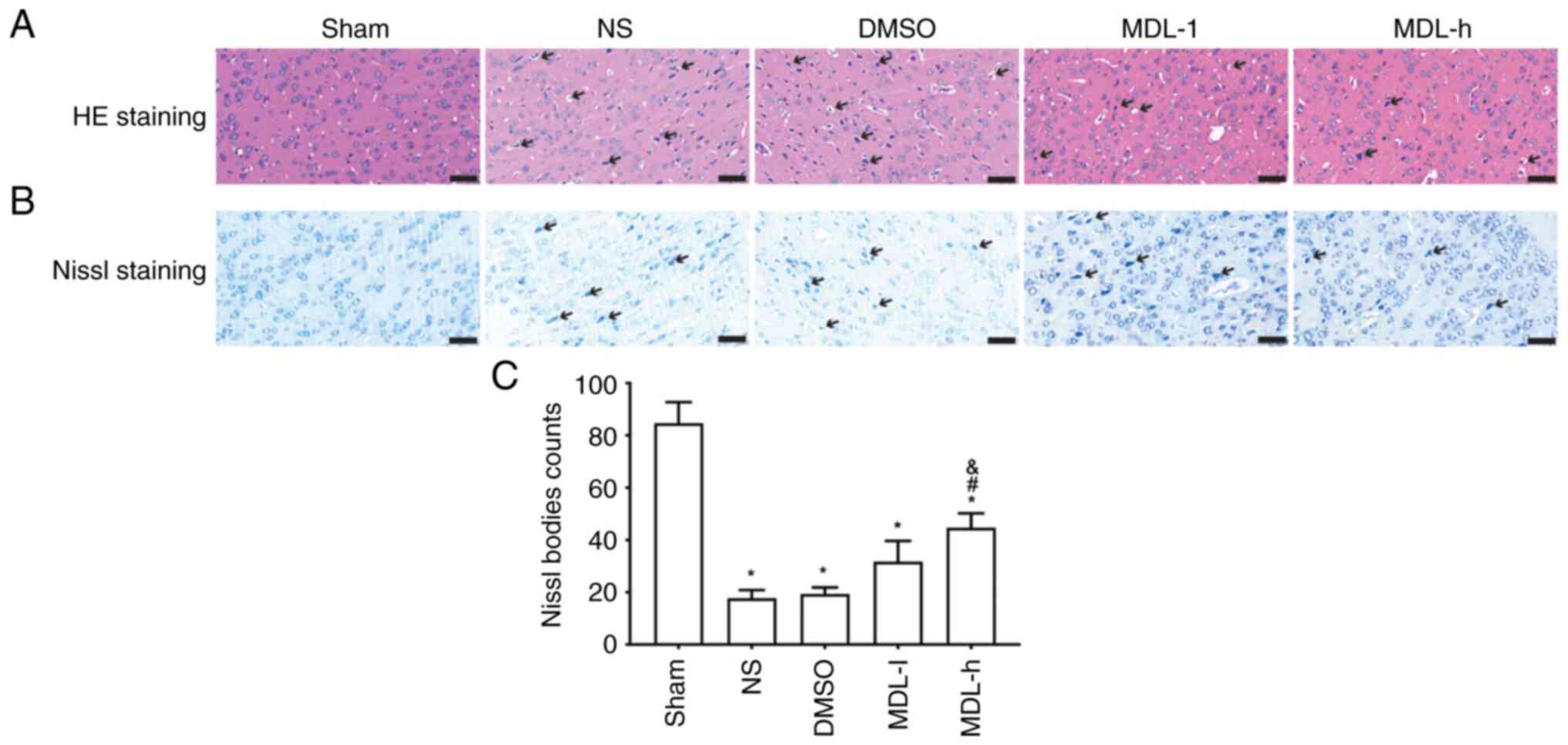
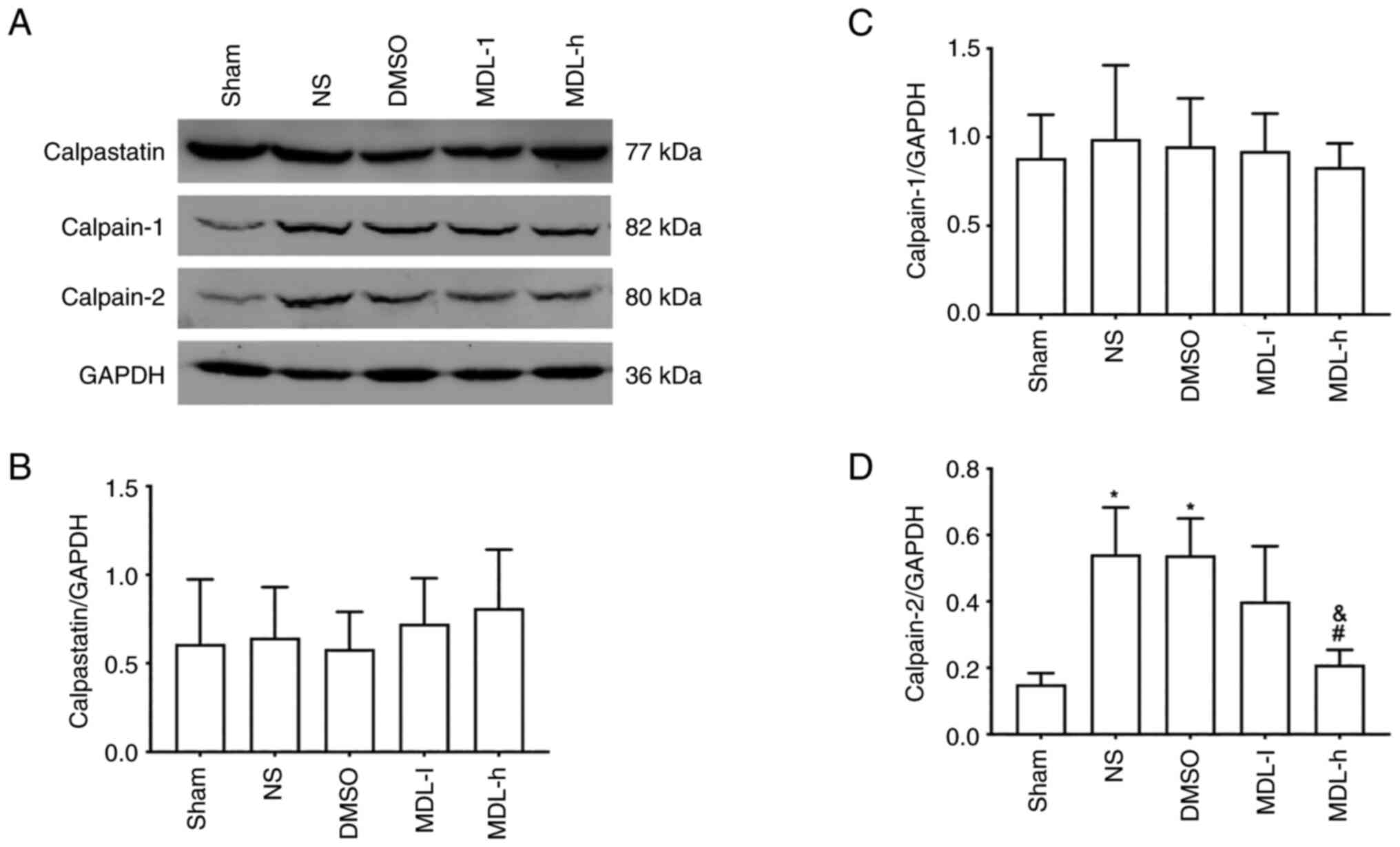
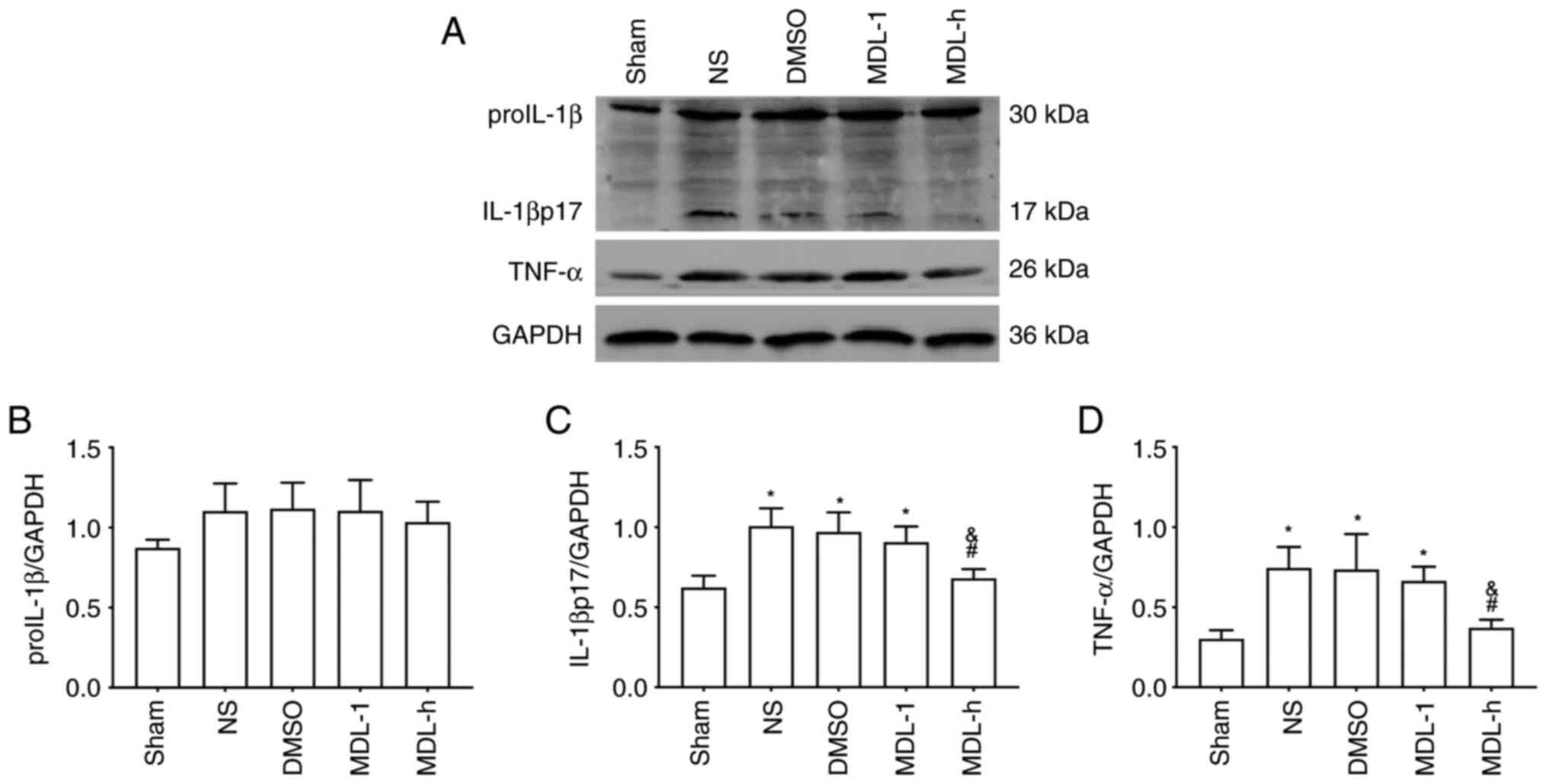
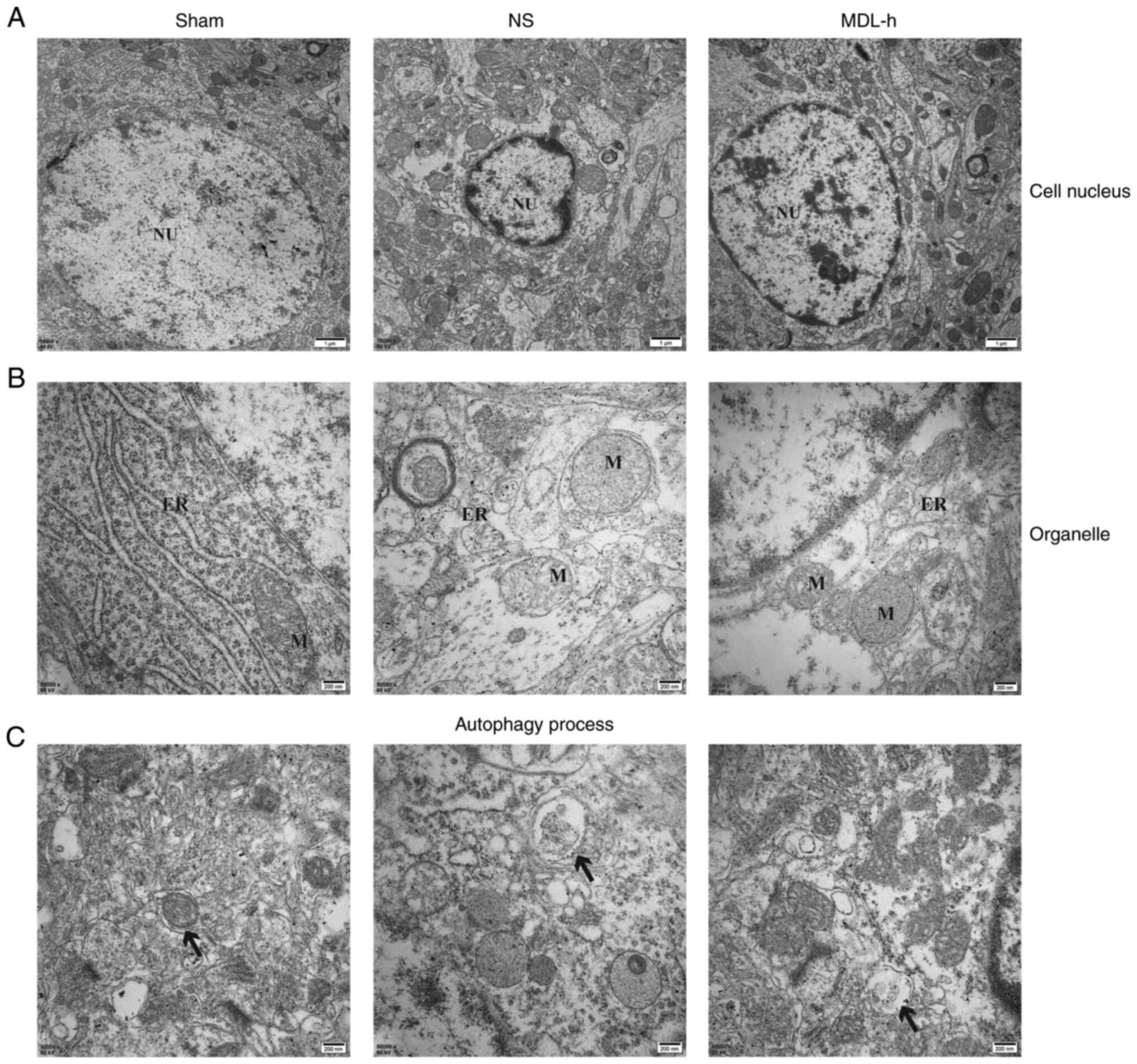
|
1
|
Andersen LW, Holmberg MJ, Berg KM, Donnino
MW and Granfeldt A: In-hospital cardiac arrest: A review. JAMA.
321:1200–1210. 2019.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
2
|
Sandroni C, D'Arrigo S and Nolan JP:
Prognostication after cardiac arrest. Crit Care.
22(150)2018.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
