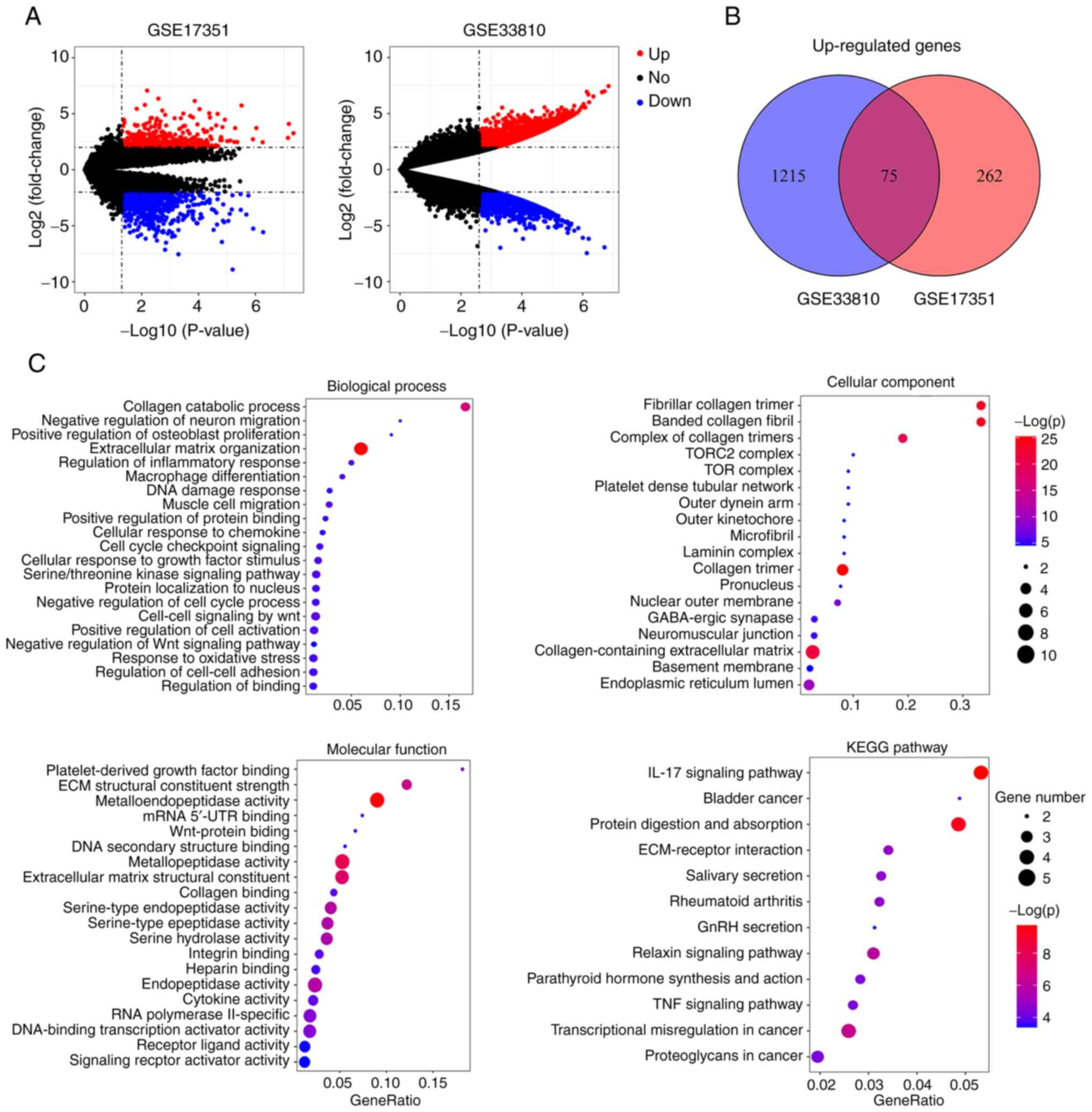
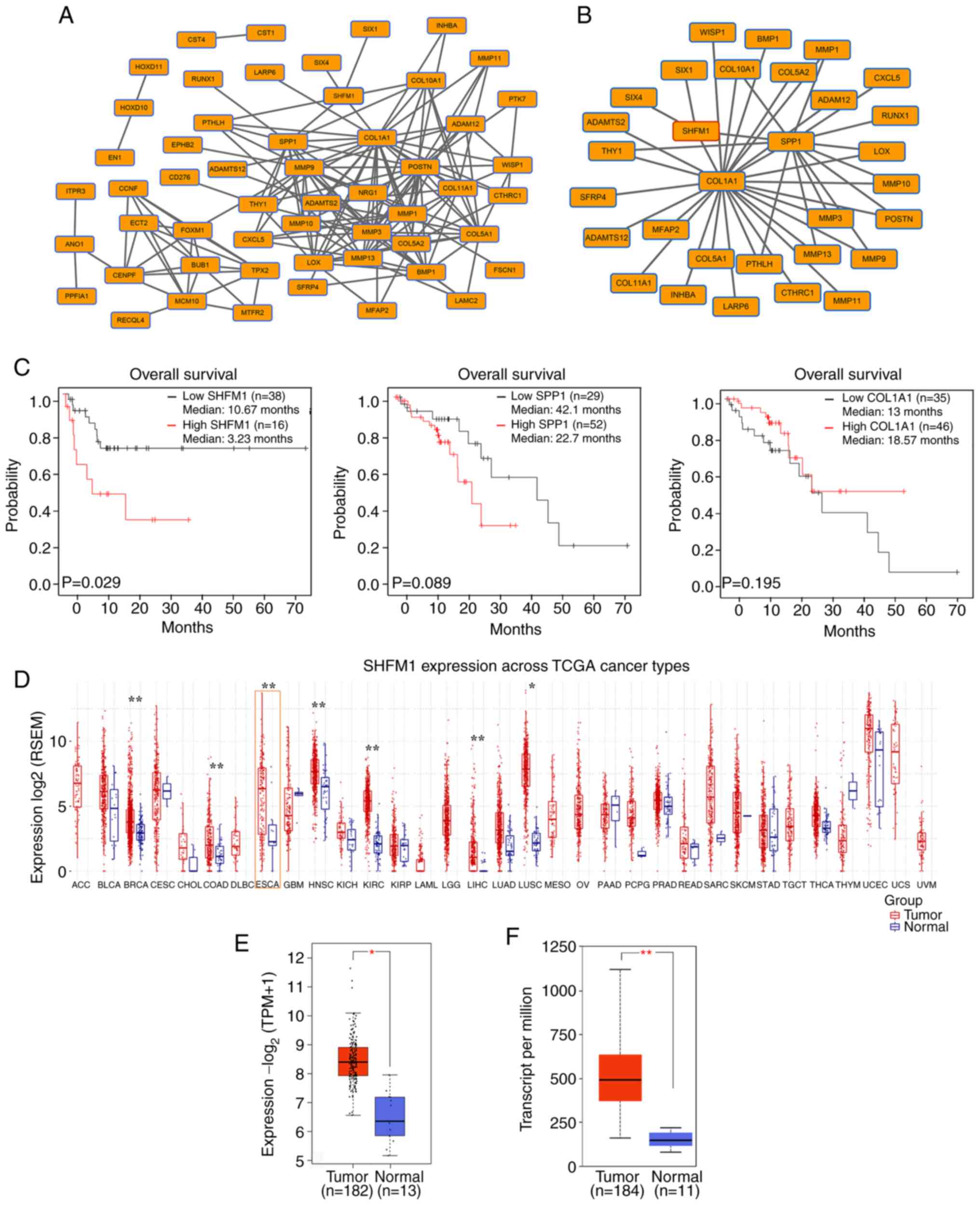
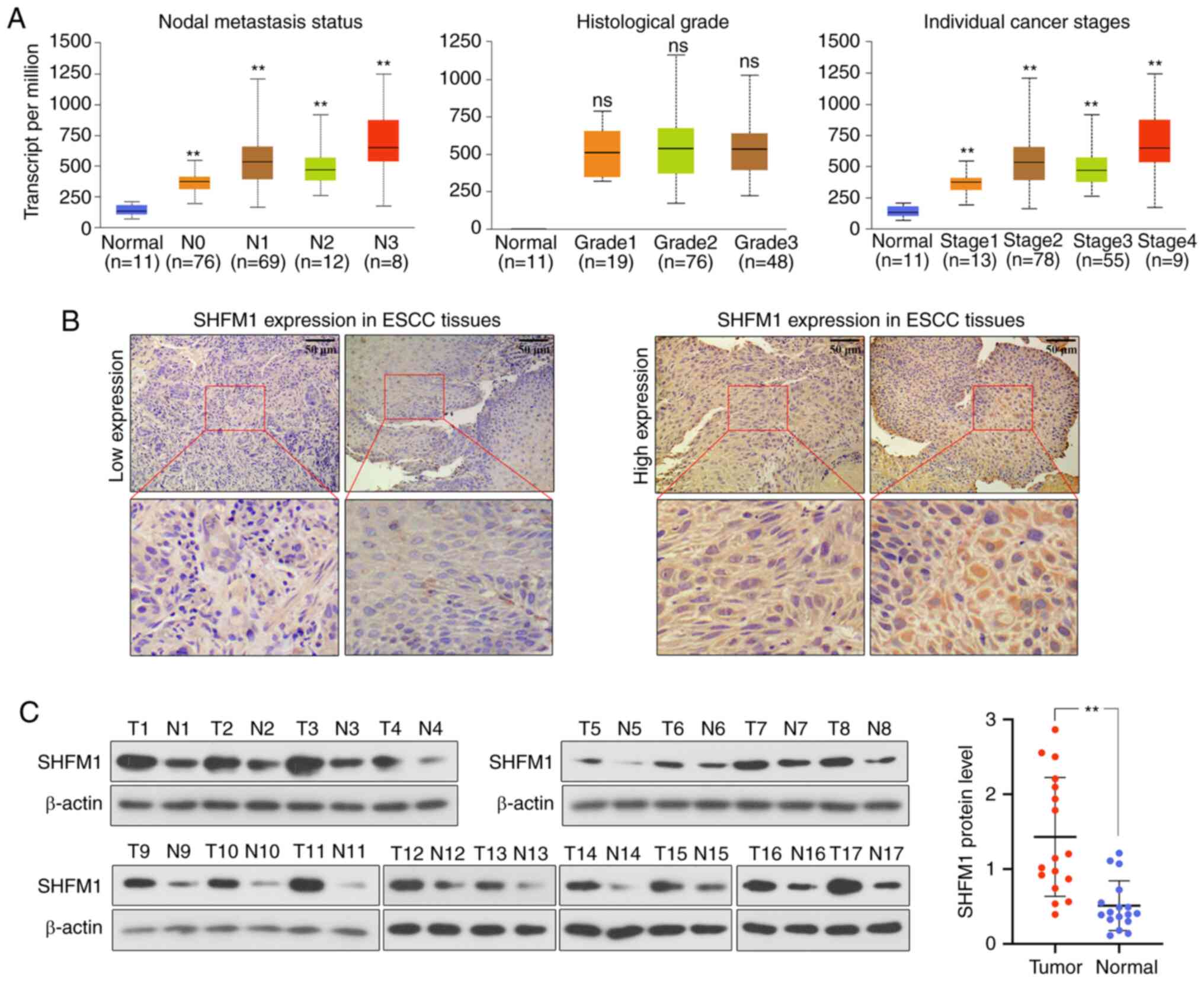
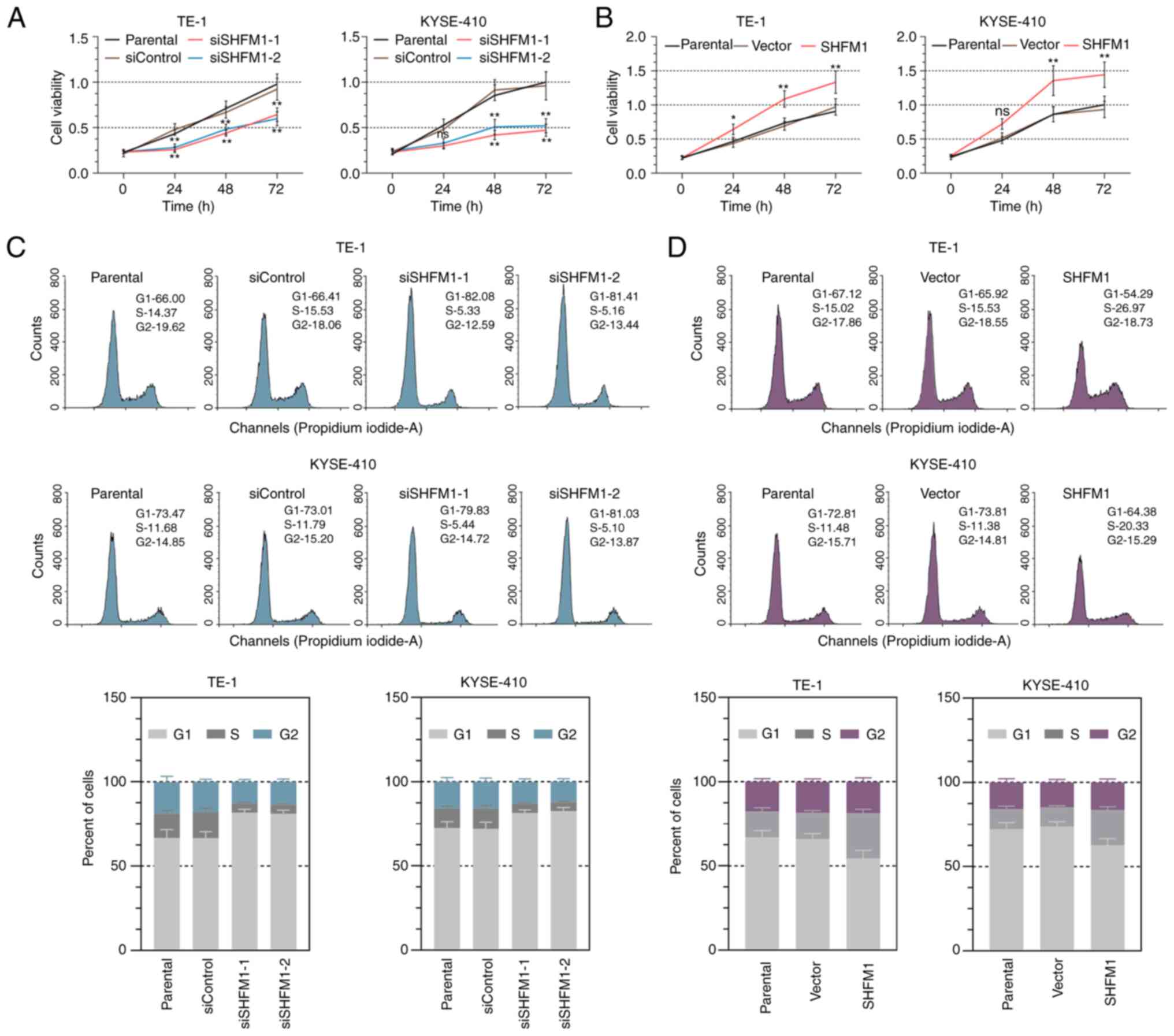
|
1
|
Zhou X, Ren T, Zan H, Hua C and Guo X:
Novel immune checkpoints in esophageal cancer: From biomarkers to
therapeutic targets. Front Immunol. 13(864202)2022.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
2
|
Jun Y, Tang Z, Luo C, Jiang B, Li X, Tao
M, Gu H, Liu L, Zhang Z, Sun S, et al: Leukocyte-mediated combined
targeted chemo and gene therapy for esophageal cancer. ACS Appl
Mater Interfaces. 12:47330–47341. 2020.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
3
|
Abnet CC, Arnold M and Wei WQ:
Epidemiology of esophageal squamous cell carcinoma.
Gastroenterology. 154:360–373. 2018.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
4
|
Yang YM, Hong P, Xu WW, He QY and Li B:
Advances in targeted therapy for esophageal cancer. Signal
Transduct Target Ther. 5(229)2020.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
5
|
Lambert AW, Pattabiraman DR and Weinberg
RA: Emerging biological principles of metastasis. Cell.
168:670–691. 2017.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
6
|
He S, Xu J, Liu X and Zhen Y: Advances and
challenges in the treatment of esophageal cancer. Acta Pharm Sin B.
11:3379–3392. 2021.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
7
|
Sharma P, Wagner K, Wolchok JD and Allison
JP: Novel cancer immunotherapy agents with survival benefit: Recent
successes and next steps. Nat Rev Cancer. 11:805–812.
