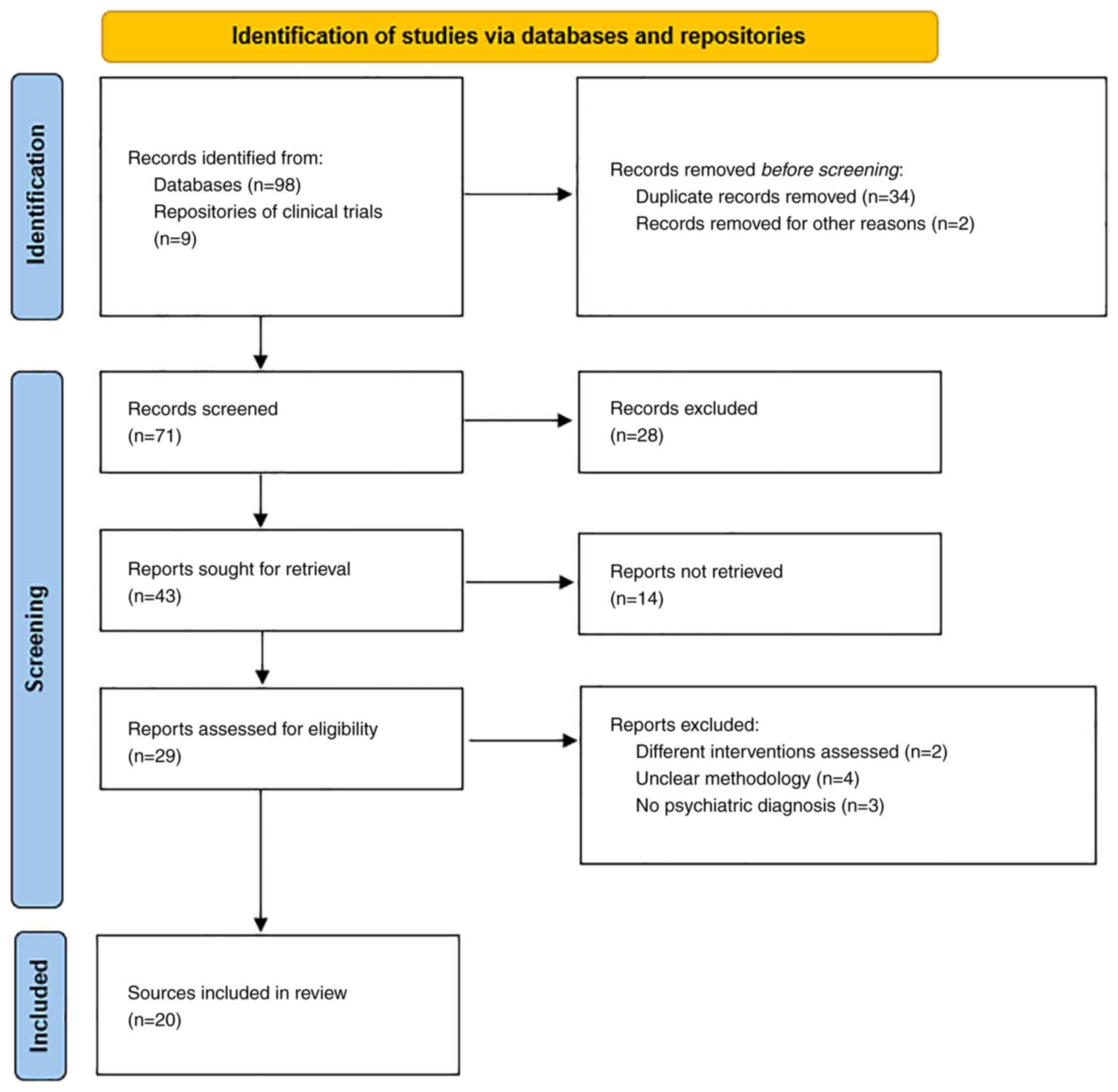
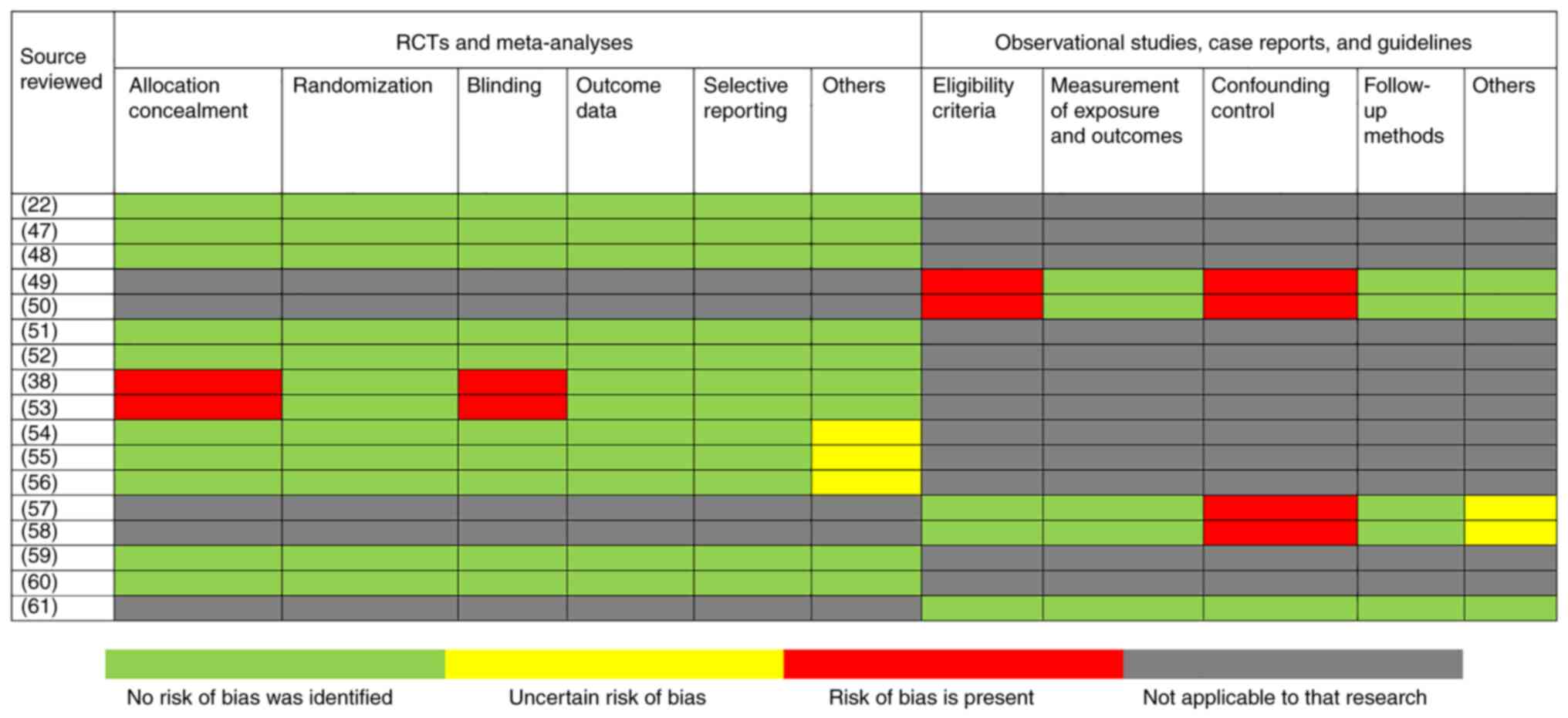
|
1
|
Cernea S, Dima L, Correll CU and Manu P:
Pharmacological management of glucose dysregulation in patients
treated with second-generation antipsychotics. Drugs. 80:1763–1781.
2020.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
2
|
Chang CK, Hayes RD, Perera G, Broadbent
MT, Fernandes AC, Lee WE, Hotopf M and Stewart R: Life expectancy
at birth for people with serious mental illness and other major
disorders from a secondary mental health care case register in
London. PLoS One. 6(e19590)2011.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
3
|
Kessing LV, Vradi E, McIntyre RS and
Andersen PK: Causes of decreased life expectancy over the life span
in bipolar disorder. J Affect Disord. 180:142–147. 2015.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
4
|
Dieset I, Andreassen OA and Haukvik UK:
Somatic comorbidity in schizophrenia: Some possible biological
mechanisms across the life span. Schizophr Bull. 42:1316–1319.
2016.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
5
|
Vasiliu O, Vasile D, Făinărea AF, Pătrașcu
MC, Morariu EA, Manolache R, Alexandru I and Androne FT: Analysis
of risk factors for antipsychotic-resistant schizophrenia in young
patients-a retrospective analysis. Rom J Mil Med. (CXXI): 25–29.
