|
1
|
Mantzorou M, Koutelidakis A, Theocharis S
and Giaginis C: Clinical value of nutritional status in cancer:
What is its impact and how it affects disease progression and
prognosis? Nutr Cancer. 69:1151–1176. 2017.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
2
|
Kim DH: Nutritional issues in patients
with cancer. Intest Res. 17:455–462. 2019.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
3
|
de Ulíbarri JI, González-Madroño A, de
Villar NGP, González P, González B, Mancha A, Rodríguez F and
Fernández G: CONUT: A tool for controlling nutritional status.
First validation in a hospital population. Nutr Hosp. 20:38–45.
2005.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
4
|
Liang RF, Li JH, Li M, Yang Y and Liu YH:
The prognostic role of controlling nutritional status scores in
patients with solid tumors. Clin Chim Acta. 474:155–158.
2017.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
5
|
Zhang Y and Zhang X: Controlling
nutritional status score, a promising prognostic marker in patients
with gastrointestinal cancers after surgery: A systematic review
and meta-analysis. Int J Surg. 55:39–45. 2018.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
6
|
Kheirouri S and Alizadeh M: Prognostic
potential of the preoperative controlling nutritional status
(CONUT) score in predicting survival of patients with cancer: A
systematic review. Adv Nutr. 12:234–250. 2021.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
7
|
Takagi K, Domagala P, Polak WG, Buettner
S, Wijnhoven BPL and Ijzermans JNM: Prognostic significance of the
controlling nutritional status (CONUT) score in patients undergoing
gastrectomy for gastric cancer: A systematic review and
meta-analysis. BMC Surgery. 19(129)2019.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
8
|
Page MJ, McKenzie JE, Bossuyt PM, Boutron
I, Hoffmann TC, Mulrow CD, Shamseer L, Tetzlaff JM, Akl EA, Brennan
SE, et al: The PRISMA 2020 statement: An updated guideline for
reporting systematic reviews. BMJ. 372(n71)2021.PubMed/NCBI View
Article : Google Scholar
|
|
9
|
Wells G, Shea B, O'Connell D, Peterson J,
Welch V, Losos M and Tugwell P: The Newcastle-Ottawa (NOS) for
assessing the quality of nonrandomized studies in meta-analysis.
Ottawa Hospital Research Institute, 2014.
|
|
10
|
Higgins JPT, Thomas J, Chandler J,
Cumpston M, Li T, Page MJ and Welch VA (eds): Cochrane Handbook for
Systematic Reviews of Interventions version 6.3 (updated February
2022). Cochrane, London, 2022. www.training.cochrane.org/handbook.
|
|
11
|
Egger M, Smith GD, Schneider M and Minder
C: Bias in meta-analysis detected by a simple, graphical test. BMJ.
315:629–634. 1997.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
12
|
Zhu X, Zhao Y, Ma F and Wu S: Controlling
nutritional status score predict the individualized survival of
patients with gastric cancer. Asia Pac J Clin Nutr. 30:51–59.
2021.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
13
|
Galizia G, Auricchio A, de Vita F,
Cardella F, Mabilia A, Basile N, Orditura M and Lieto E:
Inflammatory and nutritional status is a predictor of long-term
outcome in patients undergoing surgery for gastric cancer.
Validation of the Naples prognostic score. Ann Ital Chir.