2011.PubMed/NCBI View
Article : Google Scholar
|
|
8
|
Tan Y and Testa JR: DLX genes: Roles in
development and cancer. Cancers. 13(3005)2021.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
9
|
Zhang J, Wu J, Chen Y and Zhang W: Dlx5
promotes cancer progression through regulation of CCND1 in oral
squamous cell carcinoma (OSCC). Biochem Cell Biol. 99:424–434.
2021.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
10
|
Zhang X, Bian H, Wei W, Wang Q, Chen J,
Hei R, Chen C, Wu X, Yuan H, Gu J, et al: DLX5 promotes
osteosarcoma progression via activation of the NOTCH signaling
pathway. Am J Cancer Res. 11:3354–3374. 2021.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
11
|
Sun S, Yang F, Zhu Y and Zhang S: KDM4A
promotes the growth of non-small cell lung cancer by mediating the
expression of Myc via DLX5 through the Wnt/β-catenin signaling
pathway. Life Sci. 262(118508)2020.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
12
|
Tan Y, Cheung M, Pei J, Menges CW, Godwin
AK and Testa JR: Upregulation of DLX5 promotes ovarian cancer cell
proliferation by enhancing IRS-2-AKT signaling. Cancer Res.
70:9197–9206. 2010.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
13
|
Wang L, Zhou W, Zhong Y, Huo Y, Fan P,
Zhan S, Xiao J, Jin X, Gou S, Yin T, et al: Overexpression of G
protein-coupled receptor GPR87 promotes pancreatic cancer
aggressiveness and activates NF-κB signaling pathway. Mol Cancer.
16(61)2017.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
14
|
Zhang Y and Zhang Z: The history and
advances in cancer immunotherapy: Understanding the characteristics
of tumor-infiltrating immune cells and their therapeutic
implications. Cell Mol Immunol. 17:807–821. 2020.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
15
|
Prager I, Liesche C, van Ooijen H, Urlaub
D, Verron Q, Sandström N, Fasbender F, Claus M, Eils R, Beaudouin
J, et al: NK cells switch from granzyme B to death
receptor-mediated cytotoxicity during serial killing. J Exp Med.
216:2113–2127. 2019.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
16
|
Lourenco C, Resetca D, Redel C, Lin P,
MacDonald AS, Ciaccio R, Kenney TMG, Wei Y, Andrews DW, Sunnerhagen
M, et al: MYC protein interactors in gene transcription and cancer.
Nat Rev Cancer. 21:579–591. 2021.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
17
|
Wu X, Nelson M, Basu M, Srinivasan P,
Lazarski C, Zhang P, Zheng P and Sandler AD: MYC oncogene is
associated with suppression of tumor immunity and targeting Myc
induces tumor cell immunogenicity for therapeutic whole cell
vaccination. J Immunother Cancer. 9(e001388)2021.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
18
|
Zhang P, Wu X, Basu M, Dong C, Zheng P,
Liu Y and Sandler AD: MYCN amplification is associated with
repressed cellular immunity in neuroblastoma: An in ailico
immunological analysis of TARGET satabase. Front Immunol.
8(1473)2017.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
19
|
Casey SC, Baylot V and Felsher DW: The MYC
oncogene is a global regulator of the immune response. Blood.
131:2007–2015. 2018.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
20
|
Xu J and Testa JR: DLX5 (distal-less
homeobox 5) promotes tumor cell proliferation by transcriptionally
regulating MYC. J Biol Chem. 284:20593–20601. 2009.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
21
|
Casey SC, Baylot V and Felsher DW: MYC:
Master regulator of immune privilege. Trends Immunol. 38:298–305.
2017.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
22
|
Casey SC, Tong L, Li Y, Do R, Walz S,
Fitzgerald KN, Gouw AM, Baylot V, Gütgemann I, Eilers M and Felsher
DW: MYC regulates the antitumor immune response through CD47 and
PD-L1. Science. 352:227–231. 2016.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
23
|
Kim EY, Kim A, Kim SK and Chang YS: MYC
expression correlates with PD-L1 expression in non-small cell lung
cancer. Lung Cancer. 110:63–67. 2017.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
24
|
Liang MQ, Yu FQ and Chen C: C-Myc
regulates PD-L1 expression in esophageal squamous cell carcinoma.