2018.
|
|
6
|
Rajkumar AP, Horsdal HT, Wimberley T,
Cohen D, Mors O, Børglum AD and Gasse C: Endogenous and
antipsychotic-related risks for diabetes mellitus in young people
with schizophrenia: A Danish population-based cohort study. Am J
Psychiatry. 174:686–694. 2017.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
7
|
Vasiliu O: Therapeutic management of
schizophrenia and substance use disorders dual diagnosis-clinical
vignettes. Rom J Mil Med. 121:26–34. 2018.
|
|
8
|
Ebdrup BH, Knop FK, Ishøy PL, Rostrup E,
Fagerlund B, Lublin H and Glenthøj B: Glucagon-like peptide-1
analogs against antipsychotic-induced weight gain: Potential
physiological benefits. BMC Med. 10(92)2012.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
9
|
Kouidrat Y and Amad A: GLP-1 agonists for
metabolic disorders in schizophrenia. Schizophr Res. 204:448–449.
2019.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
10
|
Vasiliu O: Esketamine for
treatment-resistant depression: A review of clinical evidence
(Review). Exper Ther Med. 25(111)2023.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
11
|
Hatziagelaki E, Tsiavou A, Gerasimou C,
Vavougios GD, Spathis A, Laskos E, Papageorgiou C and Douzenis A:
Effects of olanzapine on cytokine profile and brain-derived
neurotrophic factor in drug-naïve subjects with first-episode
psychosis. Exp Ther Med. 17:3071–3076. 2019.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
12
|
Ermakov EA, Melamund MM, Buneva VN and
Ivanova SA: Immune system abnormalities in schizophrenia: An
integrative view and translational perspectives. Front Psychiatry.
13(880568)2022.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
13
|
Mizuki Y, Sakamoto S, Okahisa Y, Yada Y,
Hashimoto N, Takaki M and Yamada N: Mechanisms underlying the
comorbidities of schizophrenia and type 2 diabetes mellitus. Int J
Neuropsychopharmacol. 24:367–382. 2021.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
14
|
Libowitz MR and Nurmi EL: The burden of
antipsychotic-induced weight gain and metabolic syndrome in
children. Front Psychiatry. 12(623681)2021.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
15
|
Chen J, Huang XF, Shao R, Chen C and Deng
C: Molecular mechanisms of antipsychotic drug-induced diabetes.
Front Neurosci. 11(643)2017.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
16
|
Goh KK, Chen CYA, Wu TH, Chen CH and Lu
ML: Crosstalk between schizophrenia and metabolic syndrome: The
role of oxytocinergic dysfunction. Int J Mol Sci.
23(7092)2022.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
17
|
Carey ME, Barnett J, Doherty Y, Barnard K,
Daly H, French P, Gossage-Worrall R, Hadjiconstantinou M, Hind D,
Mitchell J, et al: Reducing weight gain in people with
schizophrenia, schizoaffective disorder, and first episode
psychosis: Describing the process of developing the Structured
lifestyle Education for People with SchizophrEnia (STEPWISE)
intervention. Pilot Feasibility Stud. 4(186)2018.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
18
|
Budisteanu M, Andrei E, Lica F, Hulea DS,
Velicu AC, Mihailescu I, Riga S, Arghir A, Papuc SM, Sirbu CA, et
al: Predictive factors in early onset schizophrenia. Exp Ther Med.
20(210)2020.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
19
|
Vasiliu O: Impact of SGLT2 inhibitors on
metabolic status in patients with psychiatric disorders undergoing
treatment with second-generation antipsychotics (Review). Exp Ther
Med. 25(125)2023.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
20
|
Fitzgerald I, O'Connell J, Keating D,
Hynes C, McWilliams S and Crowley EK: Metformin in the management
of antipsychotic-induced weight gain in adults with psychosis:
Development of the first evidence-based guideline using GRADE
methodology. Evid Based Ment Health. 25:15–22. 2022.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
21
|
Hiluy JC, Nazar BP, Gonçalves WS, Coutinho
W and Appolinario JC: Effectiveness of pharmacologic interventions
in the management of weight gain in patients with severe mental
illness: A systematic review and meta-analysis. Prim Care Companion
CNS Disord. 21(19r02483)2019.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
22
|
Medak KD, Shamshoum H, Peppler WT and
Wright D: GLP1 receptor agonism protects against acute
olanzapine-induced hyperglycemia. Am J Physiol Endocrinol Metab.
