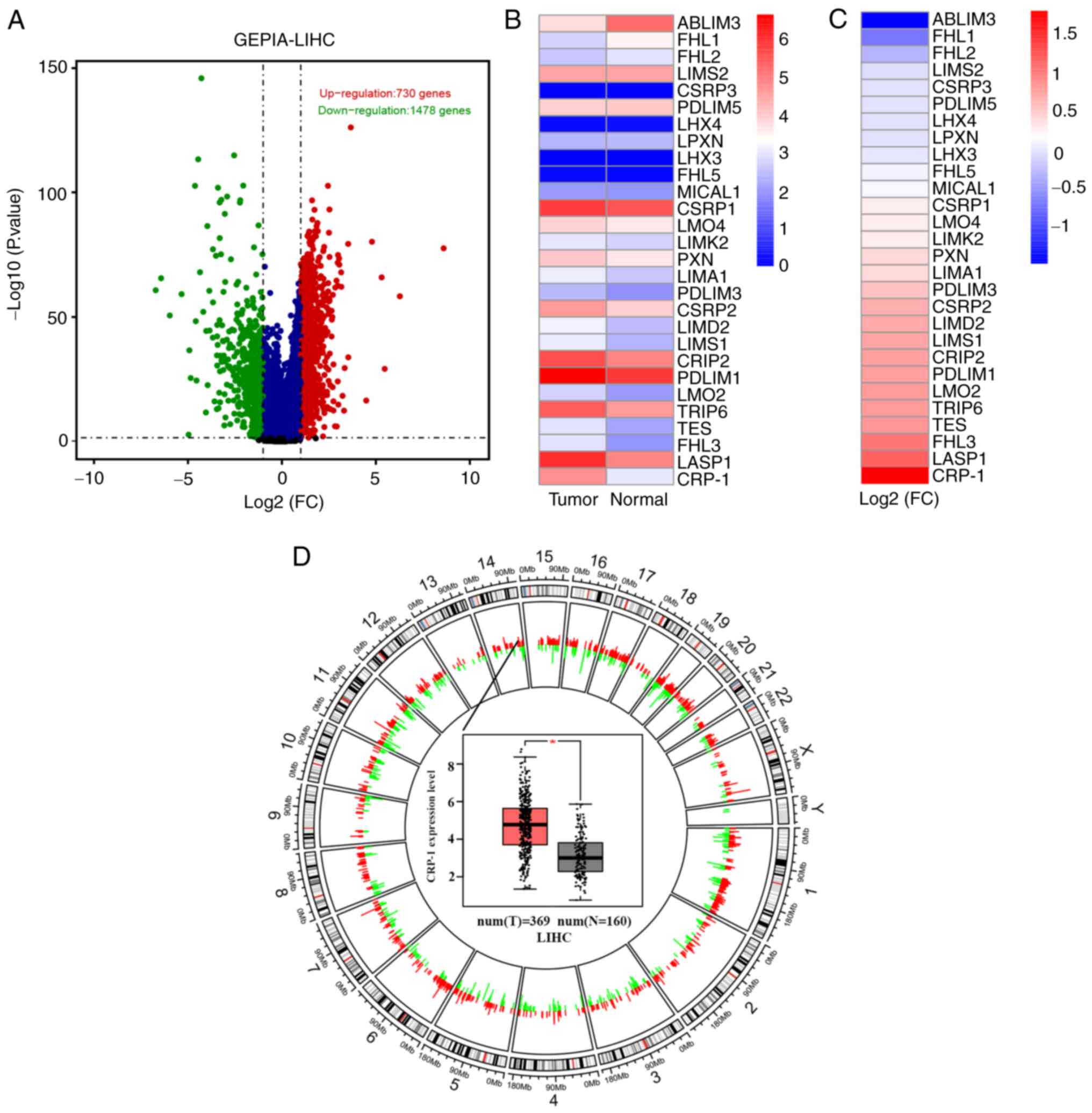
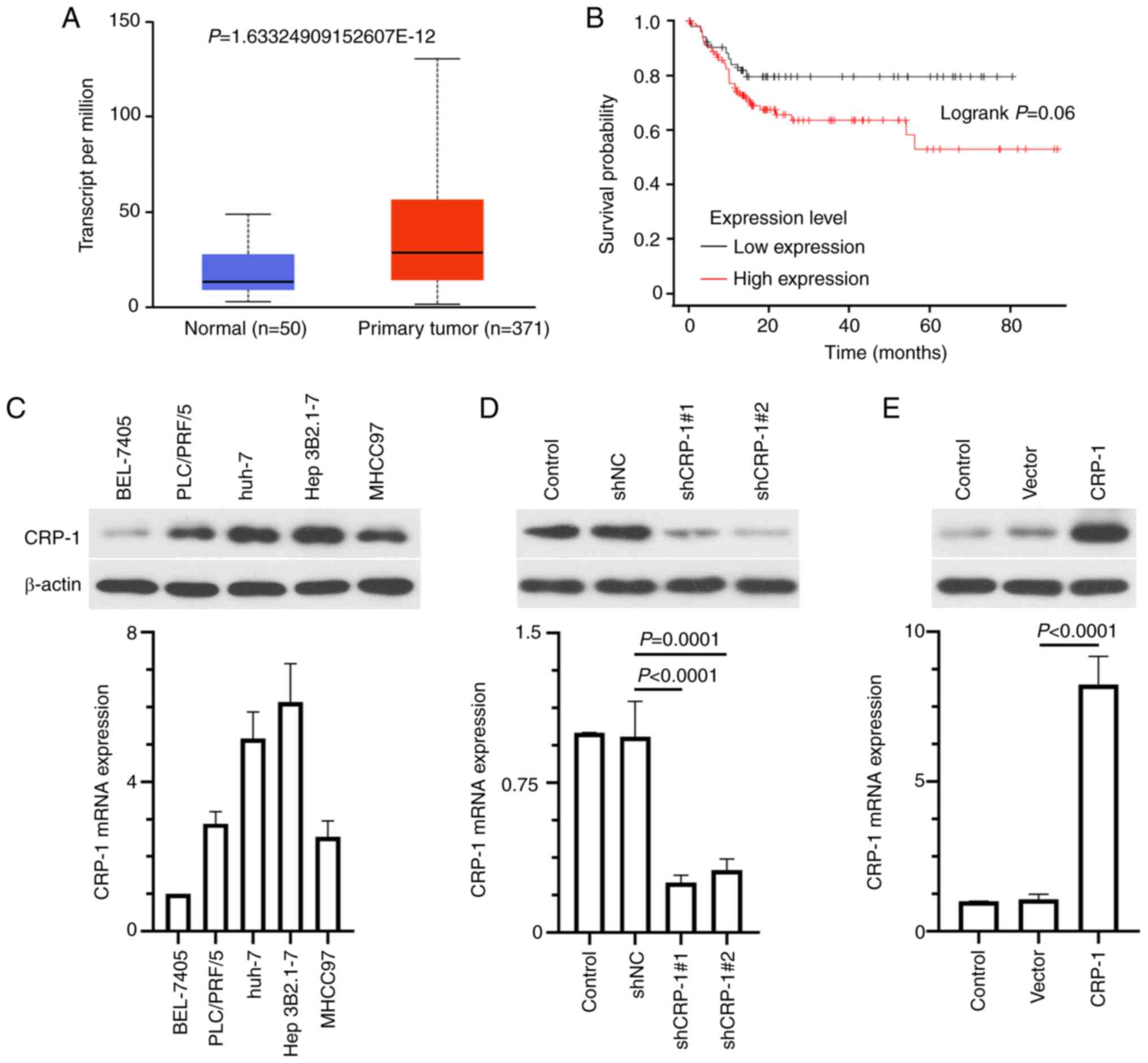
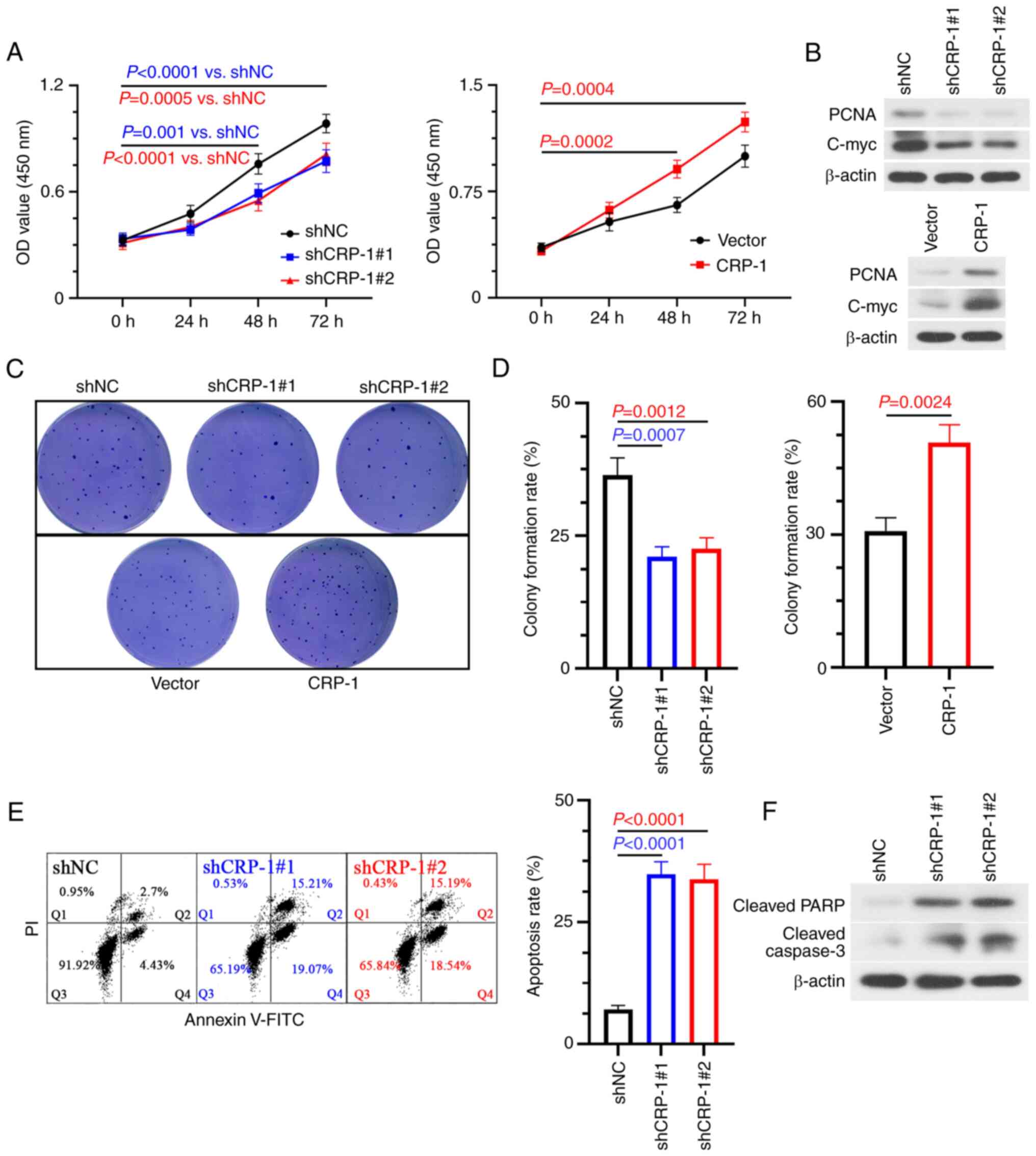
