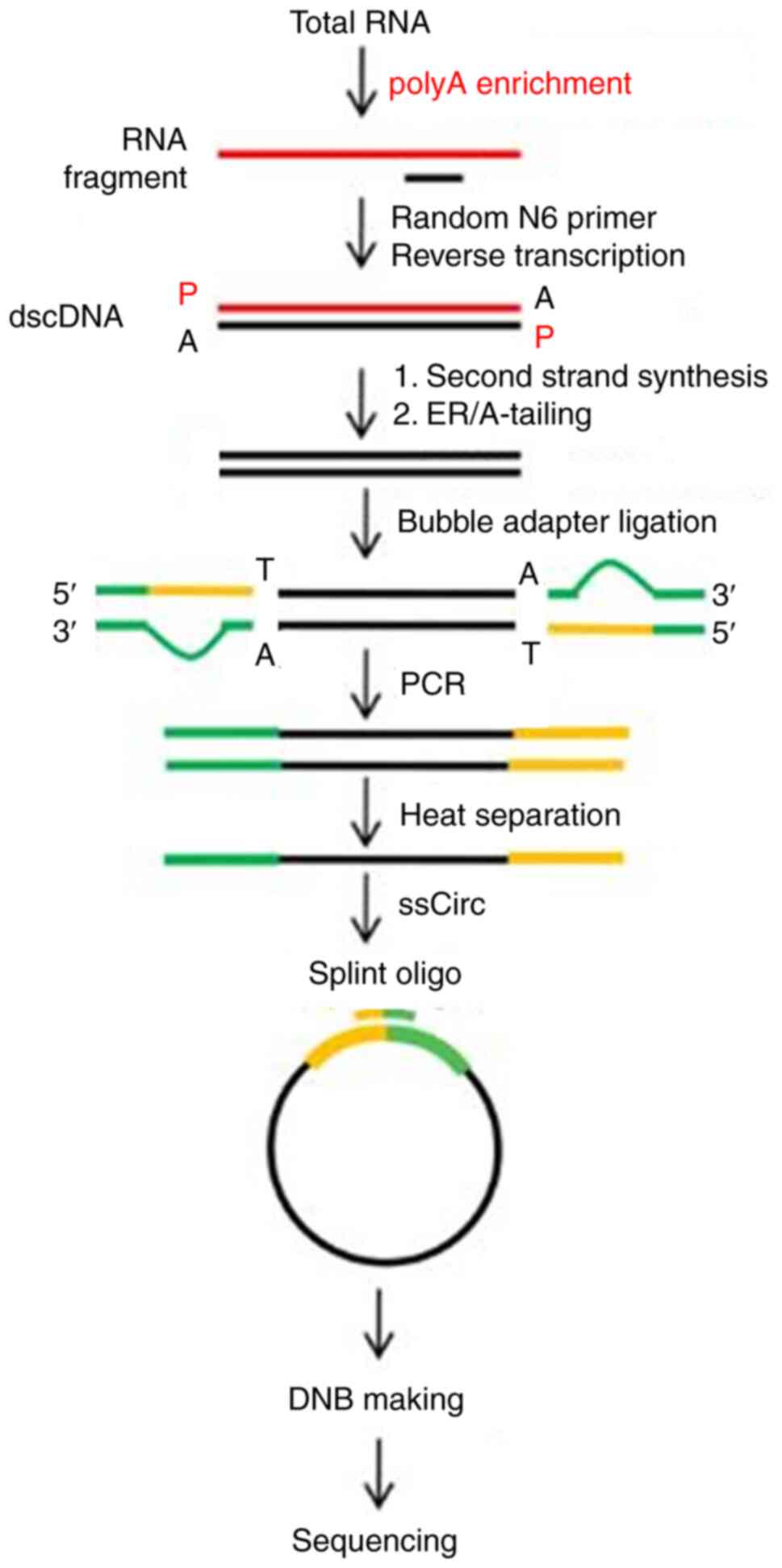
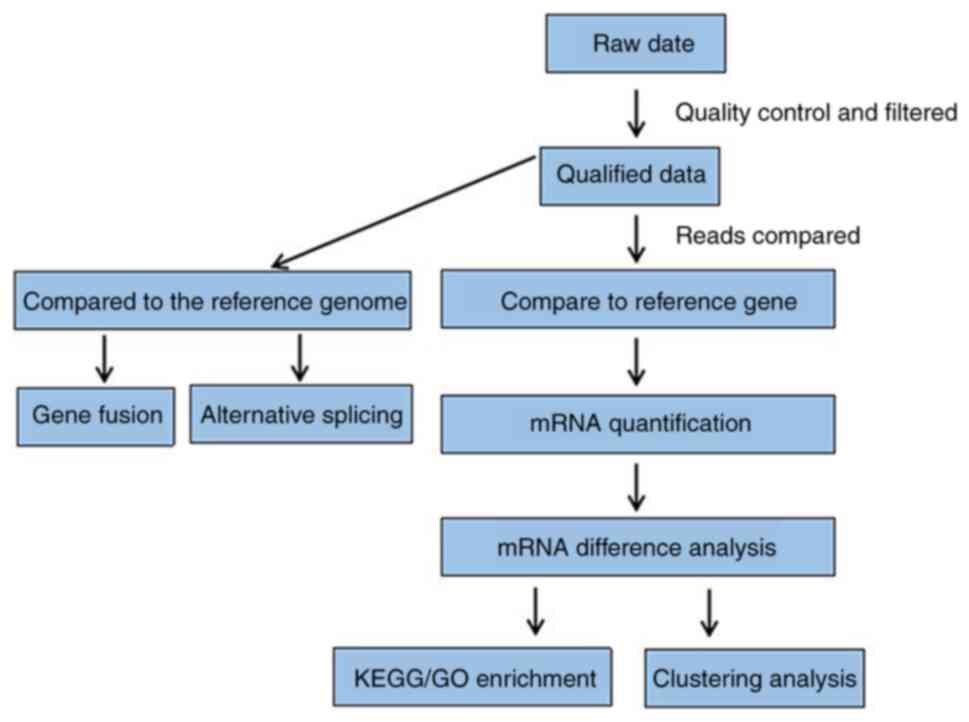
