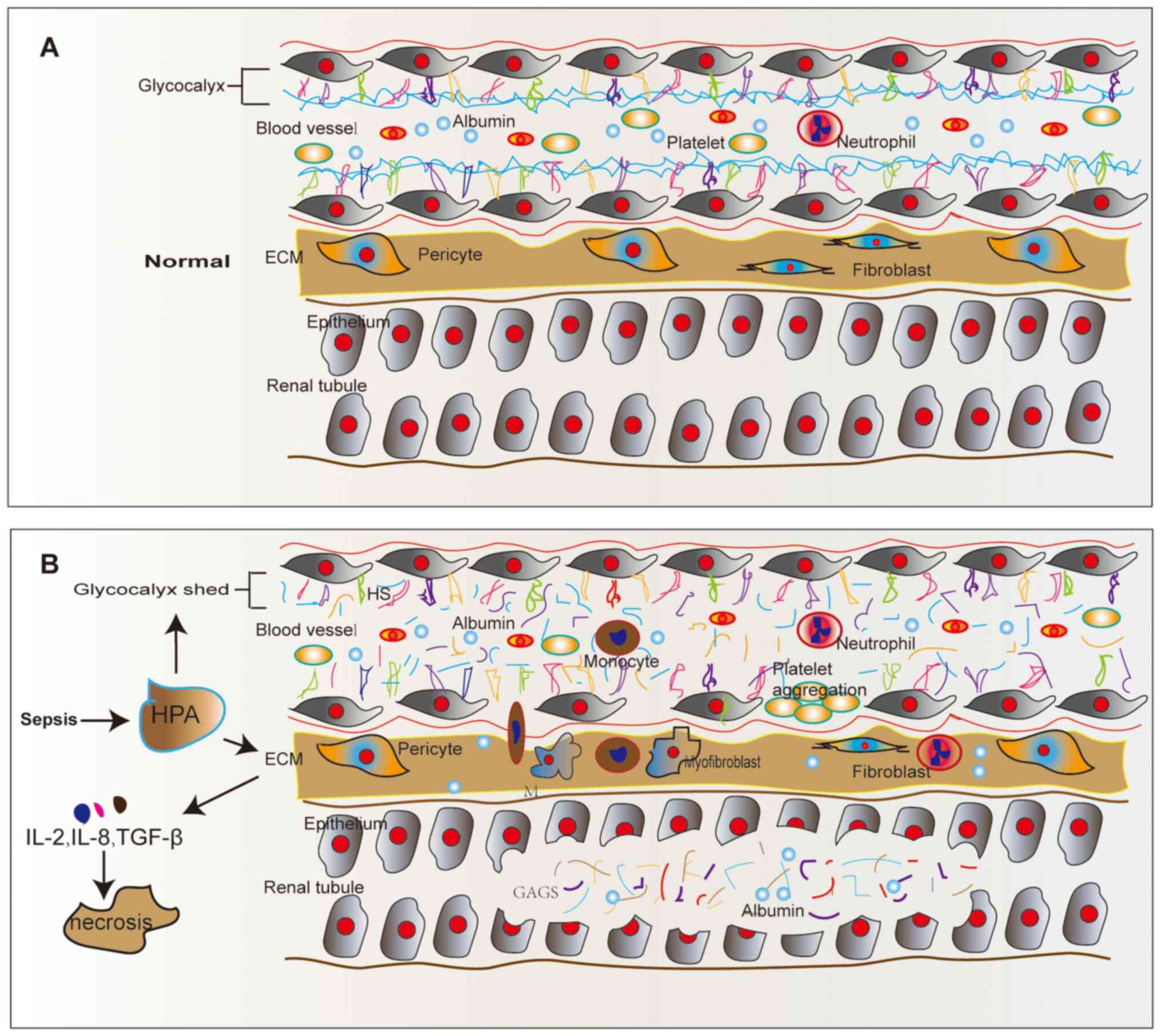
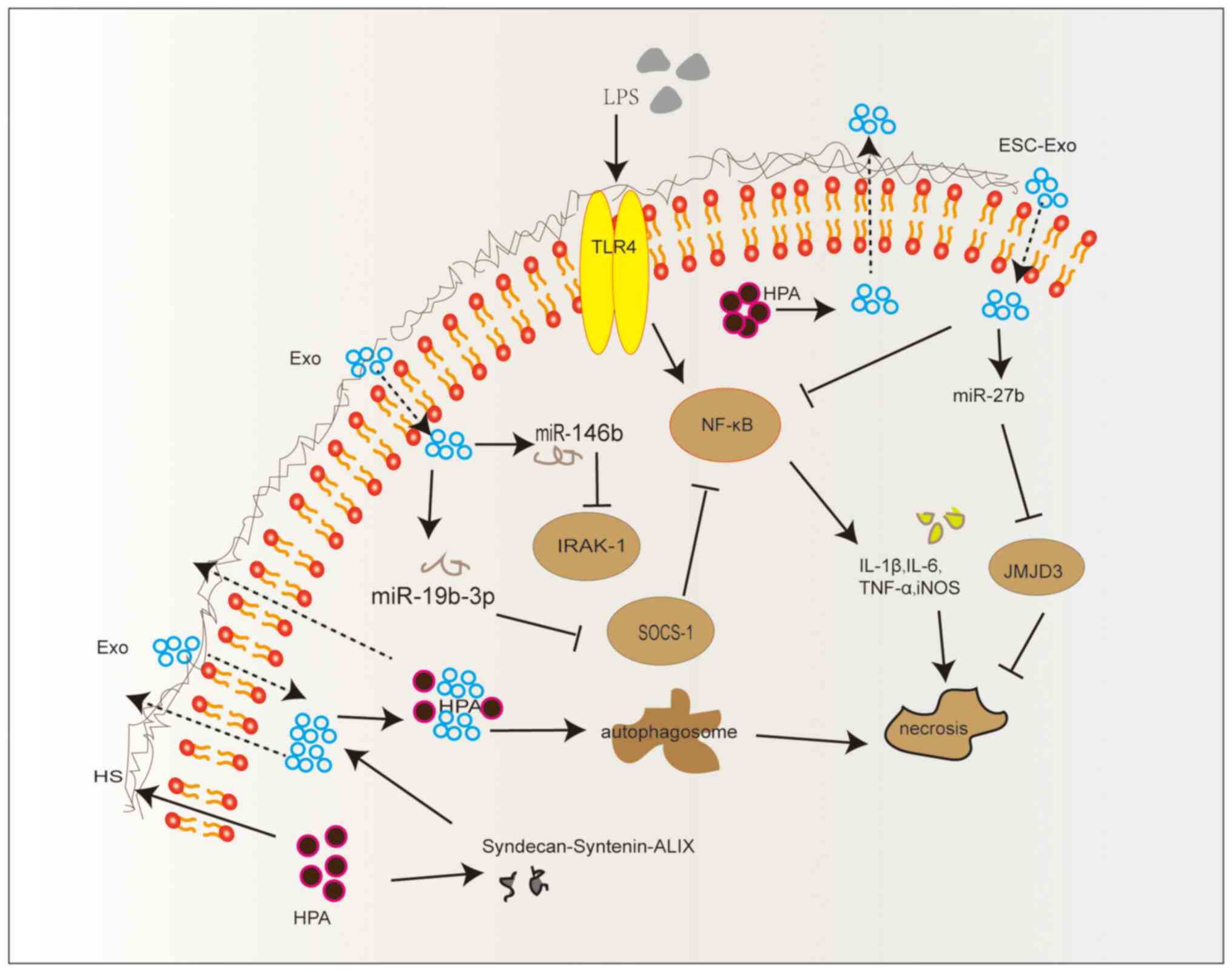
|
1
|
Lameire NH, Bagga A, Cruz D, De Maeseneer
J, Endre Z, Kellum JA, Liu KD, Mehta RL, Pannu N, Van Biesen W and
Vanholder R: .: Acute kidney injury: An increasing global concern.
Lancet. 382:170–179. 2013.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
2
|
Hoste EA and Schurgers M: Epidemiology of
acute kidney injury: How big is the problem? Crit Care Med. 36 (4
Suppl):S146–S151. 2008.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
3
|
Susantitaphong P, Cruz DN, Cerda J,
Abulfaraj M, Alqahtani F, Koulouridis I and Jaber BL: Acute Kidney
Injury Advisory Group of the American Society of Nephrology. World
incidence of AKI: A meta-analysis. Clin J Am Soc Nephrol.
8:1482–1493. 2013.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
4
|
Ronco C, Bellomo R and Kellum JA: Acute
kidney injury. Lancet. 394:1949–1964. 2019.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
5
|
Kellum JA, Chawla LS, Keener C, Singbartl
K, Palevsky PM, Pike FL, Yealy DM, Huang DT and Angus DC: ProCESS
and ProGReSS-AKI Investigators. The effects of alternative
resuscitation strategies on acute kidney injury in patients with
septic shock. Am J Respir Crit Care Med. 193:281–287.
2016.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
6
|
Mayeux PR and MacMillan-Crow LA:
Pharmacological targets in the renal peritubular microenvironment:
Implications for therapy for sepsis-induced acute kidney injury.
Pharmacol Ther. 134:139–155. 2012.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
7
|
Lygizos MI, Yang Y, Altmann CJ, Okamura K,
Hernando AA, Perez MJ, Smith LP, Koyanagi DE, Gandjeva A, Bhargava
R, et al: Heparanase mediates renal dysfunction during early sepsis
in mice. Physiol Rep. 1(e00153)2013.PubMed/NCBI View
Article : Google Scholar
|
|
8
|
Zhang Y, Huang H, Liu W, Liu S, Wang XY,
Diao ZL, Zhang AH, Guo W, Han X, Dong X and Katilov O: Endothelial
progenitor cells-derived exosomal microRNA-21-5p alleviates
sepsis-induced acute kidney injury by inhibiting RUNX1 expression.