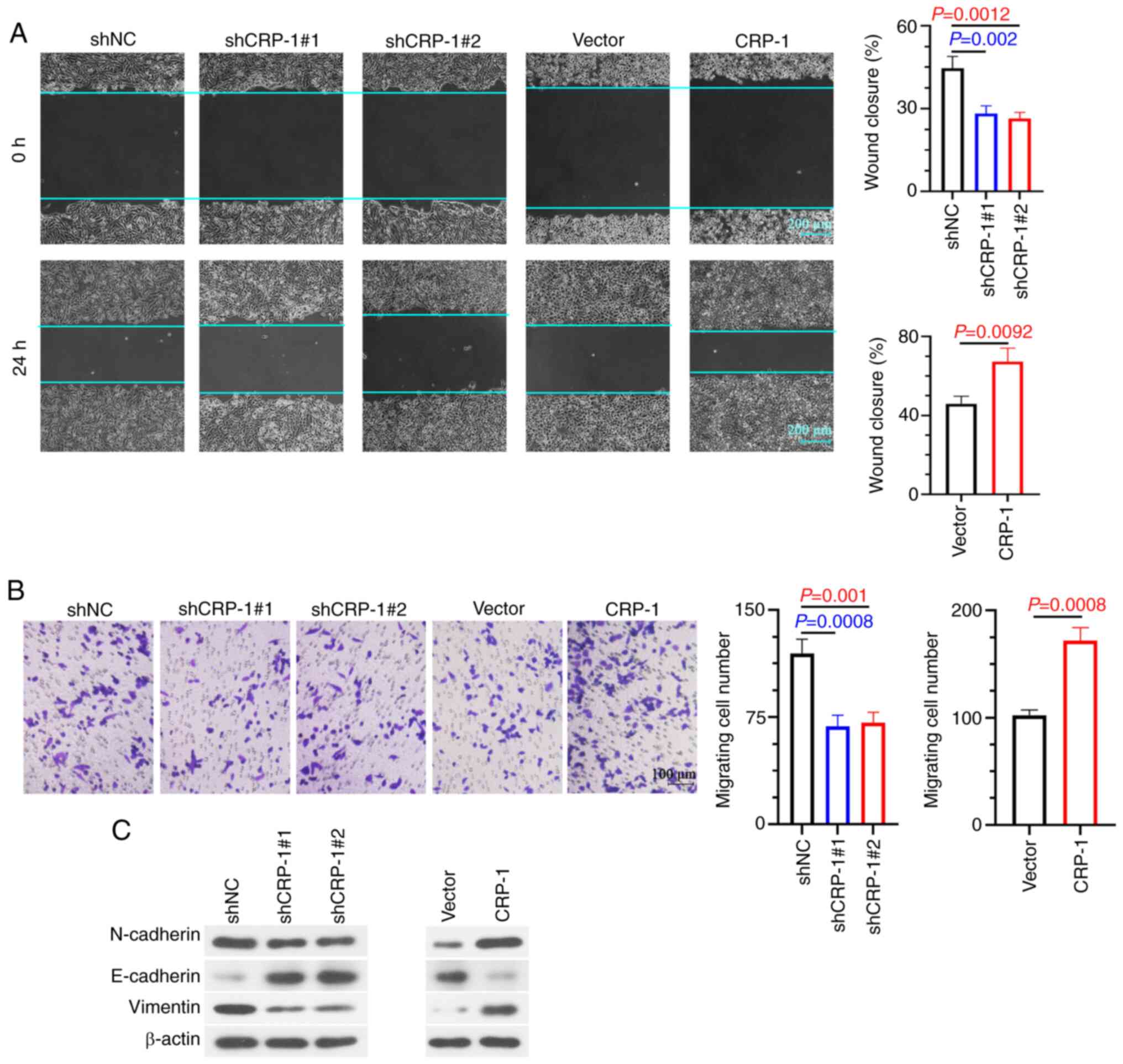
|
1
|
Chan HL and Sung JJ: Hepatocellular
carcinoma and hepatitis B virus. Semin Liver Dis. 26:153–161.
2006.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
2
|
Parkin DM, Bray F, Ferlay J and Pisani P:
Global cancer statistics, 2002. CA Cancer J Clin. 55:74–108.