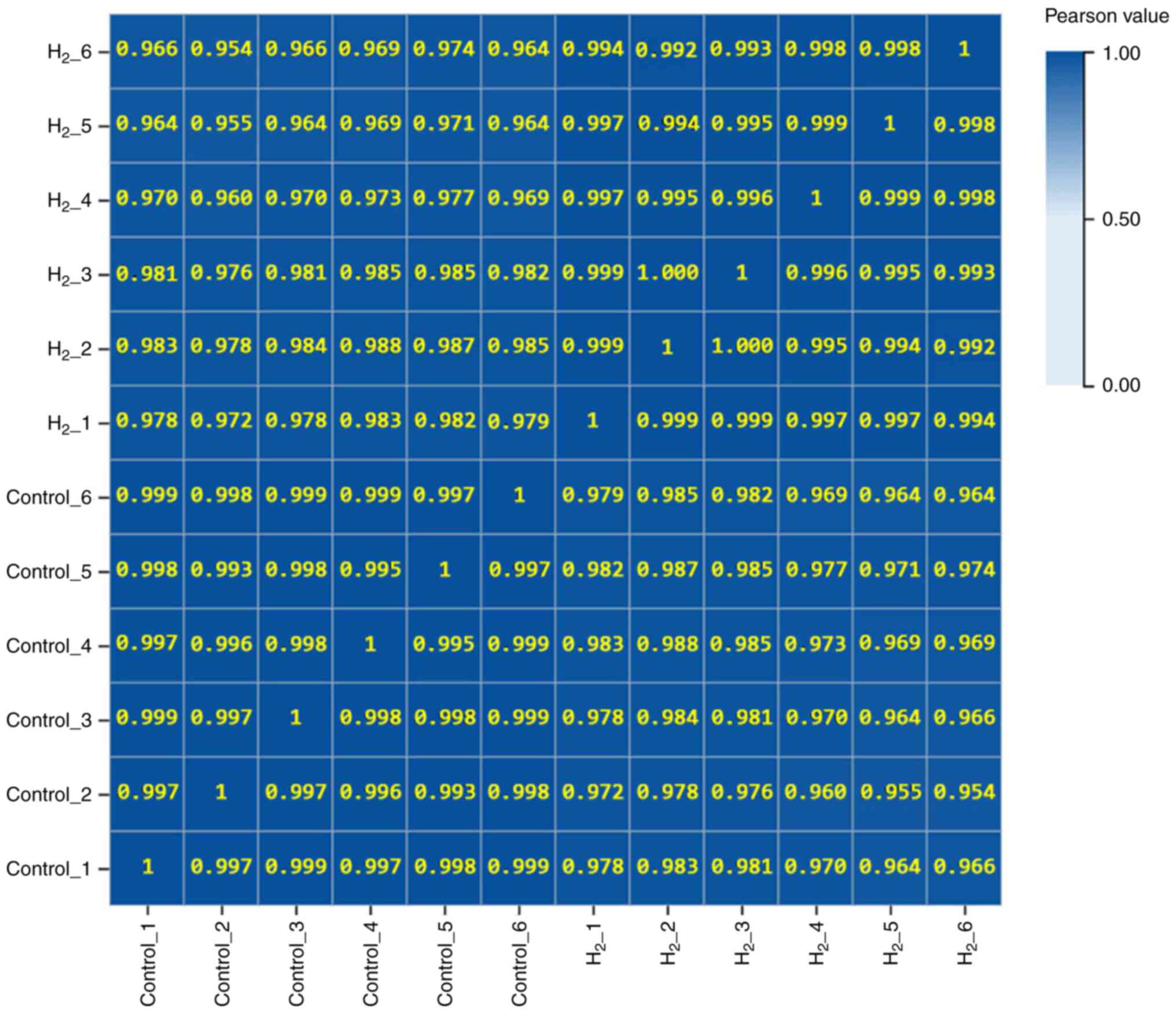
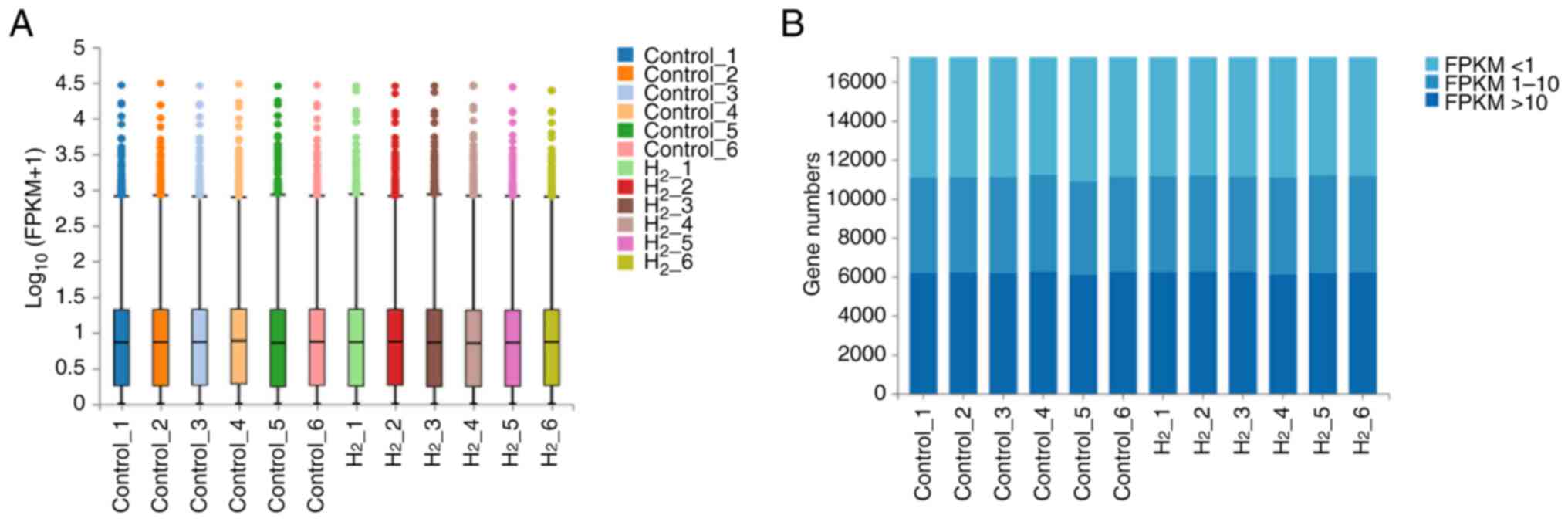
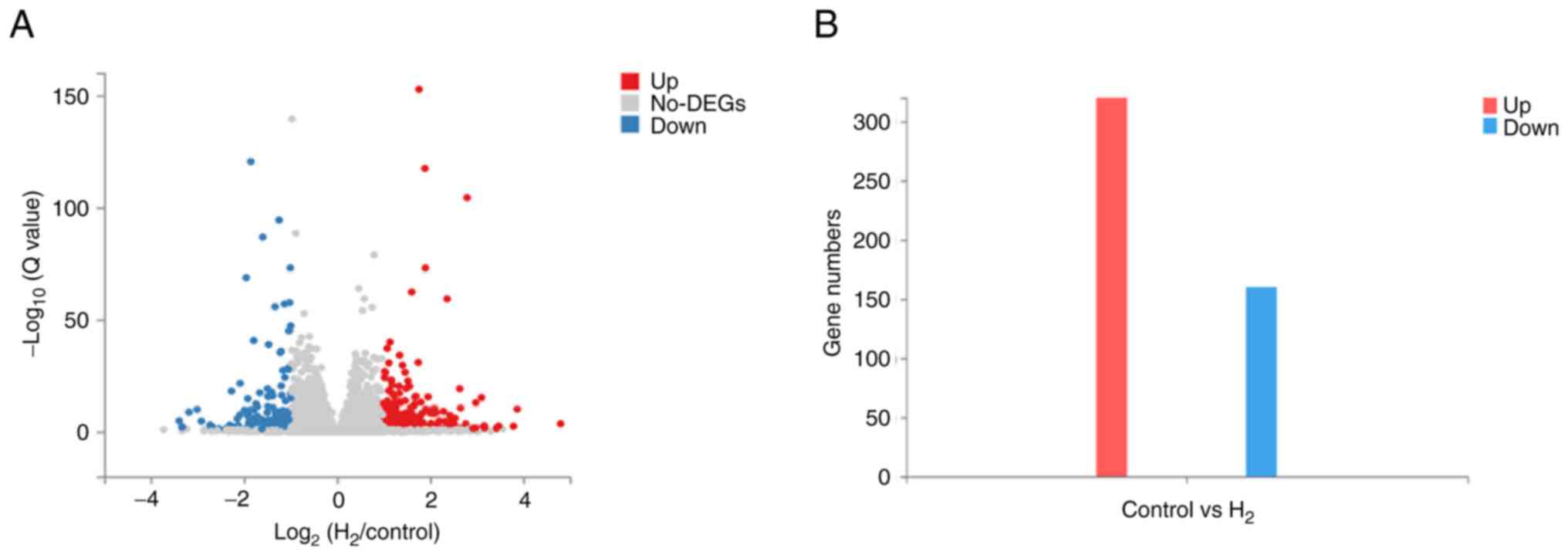