319:E1101–E1111. 2020.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
23
|
Boyda HN, Tse L, Procyshyn RM, Wong D, Wu
TH, Pang CC and Barr AM: A parametric study of the acute effects of
antipsychotic drugs on glucose sensitivity in an animal model. Prog
Neuropsychopharmacol Biol Psychiatry. 34:945–954. 2010.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
24
|
Chintoh AF, Mann SW, Lam L, Lam C, Cohn
TA, Fletcher PJ, Nobrega JN, Giacca A and Remington G: Insulin
resistance and decreased glucose-stimulated insulin secretion after
acute olanzapine administration. J Clin Psychopharmacol.
28:494–499. 2008.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
25
|
Mayfield K, Siskind D, Winckel K, Russell
AW, Kisely S, Smith G and Hollingworth S: Glucagon-like peptide-1
agonists combating clozapine-associated obesity and diabetes. J
Psychopharmacol. 30:227–236. 2016.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
26
|
Deutch AY: Liraglutide for the treatment
of antipsychotic drug-induced weight gain. JAMA Psychiatry.
74:1172–1173. 2017.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
27
|
Heppner KM, Kirigiti M, Secher A, Paulsen
SJ, Buckingham R, Pyke C, Knudsen LB, Vrang N and Grove KL:
Expression and distribution of glucagon-like peptide-1 receptor
mRNA, protein and binding in the male nonhuman primate (Macaca
mulatta) brain. Endocrinolog. 156:255–267. 2015.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
28
|
Zhong P, Zeng H, Huang M, Fu W and Chen Z:
Efficacy and safety of once-weekly semaglutide in adults with
overweight or obesity: A meta-analysis. Endocrine. 75:718–724.
2022.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
29
|
Avgerinos I, Michailidis T, Liakos A,
Karagiannis T, Matthews DR, Tsapas A and Bekiari E: Oral
semaglutide for type 2 diabetes: A systematic review and
meta-analysis. Diabetes Obes Metab. 22:335–345. 2020.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
30
|
Blair HA and Keating GM: Albiglutide: A
review of its use in patients with type 2 diabetes mellitus. Drugs.
75:651–663. 2015.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
31
|
Chudleigh RA, Platts J and Bain SC:
Comparative effectiveness of long-acting GLP-1 receptor agonists in
type-2 diabetes: A short review on the emerging data. Diabetes
Metab Syndr Obes. 13:433–438. 2020.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
32
|
Umpierrez G, Tofé Povedano S, Pérez Manghi
F, Shurzinske L and Pechtner V: Efficacy and safety of dulaglutide
monotherapy versus metformin in type 2 diabetes in a randomized
controlled trial (AWARD-3). Diabetes Care. 37:2168–2176.
2014.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
33
|
Madsbad S: Review of head-to-head
comparison of glucagon-like peptide-1 receptor agonists. Diabetes
Obes Metab. 18:317–332. 2016.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
34
|
Roca-Rodriguez MM, Muros de Fuentes MT,
Piédrola-Maroto G, Quesada-Charneco M, Maraver-Selfa S, Tinahones
FJ and Mancha-Doblas I: Lixisenatide in patients with type 2
diabetes and obesity: Beyond glycamic control. Aten Primaria.
49:294–299. 2017.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar : (In Spanish).
|
|
35
|
Rosenstock J, Raccah D, Korányi L, Maffei
L, Boka G, Miossec P and Gerich JE: Efficacy and safety of
lixisenatide once daily versus exenatide twice daily in type 2
diabetes inadequately controlled on metformin: A 24-week,
randomized, open-label, active-controlled study (GetGoal-X).
Diabetes Care. 36:2945–2951. 2013.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
36
|
Kapitza C, Forst T, Coester HV, Poitiers
F, Ruus P and Hincelin-Méry A: Pharmacodynamic characteristics of
lixisenatide once daily versus liraglutide once daily in patients
with type 2 diabetes insufficiently controlled on metformin.
Diabetes Obes Metab. 15:642–649. 2013.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
37
|
Ishøy PL, Fagerlund B, Broberg BV, Bak N,
Knop FJ, Glenthøj BY and Ebdrup BH: No cognitive-enhancing effect
of GLP-1 receptor agonism in antipsychotic-treated, obese patients
with schizophrenia. Acta Psychiatr Scand. 136:52–62.
