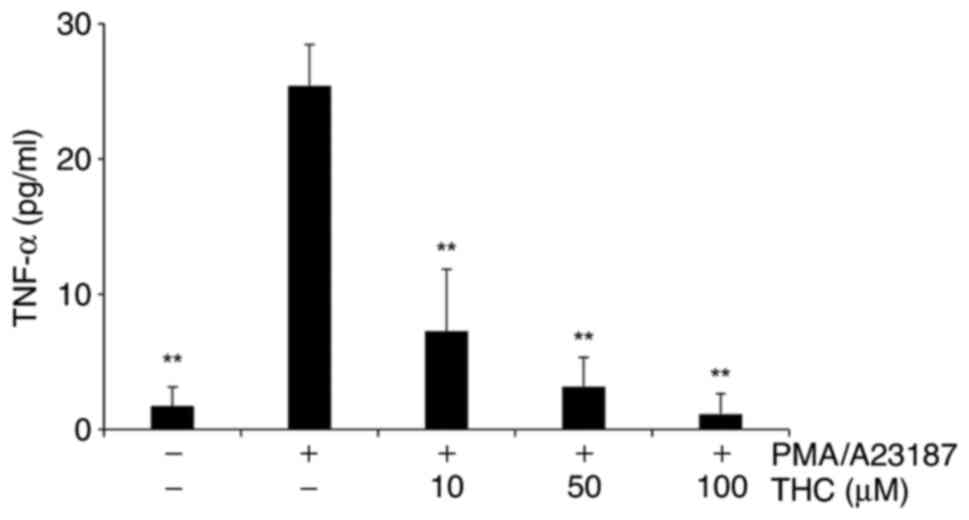
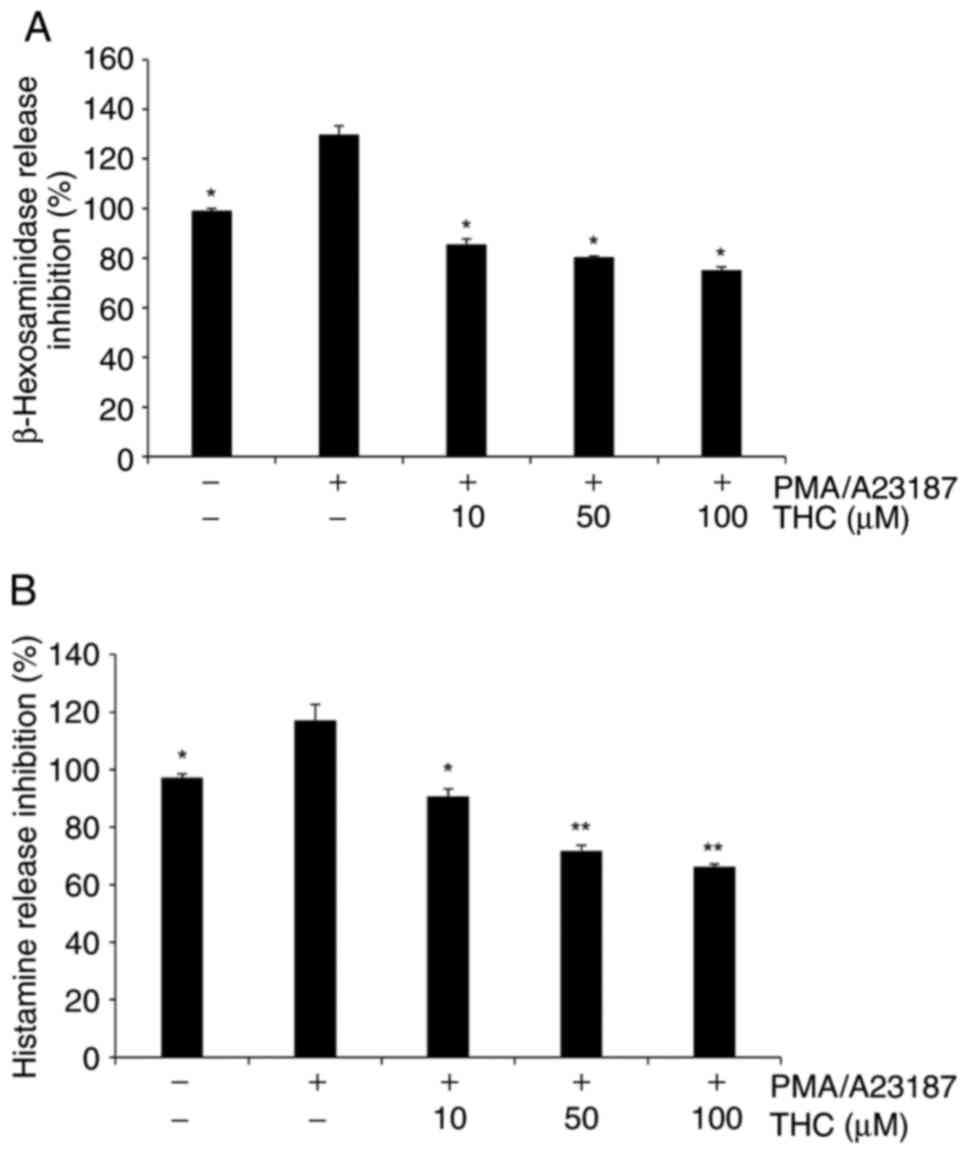
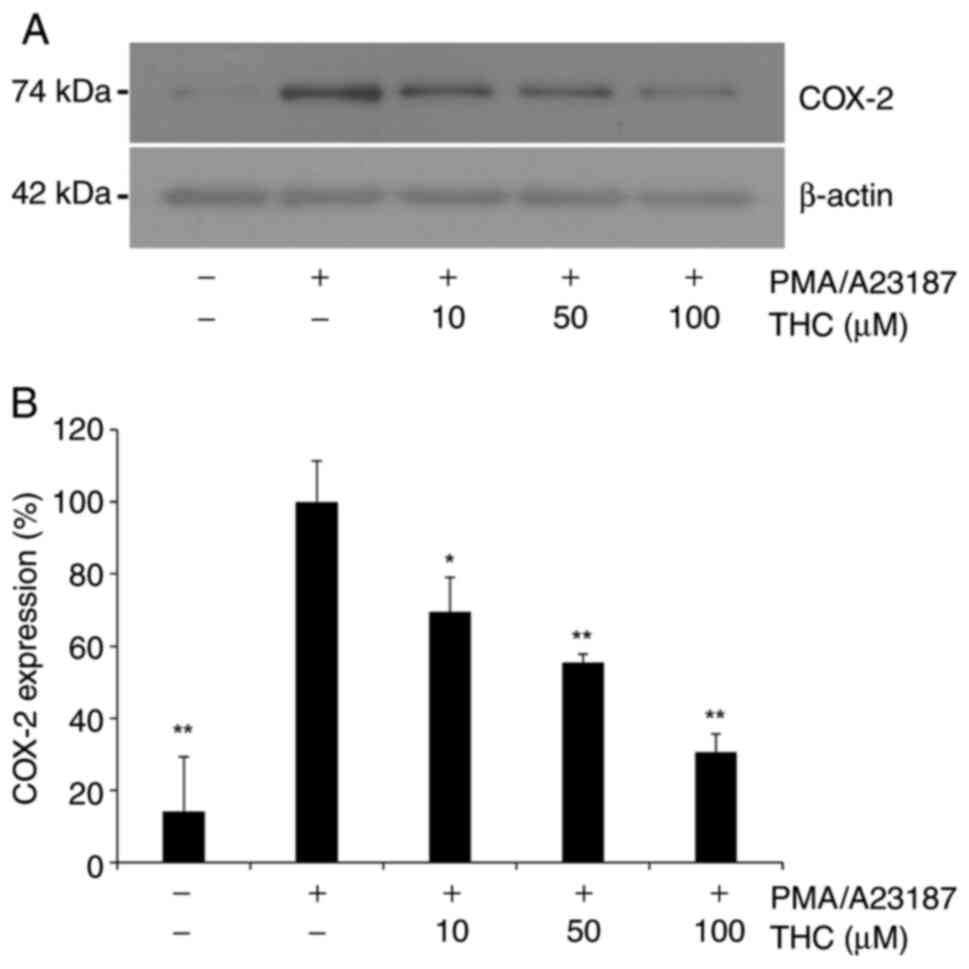
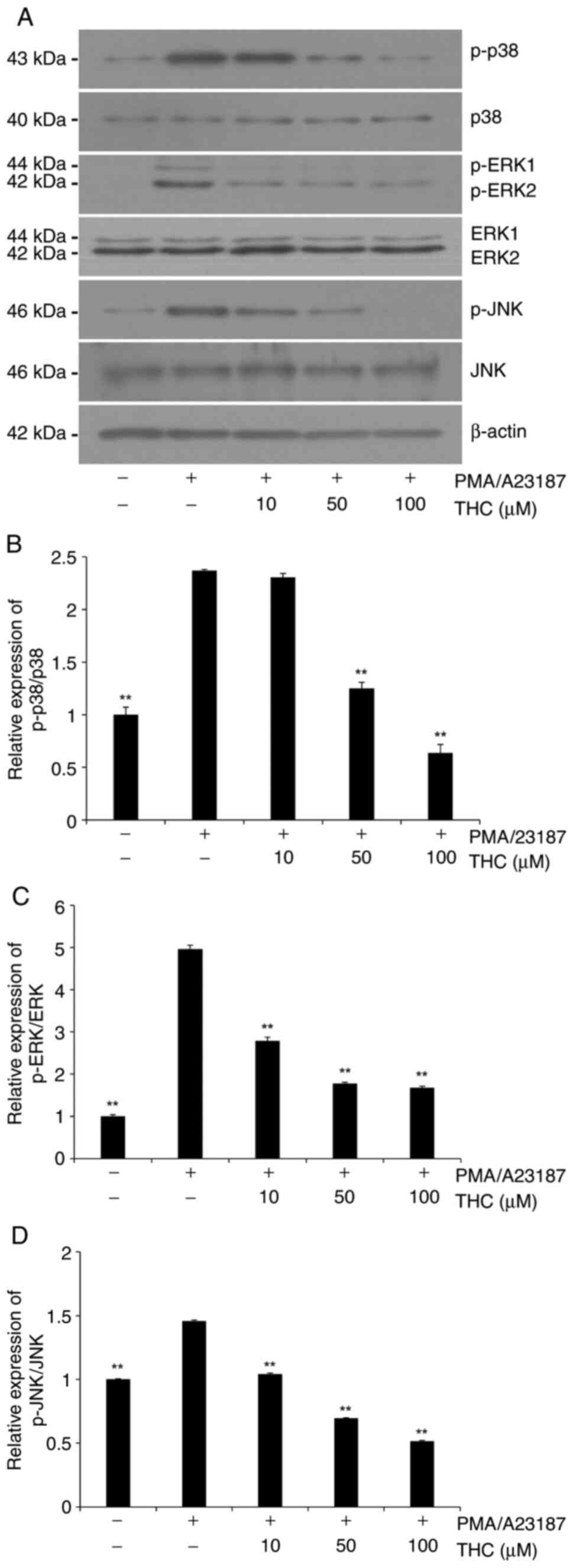
|
1
|
Marshall JS: Mast-cell responses to
pathogens. Nat Rev Immunol. 4:787–799. 2004.PubMed/NCBI View
Article : Google Scholar
|
|
2
|
Johnzon CF, Ronnberg E and Pejler G: The
role of mast cells in bacterial infection. Am J Pathol. 186:4–14.
2016.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
3
|
Wernersson S and Pejler G: Mast cell
secretory granules: Armed for battle. Nat Rev Immunol. 14:478–494.
2014.PubMed/NCBI View
Article : Google Scholar
|
|
4
|
Voehringer D: Protective and pathological
roles of mast cells and basophils. Nat Rev Immunol. 13:362–375.