3
|
Moore JC, Bartos JA, Matsuura TR and
Yannopoulos D: The future is now: Neuroprotection during
cardiopulmonary resuscitation. Curr Opin Crit Care. 23:215–222.
2017.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
4
|
Goodfellow MJ, Borcar A, Proctor JL, Greco
T, Rosenthal RE and Fiskum G: Transcriptional activation of
antioxidant gene expression by Nrf2 protects against mitochondrial
dysfunction and neuronal death associated with acute and chronic
neurodegeneration. Exp Neurol. 328(113247)2020.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
5
|
Chen H, Yoshioka H, Kim GS, Jung JE, Okami
N, Sakata H, Maier CM, Narasimhan P, Goeders CE and Chan PH:
Oxidative stress in ischemic brain damage: Mechanisms of cell death
and potential molecular targets for neuroprotection. Antioxid Redox
Signal. 14:1505–1517. 2011.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
6
|
Liu J, Liu MC and Wang KKW: Calpain in the
CNS: from synaptic function to neurotoxicity. Sci Signal.
1(re1)2008.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
7
|
Curcio M, Salazar IL, Mele M, Canzoniero
LMT and Duarte CB: Calpains and neuronal damage in the ischemic
brain: The Swiss knife in synaptic injury. Prog Neurobiol.
143:1–35. 2016.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
8
|
Martinez JA, Zhang Z, Svetlov SI, Hayes
RL, Wang KK and Larner SF: Calpain and caspase processing of
caspase-12 contribute to the ER stress-induced cell death pathway
in differentiated PC12 cells. Apoptosis. 15:1480–1493.
