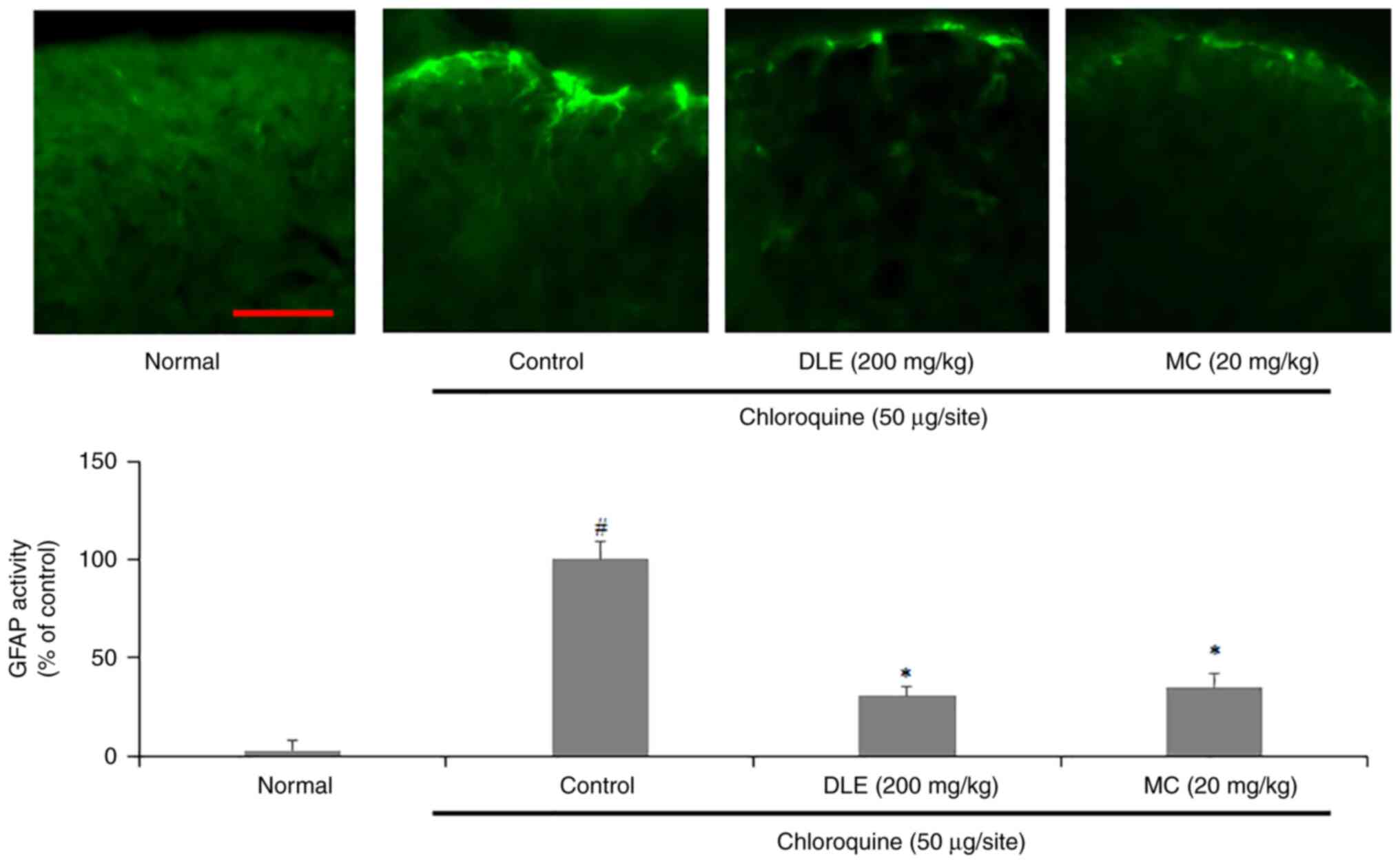
|
1
|
Savin JA: How should we define itching? J
Am Acad Dermatol. 39:268–269. 1998.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
2
|
Erturk IE, Arican O, Omurlu IK and Sut N:
Effect of the pruritus on the quality of life: A preliminary study.
Ann Dermatol. 24:406–412. 2012.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
3
|
Ikoma A, Steinhoff M, Ständer S,
Yosipovitch G and Schmelz M: The neurobiology of itch. Nat Rev
Neurosci. 7:535–547. 2006.PubMed/NCBI View
Article : Google Scholar
|
|
4
|
Dhand A and Aminoff MJ: The neurology of
itch. Brain. 137:313–322. 2014.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
5
|
Ikoma A: Updated neurophysiology of itch.
Biol Pharm Bull. 36:1235–1240. 2013.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
6
|
Jensen CJ, Massie A and De Keyser J:
Immune players in the CNS: The astrocyte. J Neuroimmune Pharmacol.
8:824–839. 2013.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
7
|
Tsuda M: Spinal dorsal horn astrocytes:
New players in chronic itch. Allergol Int. 66:31–35.
2017.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
8
|
Shiratori-Hayashi M and Tsuda M: Spinal
glial cells in itch modulation. Pharmacol Res Perspect.