2013.PubMed/NCBI View
Article : Google Scholar
|
|
5
|
Galli SJ, Grimbaldeston M and Tsai M:
Immunomodulatory mast cells: Negative, as well as positive,
regulators of immunity. Nat Rev Immunol. 8:478–486. 2008.PubMed/NCBI View
Article : Google Scholar
|
|
6
|
Cho MS, Park WS, Jung WK, Qian ZJ, Lee DS,
Choi JS, Lee DY, Park SG, Seo SK, Kim HJ, et al: Caffeic acid
phenethyl ester promotes anti-inflammatory effects by inhibiting
MAPK and NF-κB signaling in activated HMC-1 human mast cells. Pharm
Biol. 52:926–932. 2014.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
7
|
Kong R, Kang OH, Seo YS, Zhou T, Kim SA,
Shin DW and Kwon DY: MAPKs and NFkappaB pathway inhibitory effect
of bisdemethoxycurcumin on phorbol 12-myristate13-acetate and
A23187-induced inflammation in human mast cells. Mol Med Rep.
17:630–635. 2018.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
8
|
Li L, Zhang XH, Liu GR, Liu C and Dong YM:
Isoquercitrin suppresses the expression of histamine and
pro-inflammatory cytokines by inhibiting the activation of MAP
Kinases and NF-κB in human KU812 cells. Chin J Nat Med. 14:407–412.
2016.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
9
|
Cagnol S and Chambard JC: ERK and cell
death: Mechanisms of ERK-induced cell death-apoptosis, autophagy
and senescence. FEBS J. 277:2–21. 2010.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
10
|
Zhao J, Wang L, Dong X, Hu X, Zhou L, Liu
Q, Song B, Wu Q and Li L: The c-Jun N-terminal kinase (JNK) pathway
is activated in human interstitial cystitis (IC) and rat protamine
sulfate induced cystitis. Sci Rep. 6(19670)2016.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
11
|
Zhou Y, Yang Q, Xu H, Zhang J, Deng H, Gao
H, Yang J, Zhao D and Liu F: miRNA-221-3p enhances the secretion of
interleukin-4 in mast cells through the phosphatase and tensin
Homolog/p38/Nuclear Factor-kappaB pathway. PLoS One.
11(e0148821)2016.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
12
|
Bose JS, Gangan V, Jain SK and Manna SK:
Novel caffeic acid ester derivative induces apoptosis by expressing
FasL and downregulating NF-KappaB: Potentiation of cell death
mediated by chemotherapeutic agents. J Cell Physiol. 218:653–662.
2009.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
13
|
Murtaza G, Karim S, Akram MR, Khan SA,
Azhar S, Mumtaz A and Bin Asad MH: Caffeic acid phenethyl ester and
therapeutic potentials. Biomed Res Int. 2014(145342)2014.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
14
|
Armutcu F, Akyol S, Ustunsoy S and Turan
FF: Therapeutic potential of caffeic acid phenethyl ester and its
anti-inflammatory and immunomodulatory effects (Review). Exp Ther
Med. 9:1582–1588. 2015.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
15
|
Choi HG, Tran PT, Lee JH, Min BS and Kim
JA: Anti-inflammatory activity of caffeic acid derivatives isolated
from the roots of Salvia miltiorrhiza Bunge. Arch Pharm Res.
41:64–70. 2018.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
16
|
Rabe C, Steenkamp AJ, Joubert E, Burger
JFW and Ferreira D: Phenolic metabolites from rooibos tea.
Phytochemistry. 35:1559–1565. 1994.
|
|
17
|
Nagasaka R, Chotimarkorn C, Shafiqul IM,
Hori M, Ozaki H and Ushio H: Anti-inflammatory effects of
hydroxycinnamic acid derivatives. Biochem Biophys Res Commun.
358:615–619. 2007.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
18
|
Kim YC: Neuroprotective phenolics in
medicinal plants. Arch Pharm Res. 33:1611–1632. 2010.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
19
|
Lee JW, Cheong IY, Kim HS, Lee JJ, Lee YS,
Kwon YS, Kim MJ, Lee HJ, Kim SS and Chun W: Anti-inflammatory
activity of 1-docosanoyl cafferate isolated from Rhus verniciflua
in LPS-stimulated BV2 microglial cells. Korean J Physiol Pharmacol.
15:9–15. 2011.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
20
|
Itharat A and Hiransai P: Dioscoreanone
suppresses LPS-induced nitric oxide production and inflammatory
cytokine expression in RAW 264.7 macrophages by NF-κB and ERK1/2
signaling transduction. J Cell Biochem. 113:3427–3435.