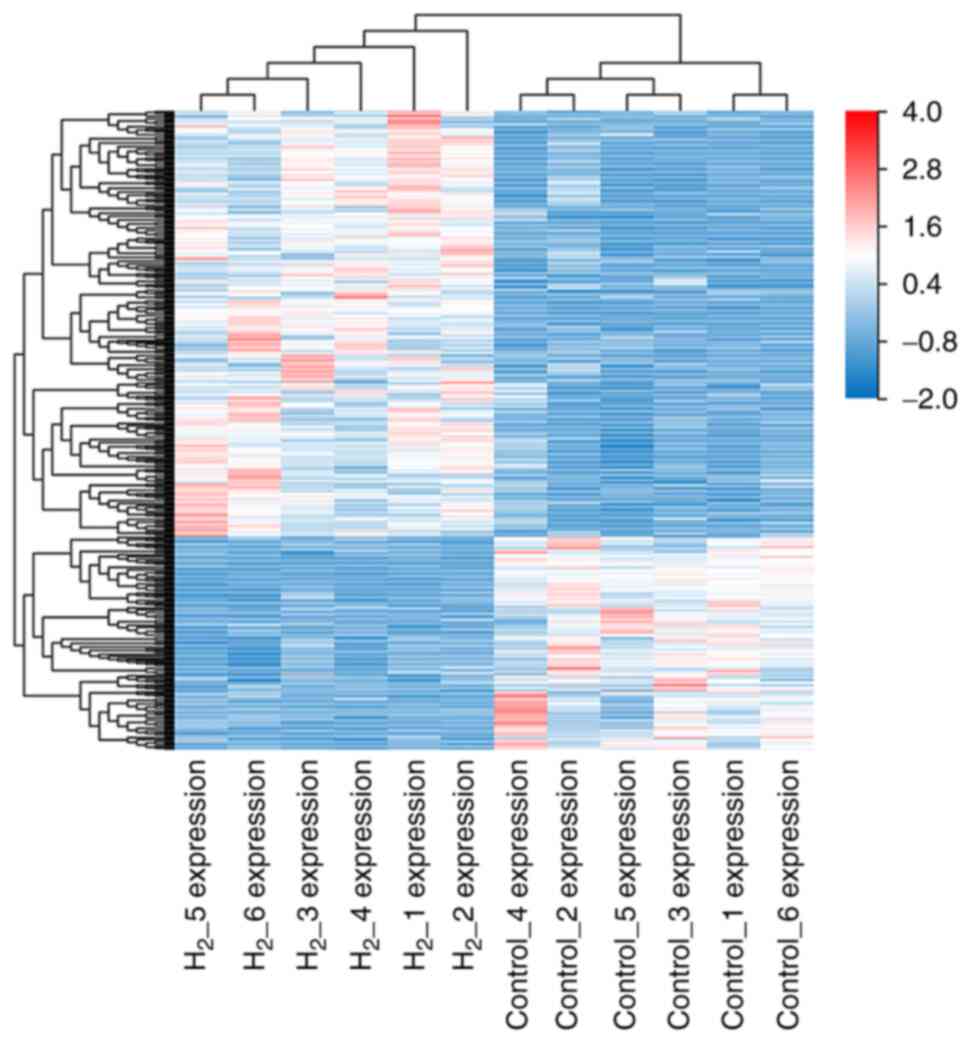
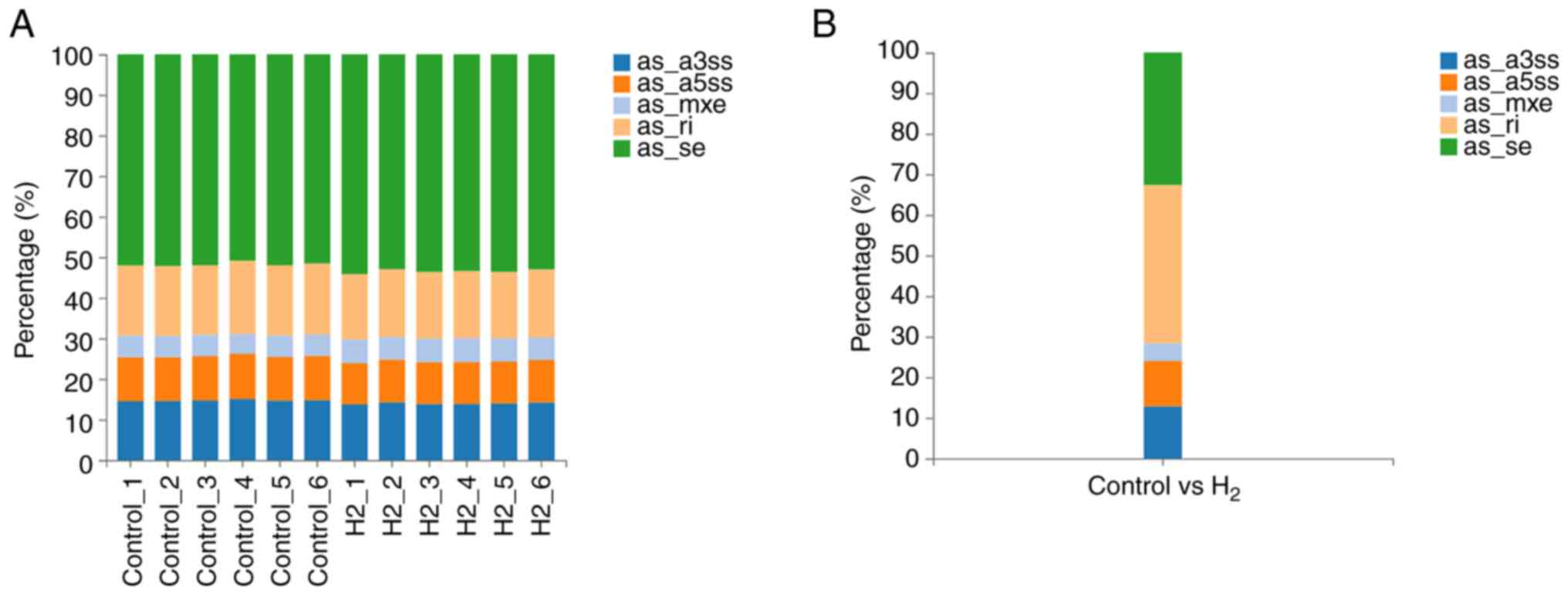
|
1
|
Agarwal S, Curtin J, Duffy B and Jaiswal
S: Biodegradable magnesium alloys for orthopaedic applications: A
review on corrosion, biocompatibility and surface modifications.