2010.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
9
|
Sanganalmath SK, Gopal P, Parker JR, Downs
RK, Parker JC Jr and Dawn B: Global cerebral ischemia due to
circulatory arrest: Insights into cellular pathophysiology and
diagnostic modalities. Mol Cell Biochem. 426:111–127.
2017.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
10
|
Dókus LE, Yousef M and Bánóczi Z:
Modulators of calpain activity: Inhibitors and activators as
potential drugs. Expert Opin Drug Discov. 15:471–486.
2020.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
11
|
Baudry M and Bi X: Calpain-1 and
calpain-2: The yin and yang of synaptic plasticity and
neurodegeneration. Trends Neurosci. 39:235–245. 2016.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
12
|
Cheng SY, Wang SC, Lei M, Wang Z and Xiong
K: Regulatory role of calpain in neuronal death. Neural Regen Res.
13:556–562. 2018.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
13
|
Wang Y, Bi X and Baudry M: Calpain-2 as a
therapeutic target for acute neuronal injury. Expert Opin Ther
Targets. 22:19–29. 2018.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
14
|
Jiao W, McDonald DQ, Coxon JM and Parker
EJ: Molecular modeling studies of peptide inhibitors highlight the
importance of conformational prearrangement for inhibition of
calpain. Biochemistry. 49:5533–5539. 2010.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
15
|
Betts R, Weinsheimer S, Blouse GE and
Anagli J: Structural determinants of the calpain inhibitory
activity of calpastatin peptide B27-WT. J Biol Chem. 278:7800–7809.
2003.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
16
|
Potz BA, Abid MR and Sellke FW: Role of
calpain in pathogenesis of human disease processes. J Nat Sci.
2(e218)2016.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
17
|
Hu J, Chen L, Huang X, Wu K, Ding S, Wang
W, Wang B, Smith C, Ren C, Ni H, et al: Calpain inhibitor MDL28170
improves the transplantation-mediated therapeutic effect of bone
marrow-derived mesenchymal stem cells following traumatic brain
injury. Stem Cell Res Ther. 10(96)2019.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
18
|
Thompson SN, Carrico KM, Mustafa AG, Bains
M and Hall ED: A pharmacological analysis of the neuroprotective
efficacy of the brain- and cell-permeable calpain inhibitor
MDL-28170 in the mouse controlled cortical impact traumatic brain
injury model. J Neurotrauma. 27:2233–2243. 2010.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
19
|
Chen LN, Yan B, Chen DP and Yao YJ:
Protective effect of calpain inhibitor-3 on hypoxic-ischemic brain
damage of neonatal rats. Zhonghua Er Ke Za Zhi. 46:13–17.
2008.PubMed/NCBI(In Chinese).
|
|
20
|
Li PA, Howlett W, He QP, Miyashita H,
Siddiqui M and Shuaib A: Postischemic treatment with calpain
inhibitor MDL 28170 ameliorates brain damage in a gerbil model of
global ischemia. Neurosci Lett. 247:17–20. 1998.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
21
|
Ravindran S and Kurian GA: Eventual
analysis of global cerebral ischemia-reperfusion injury in rat
brain: A paradigm of a shift in stress and its influence on
cognitive functions. Cell Stress Chaperones. 24:581–594.
2019.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
22
|
Tuttolomondo A, Di Raimondo D, Pecoraro R,
Arnao V, Pinto A and Licata G: Inflammation in ischemic stroke
subtypes. Curr Pharm Des. 18:4289–4310. 2012.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
23
|
Tao XG, Shi JH, Hao SY, Chen XT and Liu
BY: Protective effects of calpain inhibition on neurovascular unit
injury through downregulating nuclear factor-κB-related
inflammation during traumatic brain injury in mice. Chin Med J
(Engl). 130:187–198. 2017.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
24
|
Wang WY, Xie L, Zou XS, Li N, Yang YG, Wu
ZJ, Tian XY, Zhao GY and Chen MH: Inhibition of extracellular
signal-regulated kinase/calpain-2 pathway reduces neuroinflammation
and necroptosis after cerebral ischemia-reperfusion injury in a rat
model of cardiac arrest. Int Immunopharmacol.
93(107377)2021.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
25
|
Edinger AL and Thompson CB: Death by
design: Apoptosis, necrosis and autophagy. Curr Opin Cell Biol.