90:404–416. 2019.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
14
|
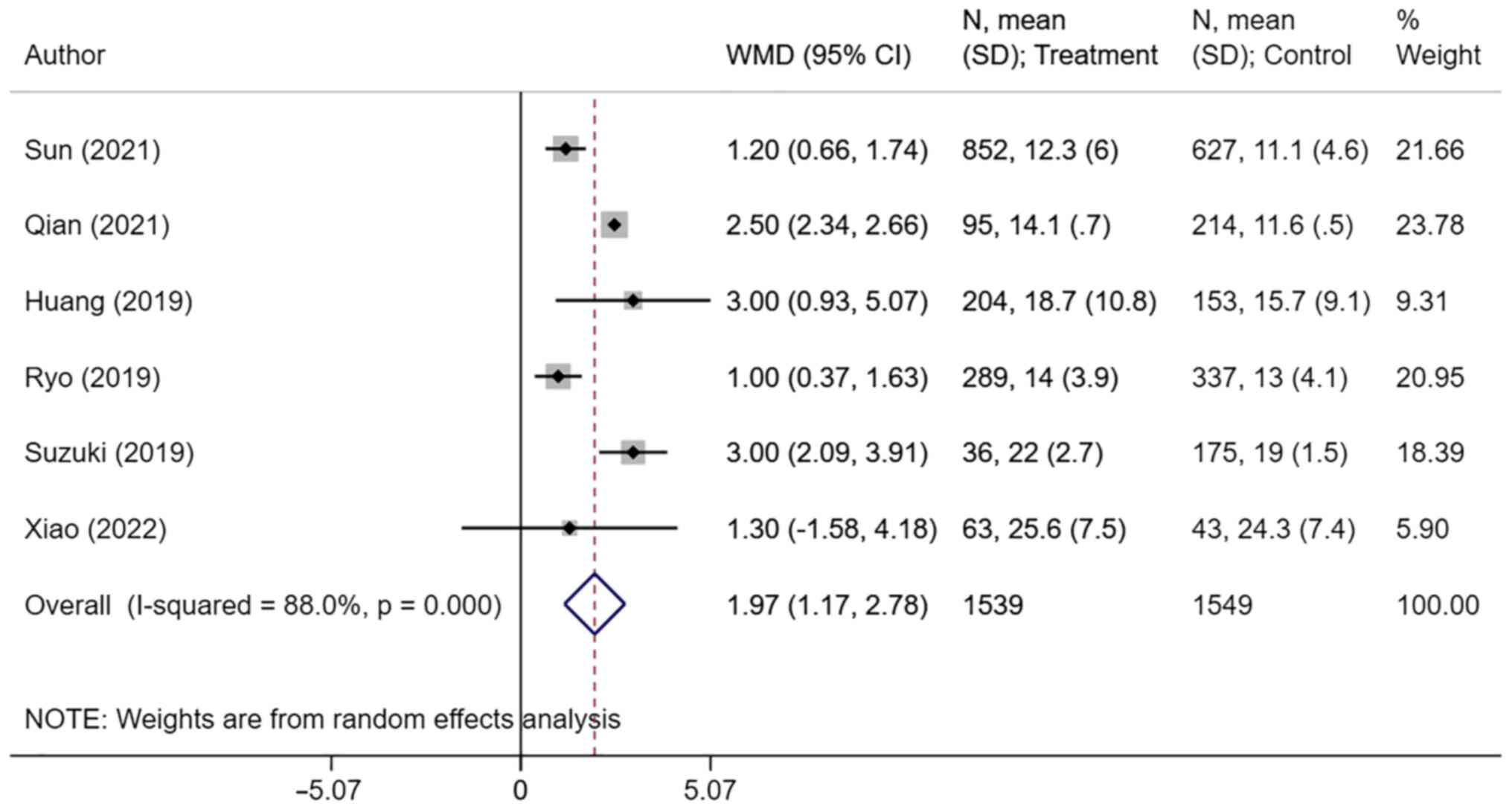
Sun F, Zhang C, Liu Z, Ai S, Guan W and
Liu S: Controlling nutritional status (CONUT) score as a predictive
marker for short-term complications following gastrectomy of
gastric cancer: A retrospective study. BMC Gastroenterol.
21(107)2021.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
15
|
Qian Y, Liu H, Pan J, Yu W, Lv J, Yan J,
Gao J, Wang X, Ge X and Zhou W: Preoperative controlling
nutritional status (CONUT) score predicts short-term outcomes of
patients with gastric cancer after laparoscopy-assisted radical
gastrectomy. World J Surg Oncol. 19(25)2021.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
16
|
Jin H, Zhu K and Wang W: The predictive
values of pretreatment controlling nutritional status (CONUT) score
in estimating short- and long-term outcomes for patients with
gastric cancer treated with neoadjuvant chemotherapy and curative
gastrectomy. J Gastric Cancer. 21:155–168. 2021.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
17
|
Akagunduz B, Demir M and Atcı MM:
Controlling nutritional status (CONUT) score is a prognostic factor
for patients with gastric cancer treated by perioperative FLOT. J
Gastrointest Cancer. 53:571–580. 2022.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
18
|
Lin JX, Lin LZ, Tang YH, Wang JB, Lu J,
Chen QY, Cao LL, Lin M, Tu RH, Huang CM, et al: Which nutritional
scoring system is more suitable for evaluating the short- or
long-term prognosis of patients with gastric cancer who underwent
radical gastrectomy? J Gastrointest Surg. 24:1969–1977.