2017.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
38
|
Siskind DJ, Russell AW, Gamble C, Winckel
K, Mayfield K, Hollingworth S, Hickman I, Siskind V and Kisely S:
Treatment of clozapine-associated obesity and diabetes with
exenatide in adults with schizophrenia: A randomized controlled
trial (CODEX). Diabetes Obes Metab. 20:1050–1055. 2018.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
39
|
Htike ZZ, Zaccardi F, Papamargaritis D,
Webb DR, Khunti K and Davies MJ: Efficacy and safety of
glucagon-like peptide-1 receptor agonists in type 2 diabetes: A
systematic review and mixed-treatment comparison analysis. Diabetes
Obes Metab. 19:524–536. 2017.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
40
|
Min T and Bain SC: The role of
tirzepatide, dual GIP and GLP-1 receptor agonist, in the management
of type 2 diabetes: The SURPASS clinical trials. Diabetes Ther.
12:143–157. 2021.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
41
|
Ludvik B, Giorgino F, Jódar E, Frias JP,
Fernández Landó L, Brown K, Bray R and Rodríguez Á: Once-weekly
tirzepatide versus once-daily insulin degludec as add-on to
metformin with or without SGLT2 inhibitors in patients with type 2
diabetes (SURPASS-3): A randomized, open-label, parallel-group,
phase 3 trial. Lancet. 398:583–598. 2021.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
42
|
Brozek JL, Akl EA, Compalati E, Kreis J,
Terraciano L, Fiocchi A, Ueffing E, Andrews J, Alonso-Coello P,
Meerpohl JJ, et al: Grading quality of evidence and strength of
recommendations in clinical practice guidelines part 3 of 3. The
GRADE approach to developing recommendations. Allergy. 66:588–595.
2011.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
43
|
Neumann I, Santesso N, Akl EA, Rind DM,
Vandvik PO, Alonso-Coello P, Agoritsas T, Mustafa RA, Alexander PE,
Schünemann H and Guyatt GH: A guide for health professionals to
interpret and use recommendations in guidelines developed with the
GRADE approach. J Clin Epidemiol. 72:45–55. 2016.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
44
|
Page MJ, McKenzie JE, Bossuyt PM, Boutron
I, Hoffmann TC, Mulrow CD, Shamseer L, Tetzlaff JM, Akl EA, Brennan
SE, et al: The PRISMA 2020 statement: An updated guideline for
reporting systematic reviews. BMJ. 372(n71)2021.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
45
|
Cooke A, Smith D and Booth A: Beyond PICO:
The SPIDER tool for qualitative evidence synthesis. Qual Health
Res. 22:1435–1443. 2012.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
46
|
Schünemann H, Brożek J, Guyatt G and Oxman
A (eds): GRADE handbook for grading quality of evidence and
strength of recommendations. Updated October 2013. The GRADE
Working Group, 2013. guidelinedevelopment.org/handbook. Accessed January
7, 2023.
|
|
47
|
Babic I, Gorak A, Engel M, Sellers D, Else
P, Osborne AL, Pai N, Huang XF, Nealon J and Weston-Green K:
Liraglutide prevents metabolic side-effects and improves
recognition and working memory during antipsychotic treatment in
rats. J Psychopharmacol. 32:578–590. 2018.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
48
|
Lykkegaard K, Larsen PJ, Vrang N, Bock C,
Bock T and Knudsen LB: The once-daily human GLP-1 analog,
liraglutide, reduces olanzapine-induced weight gain and glucose
intolerance. Schizophr Res. 103:94–103. 2008.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
49
|
Ishøy PL, Knop FK, Vilsbøll T, Glenthøj BY
and Ebdrup BH: Sustained weight loss after treatment with a
glucagon-like peptide-1 receptor agonist in an obese patient with
schizophrenia and type 2 diabetes. Am J Psychiatry. 170:681–682.
2013.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
50
|
Siskind D, Wysoczanski D, Russell A and
Ashford M: Weight loss associated with exenatide in an obese man
with diabetes commenced on clozapine. Aust N Z J Psychiatry.
50:702–703. 2016.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
51
|
Larsen JR, Vedtofte L, Jakobsen MSL,
Jespersen HR, Jakobsen MI, Svensson CK, Koyuncu K, Schjerning O,
Oturai PS, Kjaer A, et al: Effect of liraglutide treatment on
prediabetes and overweight or obesity in clozapine- or
olanzapine-treated patients with schizophrenia spectrum disorder: A
randomized clinical trial. JAMA Psychiatry. 74:719–728.
2017.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
52
|
Svensson CK, Larsen JR, Vedtofte L,
Jakobsen MSL, Jespersen HR, Jakobsen MI, Koyuncu K, Schjerning O,
Nielsen J, Ekstrøm CT, et al: One-year follow-up on liraglutide
treatment for prediabetes and overweight/obesity in clozapine- or
olanzapine-treated patients. Acta Psychiatr Scand. 139:26–36.
