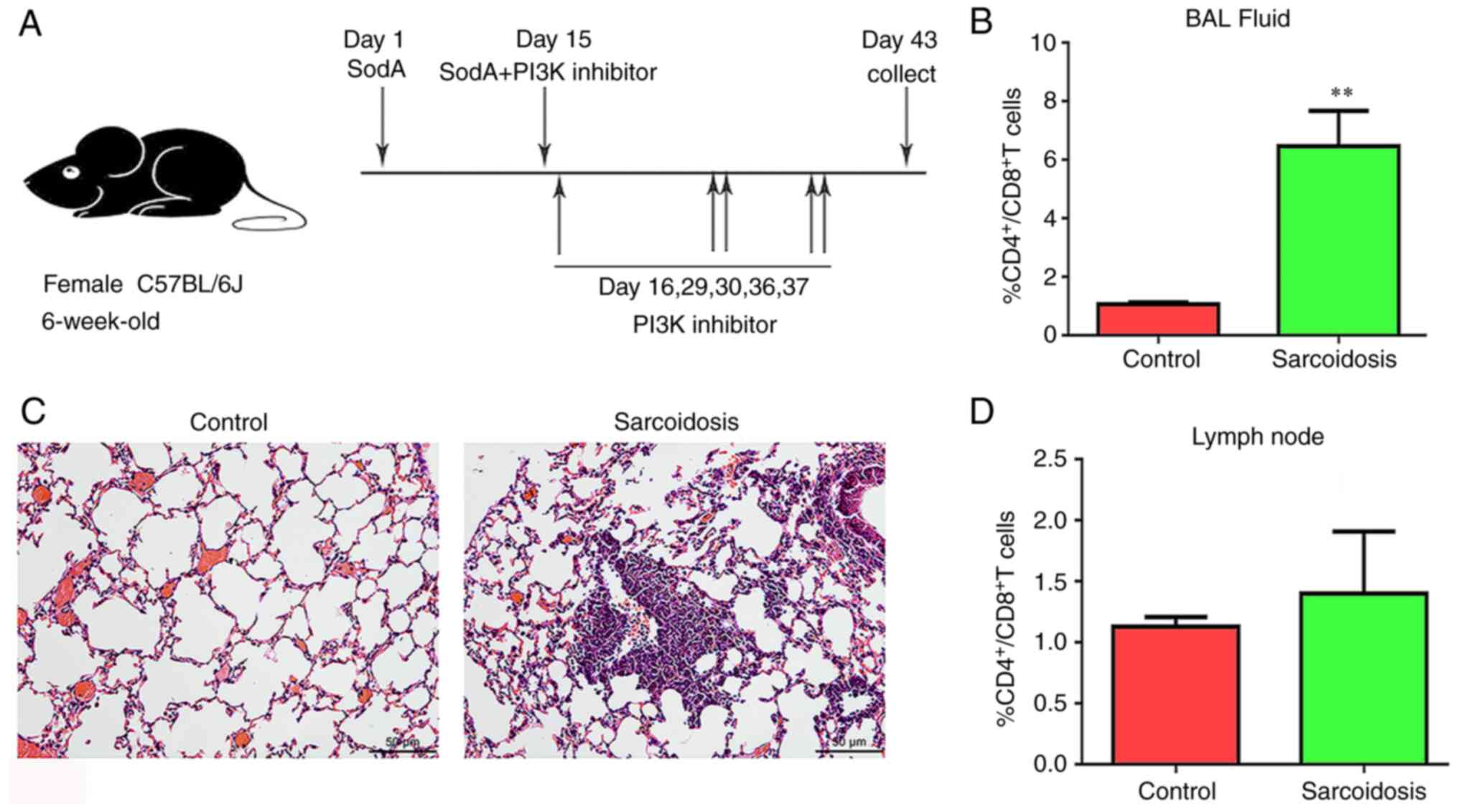
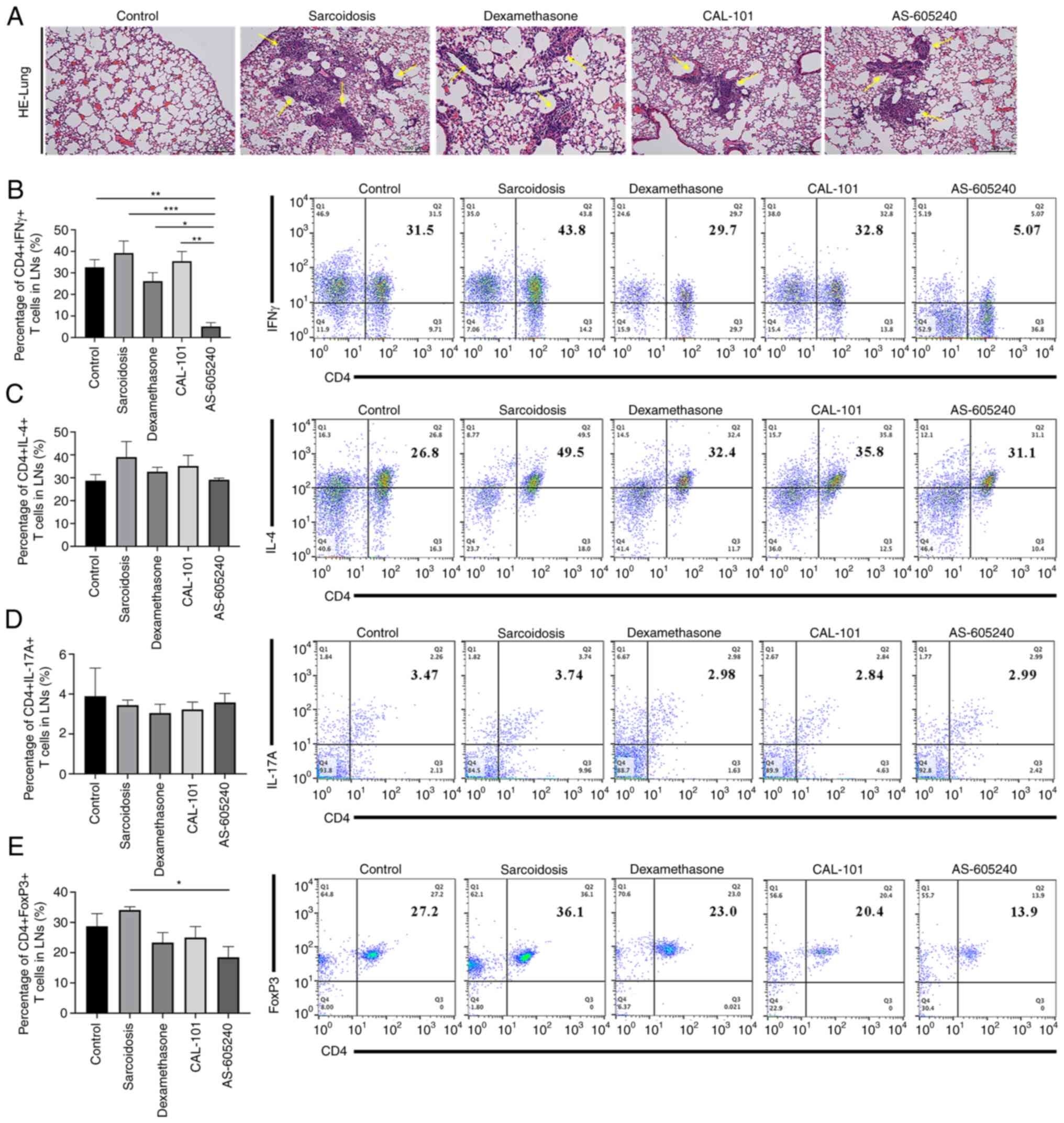
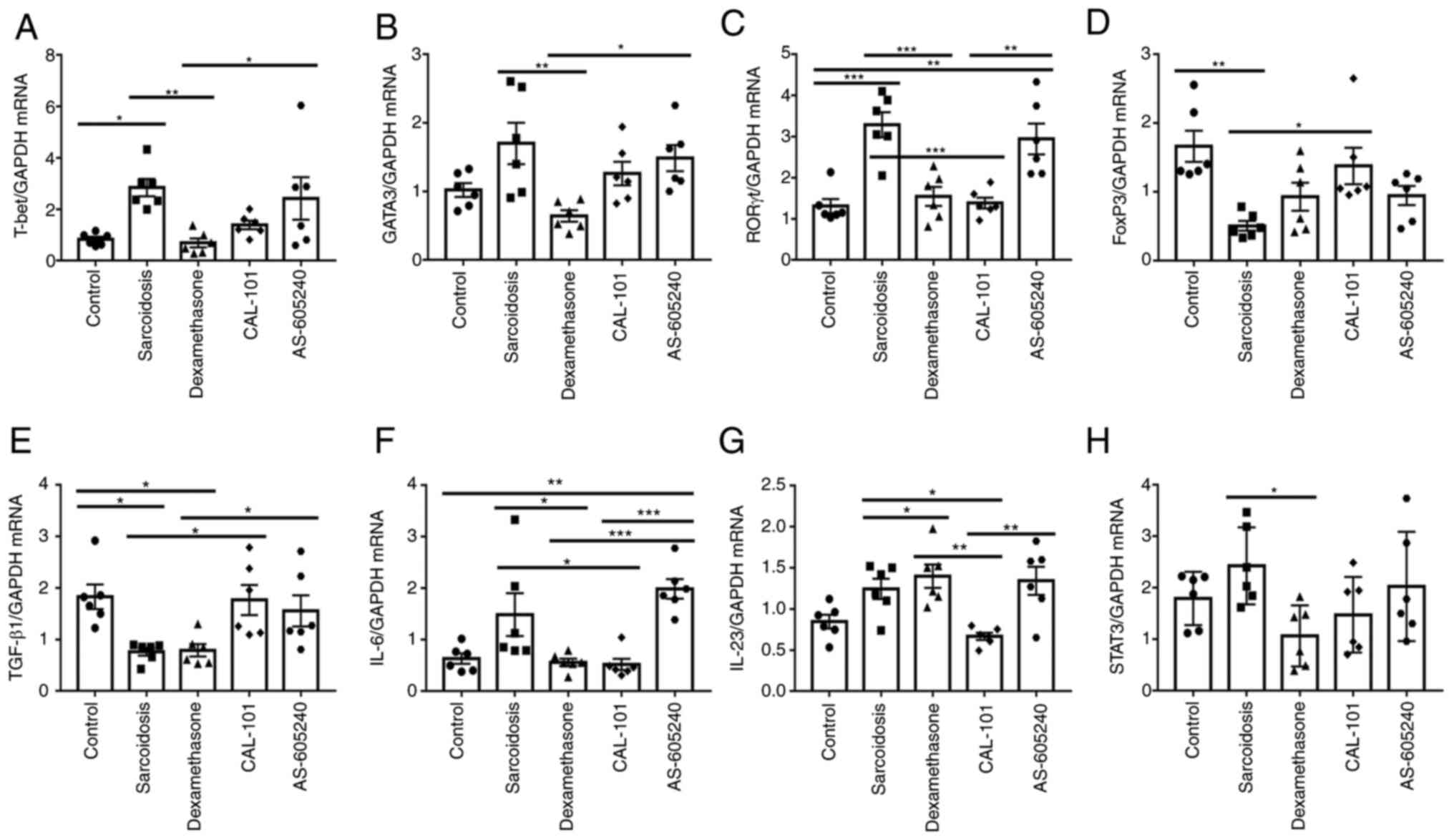
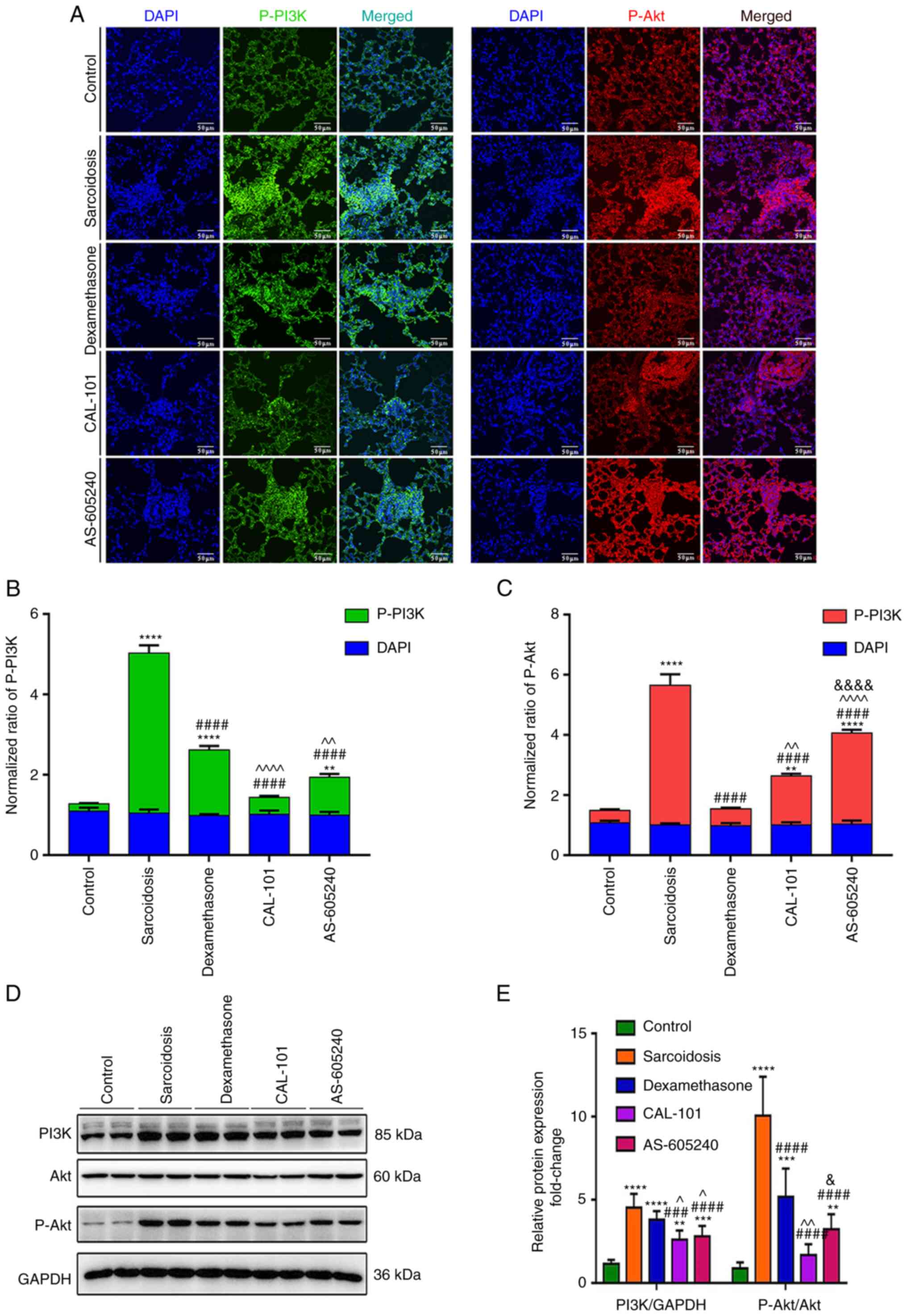
|
1
|
Broos CE, van Nimwegen M, Hoogsteden HC,
Hendriks RW, Kool M and van den Blink B: Granuloma formation in
pulmonary sarcoidosis. Front Immunol. 4(437)2013.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
2
|
Hunninghake GW, Costabel U, Ando M,
Baughman R, Cordier JF, du Bois R, Eklund A, Kitaichi M, Lynch J,
Rizzato G, et al: ATS/ERS/WASOG statement on sarcoidosis. American