2012.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
21
|
Kim YJ, Shin Y, Lee KH and Kim TJ: Anethum
graveloens flower extracts inhibited a lipopolysaccharide-induced
inflammatory response by blocking iNOS expression and NF-κB
activity in macrophages. Biosci Biotechnol Biochem. 76:1122–1127.
2012.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
22
|
Rehman MU, Yoshihisa Y, Miyamoto Y and
Shimizu T: The anti-inflammatory effects of platinum nanoparticles
on the lipopolysaccharide-induced inflammatory response in RAW
264.7 macrophages. Inflamm Res. 61:1177–1185. 2012.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
23
|
Lee Y, Shin DH, Kim JH, Hong S, Choi D,
Kim YJ, Kwak MK and Jung Y: Caffeic acid phenethyl ester-mediated
Nrf2 activation and IkappaB kinase inhibition are involved in
NFkappaB inhibitory effect: Structural analysis for NFkappaB
inhibition. Eur J Pharmacol. 643:21–28. 2010.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
24
|
Fidan H, Sahin O, Yavuz Y, Kilbas A,
Cetinkaya Z, Ela Y, Ozen OA and Altuntas I: Caffeic acid phenethyl
ester reduces mortality and sepsis-induced lung injury in rats.
Crit Care Med. 35:2822–2829. 2007.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
25
|
Schwartz LB, Lewis RA, Seldin D and Austen
KF: Acid hydrolases and tryptase from secretory granules of
dispersed human lung mast cells. J Immunol. 126:1290–1294.
1981.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
26
|
Schoonbroodt S, Legrand-Poels S,
Best-Belpomme M and Piette J: Activation of the NF-kappaB
transcription factor in a T-lymphocytic cell line by hypochlorous
acid. Biochem J. 321:777–785. 1997.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
27
|
Ock J, Kim S and Suk K: Anti-inflammatory
effects of a fluorovinyloxyacetamide compound KT-15087 in microglia
cells. Pharmacol Res. 59:414–422. 2009.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
28
|
Lee JW, Bae CJ, Choi YJ, Kim SI, Kim NH,
Lee HJ, Kim SS, Kwon YS and Chun W: 3,4,5-trihydroxycinnamic acid
inhibits LPS-Induced iNOS expression by suppressing NF-κB
Activation in BV2 microglial cells. Korean J Physiol Pharmacol.
16:107–112. 2012.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
29
|
Kunder CA, St John AL and Abraham SN: Mast
cell modulation of the vascular and lymphatic endothelium. Blood.
118:5383–5393. 2011.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
30
|
Hundley TR, Prasad AR and Beaven MA:
Elevated levels of cyclooxygenase-2 in antigen-stimulated mast
cells is associated with minimal activation of p38
mitogen-activated protein kinase. J Immunol. 167:1629–1636.
2001.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
31
|
Hu Frisk JM, Kjellen L, Melo FR, Ohrvik H
and Pejler G: Mitogen-Activated protein kinase signaling regulates
proteoglycan composition of mast cell secretory granules. Front
Immunol. 9(1670)2018.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
32
|
Kim DH, Jung WS, Kim ME, Lee HW, Youn HY,
Seon JK, Lee HN and Lee JS: Genistein inhibits proinflammatory
cytokines in human mast cell activation through the inhibition of
the ERK pathway. Int J Mol Med. 34:1669–1674. 2014.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
33
|
Su-Jin Kim SJ, Kim YJ, Lee JH, Oh SR, Park
CI, Jeong JW, Um JY, Hong SH and Ahn EM:
Genistein-4'-O-α-L-rhamnopyranosyl-(1→2)-β-D-glucopyranoside from
Sophora japonica (Leguminosae) ameliorates mast cell-mediated
allergic inflammation in vivo and in vitro. Orient Pharm Exp Med.