Cell Death Dis. 12(335)2021.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
9
|
Kellum JA and Lameire N: KDIGO AKI
Guideline Work Group. Diagnosis, evaluation, and management of
acute kidney injury: A KDIGO summary (Part 1). Crit Care.
17(204)2013.PubMed/NCBI View
Article : Google Scholar
|
|
10
|
Singer M, Deutschman CS, Seymour CW,
Shankar-Hari M, Annane D, Bauer M, Bellomo R, Bernard GR, Chiche
JD, Coopersmith CM, et al: The Third International Consensus
Definitions for Sepsis and Septic Shock (Sepsis-3). JAMA.
315:801–810. 2016.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
11
|
Bonventre JV and Yang L: Cellular
pathophysiology of ischemic acute kidney injury. J Clin Invest.
121:4210–4221. 2011.PubMed/NCBI View
Article : Google Scholar
|
|
12
|
Schrier RW, Wang W, Poole B and Mitra A:
Acute renal failure: Definitions, diagnosis, pathogenesis, and
therapy. J Clin Invest. 114:5–14. 2004.PubMed/NCBI View
Article : Google Scholar
|
|
13
|
Schmidt C, Steinke T, Moritz S, Graf BM
and Bucher M: Acute renal failure and sepsis: Just an organ
dysfunction due to septic multiorgan failure? Anaesthesist.
59:682–699. 2010.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar : (In German).
|
|
14
|
Maiden MJ, Otto S, Brealey JK, Finnis ME,
Chapman MJ, Kuchel TR, Nash CH, Edwards J and Bellomo R: Structure
and function of the kidney in septic shock. A prospective
controlled experimental study. Am J Respir Crit Care Med.
194:692–700. 2016.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
15
|
Lerolle N, Nochy D, Guérot E, Bruneval P,
Fagon JY, Diehl JL and Hill G: Histopathology of septic shock
induced acute kidney injury: Apoptosis and leukocytic infiltration.
Intensive Care Med. 36:471–478. 2010.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
16
|
Peerapornratana S, Manrique-Caballero CL,
Gómez H and Kellum JA: Acute kidney injury from sepsis: Current
concepts, epidemiology, pathophysiology, prevention and treatment.
Kidney Int. 96:1083–1099. 2019.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
17
|
Poston JT and Koyner JL: Sepsis associated
acute kidney injury. BMJ. 364(k4891)2019.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
18
|
Gomez H, Ince C, De Backer D, Pickkers P,
Payen D, Hotchkiss J and Kellum JA: A unified theory of
sepsis-induced acute kidney injury: Inflammation, microcirculatory
dysfunction, bioenergetics, and the tubular cell adaptation to
injury. Shock. 41:3–11. 2014.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
19
|
Bateman RM, Sharpe MD, Jagger JE and Ellis
CG: Sepsis impairs microvascular autoregulation and delays
capillary response within hypoxic capillaries. Crit Care.
19(389)2015.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
20
|
Ye C, Kawasaki M, Nakano K, Ohnishi T,
Watanabe E, Oda S, Nakada TA and Haneishi H: Acquisition and
analysis of microcirculation image in septic model rats. Sensors
(Basel). 22(8471)2022.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
21
|
Ince C: The microcirculation is the motor
of sepsis. Crit Care. 9 (Suppl 4):S13–S19. 2005.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
22
|
Joffre J, Hellman J, Ince C and
Ait-Oufella H: Endothelial responses in sepsis. Am J Respir Crit
Care Med. 202:361–370. 2020.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
23
|
Anniss AM and Sparrow RL: Variable
adhesion of different red blood cell products to activated vascular
endothelium under flow conditions. Am J Hematol. 82:439–445.
2007.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
24
|
Ishikawa K, Calzavacca P, Bellomo R,
Bailey M and May CN: Effect of selective inhibition of renal
inducible nitric oxide synthase on renal blood flow and function in
experimental hyperdynamic sepsis. Crit Care Med. 40:2368–2375.