2005.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
3
|
Ringelhan M, Pfister D, O'Connor T,
Pikarsky E and Heikenwalder M: The immunology of hepatocellular
carcinoma. Nat Immunol. 19:222–232. 2018.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
4
|
Petrick JL, Braunlin M, Laversanne M,
Valery PC, Bray F and McGlynn KA: International trends in liver
cancer incidence, overall and by histologic subtype, 1978-2007. Int
J Cancer. 139:1534–1545. 2016.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
5
|
Chen W, Zheng R, Baade PD, Zhang S, Zeng
H, Bray F, Jemal A, Yu XQ and He J: Cancer statistics in China,
2015. CA Cancer J Clin. 66:115–132. 2016.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
6
|
Allemani C, Matsuda T, Di Carlo V,
Harewood R, Matz M, Nikšić M, Bonaventure A, Valkov M, Johnson CJ,
Estève J, et al: Global surveillance of trends in cancer survival
2000-14 (CONCORD-3): Analysis of individual records for 37 513 025
patients diagnosed with one of 18 cancers from 322 population-based
registries in 71 countries. Lancet. 391:1023–1075. 2018.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
7
|
Finn RS: Emerging targeted strategies in
advanced hepatocellular carcinoma. Semin Liver Dis. 33 (Suppl
1):S11–19. 2013.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
8
|
Lohitesh K, Chowdhury R and Mukherjee S:
Resistance a major hindrance to chemotherapy in hepatocellular
carcinoma: An insight. Cancer Cell Int. 18(44)2018.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
9
|
Daher S, Massarwa M, Benson AA and Khoury
T: Current and future treatment of hepatocellular carcinoma: An
updated comprehensive review. J Clin Transl Hepatol. 6:69–78.
2018.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
10
|
Jurata LW, Kenny DA and Gill GN: Nuclear
LIM interactor, a rhombotin and LIM homeodomain interacting
protein, is expressed early in neuronal development. Proc Natl Acad
Sci USA. 93:11693–11698. 1996.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
11
|
Khoo C, Blanchard RK, Sullivan VK and
Cousins RJ: Human cysteine-rich intestinal protein: cDNA cloning
and expression of recombinant protein and identification in human
peripheral blood mononuclear cells. Protein Expr Purif. 9:379–387.
1997.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
12
|
Fernandes PR, Samuelson DA, Clark WR and
Cousins RJ: Immunohistochemical localization of cysteine-rich
intestinal protein in rat small intestine. Am J Physiol.
272:G751–G759. 1997.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
13
|
Cousins RJ and Lanningham-Foster L:
Regulation of cysteine-rich intestinal protein, a zinc finger
protein, by mediators of the immune response. J Infect Dis. 182
(Suppl 1):S81–S84. 2000.PubMed/NCBI View
Article : Google Scholar
|
|
14
|
Baumhoer D, Elsner M, Smida J, Zillmer S,
Rauser S, Schoene C, Balluff B, Bielack S, Jundt G, Walch A and
Nathrath M: CRIP1 expression is correlated with a favorable outcome
and less metastases in osteosarcoma patients. Oncotarget.
2:970–975. 2011.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
15
|
Ludyga N, Englert S, Pflieger K, Rauser S,
Braselmann H, Walch A, Auer G, Höfler H and Aubele M: The impact of
cysteine-rich intestinal protein 1 (CRIP1) in human breast cancer.
Mol Cancer. 12(28)2013.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
16
|
Lambropoulou M, Deftereou TE, Kynigopoulos
S, Patsias A, Anagnostopoulos C, Alexiadis G, Kotini A, Tsaroucha
A, Nikolaidou C, Kiziridou A, et al: Co-expression of galectin-3
and CRIP-1 in endometrial cancer: Prognostic value and patient
survival. Med Oncol. 33(8)2016.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
17
|
Li HG, Zhao LH, Zhang ZH, Liu JZ, Ren K,
Li SY and Su ZJ: The impact of cysteine-rich intestinal protein 1
(CRIP1) on thyroid carcinoma. Cell Physiol Biochem. 43:2037–2046.
2017.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
18
|
Wang Q, Williamson M, Bott S,
Brookman-Amissah N, Freeman A, Nariculam J, Hubank MJF, Ahmed A and
Masters JR: Hypomethylation of WNT5A, CRIP1 and S100P in prostate
cancer. Oncogene. 26:6560–6565. 2007.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
19
|
Terris B, Blaveri E, Crnogorac-Jurcevic T,
Jones M, Missiaglia E, Ruszniewski P, Sauvanet A and Lemoine NR:
Characterization of gene expression profiles in intraductal
papillary-mucinous tumors of the pancreas. Am J Pathol.