thoracic society/european respiratory society/world association of
sarcoidosis and other granulomatous disorders. Sarcoidosis Vasc
Diffuse Lung Dis. 16:149–173. 1999.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
3
|
Oswald-Richter KA, Richmond BW, Braun NA,
Isom J, Abraham S, Taylor TR, Drake JM, Culver DA, Wilkes DS and
Drake WP: Reversal of global CD4+ subset dysfunction is associated
with spontaneous clinical resolution of pulmonary sarcoidosis. J
Immunol. 190:5446–5453. 2013.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
4
|
Cinetto F and Agostini C: Advances in
understanding the immunopathology of sarcoidosis and implications
on therapy. Expert Rev Clin Immunol. 12:973–988. 2016.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
5
|
Iannuzzi MC, Rybicki BA and Teirstein AS:
Sarcoidosis. N Engl J Med. 357:2153–2165. 2007.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
6
|
Gurram RK, Kujur W, Maurya SK and Agrewala
JN: Caerulomycin A enhances transforming growth factor-β
(TGF-β)-Smad3 protein signaling by suppressing interferon-γ
(IFN-γ)-signal transducer and activator of transcription 1 (STAT1)
protein signaling to expand regulatory T cells (Tregs). J Biol
Chem. 289:17515–17528. 2014.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
7
|
Ten Berge B, KleinJan A, Muskens F, Hammad
H, Hoogsteden HC, Hendriks RW, Lambrecht BN and Van den Blink B:
Evidence for local dendritic cell activation in pulmonary
sarcoidosis. Respir Res. 13(33)2012.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
8
|
Patterson KC and Chen ES: The pathogenesis
of pulmonary sarcoidosis and implications for treatment. Chest.