2012.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
25
|
Heemskerk S, Pickkers P, Bouw MP, Draisma
A, van der Hoeven JG, Peters WH, Smits P, Russel FG and Masereeuw
R: Upregulation of renal inducible nitric oxide synthase during
human endotoxemia and sepsis is associated with proximal tubule
injury. Clin J Am Soc Nephrol. 1:853–862. 2006.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
26
|
Inkinen N, Pettilä V, Lakkisto P, Kuitunen
A, Jukarainen S, Bendel S, Inkinen O, Ala-Kokko T and Vaara ST:
FINNAKI Study Group. Association of endothelial and glycocalyx
injury biomarkers with fluid administration, development of acute
kidney injury, and 90-day mortality: Data from the FINNAKI
observational study. Ann Intensive Care. 9(103)2019.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
27
|
Gustot T: Multiple organ failure in
sepsis: Prognosis and role of systemic inflammatory response. Curr
Opin Crit Care. 17:153–159. 2011.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
28
|
Zhu J, Zhang Y, Shi L, Xia Y, Zha H, Li H
and Song Z: RP105 protects against ischemic and septic acute kidney
injury via suppressing TLR4/NF-κB signaling pathways. Int
Immunopharmacol. 109(108904)2022.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
29
|
Krivan S, Kapelouzou A, Vagios S,
Tsilimigras DI, Katsimpoulas M, Moris D, Aravanis CV, Demesticha
TD, Schizas D, Mavroidis M, et al: Increased expression of
Toll-like receptors 2, 3, 4 and 7 mRNA in the kidney and intestine
of a septic mouse model. Sci Rep. 9(4010)2019.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
30
|
Kawai T and Akira S: Signaling to
NF-kappaB by Toll-like receptors. Trends Mol Med. 13:460–469.
2007.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
31
|
Kawai T and Akira S: TLR signaling. Semin
Immunol. 19:24–32. 2007.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
32
|
Leemans JC, Stokman G, Claessen N,
Rouschop KM, Teske GJ, Kirschning CJ, Akira S, van der Poll T,
Weening JJ and Florquin S: Renal-associated TLR2 mediates
ischemia/reperfusion injury in the kidney. J Clin Invest.
115:2894–2903. 2005.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
33
|
El-Achkar TM, Huang X, Plotkin Z, Sandoval
RM, Rhodes GJ and Dagher PC: Sepsis induces changes in the
expression and distribution of Toll-like receptor 4 in the rat
kidney. Am J Physiol Renal Physiol. 290:F1034–F1043.
2006.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
34
|
Fani F, Regolisti G, Delsante M,
Cantaluppi V, Castellano G, Gesualdo L, Villa G and Fiaccadori E:
Recent advances in the pathogenetic mechanisms of sepsis-associated
acute kidney injury. J Nephrol. 31:351–359. 2018.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
35
|
Zafrani L, Gerotziafas G, Byrnes C, Hu X,
Perez J, Lévi C, Placier S, Letavernier E, Leelahavanichkul A,
Haymann JP, et al: Calpastatin controls polymicrobial sepsis by
limiting procoagulant microparticle release. Am J Respir Crit Care
Med. 185:744–755. 2012.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
36
|
Stark K and Massberg S: Interplay between
inflammation and thrombosis in cardiovascular pathology. Nat Rev
Cardiol. 18:666–682. 2021.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
37
|
Benedetti C, Waldman M, Zaza G, Riella LV
and Cravedi P: COVID-19 and the Kidneys: An update. Front Med
(Lausanne). 7(423)2020.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
38
|
Toro J, Manrique-Caballero CL and Gómez H:
Metabolic reprogramming and host tolerance: A novel concept to
understand sepsis-associated AKI. J Clin Med.
10(4184)2021.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
39
|
Wilson DF: Oxidative phosphorylation:
Regulation and role in cellular and tissue metabolism. J Physiol.
595:7023–7038. 2017.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
40
|
Waltz P, Carchman E, Gomez H and
Zuckerbraun B: Sepsis results in an altered renal metabolic and
osmolyte profile. J Surg Res. 202:8–12. 2016.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
41
|
Zhang D, Qi B, Li D, Feng J, Huang X, Ma
X, Huang L, Wang X and Liu X: Phillyrin relieves
lipopolysaccharide-induced AKI by protecting against glycocalyx
damage and inhibiting inflammatory responses. Inflammation.
43:540–551. 2020.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
42
|
Vlodavsky I, Singh P, Boyango I,
Gutter-Kapon L, Elkin M, Sanderson RD and Ilan N: Heparanase: From
basic research to therapeutic applications in cancer and
inflammation. Drug Resist Updat. 29:54–75. 2016.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
43
|
Goldberg R, Meirovitz A, Hirshoren N,
Bulvik R, Binder A, Rubinstein AM and Elkin M: Versatile role of
heparanase in inflammation. Matrix Biol. 32:234–240.