160:1745–1754. 2002.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
20
|
Groene J, Mansmann U, Meister R, Staub E,
Roepcke S, Heinze M, Klaman I, Brümmendorf T, Hermann K,
Loddenkemper C, et al: Transcriptional census of 36 microdissected
colorectal cancers yields a gene signature to distinguish UICC II
and III. Int J Cancer. 119:1829–1836. 2006.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
21
|
He G, Zou L, Zhou L, Gao P, Qian X and Cui
J: Cysteine-rich intestinal protein 1 silencing inhibits migration
and invasion in human colorectal cancer. Cell Physiol Biochem.
44:897–906. 2017.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
22
|
Livak KJ and Schmittgen TD: Analysis of
relative gene expression data using real-time quantitative PCR and
the 2(-Delta Delta C(T)) method. Methods. 25:402–408.
2001.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
23
|
Matthews JM, Lester K, Joseph S and Curtis
DJ: LIM-domain-only proteins in cancer. Nat Rev Cancer. 13:111–122.
2013.PubMed/NCBI View
Article : Google Scholar
|
|
24
|
Vilchez V, Turcios L, Marti F and Gedaly
R: Targeting Wnt/β-catenin pathway in hepatocellular carcinoma
treatment. World J Gastroenterol. 22:823–832. 2016.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
25
|
Forner A, Llovet JM and Bruix J:
Hepatocellular carcinoma. Lancet. 379:1245–1255. 2012.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
26
|
Chisari FV, Klopchin K, Moriyama T,
Pasquinelli C, Dunsford HA, Sell S, Pinkert CA, Brinster RL and
Palmiter RD: Molecular pathogenesis of hepatocellular carcinoma in
hepatitis B virus transgenic mice. Cell. 59:1145–1156.
1989.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
27
|
Grandori C, Cowley SM, James LP and
Eisenman RN: The Myc/Max/Mad network and the transcriptional
control of cell behavior. Annu Rev Cell Dev Biol. 16:653–699.
2000.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
28
|
Cole MD: The myc oncogene: Its role in
transformation and differentiation. Annu Rev Genet. 20:361–384.
1986.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
29
|
Latonen L, Järvinen PM and Laiho M:
Cytoskeleton-interacting LIM-domain protein CRP1 suppresses cell
proliferation and protects from stress-induced cell death. Exp Cell
Res. 314:738–747. 2008.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
30
|
Debatin KM: Apoptosis pathways in cancer
and cancer therapy. Cancer Immunol Immunother. 53:153–159.
2004.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
31
|
Zhang L, Zhou R, Zhang W, Yao X, Li W, Xu
L, Sun X and Zhao L: Cysteine-rich intestinal protein 1 suppresses
apoptosis and chemosensitivity to 5-fluorouracil in colorectal
cancer through ubiquitin-mediated Fas degradation. J Exp Clin
Cancer Res. 38(120)2019.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
32
|
Medina V, Edmonds B, Young GP, James R,
Appleton S and Zalewski PD: Induction of caspase-3 protease
activity and apoptosis by butyrate and trichostatin A (inhibitors
of histone deacetylase): Dependence on protein synthesis and
synergy with a mitochondrial/cytochrome c-dependent pathway. Cancer
Res. 57:3697–3707. 1997.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
33
|
Asselin E, Mills GB and Tsang BK: XIAP
regulates Akt activity and caspase-3-dependent cleavage during
cisplatin-induced apoptosis in human ovarian epithelial cancer
cells. Cancer Res. 61:1862–1868. 2001.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
34
|
Affar EB, Germain M, Winstall E,
Vodenicharov M, Shah RG, Salvesen GS and Poirier GG:
Caspase-3-mediated processing of poly(ADP-ribose) glycohydrolase
during apoptosis. J Biol Chem. 276:2935–2942. 2001.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
35
|
Sivalingam KS, Paramasivan P, Weng CF and
Viswanadha VP: Neferine potentiates the antitumor effect of
cisplatin in human lung adenocarcinoma cells via a
mitochondria-mediated apoptosis pathway. J Cell Biochem.