11:207–213. 2011.
|
|
34
|
Woolley DE and Tetlow LC: Mast cell
activation and its relation to proinflammatory cytokine production
in the rheumatoid lesion. Arthritis Res. 2:65–74. 2000.PubMed/NCBI View
Article : Google Scholar
|
|
35
|
Chen BH, Hung MH, Chen JYF, Chang HW, Yu
ML, Wan L, Tsai FJ, Wang TP, Fu TF and Chiu CC: Anti-allergic
activity of grapeseed extract (GSE) on RBL-2H3 mast cells. Food
Chem. 132:968–974. 2012.
|
|
36
|
Tang T, Scambler TE, Smallie T, Cunliffe
HE, Ross EA, Rosner DR, O'Neil JD and Clark AR: Macrophage
responses to lipopolysaccharide are modulated by a feedback loop
involving prostaglandin E2, dual specificity phosphatase 1 and
tristetraprolin. Sci Rep. 7(4350)2017.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
37
|
Johnson GL and Lapadat R:
Mitogen-activated protein kinase pathways mediated by ERK, JNK, and
p38 protein kinases. Science. 298:1911–1912. 2002.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
38
|
Kaminska B: MAPK signalling pathways as
molecular targets for anti-inflammatory therapy-from molecular
mechanisms to therapeutic benefits. Biochim Biophys Acta.
1754:253–262. 2005.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
39
|
Oliver JM, Kepley CL, Ortega E and Wilson
BS: Immunologically mediated signaling in basophils and mast cells:
Finding therapeutic targets for allergic diseases in the human
FcvarepsilonR1 signaling pathway. Immunopharmacology. 48:269–281.
2000.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
40
|
Kang OH, Jang HJ, Chae HS, Oh YC, Choi JG,
Lee YS, Kim JH, Kim YC, Sohn DH, Park H and Kwon DY:
Anti-inflammatory mechanisms of resveratrol in activated HMC-1
cells: Pivotal roles of NF-kappaB and MAPK. Pharmacol Res.
59:330–337. 2009.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
41
|
Yoo G, Lee K and Lee DC: Inhibitory
effects of 2-oxo-2H-chromen-4-yl 4-methylbenzenesulfonate on
allergic inflammatory responses in rat basophilic leukemia cells.
Int Immunopharmacol. 48:196–202. 2017.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
42
|
Wan M, Liu J and Ouyang X:
Nucleotide-binding oligomerization domain 1 regulates Porphyromonas
gingivalis-induced vascular cell adhesion molecule 1 and
intercellular adhesion molecule 1 expression in endothelial cells
through NF-κB pathway. J Periodontal Res. 50:189–196.
2015.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
43
|
Wang L, Xu Y, Yu Q, Sun Q, Xu Y, Gu Q and
Xu X: H-RN, a novel antiangiogenic peptide derived from hepatocyte
growth factor inhibits inflammation in vitro and in vivo through
PI3K/AKT/IKK/NF-κB signal pathway. Biochem Pharmacol. 89:255–265.
2014.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
44
|
Blackwell TS, Blackwell TR and Christman
JW: Impaired activation of nuclear factor-kappaB in
endotoxin-tolerant rats is associated with down-regulation of
chemokine gene expression and inhibition of neutrophilic lung
inflammation. J Immunol. 158:5934–5940. 1997.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
45
|
Lee JW, Bae CJ, Choi YJ, Kim SI, Kwon YS,
Lee HJ, Kim SS and Chun W: 3,4,5-trihydroxycinnamic acid inhibits
lipopolysaccharide (LPS)-induced inflammation by Nrf2 activation in
vitro and improves survival of mice in LPS-induced endotoxemia
model in vivo. Mol Cell Biochem. 390:143–153. 2014.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
46
|
Lee JW, Kwon JH, Lim MS, Lee HJ, Kim SS,
Lim SY and Chun W: 3,4,5-Trihydroxycinnamic acid increases
heme-oxygenase-1 (HO-1) and decreases macrophage infiltration in
LPS-induced septic kidney. Mol Cell Biochem. 397:109–116.
2014.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
47
|
Park JW, Oh JH, Hwang D, Kim SM, Min JH,
Seo JY, Chun W, Lee HJ, Oh SR, Lee JW and Ahn KS:
3,4,5Trihydroxycinnamic acid exerts antiinflammatory effects on
TNF-α/IFN-ү-stimulated HaCaT cells. Mol Med Rep.
24(509)2021.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|