2013.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
44
|
Goldberg R, Rubinstein AM, Gil N, Hermano
E, Li JP, van der Vlag J, Atzmon R, Meirovitz A and Elkin M: Role
of heparanase-driven inflammatory cascade in pathogenesis of
diabetic nephropathy. Diabetes. 63:4302–4313. 2014.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
45
|
Goldshmidt O, Zcharia E, Abramovitch R,
Metzger S, Aingorn H, Friedmann Y, Schirrmacher V, Mitrani E and
Vlodavsky I: Cell surface expression and secretion of heparanase
markedly promote tumor angiogenesis and metastasis. Proc Natl Acad
Sci USA. 99:10031–10036. 2002.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
46
|
Parish CR, Freeman C, Ziolkowski AF, He
YQ, Sutcliffe EL, Zafar A, Rao S and Simeonovic CJ: Unexpected new
roles for heparanase in type 1 diabetes and immune gene regulation.
Matrix Biol. 32:228–233. 2013.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
47
|
Meirovitz A, Goldberg R, Binder A,
Rubinstein AM, Hermano E and Elkin M: Heparanase in inflammation
and inflammation-associated cancer. FEBS J. 280:2307–2319.
2013.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
48
|
Levey AS and James MT: Acute kidney
injury. Ann Intern Med. 167:ITC66–ITC80. 2017.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
49
|
Masola V, Zaza G, Onisto M, Lupo A and
Gambaro G: Impact of heparanase on renal fibrosis. J Transl Med.
13(181)2015.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
50
|
Rosenfeldt MT and Ryan KM: The multiple
roles of autophagy in cancer. Carcinogenesis. 32:955–963.
2011.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
51
|
Bishop JR, Schuksz M and Esko JD: Heparan
sulphate proteoglycans fine-tune mammalian physiology. Nature.
446:1030–1037. 2007.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
52
|
Bernfield M, Götte M, Park PW, Reizes O,
Fitzgerald ML, Lincecum J and Zako M: Functions of cell surface
heparan sulfate proteoglycans. Annu Rev Biochem. 68:729–777.
1999.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
53
|
Goldshmidt O, Nadav L, Aingorn H, Irit C,
Feinstein N, Ilan N, Zamir E, Geiger B, Vlodavsky I and Katz BZ:
Human heparanase is localized within lysosomes in a stable form.
Exp Cell Res. 281:50–62. 2002.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
54
|
van den Hoven MJ, Rops AL, Vlodavsky I,
Levidiotis V, Berden JH and van der Vlag J: Heparanase in
glomerular diseases. Kidney Int. 72:543–548. 2007.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
55
|
Gaskin SM, Soares Da Costa TP and Hulett
MD: Heparanase: Cloning, function and regulation. Adv Exp Med Biol.
1221:189–229. 2020.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
56
|
Masola V, Bellin G, Gambaro G and Onisto
M: Heparanase: A multitasking protein involved in extracellular
matrix (ECM) remodeling and intracellular events. Cells.
7(236)2018.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
57
|
Sanderson RD, Elkin M, Rapraeger AC, Ilan
N and Vlodavsky I: Heparanase regulation of cancer, autophagy and
inflammation: new mechanisms and targets for therapy. FEBS J.
284:42–55. 2017.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
58
|
David G and Zimmermann P: Heparanase
involvement in exosome formation. Adv Exp Med Biol. 1221:285–307.
2020.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
59
|
Simons M and Raposo G: Exosomes-vesicular
carriers for intercellular communication. Curr Opin Cell Biol.
21:575–581. 2009.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
60
|
Shteingauz A, Boyango I, Naroditsky I,
Hammond E, Gruber M, Doweck I, Ilan N and Vlodavsky I: Heparanase
enhances tumor growth and chemoresistance by promoting autophagy.
Cancer Res. 75:3946–3957. 2015.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
61
|
Schmidt EP, Overdier KH, Sun X, Lin L, Liu
X, Yang Y, Ammons LA, Hiller TD, Suflita MA, Yu Y, et al: Urinary
glycosaminoglycans predict outcomes in septic shock and acute
respiratory distress syndrome. Am J Respir Crit Care Med.
194:439–449. 2016.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
62
|
Masola V, Zaza G, Bellin G, Dall'Olmo L,
Granata S, Vischini G, Secchi MF, Lupo A, Gambaro G and Onisto M:
Heparanase regulates the M1 polarization of renal macrophages and
their crosstalk with renal epithelial tubular cells after
ischemia/reperfusion injury. FASEB J. 32:742–756. 2018.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
63
|
Abassi Z, Hamoud S, Hassan A, Khamaysi I,
Nativ O, Heyman SN, Muhammad RS, Ilan N, Singh P, Hammond E, et al:
Involvement of heparanase in the pathogenesis of acute kidney
injury: Nephroprotective effect of PG545. Oncotarget.
8:34191–34204. 2017.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
64
|
Masola V, Zaza G, Gambaro G, Onisto M,
Bellin G, Vischini G, Khamaysi I, Hassan A, Hamoud S, Nativ O, et
al: Heparanase: A potential new factor involved in the renal
epithelial mesenchymal transition (EMT) induced by
ischemia/reperfusion (I/R) Injury. PLoS One.