118:2865–2876. 2017.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
36
|
Strasser A, O'Connor L and Dixit VM:
Apoptosis signaling. Annu Rev Biochem. 69:217–245. 2000.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
37
|
Torre LA, Bray F, Siegel RL, Ferlay J,
Lortet-Tieulent J and Jemal A: Global cancer statistics, 2012. CA
Cancer J Clin. 65:87–108. 2015.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
38
|
Aiello NM and Kang Y: Context-dependent
EMT programs in cancer metastasis. J Exp Med. 216:1016–1026.
2019.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
39
|
Heerboth S, Housman G, Leary M, Longacre
M, Byler S, Lapinska K, Willbanks A and Sarkar S: EMT and tumor
metastasis. Clin Transl Med. 4(6)2015.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
40
|
He G, Zhu H, Yao Y, Chai H and Wang Y,
Zhao W, Fu S and Wang Y: Cysteine-rich intestinal protein 1
silencing alleviates the migration and invasive capability
enhancement induced by excessive zinc supplementation in colorectal
cancer cells. Am J Transl Res. 11:3578–3588. 2019.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
41
|
Lamouille S, Xu J and Derynck R: Molecular
mechanisms of epithelial-mesenchymal transition. Nat Rev Mol Cell
Biol. 15:178–196. 2014.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
42
|
Mendonsa AM, Na TY and Gumbiner BM:
E-cadherin in contact inhibition and cancer. Oncogene.
37:4769–4780. 2018.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
43
|
Odero-Marah V, Hawsawi O, Henderson V and
Sweeney J: Epithelial-mesenchymal transition (EMT) and prostate
cancer. Adv Exp Med Biol. 1095:101–110. 2018.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
44
|
Liu Y, Li W, Luo J, Wu Y, Xu Y, Chen T,
Zhang W and Fu F: Cysteine-rich intestinal protein 1 served as an
epithelial ovarian cancer marker via promoting
Wnt/β-catenin-mediated EMT and tumour metastasis. Dis Markers.
2021(3566749)2021.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
45
|
Onyido EK, Sweeney E and Nateri AS:
Wnt-signalling pathways and microRNAs network in carcinogenesis:
Experimental and bioinformatics approaches. Mol Cancer.
15(56)2016.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
46
|
He S and Tang S: WNT/β-catenin signaling
in the development of liver cancers. Biomed Pharmacother.
132(110851)2020.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
47
|
Li Q, Sun M, Wang M, Feng M, Yang F, Li L,
Zhao J, Chang C, Dong H, Xie T and Chen J: Dysregulation of
Wnt/β-catenin signaling by protein kinases in hepatocellular
carcinoma and its therapeutic application. Cancer Sci.
112:1695–1706. 2021.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
48
|
Kim CJ, Terado T, Tambe Y, Mukaisho KI,
Sugihara H, Kawauchi A and Inoue H: Anti-oncogenic activities of
cyclin D1b siRNA on human bladder cancer cells via induction of
apoptosis and suppression of cancer cell stemness and invasiveness.
Int J Oncol. 52:231–240. 2018.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
49
|
Taniguchi M, Matsuura K, Nakamura R,
Kojima A, Konishi M and Akizawa T: MMP-7 cleaves amyloid β fragment
peptides and copper ion inhibits the degradation. Biometals.
30:797–807. 2017.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
50
|
Baarsma HA, Königshoff M and Gosens R: The
WNT signaling pathway from ligand secretion to gene transcription:
Molecular mechanisms and pharmacological targets. Pharmacol Ther.
138:66–83. 2013.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
51
|
Zhang LZ, Huang LY, Huang AL, Liu JX and
Yang F: CRIP1 promotes cell migration, invasion and
epithelial-mesenchymal transition of cervical cancer by activating
the Wnt/β-catenin signaling pathway. Life Sci. 207:420–427.
2018.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|