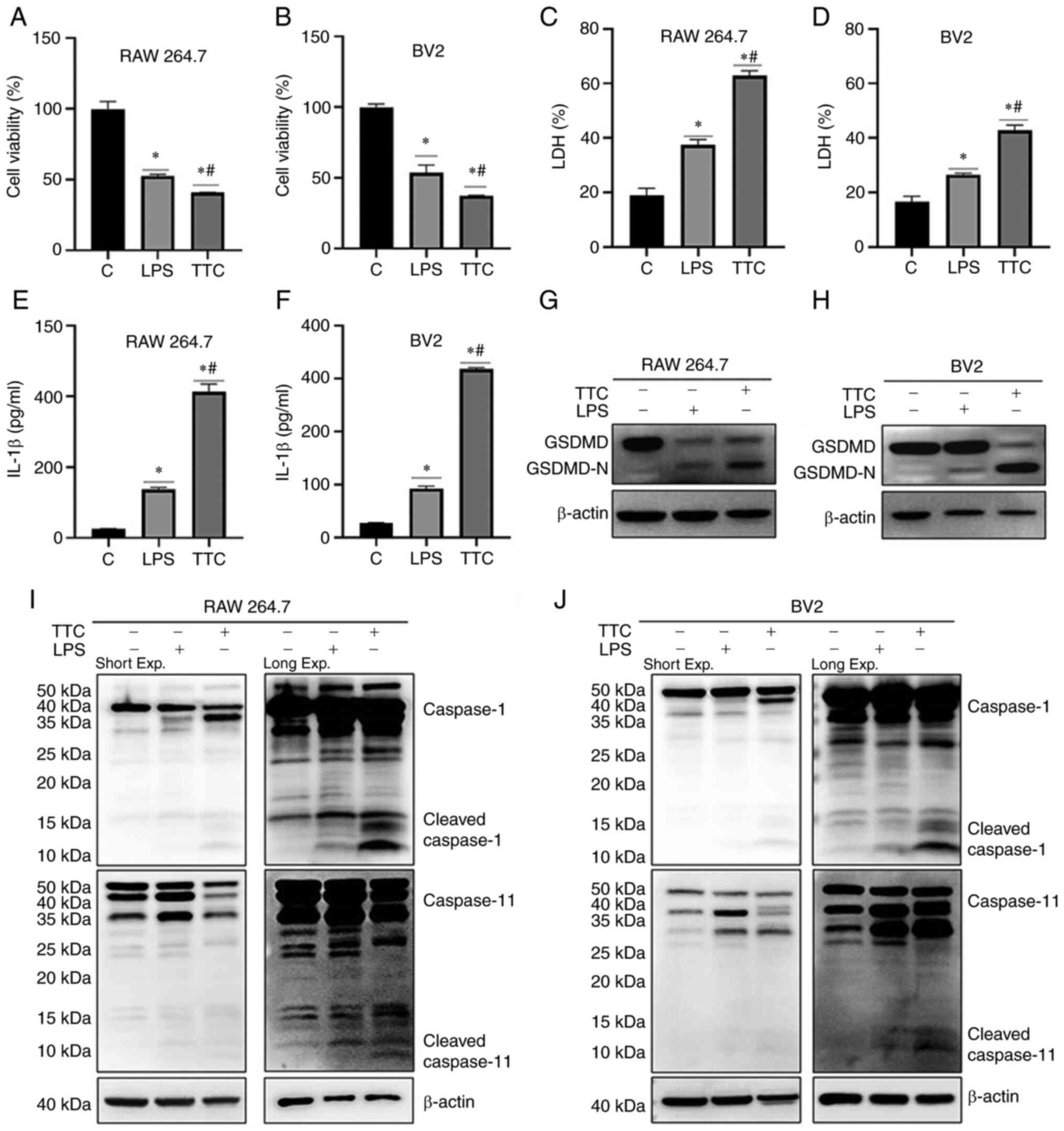
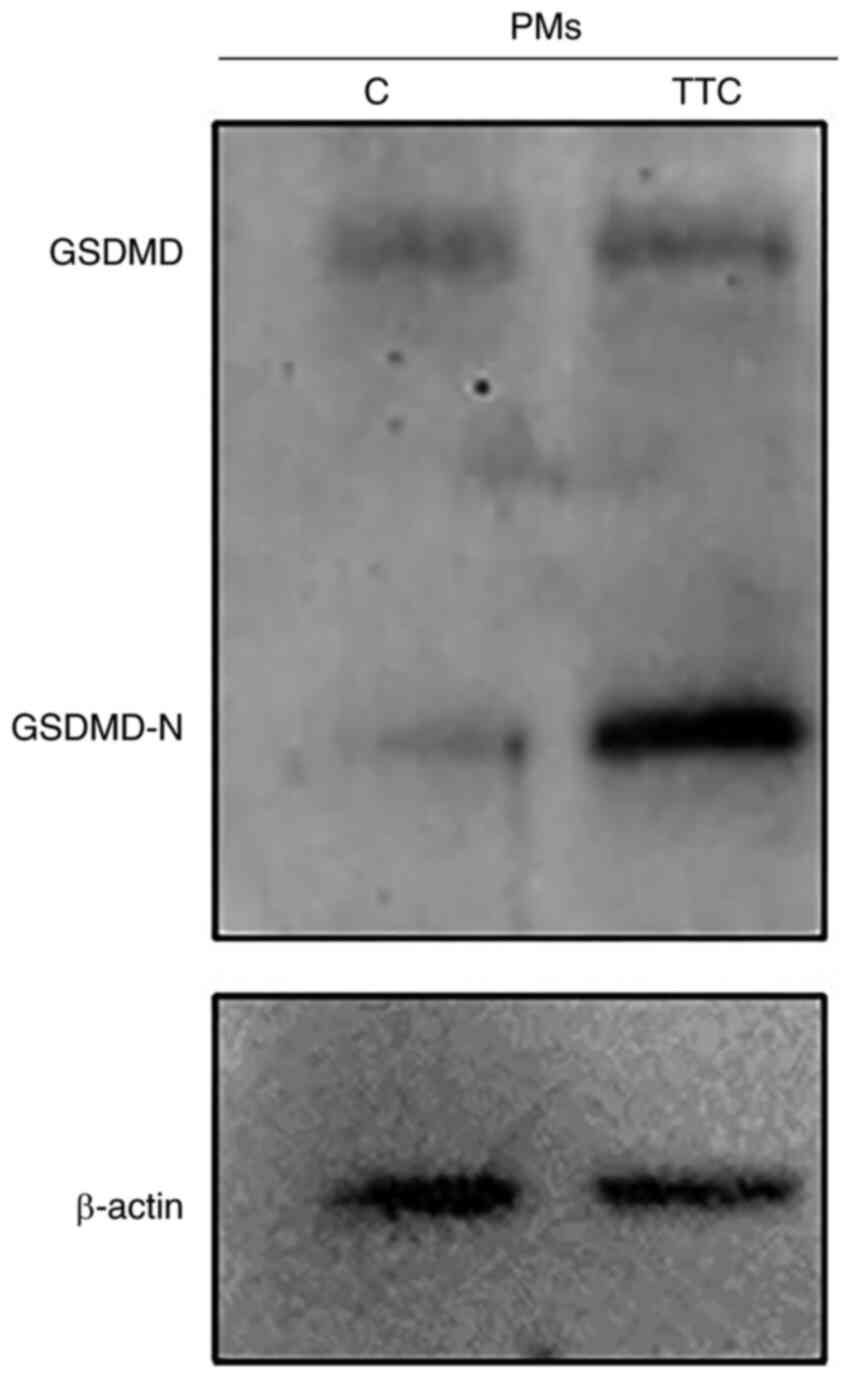
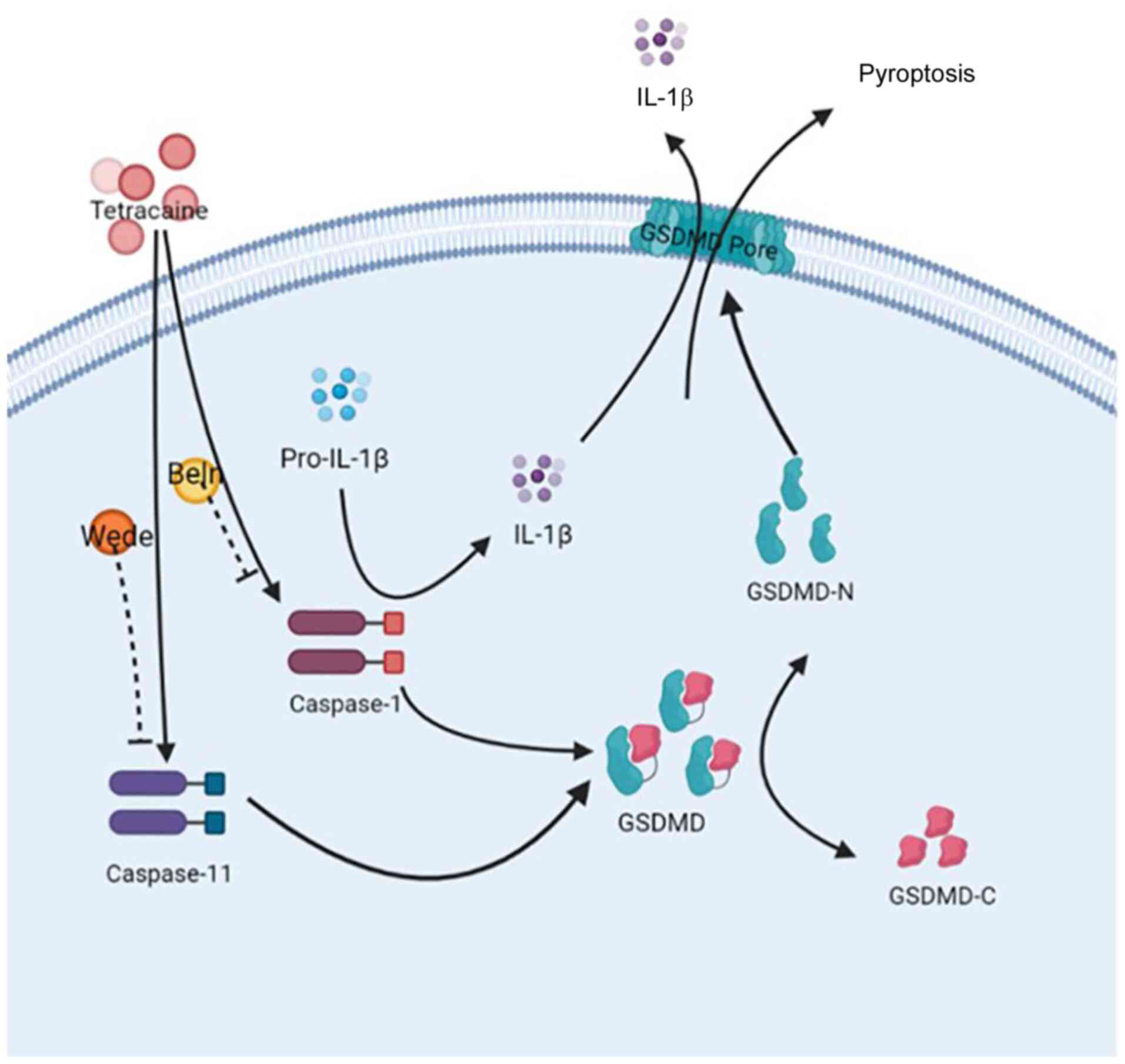
|
1
|
Wadlund DL: Local anesthetic systemic
toxicity. AORN J. 106:367–377. 2017.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
2
|
Macfarlane AJR, Gitman M, Bornstein KJ,
El-Boghdadly K and Weinberg G: Updates in our understanding of
local anaesthetic systemic toxicity: A narrative review.