11(e0160074)2016.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
65
|
Abu-Tayeh Suleiman H, Said S, Ali Saleh H,
Gamliel-Lazarovich A, Haddad E, Minkov I, Zohar Y, Ilan N,
Vlodavsky I, Abassi Z and Assady S: Heparanase increases podocyte
survival and autophagic flux after adriamycin-induced injury. Int J
Mol Sci. 23(12691)2022.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
66
|
Ilan N, Elkin M and Vlodavsky I:
Regulation, function and clinical significance of heparanase in
cancer metastasis and angiogenesis. Int J Biochem Cell Biol.
38:2018–2039. 2006.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
67
|
Parish CR, Freeman C and Hulett MD:
Heparanase: A key enzyme involved in cell invasion. Biochim Biophys
Acta. 1471:M99–M108. 2001.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
68
|
Secchi MF, Masola V, Zaza G, Lupo A,
Gambaro G and Onisto M: Recent data concerning heparanase: Focus on
fibrosis, inflammation and cancer. Biomol Concepts. 6:415–421.
2015.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
69
|
Vlodavsky I, Beckhove P, Lerner I, Pisano
C, Meirovitz A, Ilan N and Elkin M: Significance of heparanase in
cancer and inflammation. Cancer Microenviron. 5:115–132.
2012.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
70
|
Vreys V and David G: Mammalian heparanase:
What is the message? J Cell Mol Med. 11:427–452. 2007.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
71
|
Sanderson RD, Bandari SK and Vlodavsky I:
Proteases and glycosidases on the surface of exosomes: Newly
discovered mechanisms for extracellular remodeling. Matrix Biol.
75-76:160–169. 2019.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
72
|
Xavier RJ and Podolsky DK: Unravelling the
pathogenesis of inflammatory bowel disease. Nature. 448:427–434.
2007.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
73
|
Belmiro CL, Souza HS, Elia CC,
Castelo-Branco MT, Silva FR, Machado RL and Pavão MS: Biochemical
and immunohistochemical analysis of glycosaminoglycans in inflamed
and non-inflamed intestinal mucosa of patients with Crohn's
disease. Int J Colorectal Dis. 20:295–304. 2005.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
74
|
Abassi Z and Goligorsky MS: Heparanase in
acute kidney injury. Adv Exp Med Biol. 1221:685–702.
2020.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
75
|
Axelsson J, Xu D, Kang BN, Nussbacher JK,
Handel TM, Ley K, Sriramarao P and Esko JD: Inactivation of heparan
sulfate 2-O-sulfotransferase accentuates neutrophil infiltration
during acute inflammation in mice. Blood. 120:1742–1751.
2012.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
76
|
Götte M: Syndecans in inflammation. FASEB
J. 17:575–591. 2003.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
77
|
Carter NM, Ali S and Kirby JA: Endothelial
inflammation: The role of differential expression of
N-deacetylase/N-sulphotransferase enzymes in alteration of the
immunological properties of heparan sulphate. J Cell Sci. 116(Pt
17):3591–3600. 2003.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
78
|
Uchimido R, Schmidt EP and Shapiro NI: The
glycocalyx: A novel diagnostic and therapeutic target in sepsis.
Crit Care. 23(16)2019.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
79
|
Becker BF, Jacob M, Leipert S, Salmon AH
and Chappell D: Degradation of the endothelial glycocalyx in
clinical settings: Searching for the sheddases. Br J Clin
Pharmacol. 80:389–402. 2015.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
80
|
Lupu F, Kinasewitz G and Dormer K: The
role of endothelial shear stress on haemodynamics, inflammation,
coagulation and glycocalyx during sepsis. J Cell Mol Med.
24:12258–12271. 2020.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
81
|
Ponticelli C: Ischaemia-reperfusion
injury: A major protagonist in kidney transplantation. Nephrol Dial
Transplant. 29:1134–1140. 2014.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
82
|
Bayam E, Kalçık M, Gürbüz AS, Yesin M,
Güner A, Gündüz S, Gürsoy MO, Karakoyun S, Cerşit S, Kılıçgedik A,
et al: The relationship between heparanase levels, thrombus burden
and thromboembolism in patients receiving unfractionated heparin
treatment for prosthetic valve thrombosis. Thromb Res. 171:103–110.
2018.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
83
|
Masola V, Gambaro G, Tibaldi E, Brunati
AM, Gastaldello A, D'Angelo A, Onisto M and Lupo A: Heparanase and
syndecan-1 interplay orchestrates fibroblast growth
factor-2-induced epithelial-mesenchymal transition in renal tubular
cells. J Biol Chem. 287:1478–1488. 2012.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
84
|
Jiang P and Mizushima N: Autophagy and
human diseases. Cell Res. 24:69–79. 2014.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
85
|
He C and Klionsky DJ: Regulation
mechanisms and signaling pathways of autophagy. Annu Rev Genet.