Am J Transl Res. 12:379–388. 2020.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
25
|
Chiossone L, Vienne M, Kerdiles YM and
Vivier E: Natural killer cell immunotherapies against cancer:
Checkpoint inhibitors and more. Semin Immunol. 31:55–63.
2017.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
26
|
Livak KJ and Schmittgen TD: Analysis of
relative gene expression data using real-time quantitative PCR and
the 2(-Delta Delta C(T)) method. Methods. 25:402–408.
2001.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
27
|
Sun X, Zhang J, Hou Z, Han Q, Zhang C and
Tian Z: MiR-146a is directly regulated by STAT3 in human
hepatocellular carcinoma cells and involved in anti-tumor immune
suppression. Cell Cycle. 14:243–252. 2015.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
28
|
Percie N, Hurst V, Ahluwalia A, Alam S,
Avey MT, Baker M, Browne WJ, Clark A, Cuthill IC, Dirnagl U, et al:
The ARRIVE guidelines 2.0: Updated guidelines for reporting animal
research. PLoS Biol. 18(e3000410)2020.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
29
|
Lian Y, Niu X, Cai H, Yang X, Ma H, Ma S,
Zhang Y and Chen Y: Clinicopathological significance of c-MYC in
esophageal squamous cell carcinoma. Tumour Biol.
39(1010428317715804)2017.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
30
|
Ito S, Okano S, Morita M, Saeki H,
Tsutsumi S, Tsukihara H, Nakashima Y, Ando K, Imamura Y, Ohgaki K,
et al: Expression of PD-L1 and HLA class I in esophageal squamous
cell carcinoma: Prognostic factors for patient outcome. Ann Surg
Oncol. 23:508–515. 2016.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
31
|
Sefid F, Payandeh Z, Azamirad G, Baradaran
B, Afjadi MN, Islami M, Darvish M, Kalantar SM, Kahroba H and
Ardakani MA: Atezolizumab and granzyme B as immunotoxin against
PD-L1 antigen; an insilico study. In Silico Pharmacol.
9(20)2021.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
32
|
Li Y, Wang X, Shi L, Xu J and Sun B:
Predictions for high and expression resulting in a poor prognosis
in esophageal squamous cell carcinoma by bioinformatics analyses.
Transl Cancer Res. 9:85–94. 2020.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
33
|
Fang S, Dai Y, Mei Y, Yang M, Hu L, Yang
H, Guan X and Li J: Clinical significance and biological role of
cancer-derived type I collagen in lung and esophageal cancers.
Thorac Cancer. 10:277–288. 2019.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
34
|
Li M, Wang K, Pang Y, Zhang H, Peng H, Shi
Q, Zhang Z, Cui X and Li F: Secreted phosphoprotein 1 (SPP1) and
fibronectin 1 (FN1) are associated with progression and prognosis
of esophageal cancer as identified by integrated expression
profiles analysis. Med Sci Monit. 26(e920355)2020.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
35
|
Karsli-Ceppioglu S, Dagdemir A, Judes G,
Lebert A, Penault-Llorca F, Bignon YJ and Bernard-Gallon D: The
epigenetic landscape of promoter genome-wide analysis in breast
cancer. Sci Rep. 7(6597)2017.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
36
|
Tamilzhalagan S, Muthuswami M, Periasamy
J, Lee MH, Rha SY, Tan P and Ganesan K: Upregulated, 7q21-22
amplicon candidate gene SHFM1 confers oncogenic advantage by
suppressing p53 function in gastric cancer. Cell Signal.
27:1075–1086. 2015.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
37
|
Huang Y, Yang Q, Zheng Y, Lin L, Xu X, Xu
XE, Silva TC, Hazawa M, Peng L, Cao H, et al: Activation of
bivalent factor DLX5 cooperates with master regulator TP63 to
promote squamous cell carcinoma. Nucleic Acids Res. 49:9246–9263.
2021.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
38
|
Zhao Y, Wei L, Shao M, Huang X, Chang J,
Zheng J, Chu J, Cui Q, Peng L, Luo Y, et al: BRCA1-associated
protein increases invasiveness of esophageal squamous cell
carcinoma. Gastroenterology. 153:1304–1319.e1305. 2017.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
39
|
Haria D, Trinh BQ, Ko SY, Barengo N, Liu J
and Naora H: The homeoprotein DLX4 stimulates NF-κB activation and
CD44-mediated tumor-mesothelial cell interactions in ovarian
cancer. Am J Pathol. 185:2298–2308. 2015.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
40
|
Chen L and Han X: Anti-PD-1/PD-L1 therapy
of human cancer: Past, present, and future. J Clin Invest.