Mater Sci Eng C Mater Biol Appl. 68:948–963. 2016.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
2
|
Maradze D, Musson D, Zheng Y, Cornish J,
Lewis M and Liu Y: High magnesium corrosion rate has an effect on
osteoclast and mesenchymal stem cell role during bone remodelling.
Sci Rep. 8(10003)2018.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
3
|
Zhang Y, Xu J, Ruan YC, Yu MK, O'Laughlin
M, Wise H, Chen D, Tian L, Shi D, Wang J, et al: Implant-derived
magnesium induces local neuronal production of CGRP to improve
bone-fracture healing in rats. Nat Med. 22:1160–1169.
2016.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
4
|
Zhai Z, Qu X, Li H, Yang K, Wan P, Tan L,
Ouyang Z, Liu X, Tian B, Xiao F, et al: The effect of metallic
magnesium degradation products on osteoclast-induced osteolysis and
attenuation of NF-κB and NFATc1 signaling. Biomaterials.
35:6299–6310. 2014.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
5
|
Luo Y, Wang J, Ong MTY, Yung PS, Wang J
and Qin L: Update on the research and development of
magnesium-based biodegradable implants and their clinical
translation in orthopaedics. Biomater Transl. 2:188–196.
2021.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
6
|
Lin Y, Ohkawara B, Ito M, Misawa N,
Miyamoto K, Takegami Y, Masuda A, Toyokuni S and Ohno K: Molecular
hydrogen suppresses activated Wnt/β-catenin signaling. Sci Rep.
6(31986)2016.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
7
|
Guo JD, Li L, Shi YM, Wang HD and Hou SX:
Hydrogen water consumption prevents osteopenia in ovariectomized
rats. Br J Pharmacol. 168:1412–1420. 2013.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
8
|
Sun Y, Shuang F, Chen DM and Zhou RB:
Treatment of hydrogen molecule abates oxidative stress and
alleviates bone loss induced by modeled microgravity in rats.
Osteoporos Int. 24:969–978. 2013.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
9
|
Yoneda T, Tomofuji T, Kunitomo M, Ekuni D,
Irie K, Azuma T, Machida T, Miyai H, Fujimori K and Morita M:
Preventive effects of drinking hydrogen-rich water on gingival
oxidative stress and alveolar bone resorption in rats fed a
high-fat diet. Nutrients. 9(64)2017.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
10
|
Callaway DA and Jiang JX: Reactive oxygen
species and oxidative stress in osteoclastogenesis, skeletal aging
and bone diseases. J Bone Miner Metab. 33:359–370. 2015.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
11
|
Li DZ, Zhang QX, Dong XX, Li HD and Ma X:
Treatment with hydrogen molecules prevents RANKL-induced osteoclast
differentiation associated with inhibition of ROS formation and
inactivation of MAPK, AKT and NF-κB pathways in murine RAW264.7
cells. J Bone Miner Metab. 32:494–504. 2014.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
12
|
Boyde A, Ali NN and Jones SJ: Resorption
of dentine by isolated osteoclasts in vitro. Br Dent J.
156:216–220. 1984.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
13
|
Chambers TJ, Revell PA, Fuller K and
Athanasou NA: Resorption of bone by isolated rabbit osteoclasts. J
Cell Sci. 66:383–399. 1984.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
14
|
Destaing O, Saltel F, Géminard JC, Jurdic
P and Bard F: Podosomes display actin turnover and dynamic
self-organization in osteoclasts expressing actin-green fluorescent
protein. Mol Biol Cell. 14:407–416. 2003.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
15
|
Parfitt AM: Targeted and nontargeted bone
remodeling: Relationship to basic multicellular unit origination
and progression. Bone. 30:5–7. 2002.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
16
|
Manolagas SC: Birth and death of bone
cells: Basic regulatory mechanisms and implications for the
pathogenesis and treatment of osteoporosis. Endocr Rev. 21:115–137.
