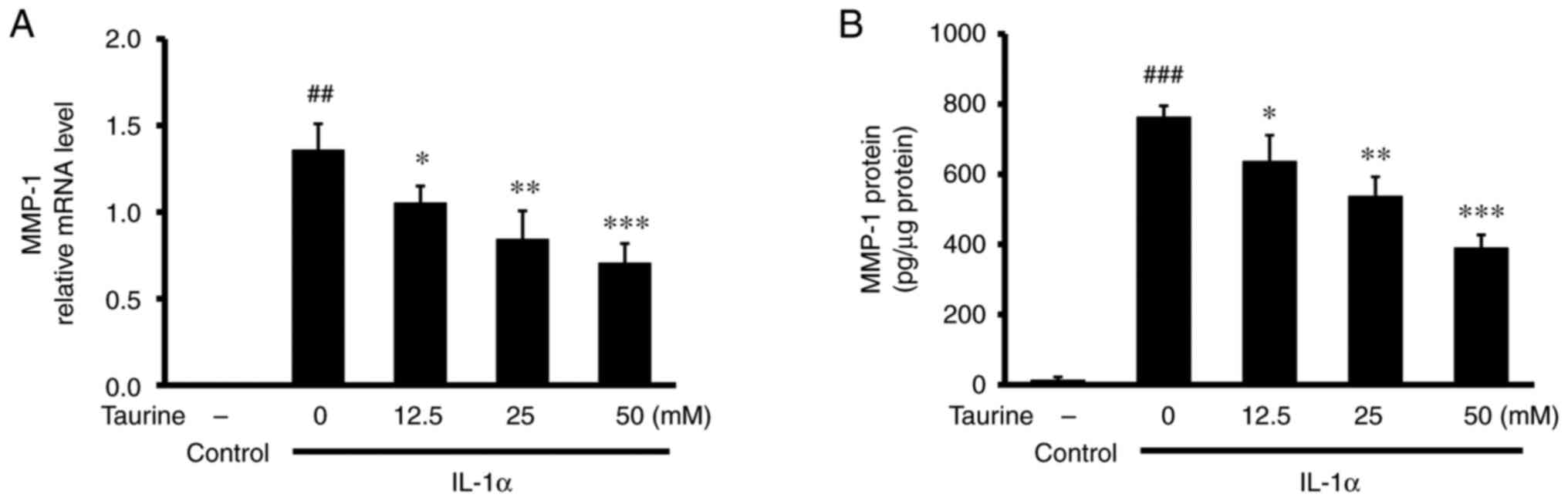
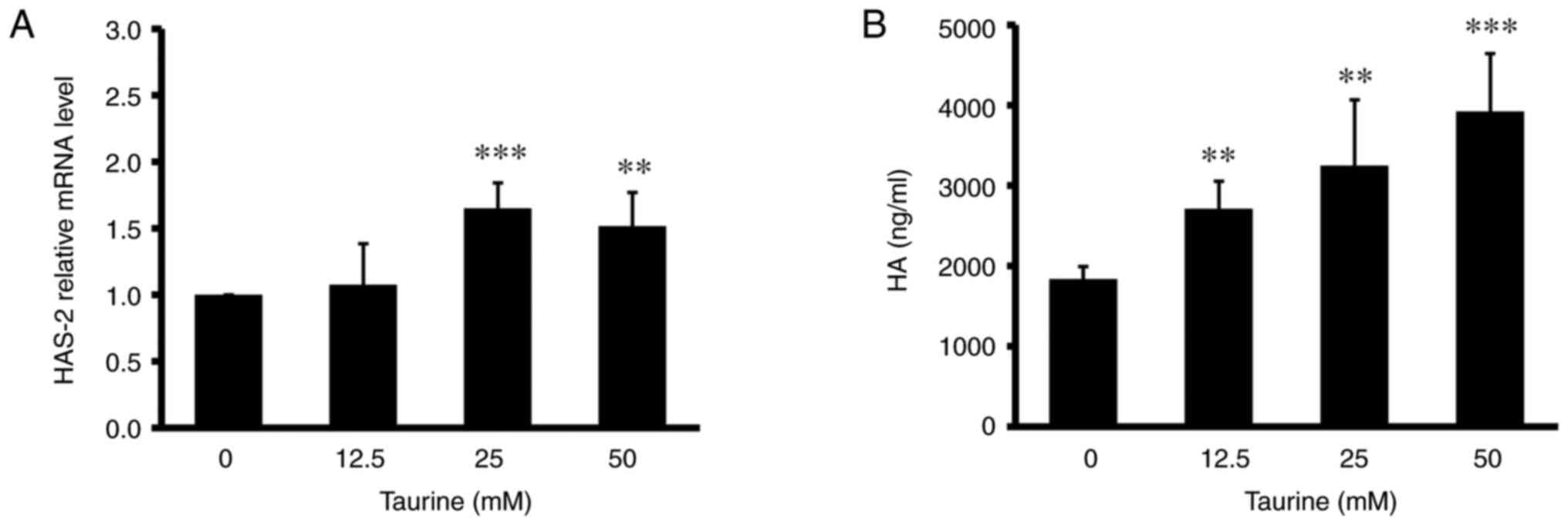
|
1
|
Bouwstra JA and Ponec M: The skin barrier
in healthy and diseased state. Biochim Biophys Acta.