Anaesthesia. 76 (Suppl 1):S27–S39. 2021.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
3
|
Zhao W, Liu Z, Yu X, Lai L, Li H, Liu Z,
Li L, Jiang S, Xia Z and Xu SY: iTRAQ proteomics analysis reveals
that PI3K is highly associated with bupivacaine-induced
neurotoxicity pathways. Proteomics. 16:564–575. 2016.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
4
|
Yu XJ, Zhao W, Li YJ, Li FX, Liu ZJ, Xu
HL, Lai LY, Xu R and Xu SY: Neurotoxicity comparison of two types
of local anaesthetics: Amide-bupivacaine versus ester-procaine. Sci
Rep. 7(45316)2017.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
5
|
Grant SA and Hoffman RS: Use of
tetracaine, epinephrine, and cocaine as a topical anesthetic in the
emergency department. Ann Emerg Med. 21:987–997. 1992.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
6
|
Werdehausen R, Braun S, Fazeli S, Hermanns
H, Hollmann MW, Bauer I and Stevens MF: Lipophilicity but not
stereospecificity is a major determinant of local
anaesthetic-induced cytotoxicity in human T-lymphoma cells. Eur J
Anaesthesiol. 29:35–41. 2012.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
7
|
Song Z and Fan TJ: Tetracaine induces
apoptosis through a mitochondrion-dependent pathway in human
corneal stromal cells in vitro. Cutan Ocul Toxicol. 37:350–358.
2018.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
8
|
Pang X and Fan TJ: Cytotoxic effect and
possible mechanisms of Tetracaine on human corneal epithelial cells
in vitro. Int J Ophthalmol. 9:497–504. 2016.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
9
|
Koizumi Y, Matsumoto M, Yamashita A,
Tsuruta S, Ohtake T and Sakabe T: The effects of an AMPA receptor
antagonist on the neurotoxicity of tetracaine intrathecally
administered in rabbits. Anesth Analg. 102:930–936. 2006.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
10
|
Barreda DR, Neely HR and Flajnik MF:
Evolution of myeloid cells. Microbiol Spectr. 4:2016.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
11
|
Mahajan A and Derian A: Local anesthetic
toxicity. In: StatPearls StatPearls Publishing Copyright ©. 2023,
StatPearls Publishing LLC., Treasure Island (FL) ineligible
companies. Disclosure: Armen Derian declares no relevant financial
relationships with ineligible companies, 2023.
|
|
12
|
Groban L: Central nervous system and
cardiac effects from long-acting amide local anesthetic toxicity in
the intact animal model. Reg Anesth Pain Med. 28:3–11.
2003.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
13
|
Henn A, Lund S, Hedtjärn M, Schrattenholz
A, Pörzgen P and Leist M: The suitability of BV2 cells as
alternative model system for primary microglia cultures or for
animal experiments examining brain inflammation. ALTEX. 26:83–94.
2009.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
14
|
Gao W, Li Y, Liu X, Wang S, Mei P, Chen Z,
Liu K, Li S, Xu XW, Gan J, et al: TRIM21 regulates pyroptotic cell
death by promoting Gasdermin D oligomerization. Cell Death Differ.
29:439–450. 2022.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
15
|
Orning P, Lien E and Fitzgerald KA:
Gasdermins and their role in immunity and inflammation. J Exp Med.
216:2453–2465. 2019.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
16
|
Broz P, Pelegrín P and Shao F: The
gasdermins, a protein family executing cell death and inflammation.
Nat Rev Immunol. 20:143–157. 2020.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
17
|
Ding J, Wang K, Liu W, She Y, Sun Q, Shi
J, Sun H, Wang DC and Shao F: Pore-forming activity and structural
autoinhibition of the gasdermin family. Nature. 535:111–116.
2016.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
18
|
Fang Y, Tian S, Pan Y, Li W, Wang Q, Tang
Y, Yu T, Wu X, Shi Y, Ma P and Shu Y: Pyroptosis: A new frontier in
cancer. Biomed Pharmacother. 121(109595)2020.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
19
|
Evavold CL, Ruan J, Tan Y, Xia S, Wu H and
Kagan JC: The pore-forming protein gasdermin D regulates
interleukin-1 secretion from living macrophages. Immunity.