16:663–669. 2004.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
26
|
Ashrafi G and Schwarz TL: The pathways of
mitophagy for quality control and clearance of mitochondria. Cell
Death Differ. 20:31–42. 2013.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
27
|
Zheng JH, Xie L, Li N, Fu ZY, Tan XF, Tao
R, Qin T and Chen MH: PD98059 protects the brain against
mitochondrial-mediated apoptosis and autophagy in a cardiac arrest
rat model. Life Sci. 232(116618)2019.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
28
|
Li Y, He Z, Lv H, Chen W and Chen J:
Calpain-2 plays a pivotal role in the inhibitory effects of
propofol against TNF-α-induced autophagy in mouse hippocampal
neurons. J Cell Mol Med. 24:9287–9299. 2020.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
29
|
Chen MH, Liu TW, Xie L, Song FQ, He T,
Zeng ZY and Mo SR: Ventricular fibrillation induced by
transoesophageal cardiac pacing: a new model of cardiac arrest in
rats. Resuscitation. 74:546–551. 2007.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
30
|
Du PR, Lu HT, Lin XX, Wang LF, Wang YX, Gu
XM, Bai XZ, Tao K and Zhou JJ: Calpain inhibition ameliorates scald
burn-induced acute lung injury in rats. Burns Trauma.
6(28)2018.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
31
|
Jia X, Koenig MA, Shin HC, Zhen G, Pardo
CA, Hanley DF, Thakor NV and Geocadin RG: Improving neurological
outcomes post-cardiac arrest in a rat model: Immediate hypothermia
and quantitative EEG monitoring. Resuscitation. 76:431–442.
2008.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
32
|
Cataldo F, Peche LY, Klaric E, Brancolini
C, Myers MP, Demarchi F and Schneider C: CAPNS1 regulates USP1
stability and maintenance of genome integrity. Mol Cell Biol.
33:2485–2496. 2013.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
33
|
Zheng P, Chen X, Xie J, Chen X, Lin S, Ye
L, Chen L, Lin J, Yu X and Zheng M: Capn4 is induced by and
required for Epstein-Barr virus latent membrane protein 1 promotion
of nasopharyngeal carcinoma metastasis through ERK/AP-1 signaling.
Cancer Sci. 111:72–83. 2020.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
34
|
Zhu H, Yoshimoto T, Imajo-Ohmi S,
Dazortsava M, Mathivanan A and Yamashima T: Why are hippocampal CA1
neurons vulnerable but motor cortex neurons resistant to transient
ischemia? J Neurochem. 120:574–585. 2012.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
35
|
Fukuda S, Harada K, Kunimatsu M, Sakabe T
and Yoshida K: Postischemic reperfusion induces alpha-fodrin
proteolysis by m-calpain in the synaptosome and nucleus in rat
brain. J Neurochem. 70:2526–2532. 1998.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
36
|
Zang Y, Chen SX, Liao GJ, Zhu HQ, Wei XH,
Cui Y, Na XD, Pang RP, Xin WJ, Zhou LJ and Liu XG: Calpain-2
contributes to neuropathic pain following motor nerve injury via
up-regulating interleukin-6 in DRG neurons. Brain Behav Immun.
44:37–47. 2015.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
37
|
Li Y, Bondada V, Joshi A and Geddes JW:
Calpain 1 and calpastatin expression is developmentally regulated
in rat brain. Exp Neurol. 220:316–319. 2009.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
38
|
Xiong XY, Liu L and Yang QW: Functions and
mechanisms of microglia/macrophages in neuroinflammation and
neurogenesis after stroke. Prog Neurobiol. 142:23–44.
2016.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
39
|
Lopez-Castejon G and Brough D:
Understanding the mechanism of IL-1β secretion. Cytokine Growth
Factor Rev. 22:189–195. 2011.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
40
|
Chen Y, Su Z and Liu F: Effects of
functionally diverse calpain system on immune cells. Immunol Res.
69:8–17. 2021.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
41
|
Guo MM, Qu SB, Lu HL, Wang WB, He ML, Su
JL, Chen J and Wang Y: Biochanin A alleviates cerebral
ischemia/reperfusion injury by suppressing endoplasmic reticulum
stress-induced apoptosis and p38MAPK signaling pathway in vivo and
in vitro. Front Endocrinol (Lausanne). 12(646720)2021.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
42
|
Thompson J, Maceyka M and Chen Q:
Targeting ER stress and calpain activation to reverse age-dependent
mitochondrial damage in the heart. Mech Ageing Dev.