2000.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
17
|
Toor SM, Wani S and Albagha OME:
Comprehensive transcriptomic profiling of murine osteoclast
differentiation reveals novel differentially expressed genes and
LncRNAs. Front Genet. 12(781272)2021.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
18
|
Liu Y, Wang DL, Huang YC, Wang TB and Zeng
H: Hydrogen inhibits the osteoclastogenesis of mouse bone marrow
mononuclear cells. Mater Sci Eng C Mater Biol Appl.
110(110640)2020.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
19
|
Chen X, Cui J, Zhai X, Zhang J, Gu Z, Zhi
X, Weng W, Pan P, Cao L, Ji F, et al: Inhalation of hydrogen of
different concentrations ameliorates spinal cord injury in mice by
protecting spinal cord neurons from apoptosis, oxidative injury and
mitochondrial structure damages. Cell Physiol Biochem. 47:176–190.
2018.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
20
|
Zhang Y, Guan H, Li J, Fang Z, Chen W and
Li F: Amlexanox suppresses osteoclastogenesis and prevents
Ovariectomy-Induced bone loss. Sci Rep. 5(13575)2015.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
21
|
Chen X, Zhi X, Cao L, Weng W, Pan P, Hu H,
Liu C, Zhao Q, Zhou Q, Cui J and Su J: Matrine derivate MASM
uncovers a novel function for ribosomal protein S5 in
osteoclastogenesis and postmenopausal osteoporosis. Cell Death Dis.
8(e3037)2017.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
22
|
Love MI, Huber W and Anders S: Moderated
estimation of fold change and dispersion for RNA-seq data with
DESeq2. Genome Biol. 15(550)2014.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
23
|
Langmead B and Salzberg SL: Fast
gapped-read alignment with Bowtie 2. Nat Methods. 9:357–359.
2012.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
24
|
Li B and Dewey CN: RSEM: Accurate
transcript quantification from RNA-Seq data with or without a
reference genome. BMC Bioinformatics. 12(323)2011.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
25
|
Kim D, Langmead B and Salzberg SL: HISAT:
A fast spliced aligner with low memory requirements. Nat Methods.
12:357–360. 2015.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
26
|
Shen S, Park JW, Lu ZX, Lin L, Henry MD,
Wu YN, Zhou Q and Xing Y: rMATS: Robust and flexible detection of
differential alternative splicing from replicate RNA-Seq data. Proc
Natl Acad Sci USA. 111:5593–5601. 2014.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
27
|
Benelli M, Pescucci C, Marseglia G,
Severgnini M, Torricelli F and Magi A: Discovering chimeric
transcripts in paired-end RNA-seq data by using EricScript.
Bioinformatics. 28:3232–3239. 2012.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
28
|
Guo J, Dong W, Jin L, Wang P, Hou Z and
Zhang Y: Hydrogen-rich saline prevents bone loss in diabetic rats
induced by streptozotocin. Int Orthop. 41:2119–2128.
2017.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
29
|
Ohsawa I, Ishikawa M, Takahashi K,
Watanabe M, Nishimaki K, Yamagata K, Katsura K, Katayama Y, Asoh S
and Ohta S: Hydrogen acts as a therapeutic antioxidant by
selectively reducing cytotoxic oxygen radicals. Nat Med.
13:688–694. 2007.PubMed/NCBI View
Article : Google Scholar
|
|
30
|
Wu D, Liang M, Dang H, Fang F, Xu F and
Liu C: Hydrogen protects against hyperoxia-induced apoptosis in
type II alveolar epithelial cells via activation of PI3K/Akt/Foxo3a
signaling pathway. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 495:1620–1627.
2018.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
31
|
Chen K, Liu Y, He J, Pavlos N, Wang C,
Kenny J, Yuan J, Zhang Q, Xu J and He W: Steroid-induced
osteonecrosis of the femoral head reveals enhanced reactive oxygen
species and hyperactive osteoclasts. Int J Biol Sci. 16:1888–1900.