125:3384–3391. 2015.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
41
|
Doi T, Piha-Paul SA, Jalal SI, Saraf S,
Lunceford J, Koshiji M and Bennouna J: Safety and antitumor
activity of the anti-programmed death-1 antibody pembrolizumab in
patients with advanced esophageal carcinoma. J Clin Oncol.
36:61–67. 2018.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
42
|
Wang X, Teng F, Kong L and Yu J: PD-L1
expression in human cancers and its association with clinical
outcomes. Onco Targets Ther. 9:5023–5039. 2016.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
43
|
Zhou C, Che G, Zheng X, Qiu J, Xie Z, Cong
Y, Pei X, Zhang H, Sun H and Ma H: Expression and clinical
significance of PD-L1 and c-Myc in non-small cell lung cancer. J
Cancer Res Clin Oncol. 145:2663–2674. 2019.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
44
|
Qu S, Jiao Z, Lu G, Yao B, Wang T, Rong W,
Xu J, Fan T, Sun X, Yang R, et al: PD-L1 lncRNA splice isoform
promotes lung adenocarcinoma progression via enhancing c-Myc
activity. Genome Biol. 22(104)2021.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
45
|
Han H, Jain AD, Truica MI,
Izquierdo-Ferrer J, Anker JF, Lysy B, Sagar V, Luan Y, Chalmers ZR,
Unno K, et al: Small-molecule MYC inhibitors suppress tumor growth
and enhance immunotherapy. Cancer Cell. 36:483–497.e415.
2019.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
46
|
Wu Y, Xie J, Jin X, Lenchine RV, Wang X,
Fang DM, Nassar ZD, Butler LM, Li J and Proud CG: eEF2K enhances
expression of PD-L1 by promoting the translation of its mRNA.
Biochem J. 477:4367–4381. 2020.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
47
|
Uppendahl LD, Felices M, Bendzick L, Ryan
C, Kodal B, Hinderlie P, Boylan KLM, Skubitz APN, Miller JS and
Geller MA: Cytokine-induced memory-like natural killer cells have
enhanced function, proliferation, and in vivo expansion against
ovarian cancer cells. Gynecol Oncol. 153:149–157. 2019.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
48
|
Lorenzo-Herrero S, Sordo-Bahamonde C,
González S and López-Soto A: A flow cytometric NK cell-mediated
cytotoxicity assay to evaluate anticancer immune responses in
vitro. Methods Mol Biol. 1884:131–139. 2019.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
49
|
Prager I and Watzl C: Mechanisms of
natural killer cell-mediated cellular cytotoxicity. J Leukoc Biol.
105:1319–1329. 2019.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
50
|
Zhou Z, He H, Wang K, Shi X, Wang Y, Su Y,
Wang Y, Li D, Liu W, Zhang Y, et al: Granzyme A from cytotoxic
lymphocytes cleaves GSDMB to trigger pyroptosis in target cells.
Science. 368(eaaz7548)2020.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
51
|
Cerwenka A and Lanier LL: Natural killer
cell memory in infection, inflammation and cancer. Nat Rev Immunol.
16:112–123. 2016.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
52
|
Aptsiauri N, Ruiz-Cabello F and Garrido F:
The transition from HLA-I positive to HLA-I negative primary
tumors: The road to escape from T-cell responses. Curr Opin
Immunol. 51:123–132. 2018.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
53
|
Ramia E, Chiaravalli AM, Eddine FBN,
Tedeschi A, Sessa F, Accolla RS and Forlani G: CIITA-related block
of HLA class II expression, upregulation of HLA class I, and
heterogeneous expression of immune checkpoints in hepatocarcinomas:
Implications for new therapeutic approaches. Oncoimmunology.
8(1548243)2019.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
54
|
Garrido F, Aptsiauri N, Doorduijn EM, Lora
AM and van Hall T: The urgent need to recover MHC class I in
cancers for effective immunotherapy. Curr Opin Immunol. 39:44–51.
2016.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|