9(e00754)2021.PubMed/NCBI View
Article : Google Scholar
|
|
9
|
Shiratori-Hayashi M, Yamaguchi C, Eguchi
K, Shiraishi Y, Kohno K, Mikoshiba K, Inoue K, Nishida M and Tsuda
M: Astrocytic STAT3 activation and chronic itch require
IP3R1/TRPC-dependent Ca2+ signals in mice. J
Allergy Clin Immunol. 147:1341–1353. 2021.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
10
|
Koga K, Yamagata R, Kohno K, Yamane T,
Shiratori-Hayashi M, Kohro Y, Tozaki-Saitoh H and Tsuda M:
Sensitization of spinal itch transmission neurons in a mouse model
of chronic itch requires an astrocytic factor. J Allergy Clin
Immunol. 145:183–191.e10. 2020.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
11
|
Sriram K, Benkovic SA, Hebert MA, Miller
DB and O'Callaghan JP: Induction of gp130-related cytokines and
activation of JAK2/STAT3 pathway in astrocytes precedes
up-regulation of glial fibrillary acidic protein in the
1-methyl-4-phenyl-1, 2, 3, 6-tetrahydropyridine model of
neurodegeneration: Key signaling pathway for astrogliosis in vivo?
J Biol Chem. 279:19936–19947. 2004.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
12
|
Ceyzériat K, Abjean L, Carrillo-de Sauvage
MA, Ben Haim L and Escartin C: The complex STATes of astrocyte
reactivity: How are they controlled by the JAK-STAT3 pathway?
Neuroscience. 330:205–218. 2016.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
13
|
Moghaddam AH, Nabavi SM, Nabavi SF,
Bigdellou R, Mohammadzadeh S and Ebrahimzadeh MA: Antioxidant,
antihemolytic and nephroprotective activity of aqueous extract of
Diospyros lotus seeds. Acta Pol Pharm. 69:687–692. 2012.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
14
|
Rauf A, Abu-Izneid T, Alhumaydhi FA,
Muhammad N, Aljohani ASM, Naz S, Bawazeer S, Wadood A and Mubarak
MS: In vivo analgesic, anti-inflammatory, and sedative activity and
a molecular docking study of dinaphthodiospyrol G isolated from
Diospyros lotus. BMC Complement Med Ther. 20(237)2020.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
15
|
Cho BO, Yin HH, Park SH, Byun EB, Ha HY
and Jang SI: Anti-inflammatory activity of myricetin from Diospyros
lotus through suppression of NF-κB and STAT1 activation and
Nrf2-mediated HO-1 induction in lipopolysaccharide-stimulated
RAW264.7 macrophages. Biosci Biotechnol Biochem. 80:1520–1530.
2016.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
16
|
Cho BO, Che DN, Yin HH, Shin JY and Jang
SI: Diospyros lotus leaf and grapefruit stem extract
synergistically ameliorate atopic dermatitis-like skin lesion in
mice by suppressing infiltration of mast cells in skin lesions.
Biomed Pharmacother. 89:819–826. 2017.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
17
|
Kim BM, Cho BO and Jang SI: Anti-obesity
effects of Diospyros lotus leaf extract in mice with high-fat
diet-induced obesity. Int J Mol Med. 43:603–613. 2019.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
18
|
Jeonju University Institutional Animal
Care and Use Committee: Animal Testing Ethics. https://www.jj.ac.kr/sanhak/ethics/iacuc.jsp. Accessed
May 3, 2023.
|
|
19
|
Cho BO, Shin JY, Kim JS, Che DN, Kang HJ,
Kang HJ, Oh H and Kim YS: Enzyme-treated date plum leave extract
ameliorates atopic dermatitis-like skin lesion in hairless mice.
Asian Pac J Trop Biomed. 10(239)2020.
|
|
20
|
Ivashkiv LB and Hu X: Signaling by stats.
Arthritis Res Ther. 6:1–10. 2004.PubMed/NCBI View
Article : Google Scholar
|
|
21
|
Shiratori-Hayashi M, Koga K, Tozaki-Saitoh
H, Kohro Y, Toyonaga H, Yamaguchi C, Hasegawa A, Nakahara T,
Hachisuka J, Akira S, et al: STAT3-dependent reactive astrogliosis
in the spinal dorsal horn underlies chronic itch. Nat Med.
21:927–931. 2015.PubMed/NCBI View
Article : Google Scholar
|
|
22
|
Lundstrom K, Pham HT and Dinh LD:
Interaction of plant extracts with central nervous system
receptors. Medicines. 4(12)2017.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
23
|
Roschek B Jr, Fink RC, McMichael M and
Alberte RS: Nettle extract (Urtica dioica) affects key receptors
and enzymes associated with allergic rhinitis. Phytother Res.
23:920–926. 2009.PubMed/NCBI View
Article : Google Scholar
|
|
24
|
Sun YG and Chen ZF: A gastrin-releasing
peptide receptor mediates the itch sensation in the spinal cord.
Nature. 448:700–703. 2007.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
25
|
Liu Q, Tang Z, Surdenikova L, Kim S, Patel
KN, Kim A, Ru F, Guan Y, Weng HJ, Geng Y, et al: Sensory
neuron-specific GPCR Mrgprs are itch receptors mediating
chloroquine-induced pruritus. Cell. 139:1353–1365. 2009.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
26
|
O'Callaghan JP, Kelly KA, VanGilder RL,
Sofroniew MV and Miller DB: . Early activation of STAT3 regulates
reactive astrogliosis induced by diverse forms of neurotoxicity.
PLoS One. 9(e102003)2014.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
27
|
Green D and Dong X: Supporting itch: A new
role for astrocytes in chronic itch. Nat Med. 21:841–842.
2015.PubMed/NCBI View
Article : Google Scholar
|
|
28
|
Cho BO, Che DN, Shin JY, Kang HJ, Kim JH,
Kim HY, Cho WG and Jang SI: Ameliorative effects of Diospyros lotus
leaf extract against UVB-induced skin damage in BALB/c mice. Biomed
Pharmacother. 95:264–274. 2017.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|