2019.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
53
|
Siskind D, Russell A and Kisely S: T44.
12-Month follow-up of metabolic measures following a randomised
controlled trial of treatment of clozapine associated obesity and
diabetes with exenatide (CODEX). Schizophr Bull. 46
(Suppl.1)(S248)2020.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
54
|
Ishøy PL, Knop FK, Broberg BV, Bak N,
Andersen UB, Jørgensen NR, Holst JJ, Glenthøj BY and Ebdrup BH:
Effect of GLP-1 receptor agonist treatment on body weight in obese
antipsychotic-treated patients with schizophrenia: A randomized,
placebo-controlled trial. Diabetes Obes Metab. 19:162–171.
2017.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
55
|
U.S. National Library of Medicine:
Exenatide for the treatment of weight gain associated with
olanzapine in obese adults. NCT00845507. https://clinicaltrials.gov/ct2/show/results/NCT00845507.
Accessed June 10, 2022.
|
|
56
|
Whicher CA, Price HC, Phiri P, Rathod S,
Barnard-Kelly K, Ngianga K, Thorne K, Asher C, Peveler RC, McCarthy
J and Holt RIG: The use of liraglutide 3.0 mg daily in the
management of overweight and obesity in people with schizophrenia,
schizoaffective disorder and first episode psychosis: Results of a
pilot randomized, double-blind, placebo-controlled trial. Diabetes
Obes Metab. 23:1262–1271. 2021.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
57
|
Perlis LT, Lamberti JS and Miedlich SU:
Glucagon-like peptide analogs are superior for diabetes and weight
control in patients on antipsychotic medications: A retrospective
cohort study. Prim Care Companion CNS Disord.
22(19m02504)2020.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
58
|
Lee SE, Lee NY, Kim SH, Kim KA and Kim YS:
Effect of liraglutide 3.0 mg treatment on weight reduction in obese
antipsychotic-treated patients. Psychiatry Res.
299(113830)2021.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
59
|
Siskind D, Hahn M, Correll CU, Fink-Jensen
A, Russell AW, Bak N, Broberg BV, Larsen J, Ishøy PL, Vilsbøll T,
et al: Glucagon-like peptide-1 receptor agonists for
antipsychotic-associated cardio-metabolic risk factors: A
systematic review and individual participant data meta-analysis.
Diabetes Obes Metab. 21:293–302. 2019.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
60
|
Wang Y, Wang D, Cheng J, Fang X, Chen Y,
Yu L, Ren J, Tian Y and Zhang C: Efficacy and tolerability of
pharmacological interventions on metabolic disturbances induced by
atypical antipsychotics in adults: A systematic review and network
meta-analysis. J Psychopharmacol. 35:1111–1119. 2021.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
61
|
Cooper SJ and Reynolds GP: With expert
co-authors (in alphabetical order). Barnes T, England E, Haddad PM,
Heald A, Holt R, Lingford-Hughes A, Osborn D, et al: BAP guidelines
on the management of weight gain, metabolic disturbances and
cardiovascular risk associated with psychosis and antipsychotic
drug treatment. J Psychopharmacol. 30:717–748. 2016.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
62
|
U.S. National Library of Medicine.
Semaglutide in comorbid schizophrenia spectrum disorder and obesity
(Sema). NCT05333003. Retrieved online at https://clinicaltrials.gov/ct2/show/NCT05333003
(accessed June 10, 2022).
|
|
63
|
Sailer CO, Sulieman I, Macedo CT, Parodi
MR, Machuca M, Sanchez CJS, Murrieta CGI, Delgoshaie N, Nanbu DY,
Sarmento R, et al: The glucagon like peptide-1 analogue dulaglutide
to prevent antipsychotic induced weight gain-a study protocol
proposal. Prin Pract Clin Res. 5:19–26. 2019.
|
|
64
|
Queensland Centre for Mental Health
Research: Cadence-CoaST clinical trial. https://qcmhr.org/research/studies-recruiting-participants/2759-2/.
Accessed June 10, 2022.
|
|
65
|
Shetty R, Basheer FT, poojari PG, Thunga
G, Chandran VP and Acharya LD: Adverse drug reactions of GLP-1
agonists: A systematic review of case reports. Diabetes Metab
Syndr. 16(102427)2022.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|