48:35–44.e6. 2018.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
20
|
Jorgensen I, Rayamajhi M and Miao EA:
Programmed cell death as a defence against infection. Nat Rev
Immunol. 17:151–164. 2017.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
21
|
Zhang L, Xing R, Huang Z, Zhang N, Zhang
L, Li X and Wang P: Inhibition of synovial macrophage pyroptosis
alleviates synovitis and fibrosis in knee osteoarthritis. Mediators
Inflamm. 2019(2165918)2019.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
22
|
Fisch D, Bando H, Clough B, Hornung V,
Yamamoto M, Shenoy AR and Frickel EM: Human GBP1 is a
microbe-specific gatekeeper of macrophage apoptosis and pyroptosis.
EMBO J. 38(e100926)2019.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
23
|
Frangogiannis NG: Regulation of the
inflammatory response in cardiac repair. Circ Res. 110:159–173.
2012.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
24
|
Zhang Y, Chen X, Gueydan C and Han J:
Plasma membrane changes during programmed cell deaths. Cell Res.
28:9–21. 2018.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
25
|
Scully AC and Boynton JR: Antibiotics and
local anesthetics: Drug considerations for the child patient. J
Mich Dent Assoc. 99:36–41, 71. 2017.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
26
|
Kose AA, Karabaggli Y, Kiremitci A, Kocman
E and Cetin C: Do local anesthetics have antibacterial effect on
Staphylococcus aureus under in vivo conditions? An experimental
study. Dermatol Surg. 36:848–852. 2010.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
27
|
Liu Z, Wang M, Wang X, Bu Q, Wang Q, Su W,
Li L, Zhou H and Lu L: XBP1 deficiency promotes hepatocyte
pyroptosis by impairing mitophagy to activate mtDNA-cGAS-STING
signaling in macrophages during acute liver injury. Redox Biol.
52(102305)2022.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
28
|
Wang Y, Gao W, Shi X, Ding J, Liu W, He H,
Wang K and Shao F: Chemotherapy drugs induce pyroptosis through
caspase-3 cleavage of a gasdermin. Nature. 547:99–103.
2017.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
29
|
Bertheloot D, Latz E and Franklin BS:
Necroptosis, pyroptosis and apoptosis: An intricate game of cell
death. Cell Mol Immunol. 18:1106–1121. 2021.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
30
|
Jiang X, Stockwell BR and Conrad M:
Ferroptosis: Mechanisms, biology and role in disease. Nat Rev Mol
Cell Biol. 22:266–282. 2021.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
31
|
Moujalled D, Strasser A and Liddell JR:
Molecular mechanisms of cell death in neurological diseases. Cell
Death Differ. 28:2029–2044. 2021.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
32
|
Ding XD, Cao YY, Li L and Zhao GY:
Dexmedetomidine reduces the lidocaine-induced neurotoxicity by
inhibiting inflammasome activation and reducing pyroptosis in rats.
Biol Pharm Bull. 44:902–909. 2021.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
33
|
Shi M, Chen J, Liu T, Dai W, Zhou Z, Chen
L and Xie Y: Protective effects of remimazolam on cerebral
ischemia/reperfusion injury in rats by inhibiting of NLRP3
inflammasome-dependent pyroptosis. Drug Des Devel Ther. 16:413–423.
2022.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
34
|
Ye Z, Li Q, Guo Q, Xiong Y, Guo D, Yang H
and Shu Y: Ketamine induces hippocampal apoptosis through a
mechanism associated with the caspase-1 dependent pyroptosis.
Neuropharmacology. 128:63–75. 2018.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
35
|
Li Y, Wu ZY, Zheng WC, Wang JX, Yue-Xin
Song RX and Gao JG: Esketamine alleviates postoperative cognitive
decline via stimulator of interferon genes/TANK-binding kinase 1
signaling pathway in aged rats. Brain Res Bull. 187:169–180.