192(111380)2020.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
43
|
Li W, Zhu J, Dou J, She H, Tao K, Xu H,
Yang Q and Mao Z: Phosphorylation of LAMP2A by p38 MAPK couples ER
stress to chaperone-mediated autophagy. Nat Commun.
8(1763)2017.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
44
|
Lépine S, Allegood JC, Edmonds Y, Milstien
S and Spiegel S: Autophagy induced by deficiency of
sphingosine-1-phosphate phosphohydrolase 1 is switched to apoptosis
by calpain-mediated autophagy-related gene 5 (Atg5) cleavage. J
Biol Chem. 286:44380–44390. 2011.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
45
|
So KY, Lee BH and Oh SH: The critical role
of autophagy in cadmium-induced immunosuppression regulated by
endoplasmic reticulum stress-mediated calpain activation in
RAW264.7 mouse monocytes. Toxicology. 393:15–25. 2018.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
46
|
Demarchi F, Bertoli C, Copetti T, Tanida
I, Brancolini C, Eskelinen EL and Schneider C: Calpain is required
for macroautophagy in mammalian cells. J Cell Biol. 175:595–605.
2006.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
47
|
Li XY, Meng L, Wang F, Hu XJ and Yu YC:
Sodium fluoride induces apoptosis and autophagy via the endoplasmic
reticulum stress pathway in MC3T3-E1 osteoblastic cells. Mol Cell
Biochem. 454:77–85. 2019.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
48
|
Qu X, Yu J, Bhagat G, Furuya N, Hibshoosh
H, Troxel A, Rosen J, Eskelinen EL, Mizushima N, Ohsumi Y, et al:
Promotion of tumorigenesis by heterozygous disruption of the beclin
1 autophagy gene. J Clin Invest. 112:1809–1820. 2003.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
49
|
Glick D, Barth S and Macleod KF:
Autophagy: Cellular and molecular mechanisms. J Pathol. 221:3–12.
2010.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
50
|
Kaur J and Debnath J: Autophagy at the
crossroads of catabolism and anabolism. Nat Rev Mol Cell Biol.
16:461–472. 2015.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
51
|
Klionsky DJ, Abdalla FC, Abeliovich H,
Abraham RT, Acevedo-Arozena A, Adeli K, Agholme L, Agnello M,
Agostinis P, Aguirre-Ghiso JA, et al: Guidelines for the use and
interpretation of assays for monitoring autophagy. Autophagy.
8:445–544. 2012.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
52
|
Gustafsson AB and Gottlieb RA: Autophagy
in ischemic heart disease. Circ Res. 104:150–158. 2009.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
53
|
Nguyen Thi PAN, Chen MH, Li N, Zhuo XJ and
Xie L: PD98059 protects brain against cells death resulting from
ROS/ERK activation in a cardiac arrest rat model. Oxid Med Cell
Longev. 2016(3723762)2016.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
54
|
Xie RJ, Hu XX, Zheng L, Cai S, Chen YS,
Yang Y, Yang T, Han B and Yang Q: Calpain-2 activity promotes
aberrant endoplasmic reticulum stress-related apoptosis in
hepatocytes. World J Gastroenterol. 26:1450–1462. 2020.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
55
|
Ly LD, Xu S, Choi SK, Ha CM, Thoudam T,
Cha SK, Wiederkehr A, Wollheim CB, Lee IK and Park KS: Oxidative
stress and calcium dysregulation by palmitate in type 2 diabetes.
Exp Mol Med. 49(e291)2017.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
56
|
Zhao Q, Guo Z, Deng W, Fu S, Zhang C, Chen
M, Ju W, Wang D and He X: Calpain 2-mediated autophagy defect
increases susceptibility of fatty livers to ischemia-reperfusion
injury. Cell Death Dis. 7(e2186)2016.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
57
|
Liu Y, Che X, Zhang H, Fu X, Yao Y, Luo J,
Yang Y, Cai R, Yu X, Yang J and Zhou MS: . CAPN1
(Calpain1)-mediated impairment of autophagic flux contributes to
cerebral ischemia-induced neuronal damage. Stroke. 52:1809–1821.
2021.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|