1758:2080–2095. 2006.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
2
|
Proksch E, Brandner JM and Jensen JM: The
skin: an indispensable barrier. Exp Dermatol. 17:1063–1072.
2008.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
3
|
van Smeden J, Janssens M, Gooris GS and
Bouwstra JA: The important role of stratum corneum lipids for the
cutaneous barrier function. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1841:295–313.
2014.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
4
|
Rawlings AV and Harding CR: Moisturization
and skin barrier function. Dermatol Ther. 17 (Suppl 1):S43–S48.
2004.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
5
|
Kezic S and Jakasa I: Filaggrin and skin
barrier function. Curr Probl Dermatol. 49:1–7. 2016.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
6
|
Kirschner N and Brandner JM: Barriers and
more: Functions of tight junction proteins in the skin. Ann N Y
Acad Sci. 1257:158–166. 2012.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
7
|
Brandner JM: Importance of tight junctions
in relation to skin barrier function. Curr Probl Dermatol.
49:27–37. 2016.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
8
|
Boguniewicz M and Leung DY: Atopic
dermatitis: A disease of altered skin barrier and immune
dysregulation. Immunol Rev. 242:233–246. 2011.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
9
|
Ruiz Martínez MA, Peralta Galisteo S,
Castán H and Morales*Hernández ME: Role of proteoglycans on skin
ageing: A review. Int J Cosmet Sci. 42:529–535. 2020.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
10
|
Baumann L: Skin ageing and its treatment.
J Pathol. 211:241–251. 2007.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
11
|
Huxtable RJ: Physiological actions of
taurine. Physiol Rev. 72:101–163. 1992.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
12
|
Janeke G, Siefken W, Carstensen S,
Springmann G, Bleck O, Steinhart H, Höger P, Wittern KP, Wenck H,
Stäb F, et al: Role of taurine accumulation in keratinocyte
hydration. J Invest Dermatol. 121:354–361. 2003.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
13
|
Warskulat U, Reinen A, Grether-Beck S,
Krutmann J and Häussinger D: The osmolyte strategy of normal human
keratinocytes in maintaining cell homeostasis. J Invest Dermatol.
123:516–521. 2004.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
14
|
El-Chami C, Haslam IS, Steward MC and
O'Neill CA: Organic osmolytes preserve the function of the
developing tight junction in ultraviolet B-irradiated rat epidermal
keratinocytes. Sci Rep. 26(5167)2018.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
15
|
Yoshimura T, Manabe C, Inokuchi Y, Mutou
C, Nagahama T and Murakami S: Protective effect of taurine on
UVB-induced skin aging in hairless mice. Biomed Pharmacother.
141(111898)2021.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
16
|
Değim Z, Celebi N, Sayan H, Babül A,
Erdoğan D and Take G: An investigation on skin wound healing in
mice with a taurine-chitosan gel formulation. Amino Acids.
22:187–198. 2002.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
17
|
Park S, Kim H and Kim SJ: Stimulation of
ERK2 by taurine with enhanced alkaline phosphatase activity and
collagen synthesis in osteoblast-like UMR-106 cells. Biochem
Pharmacol. 62:1107–1111. 2001.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
18
|
Kojima H, Ando Y, Idehara K, Katoh M,
Kosaka T, Miyaoka E, Shinoda S, Suzuki T, Yamaguchi Y, Yoshimura I,
et al: Validation study of the in vitro skin irritation test with
the LabCyte EPI-MODEL24. Altern Lab Anim. 40:33–50. 2012.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
19
|
Livak KJ and Schmittgen TD: Analysis of
relative gene expression data using real-time quantitative PCR and
the 2(-Delta Delta C(T)) method. Methods. 25:402–408.
2001.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
20
|
Anderheggen B, Jassoy C, Waldmann-Laue M,
Förster T, Wadle A and Doering T: Taurine improves epidermal
barrier properties stressed by surfactants-a role for osmolytes in
barrier homeostasis. J Cosmet Sci. 57:1–10. 2006.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
21
|
Yoshimura T, Inokuchi Y, Mutou C, Sakurai
T, Nagahama T and Murakami S: Age-related decline in the taurine
content of the skin in rodents. Amino Acids. 53:429–434.
2021.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
22
|
Rissmann R, Oudshoorn MH, Hennink WE,
Ponec M and Bouwstra JA: Skin barrier disruption by acetone:
observations in a hairless mouse skin model. Arch Dermatol Res.