2020.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
19
|
Huang Y, Huang Y, Lu M, Sun W, Sun X, Chen
X and Li L, Chandoo A and Li L: Controlling nutritional status
(CONUT) score is a predictor of post-operative outcomes in elderly
gastric cancer patients undergoing curative gastrectomy: A
prospective study. Cancer Manag Res. 11:9793–9800. 2019.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
20
|
Jeon CH, Park KB, Jung YJ, Seo HS, Park
CH, Song KY and Lee HH: Modified controlling nutritional status
score: A refined prognostic indicator depending on the stage of
gastric cancer. Surg Oncol. 34:261–269. 2020.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
21
|
Hirahara N, Tajima Y, Fujii Y, Kaji S,
Kawabata Y, Hyakudomi R, Yamamoto T and Taniura T: Controlling
nutritional status (CONUT) as a prognostic immunonutritional
biomarker for gastric cancer after curative gastrectomy: A
propensity score-matched analysis. Surg Endosc. 33:4143–4152.
2019.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
22
|
Kuroda D, Sawayama H, Kurashige J,
Iwatsuki M, Eto T, Tokunaga R, Kitano Y, Yamamura K, Ouchi M,
Nakamura K, et al: Controlling nutritional status (CONUT) score is
a prognostic marker for gastric cancer patients after curative
resection. Gastric Cancer. 21:204–212. 2018.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
23
|
Zheng ZF, Lu J, Xie JW, Wang JB, Lin JX,
Chen QY, Cao LL, Lin M, Tu RH, Zheng CH, et al: Preoperative
skeletal muscle index vs the controlling nutritional status score:
Which is a better objective predictor of long-term survival for
gastric cancer patients after radical gastrectomy? Cancer Med.
7:3537–3547. 2018.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
24
|
Liu X, Zhang D, Lin E, Chen Y, Li W, Chen
Y, Sun X and Zhou Z: Preoperative controlling nutritional status
(CONUT) score as a predictor of long-term outcome after curative
resection followed by adjuvant chemotherapy in stage II-III gastric
cancer. BMC Cancer. 18(699)2018.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
25
|
Ryo S, Kanda M, Ito S, Mochizuki Y,
Teramoto H, Ishigure K, Murai T, Asada T, Ishiyama A, Matsushita H,
et al: The controlling nutritional status score serves as a
predictor of short- and long-term outcomes for patients with stage
2 or 3 gastric cancer: Analysis of a multi-institutional data set.
Ann Surg Oncol. 26:456–464. 2019.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
26
|
Suzuki S, Kanaji S, Yamamoto M, Oshikiri
T, Nakamura T and Kakeji Y: Controlling nutritional status (CONUT)
score predicts outcomes of curative resection for gastric cancer in
the elderly. World J Surg. 43:1076–1084. 2019.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
27
|
Xiao Q, Li X, Duan B, Li X, Liu S, Xu B,
Shi S, Zhang J, Qin H, Duan X, et al: Clinical significance of
controlling nutritional status score (CONUT) in evaluating outcome
of postoperative patients with gastric cancer. Sci Rep.
12(93)2022.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
28
|
Aoyama T, Komori K, Nakazano M, Hara K,
Tamagawa H, Kazama K, Hashimoto I, Yamada T, Maezawa Y, Segami K,
et al: The clinical influence of the CONUT score on survival of
patients with gastric cancer receiving curative treatment. In Vivo.
36:942–948. 2022.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
29
|
Elinav E, Nowarski R, Thaiss CA, Hu B, Jin
C and Flavell RA: Inflammation-induced cancer: crosstalk between
tumours, immune cells and microorganisms. Nat Rev Cancer.