43:67–93. 2009.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
86
|
Singh R and Cuervo AM: Autophagy in the
cellular energetic balance. Cell Metab. 13:495–504. 2011.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
87
|
Melk A, Baisantry A and Schmitt R: The yin
and yang of autophagy in acute kidney injury. Autophagy.
12:596–597. 2016.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
88
|
Kim WY, Nam SA, Song HC, Ko JS, Park SH,
Kim HL, Choi EJ, Kim YS, Kim J and Kim YK: The role of autophagy in
unilateral ureteral obstruction rat model. Nephrology (Carlton).
17:148–159. 2012.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
89
|
Zhang M, Sui W, Xing Y, Cheng J, Cheng C,
Xue F, Zhang J, Wang X, Zhang C, Hao P and Zhang Y: Angiotensin IV
attenuates diabetic cardiomyopathy via suppressing FoxO1-induced
excessive autophagy, apoptosis and fibrosis. Theranostics.
11:8624–8639. 2021.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
90
|
Jin H and Zhou S: The functions of
heparanase in human diseases. Mini Rev Med Chem. 17:541–548.
2017.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
91
|
White E: Deconvoluting the
context-dependent role for autophagy in cancer. Nat Rev Cancer.
12:401–410. 2012.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
92
|
Saiki S, Sasazawa Y, Imamichi Y, Kawajiri
S, Fujimaki T, Tanida I, Kobayashi H, Sato F, Sato S, Ishikawa K,
et al: Caffeine induces apoptosis by enhancement of autophagy via
PI3K/Akt/mTOR/p70S6K inhibition. Autophagy. 7:176–187.
2011.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
93
|
Ferro V, Dredge K, Liu L, Hammond E,
Bytheway I, Li C, Johnstone K, Karoli T, Davis K, Copeman E and
Gautam A: PI-88 and novel heparan sulfate mimetics inhibit
angiogenesis. Semin Thromb Hemost. 33:557–568. 2007.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
94
|
Rabelink TJ, van den Berg BM, Garsen M,
Wang G, Elkin M and van der Vlag J: Heparanase: Roles in cell
survival, extracellular matrix remodelling and the development of
kidney disease. Nat Rev Nephrol. 13:201–212. 2017.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
95
|
Suchorska WM and Lach MS: The role of
exosomes in tumor progression and metastasis (Review). Oncol Rep.
35:1237–1244. 2016.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
96
|
Oosthuyzen W, Sime NE, Ivy JR, Turtle EJ,
Street JM, Pound J, Bath LE, Webb DJ, Gregory CD, Bailey MA and
Dear JW: Quantification of human urinary exosomes by nanoparticle
tracking analysis. J Physiol. 591:5833–5842. 2013.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
97
|
Petrik J and Seghatchian J: Big things
from small packages: The multifaceted roles of extracellular
vesicles in the components quality, therapy and infection. Transfus
Apher Sci. 55:4–8. 2016.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
98
|
Conlan RS, Pisano S, Oliveira MI, Ferrari
M and Mendes Pinto I: Exosomes as reconfigurable therapeutic
systems. Trends Mol Med. 23:636–650. 2017.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
99
|
Essandoh K, Yang L, Wang X, Huang W, Qin
D, Hao J, Wang Y, Zingarelli B, Peng T and Fan GC: Blockade of
exosome generation with GW4869 dampens the sepsis-induced
inflammation and cardiac dysfunction. Biochim Biophys Acta.
1852:2362–2371. 2015.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
100
|
Kanki M, Moriguchi A, Sasaki D, Mitori H,
Yamada A, Unami A and Miyamae Y: Identification of urinary miRNA
biomarkers for detecting cisplatin-induced proximal tubular injury
in rats. Toxicology. 324:158–168. 2014.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
101
|
Viñas JL, Spence M, Porter CJ, Douvris A,
Gutsol A, Zimpelmann JA, Campbell PA and Burns KD: micro-RNA-486-5p
protects against kidney ischemic injury and modifies the apoptotic
transcriptome in proximal tubules. Kidney Int. 100:597–612.
2021.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
102
|
Sun J, Sun X, Chen J, Liao X, He Y, Wang
J, Chen R, Hu S and Qiu C: microRNA-27b shuttled by mesenchymal
stem cell-derived exosomes prevents sepsis by targeting JMJD3 and
downregulating NF-κB signaling pathway. Stem Cell Res Ther.
12(14)2021.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
103
|
Zhang R, Zhu Y, Li Y, Liu W, Yin L, Yin S,
Ji C, Hu Y, Wang Q, Zhou X, et al: Human umbilical cord mesenchymal
stem cell exosomes alleviate sepsis-associated acute kidney injury
via regulating microRNA-146b expression. Biotechnol Lett.