301:609–613. 2009.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
23
|
Griswold DE, Connor JR, Dalton BJ, Lee JC,
Simon P, Hillegass L, Sieg DJ and Hanna N: Activation of the IL-1
gene in UV-irradiated mouse skin: Association with inflammatory
sequelae and pharmacologic intervention. J Invest Dermatol.
97:1019–1023. 1991.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
24
|
Wang X, Bi Z, Chu W and Wan Y: IL-1
receptor antagonist attenuates MAP kinase/AP-1 activation and MMP1
expression in UVA-irradiated human fibroblasts induced by culture
medium from UVB-irradiated human skin keratinocytes. Int J Mol Med.
16:1117–1124. 2005.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
25
|
Coderch L, López O, de la Maza A and Parra
JL: Ceramides and skin function. Am J Clin Dermatol. 4:107–129.
2003.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
26
|
Kim Y and Lim KM: Skin barrier dysfunction
and filaggrin. Arch Pharm Res. 44:36–48. 2021.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
27
|
El-Chami C, Foster AR, Johnson C, Clausen
RP, Cornwell P, Haslam IS, Steward MC, Watson REB, Young HS and
O'Neill CA: Organic osmolytes increase expression of specific tight
junction proteins in skin and alter barrier function in
keratinocytes. Br J Dermatol. 184:482–494. 2021.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
28
|
Lambert IH: Regulation of the cellular
content of the organic osmolyte taurine in mammalian cells.
Neurochem Res. 29:27–63. 2004.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
29
|
Bravo B, Correia P, Gonçalves Junior JE,
Sant'Anna B and Kerob D: Benefits of topical hyaluronic acid for
skin quality and signs of skin aging: From literature review to
clinical evidence. Dermatol Ther. 35(e15903)2022.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
30
|
Itano N, Sawai T, Yoshida M, Lenas P,
Yamada Y, Imagawa M, Shinomura T, Hamaguchi M, Yoshida Y, Ohnuki Y,
et al: Three isoforms of mammalian hyaluronan synthases have
distinct enzymatic properties. J Biol Chem. 274:25085–25092.
1999.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
31
|
Jacobson A, Brinck J, Briskin MJ, Spicer
AP and Heldin P: Expression of human hyaluronan synthases in
response to external stimuli. Biochem J. 348:29–35. 2000.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
32
|
Nyström A and Bruckner-Tuderman L: Matrix
molecules and skin biology. Semin Cell Dev Biol. 89:136–146.
2019.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
33
|
Varani J, Dame MK, Rittie L, Fligiel SE,
Kang S, Fisher GJ and Voorhees JJ: Decreased collagen production in
chronologically aged skin: Roles of age-dependent alteration in
fibroblast function and defective mechanical stimulation. Am J
Pathol. 168:1861–1868. 2006.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
34
|
Cole MA, Quan T, Voorhees JJ and Fisher
GJ: Extracellular matrix regulation of fibroblast function:
redefining our perspective on skin aging. J Cell Commun Signal.
12:35–43. 2018.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
35
|
Nishimori Y, Edwards C, Pearse A,
Matsumoto K, Kawai M and Marks R: Degenerative alterations of
dermal collagen fiber bundles in photodamaged human skin and
UV-irradiated hairless mouse skin: possible effect on decreasing
skin mechanical properties and appearance of wrinkles. J Invest
Dermatol. 117:1458–1463. 2001.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
36
|
Sárdy M: Role of matrix metalloproteinases
in skin ageing. Connect Tissue Res. 50:132–138. 2009.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
37
|
Pittayapruek P, Meephansan J, Prapapan O,
Komine M and Ohtsuki M: Role of matrix metalloproteinases in
photoaging and photocarcinogenesis. Int J Mol Sci.
17(868)2016.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
38
|
Kim MS, Kim YK, Cho KH and Chung JH:
Regulation of type I procollagen and MMP-1 expression after single
or repeated exposure to infrared radiation in human skin. Mech
Ageing Dev. 127:875–882. 2006.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
39
|
Röck K, Grandoch M, Majora M, Krutmann J
and Fischer JW: Collagen fragments inhibit hyaluronan synthesis in
skin fibroblasts in response to ultraviolet B (UVB): New insights
into mechanisms of matrix remodeling. J Biol Chem. 286:18268–18276.
2011.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
40
|
Varani J, Warner RL, Gharaee-Kermani M,
Phan SH, Kang S, Chung JH, Wang ZQ, Datta SC, Fisher GJ and
Voorhees JJ: Vitamin A antagonizes decreased cell growth and
elevated collagen-degrading matrix metalloproteinases and
stimulates collagen accumulation in naturally aged human skin. J
Invest Dermatol. 114:480–486. 2000.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|