153:1432–1442. 2018.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
9
|
Miyara M, Amoura Z, Parizot C, Badoual C,
Dorgham K, Trad S, Kambouchner M, Valeyre D, Chapelon-Abric C,
Debré P, et al: The immune paradox of sarcoidosis and regulatory T
cells. J Exp Med. 203:359–370. 2006.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
10
|
Idali F, Wahlström J, Müller-Suur C,
Eklund A and Grunewald J: Analysis of regulatory T cell associated
forkhead box P3 expression in the lungs of patients with
sarcoidosis. Clin Exp Immunol. 152:127–137. 2008.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
11
|
Prasse A, Zissel G, Lützen N, Schupp J,
Schmiedlin R, Gonzalez-Rey E, Rensing-Ehl A, Bacher G, Cavalli V,
Bevec D, et al: Inhaled vasoactive intestinal peptide exerts
immunoregulatory effects in sarcoidosis. Am J Respir Crit Care Med.
182:540–548. 2010.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
12
|
Taflin C, Miyara M, Nochy D, Valeyre D,
Naccache JM, Altare F, Salek-Peyron P, Badoual C, Bruneval P,
Haroche J, et al: FoxP3+ regulatory T cells suppress early stages
of granuloma formation but have little impact on sarcoidosis
lesions. Am J Pathol. 174:497–508. 2009.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
13
|
Rappl G, Pabst S, Riemann D, Schmidt A,
Wickenhauser C, Schütte W, Hombach AA, Seliger B, Grohé C and Abken
H: Regulatory T cells with reduced repressor capacities are
extensively amplified in pulmonary sarcoid lesions and sustain
granuloma formation. Clin Immunol. 140:71–83. 2011.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
14
|
Ding J, Dai J, Cai H, Gao Q and Wen Y:
Extensively disturbance of regulatory T cells-Th17 cells balance in
stage II pulmonary sarcoidosis. Int J Med Sci. 14:1136–1142.
2017.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
15
|
Zissel G and Müller-Quernheim J: Cellular
players in the immunopathogenesis of sarcoidosis. Clin Chest Med.
36:549–560. 2015.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
16
|
Zhang B, Zhao F, Mao H, Ma W, Zhang Y,
Zhang X, Ding J, Gao Q and Wen Y: Interleukin 33 ameliorates
disturbance of regulatory T cells in pulmonary sarcoidosis. Int
Immunopharmacol. 64:208–216. 2018.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
17
|
Zhang B, Dai Q, Jin X, Liang D, Li X, Lu
H, Liu Y, Ding J, Gao Q and Wen Y: Phosphoinositide
3-kinase/protein kinase B inhibition restores regulatory T cell's
function in pulmonary sarcoidosis. J Cell Physiol. 234:19911–19920.
2019.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
18
|
Huynh A, DuPage M, Priyadharshini B, Sage
PT, Quiros J, Borges CM, Townamchai N, Gerriets VA, Rathmell JC,
Sharpe AH, et al: Control of PI(3) kinase in Treg cells maintains
homeostasis and lineage stability. Nat Immunol. 16:188–196.