2022.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
36
|
Sun L, Ma W, Gao W, Xing Y, Chen L, Xia Z,
Zhang Z and Dai Z: Propofol directly induces caspase-1-dependent
macrophage pyroptosis through the NLRP3-ASC inflammasome. Cell
Death Dis. 10(542)2019.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
37
|
Liu Z, Meng Y, Miao Y, Yu L and Yu Q:
Propofol reduces renal ischemia/reperfusion-induced acute lung
injury by stimulating sirtuin 1 and inhibiting pyroptosis. Aging
(Albany NY). 13:865–876. 2020.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
38
|
Dai J, Li X, Wang C, Gu S, Dai L, Zhang J,
Fan Y and Wu J: Repeated neonatal sevoflurane induced
neurocognitive impairment through NF-κB-mediated pyroptosis. J
Neuroinflammation. 18(180)2021.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
39
|
Deng L, Jiang L, Wei N, Zhang J and Wu X:
Anesthetic sevoflurane simultaneously regulates autophagic flux and
pyroptotic cell death-associated cellular inflammation in the
hypoxic/re-oxygenated cardiomyocytes: Identification of sevoflurane
as putative drug for the treatment of myocardial
ischemia-reperfusion injury. Eur J Pharmacol.
936(175363)2022.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
40
|
Chen C, Zuo J and Zhang H: Sevoflurane
post-treatment mitigates oxygen-glucose deprivationinduced
pyroptosis of hippocampal neurons by regulating the Mafb/DUSP14
axis. Curr Neurovasc Res. 19:245–254. 2022.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
41
|
Zheng F, Wu X, Zhang J and Fu Z:
Sevoflurane suppresses NLRP3 inflammasome-mediated pyroptotic cell
death to attenuate lipopolysaccharide-induced acute lung injury
through inducing GSK-3β phosphorylation and activation. Int
Immunopharmacol. 109(108800)2022.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
42
|
Litz RJ, Bleyl JU, Frank M and Albrecht
DM: Combined anesthesia procedures. Anaesthesist. 48:359–372.
1999.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar : (In German).
|
|
43
|
Kayagaki N, Stowe IB, Lee BL, O'Rourke K,
Anderson K, Warming S, Cuellar T, Haley B, Roose-Girma M, Phung QT,
et al: Caspase-11 cleaves gasdermin D for non-canonical
inflammasome signalling. Nature. 526:666–671. 2015.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
44
|
Shi J, Zhao Y, Wang K, Shi X, Wang Y,
Huang H, Zhuang Y, Cai T, Wang F and Shao F: Cleavage of GSDMD by
inflammatory caspases determines pyroptotic cell death. Nature.
526:660–665. 2015.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
45
|
Lamkanfi M and Dixit VM: Mechanisms and
functions of inflammasomes. Cell. 157:1013–1022. 2014.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
46
|
Shi J, Zhao Y, Wang Y, Gao W, Ding J, Li
P, Hu L and Shao F: Inflammatory caspases are innate immune
receptors for intracellular LPS. Nature. 514:187–192.
2014.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
47
|
Hagar JA, Powell DA, Aachoui Y, Ernst RK
and Miao EA: Cytoplasmic LPS activates caspase-11: Implications in
TLR4-independent endotoxic shock. Science. 341:1250–1253.
2013.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
48
|
Dickerson DM and Apfelbaum JL: Local
anesthetic systemic toxicity. Aesthet Surg J. 34:1111–1119.
2014.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
49
|
Hu JJ, Liu X, Xia S, Zhang Z, Zhang Y,
Zhao J, Ruan J, Luo X, Lou X, Bai Y, et al: FDA-approved disulfiram
inhibits pyroptosis by blocking gasdermin D pore formation. Nat
Immunol. 21:736–745. 2020.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
50
|
Humphries F, Shmuel-Galia L,
Ketelut-Carneiro N, Li S, Wang B, Nemmara VV, Wilson R, Jiang Z,
Khalighinejad F, Muneeruddin K, et al: Succination inactivates
gasdermin D and blocks pyroptosis. Science. 369:1633–1637.
2020.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
51
|
Ma X, Hao J, Wu J, Li Y, Cai X and Zheng
Y: Prussian blue nanozyme as a pyroptosis inhibitor alleviates
neurodegeneration. Adv Mater. 34(e2106723)2022.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|