42:669–679. 2020.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
104
|
Juan CX, Mao Y, Cao Q, Chen Y, Zhou LB, Li
S, Chen H, Chen JH, Zhou GP and Jin R: Exosome-mediated pyroptosis
of miR-93-TXNIP-NLRP3 leads to functional difference between M1 and
M2 macrophages in sepsis-induced acute kidney injury. J Cell Mol
Med. 25:4786–4799. 2021.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
105
|
Lv LL, Feng Y, Wu M, Wang B, Li ZL, Zhong
X, Wu WJ, Chen J, Ni HF, Tang TT, et al: Exosomal miRNA-19b-3p of
tubular epithelial cells promotes M1 macrophage activation in
kidney injury. Cell Death Differ. 27:210–226. 2020.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
106
|
Thompson CA, Purushothaman A, Ramani VC,
Vlodavsky I and Sanderson RD: Heparanase regulates secretion,
composition, and function of tumor cell-derived exosomes. J Biol
Chem. 288:10093–10099. 2013.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
107
|
Roucourt B, Meeussen S, Bao J, Zimmermann
P and David G: Heparanase activates the syndecan-syntenin-ALIX
exosome pathway. Cell Res. 25:412–428. 2015.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
108
|
Bernfield M and Sanderson RD: Syndecan, a
developmentally regulated cell surface proteoglycan that binds
extracellular matrix and growth factors. Philos Trans R Soc Lond B
Biol Sci. 327:171–186. 1990.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
109
|
Baietti MF, Zhang Z, Mortier E, Melchior
A, Degeest G, Geeraerts A, Ivarsson Y, Depoortere F, Coomans C,
Vermeiren E, et al: Syndecan-syntenin-ALIX regulates the biogenesis
of exosomes. Nat Cell Biol. 14:677–685. 2012.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
110
|
Bandari SK, Purushothaman A, Ramani VC,
Brinkley GJ, Chandrashekar DS, Varambally S, Mobley JA, Zhang Y,
Brown EE, Vlodavsky I and Sanderson RD: Chemotherapy induces
secretion of exosomes loaded with heparanase that degrades
extracellular matrix and impacts tumor and host cell behavior.
Matrix Biol. 65:104–118. 2018.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
111
|
Cummings JJ, Shaw AD, Shi J, Lopez MG,
O'Neal JB and Billings FT IV: Intraoperative prediction of cardiac
surgery-associated acute kidney injury using urinary biomarkers of
cell cycle arrest. J Thorac Cardiovasc Surg. 157:1545–1553.e5.
2019.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
112
|
Parikh CR, Thiessen-Philbrook H, Garg AX,
Kadiyala D, Shlipak MG, Koyner JL, Edelstein CL, Devarajan P, Patel
UD, Zappitelli M, et al: Performance of kidney injury molecule-1
and liver fatty acid-binding protein and combined biomarkers of AKI
after cardiac surgery. Clin J Am Soc Nephrol. 8:1079–1088.
2013.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
113
|
Nakamura T, Sugaya T, Node K, Ueda Y and
Koide H: Urinary excretion of liver-type fatty acid-binding protein
in contrast medium-induced nephropathy. Am J Kidney Dis.
47:439–444. 2006.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
114
|
Mori K, Lee HT, Rapoport D, Drexler IR,
Foster K, Yang J, Schmidt-Ott KM, Chen X, Li JY, Weiss S, et al:
Endocytic delivery of lipocalin-siderophore-iron complex rescues
the kidney from ischemia-reperfusion injury. J Clin Invest.
115:610–621. 2005.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
115
|
Chen S, He Y, Hu Z, Lu S, Yin X, Ma X, Lv
C and Jin G: Heparanase mediates intestinal inflammation and injury
in a mouse model of sepsis. J Histochem Cytochem. 65:241–249.
2017.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
116
|
Kiyan Y, Tkachuk S, Kurselis K, Shushakova
N, Stahl K, Dawodu D, Kiyan R, Chichkov B and Haller H:
Heparanase-2 protects from LPS-mediated endothelial injury by
inhibiting TLR4 signalling. Sci Rep. 9(13591)2019.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
117
|
McKenzie E, Tyson K, Stamps A, Smith P,
Turner P, Barry R, Hircock M, Patel S, Barry E, Stubberfield C, et
al: Cloning and expression profiling of Hpa2, a novel mammalian
heparanase family member. Biochem Biophys Res Commun.
276:1170–1177. 2000.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
118
|
Pinhal MAS, Melo CM and Nader HB: The good
and bad sides of heparanase-1 and heparanase-2. Adv Exp Med Biol.
1221:821–845. 2020.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
119
|
Bashkin P, Doctrow S, Klagsbrun M, Svahn
CM, Folkman J and Vlodavsky I: Basic fibroblast growth factor binds
to subendothelial extracellular matrix and is released by
heparitinase and heparin-like molecules. Biochemistry.
28:1737–1743. 1989.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|