2020.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
32
|
Bartell SM, Kim HN, Ambrogini E, Han L,
Iyer S, Serra Ucer S, Rabinovitch P, Jilka RL, Weinstein RS, Zhao
H, et al: FoxO proteins restrain osteoclastogenesis and bone
resorption by attenuating H2O2 accumulation.
Nat Commun. 5(3773)2014.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
33
|
Kim H, Lee YD, Kim HJ, Lee ZH and Kim HH:
SOD2 and Sirt3 control osteoclastogenesis by regulating
mitochondrial ROS. J Bone Miner Res. 32:397–406. 2017.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
34
|
Lee NK, Choi YG, Baik JY, Han SY, Jeong
DW, Bae YS, Kim N and Lee SY: A crucial role for reactive oxygen
species in RANKL-induced osteoclast differentiation. Blood.
106:852–859. 2005.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
35
|
Kim MS, Yang YM, Son A, Tian YS, Lee SI,
Kang SW, Muallem S and Shin DM: RANKL-mediated reactive oxygen
species pathway that induces long lasting Ca2+
oscillations essential for osteoclastogenesis. J Biol Chem.
285:6913–6921. 2010.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
36
|
Ha H, Kwak HB, Lee SW, Jin HM, Kim HM, Kim
HH and Lee ZH: Reactive oxygen species mediate RANK signaling in
osteoclasts. Exp Cell Res. 301:119–127. 2004.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
37
|
Bhatt NY, Kelley TW, Khramtsov VV, Wang Y,
Lam GK, Clanton TL and Marsh CB: Macrophage-colony-stimulating
factor-induced activation of extracellular-regulated kinase
involves phosphatidylinositol 3-kinase and reactive oxygen species
in human monocytes. J Immunol. 169:6427–6434. 2002.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
38
|
Fan Z, Gao Y, Huang Z, Xue F, Wu S, Yang
J, Zhu L and Fu L: Protective effect of hydrogen-rich saline on
pressure overload-induced cardiac hypertrophyin rats: Possible role
of JAK-STAT signaling. BMC Cardiovasc Disord. 18(32)2018.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
39
|
Chen Y, Jiang J, Miao H, Chen X, Sun X and
Li Y: Hydrogen-rich saline attenuates vascular smooth muscle cell
proliferation and neointimal hyperplasia by inhibiting reactive
oxygen species production and inactivating the Ras-ERK1/2-MEK1/2
and Akt pathways. Int J Mol Med. 31:597–606. 2013.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
40
|
Qiu X, Li H, Tang H, Jin Y, Li W, YuSun
PingFeng, Sun X and Xia Z: Hydrogen inhalation ameliorates
lipopolysaccharide-induced acute lung injury in mice. Int
Immunopharmacol. 11:2130–2137. 2011.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
41
|
Wang K, Song X, Duan S, Fang W, Huan X,
Cao Y, Tang J and Wang L: Hydrogen-rich saline prevents the down
regulation of claudin-5 protein in septic rat lung via the PI3K/Akt
signaling pathway. Int J Clin Exp Med. 10:11717–11727. 2017.
|
|
42
|
Zhang Y, Liu Y and Zhang J: . Saturated
hydrogen saline attenuates endotoxin-induced lung dysfunction. J
Surg Res. 198:41–49. 2015.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
43
|
Liu H, Liang X, Wang D, Zhang H, Liu L,
Chen H, Li Y, Duan Q and Xie K: Combination therapy with nitric
oxide and molecular hydrogen in a murine model of acute lung
injury. Shock. 43:504–511. 2015.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
44
|
Takayanagi H, Kim S, Matsuo K, Suzuki H,
Suzuki T, Sato K, Yokochi T, Oda H, Nakamura K, Ida N, et al: RANKL
maintains bone homeostasis through c-Fos-dependent induction of
interferon-β. Nature. 416:744–749. 2002.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
45
|
Grigoriadis AE, Wang ZQ, Cecchini MG,
Hofstetter W, Felix R, Fleisch HA and Wagner EF: c-Fos: A key
regulator of osteoclast-macrophage lineage determination and bone
remodeling. Science. 266:443–448. 1994.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
46
|
Jiao Z, Xu W, Zheng J, Shen P, Qin A,
Zhang S and Yang C: Kaempferide prevents titanium particle induced
osteolysis by suppressing JNK activation during osteoclast
formation. Sci Rep. 7(16665)2017.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|