13:759–771. 2013.PubMed/NCBI View
Article : Google Scholar
|
|
30
|
Alwarawrah Y, Kiernan K and MacIver NJ:
Changes in nutritional status impact immune cell metabolism and
function. Front Immunol. 9(1055)2018.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
31
|
Alifano M, Mansuet-Lupo A, Lococo F, Roche
N, Bobbio A, Canny E, Schussler O, Dermine H, Régnard JF, Burroni
B, et al: Systemic inflammation, nutritional status and tumor
immune microenvironment determine outcome of resected non-small
cell lung cancer. PLoS One. 9(e106914)2014.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
32
|
Huang Y, Alzahrani NA, Chua TC, Huo YR,
Liauw W and Morris DL: Impacts of preoperative serum albumin level
on outcomes of cytoreductive surgery and perioperative
intraperitoneal chemotherapy. Ann Surg Oncol. 23:2411–2418.
2016.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
33
|
Nozoe T, Ninomiya M, Maeda T, Matsukuma A,
Nakashima H and Ezaki T: Prognostic nutritional index: A tool to
predict the biological aggressiveness of gastric carcinoma. Surg
Today. 40:440–443. 2010.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
34
|
Tokunaga R, Sakamoto Y, Nakagawa S,
Miyamoto Y, Yoshida N, Oki E, Watanabe M and Baba H: Prognostic
nutritional index predicts severe complications, recurrence, and
poor prognosis in patients with colorectal cancer undergoing
primary tumor resection. Dis Colon Rectum. 58:1048–1057.
2015.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
35
|
Sun K, Chen S, Xu J, Li G and He Y: The
prognostic significance of the prognostic nutritional index in
cancer: A systematic review and meta-analysis. J Cancer Res Clin
Oncol. 140:1537–1549. 2014.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
36
|
Mellor KL, Powell AGMT and Lewis WG:
Systematic review and meta-analysis of the prognostic significance
of neutrophil-lymphocyte ratio (NLR) after R0 gastrectomy for
cancer. J Gastrointest Cancer. 49:237–244. 2018.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
37
|
Zhang LX, Wei ZJ, Xu AM and Zang JH: Can
the neutrophil-lymphocyte ratio and platelet-lymphocyte ratio be
beneficial in predicting lymph node metastasis and promising
prognostic markers of gastric cancer patients? Tumor maker
retrospective study. Int J Surg. 56:320–327. 2018.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
38
|
Tan D, Fu Y, Tong W and Li F: Prognostic
significance of lymphocyte to monocyte ratio in colorectal cancer:
A meta-analysis. Int J Surg. 55:128–138. 2018.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
39
|
Lin ZX, Ruan DY, Jia CC, Wang TT, Cheng
JT, Huang HQ and Wu XY: Controlling nutritional status (CONUT)
score-based nomogram to predict overall survival of patients with
HBV-associated hepatocellular carcinoma after curative hepatectomy.
Clin Transl Oncol. 22:370–380. 2020.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
40
|
Lee SC, Lee JG, Lee SH, Kim EY, Chang J,
Kim DJ, Paik HC, Chung KY and Jung JY: Prediction of postoperative
pulmonary complications using preoperative controlling nutritional
status (CONUT) score in patients with resectable non-small cell
lung cancer. Sci Rep. 10(12385)2020.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
41
|
Iseki Y, Shibutani M, Maeda K, Nagahara H,
Ohtani H, Sugano K, Ikeya T, Muguruma K, Tanaka H, Toyokawa T, et
al: Impact of the preoperative controlling nutritional status
(CONUT) score on the survival after curative surgery for colorectal
cancer. PLoS One. 10(e0132488)2015.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
42
|
Cengiz O, Kocer B, Sürmeli S, Santicky MJ
and Soran A: Are pretreatment serum albumin and cholesterol levels
prognostic tools in patients with colorectal carcinoma? Med Sci
Monit. 12:CR240–CR247. 2006.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
43
|
Niendorf A, Nägele H, Gerding D,
Meyer-Pannwitt U and Gebhardt A: Increased LDL receptor mRNA
expression in colon cancer is correlated with a rise in plasma
cholesterol levels after curative surgery. Int J Cancer.
