasmic reticulum adaptor that facilitates innate immune
signalling. Nature. 455:674. 2008.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
42
|
Ma R, Ortiz Serrano TP, Davis J, Prigge AD
and Ridge KM: The cGAS-STING pathway: The role of self-DNA sensing
in inflammatory lung disease. FASEB J. 34:13156–13170.
2020.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
43
|
Hao F: An overview of the crosstalk
between YAP and cGAS-STING signaling in non-small cell lung cancer:
It takes two to tango. Clin Transl Oncol. 24:1661–1672.
2022.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
44
|
Xu D, Tian Y, Xia Q and Ke B: The
cGAS-STING pathway: Novel perspectives in liver diseases. Front
Immunol. 12(682736)2021.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
45
|
Wan DS, Jiang W and Hao JW: Research
advances in how the cGAS-STING pathway controls the cellular
inflammatory response. Front Immunol. 11(615)2020.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
46
|
Cao DJ, Schiattarella GG, Villalobos E,
Jiang N, May HI, Li T, Chen ZJ, Gillette TG and Hill JA: Cytosolic
DNA sensing promotes macrophage transformation and governs
myocardial ischemic injury. Circulation. 137:2613–2634.
2018.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
47
|
King KR, Aguirre AD, Ye YX, Sun Y, Roh JD,
Ng RP Jr, Kohler RH, Arlauckas SP, Iwamoto Y, Savol A, et al: IRF3
and type I interferons fuel a fatal response to myocardial
infarction. Nat Med. 23:1481–1487. 2017.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
48
|
Chen HL, Jia WJ, Li HE, Han H, Li F, Zhang
XLN, Li JJ, Yuan Y and Wu CY: Scutellarin exerts anti-inflammatory
effects in activated microglia/brain macrophage in cerebral
ischemia and in activated BV-2 microglia through regulation of
MAPKs signaling pathway. Neuromolecular Med. 22:264–277.
2020.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
49
|
Yuan Y, Zha H, Rangarajan P, Ling EA and
Wu C: Anti-inflammatory effects of edaravone and scutellarin in
activated microglia in experimentally induced ischemia injury in
rats and in BV-2 microglia. BMC Neurosci. 15(125)2014.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
50
|
Deng M, Sun J, Peng L, Huang Y, Jiang W,
Wu S, Zhou L, Chung S and Cheng X: Scutellarin acts on the AR-NOX
axis to remediate oxidative stress injury in a mouse model of
cerebral ischemia/reperfusion injury. Phytomedicine.
103(154214)2022.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
51
|
Zhang Y, Zhang Z, Wang J, Zhang X, Zhao J,
Bai N, Vijayalakshmi A and Huo Q: Scutellarin alleviates cerebral
ischemia/reperfusion by suppressing oxidative stress and
inflammatory responses via MAPK/NF-κB pathways in rats. Environ
Toxicol. 37:2889–2896. 2022.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
52
|
Hwang I, Uchida H, Dai Z, Li F, Sanchez T,
Locasale JW, Cantley LC, Zheng H and Paik J: Cellular stress
signaling activates type-I IFN response through FOXO3-regulated
lamin posttranslational modification. Nat Commun.
12(640)2021.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|