2015.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
19
|
Greaves SA, Peterson JN, Strauch P, Torres
RM and Pelanda R: Active PI3K abrogates central tolerance in
high-avidity autoreactive B cells. J Exp Med. 216:1135–1153.
2019.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
20
|
Swaisgood CM, Oswald-Richter K, Moeller
SD, Klemenc JM, Ruple LM, Farver CF, Drake JM, Culver DA and Drake
WP: Development of a sarcoidosis murine lung granuloma model using
mycobacterium superoxide dismutase A peptide. Am J Respir Cell Mol
Biol. 44:166–174. 2011.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
21
|
Livak KJ and Schmittgen TD: Analysis of
relative gene expression data using real-time quantitative PCR and
the 2(-Delta Delta C(T)) method. Methods. 25:402–408.
2001.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
22
|
Abdel-Magid AF: Potential of PI3Kβ
inhibitors in the treatment of cancer and other diseases. ACS Med
Chem Lett. 8:778–780. 2017.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
23
|
Rathinaswamy MK and Burke JE: Class I
phosphoinositide 3-kinase (PI3K) regulatory subunits and their
roles in signaling and disease. Adv Biol Regul.
75(100657)2020.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
24
|
Scott WJ, Hentemann MF, Rowley RB, Bull
CO, Jenkins S, Bullion AM, Johnson J, Redman A, Robbins AH, Esler
W, et al: Discovery and SAR of novel
2,3-dihydroimidazo[1,2-c]quinazoline PI3K inhibitors:
Identification of copanlisib (BAY 80-6946). ChemMedChem.
11:1517–1530. 2016.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
25
|
Lannutti BJ, Meadows SA, Herman SE,
Kashishian A, Steiner B, Johnson AJ, Byrd JC, Tyner JW, Loriaux MM,
Deininger M, et al: CAL-101, a p110delta selective
phosphatidylinositol-3-kinase inhibitor for the treatment of B-cell
malignancies, inhibits PI3K signaling and cellular viability.
Blood. 117:591–594. 2011.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
26
|
Furet P, Guagnano V, Fairhurst RA,
Imbach-Weese P, Bruce I, Knapp M, Fritsch C, Blasco F, Blanz J,
Aichholz R, et al: Discovery of NVP-BYL719 a potent and selective
phosphatidylinositol-3 kinase alpha inhibitor selected for clinical
evaluation. Bioorg Med Chem Lett. 23:3741–3748. 2013.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
27
|
Burris HA III, Flinn IW, Patel MR, Fenske
TS, Deng C, Brander DM, Gutierrez M, Essell JH, Kuhn JG, Miskin HP,
et al: Umbralisib, a novel PI3Kδ and casein kinase-1ε inhibitor, in
relapsed or refractory chronic lymphocytic leukaemia and lymphoma:
An open-label, phase 1, dose-escalation, first-in-human study.
Lancet Oncol. 19:486–496. 2018.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
28
|
Patel RK and Mohan C: PI3K/AKT signaling
and systemic autoimmunity. Immunol Res. 31:47–55. 2005.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
29
|
Adefemi F, Fruman DA and Marshall AJ: A
case for phosphoinositide 3-kinase-targeted therapy for infectious
disease. J Immunol. 205:3237–3245. 2020.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
30
|
Franks SE, Getahun A and Cambier JC: A
precision B cell-targeted therapeutic approach to autoimmunity
caused by phosphatidylinositol 3-kinase pathway dysregulation. J
Immunol. 202:3381–3393. 2019.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
31
|
Winkler DG, Faia KL, DiNitto JP, Ali JA,
White KF, Brophy EE, Pink MM, Proctor JL, Lussier J, Martin CM, et
al: PI3K-δ and PI3K-γ inhibition by IPI-145 abrogates immune
responses and suppresses activity in autoimmune and inflammatory
disease models. Chem Biol. 20:1364–1374. 2013.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
32
|
Steinbach EC, Kobayashi T, Russo SM,
Sheikh SZ, Gipson GR, Kennedy ST, Uno JK, Mishima Y, Borst LB, Liu
B, et al: Innate PI3K p110δ regulates Th1/Th17 development and
microbiota-dependent colitis. J Immunol. 192:3958–3968.