61:461–464. 1995.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
44
|
Vitols S, Gahrton G, Björkholm M and
Peterson C: Hypocholesterolaemia in malignancy due to elevated
low-density-lipoprotein-receptor activity in tumour cells: evidence
from studies in patients with leukaemia. Lancet. 2:1150–1154.
1985.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
45
|
Notarnicola M, Altomare DF, Correale M,
Ruggieri E, D'Attoma B, Mastrosimini A, Guerra V and Caruso MG:
Serum lipid profile in colorectal cancer patients with and without
synchronous distant metastases. Oncology. 68:371–374.
2005.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
46
|
Zhang X, Hurng J, Rateri DL, Daugherty A,
Schmid-Schönbein GW and Shin HY: Membrane cholesterol modulates the
fluid shear stress response of polymorphonuclear leukocytes via its
effects on membrane fluidity. Am J Physiol Cell Physiol.
301:C451–C460. 2011.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
47
|
Oliver MF: Serum cholesterol-the knave of
hearts and the joker. Lancet. 2:1090–1095. 1981.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
48
|
Oñate-Ocaña LF, Aiello-Crocifoglio V,
Gallardo-Rincón D, Herrera-Goepfert R, Brom-Valladares R, Carrillo
JF, Cervera E and Mohar-Betancourt A: Serum albumin as a
significant prognostic factor for patients with gastric carcinoma.
Ann Surg Oncol. 14:381–389. 2007.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
49
|
Crumley ABC, Stuart RC, McKernan M and
McMillan DC: Is hypoalbuminemia an independent prognostic factor in
patients with gastric cancer? World J Surg. 34:2393–2398.
2010.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
50
|
Okuyama H, Ichikawa Y, Sun Y, Hamazaki T
and Lands WEM: Cancer and all-cause mortalities are lower in the
higher total cholesterol groups among general populations. World
Rev Nutr Diet. 96:37–54. 2007.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
51
|
Strasak AM, Pfeiffer RM, Brant LJ, Rapp K,
Hilbe W, Oberaigner W, Lang S, Borena W, Concin H, Diem G, et al:
Time-dependent association of total serum cholesterol and cancer
incidence in a cohort of 172,210 men and women: A prospective
19-year follow-up study. Ann Oncol. 20:1113–1120. 2009.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
52
|
Zhou P, Li B, Liu B, Chen T and Xiao J:
Prognostic role of serum total cholesterol and high-density
lipoprotein cholesterol in cancer survivors: A systematic review
and meta-analysis. Clin Chim Acta. 477:94–104. 2018.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
53
|
Saito H, Kono Y, Murakami Y, Shishido Y,
Kuroda H, Yamamoto M, Fukumoto Y, Osaki T, Ashida K and Fujiwara Y:
Prognostic significance of pre- and postoperative lymphocyte counts
in patients with gastric cancer. Dig Surg. 36:137–143.
2019.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
54
|
Tokunaga R, Sakamoto Y, Nakagawa S, Ohuchi
M, Izumi D, Kosumi K, Taki K, Higashi T, Miyamoto Y, Yoshida N, et
al: CONUT: A novel independent predictive score for colorectal
cancer patients undergoing potentially curative resection. Int J
Colorectal Dis. 32:99–106. 2017.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
55
|
Zheng Y, Bao L, Wang W, Wang Q, Pan Y and
Gao X: Prognostic impact of the Controlling Nutritional Status
score following curative nephrectomy for patients with renal cell
carcinoma. Medicine (Baltimore). 97(e13409)2018.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
56
|
Gallagher EJ and LeRoith D: Obesity and
diabetes: The increased risk of cancer and cancer-related
mortality. Physiol Rev. 95:727–748. 2015.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
57
|
Karczewski J, Begier-Krasińska B,
Staszewski R, Popławska E, Gulczynska-Elhadi K and Dobrowolska A:
Obesity and the risk of gastrointestinal cancers. Dig Dis Sci.
64:2740–2749. 2019.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|