2014.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
33
|
Juarez M, Diaz N, Johnston GI, Nayar S,
Payne A, Helmer E, Cain D, Williams P, Devauchelle-Pensec V, Fisher
BA, et al: A phase 2 randomized, double-blind, placebo-controlled,
proof-of-concept study of oral seletalisib in primary Sjögren's
syndrome. Rheumatology (Oxford). 60:1364–1375. 2021.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
34
|
Horak F, Puri KD, Steiner BH, Holes L,
Xing G, Zieglmayer P, Zieglmayer R, Lemell P and Yu A: Randomized
phase 1 study of the phosphatidylinositol 3-kinase δ inhibitor
idelalisib in patients with allergic rhinitis. J Allergy Clin
Immunol. 137:1733–1741. 2016.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
35
|
Perry MWD, Bjorhall K, Bold P, Brűlls M,
Börjesson U, Carlsson J, Chang HA, Chen Y, Eriksson A, Fihn BM, et
al: Discovery of AZD8154, a dual PI3Kγδ inhibitor for the treatment
of asthma. J Med Chem. 64:8053–8075. 2021.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
36
|
Stark AK, Davenport ECM, Patton DT,
Scudamore CL, Vanhaesebroeck B, Veldhoen M, Garden OA and Okkenhaug
K: Loss of phosphatidylinositol 3-kinase activity in regulatory T
cells leads to neuronal inflammation. J Immunol. 205:78–89.
2020.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
37
|
Li H, Park D, Abdul-Muneer PM, Xu B, Wang
H, Xing B, Wu D and Li S: PI3Kγ inhibition alleviates symptoms and
increases axon number in experimental autoimmune encephalomyelitis
mice. Neuroscience. 253:89–99. 2013.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
38
|
Zillikens H, Kasprick A, Osterloh C, Gross
N, Radziewitz M, Hass C, Hartmann V, Behnen-Härer M, Ernst N, Boch
K, et al: Topical application of the PI3Kβ-selective small molecule
inhibitor TGX-221 Is an effective treatment option for experimental
epidermolysis bullosa acquisita. Front Med (Lausanne).
8(713312)2021.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
39
|
Hawkins PT and Stephens LR: PI3K
signalling in inflammation. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1851:882–897.
2015.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
40
|
Liu Y, Qiu L, Wang Y, Aimurola H, Zhao Y,
Li S and Xu Z: The circulating Treg/Th17 cell ratio is correlated
with relapse and treatment response in pulmonary sarcoidosis
patients after corticosteroid withdrawal. PLoS One.
11(e0148207)2016.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
41
|
Uehara M, McGrath MM, Ohori S, Solhjou Z,
Banouni N, Routray S, Evans C, DiNitto JP, Elkhal A, Turka LA, et
al: Regulation of T cell alloimmunity by PI3Kγ and PI3Kδ. Nat
Commun. 8(951)2017.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
42
|
Gamper CJ and Powell JD: All PI3Kinase
signaling is not mTOR: Dissecting mTOR-dependent and independent
signaling pathways in T cells. Front Immunol. 3(312)2012.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
43
|
Lim EL and Okkenhaug K: Phosphoinositide
3-kinase δ is a regulatory T-cell target in cancer immunotherapy.
Immunology. 157:210–218. 2019.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
44
|
Vanhaesebroeck B, Perry MWD, Brown JR,
André F and Okkenhaug K: PI3K inhibitors are finally coming of age.
Nat Rev Drug Discov. 20:741–769. 2021.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
45
|
Randis TM, Puri KD, Zhou H and Diacovo TG:
Role of PI3Kdelta and PI3Kgamma in inflammatory arthritis and
tissue localization of neutrophils. Eur J Immunol. 38:1215–1224.
2008.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
46
|
Williams O, Houseman BT, Kunkel EJ,
Aizenstein B, Hoffman R, Knight ZA and Shokat KM: Discovery of dual
inhibitors of the immune cell PI3Ks p110delta and p110gamma: A
prototype for new anti-inflammatory drugs. Chem Biol. 17:123–134.
2010.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|