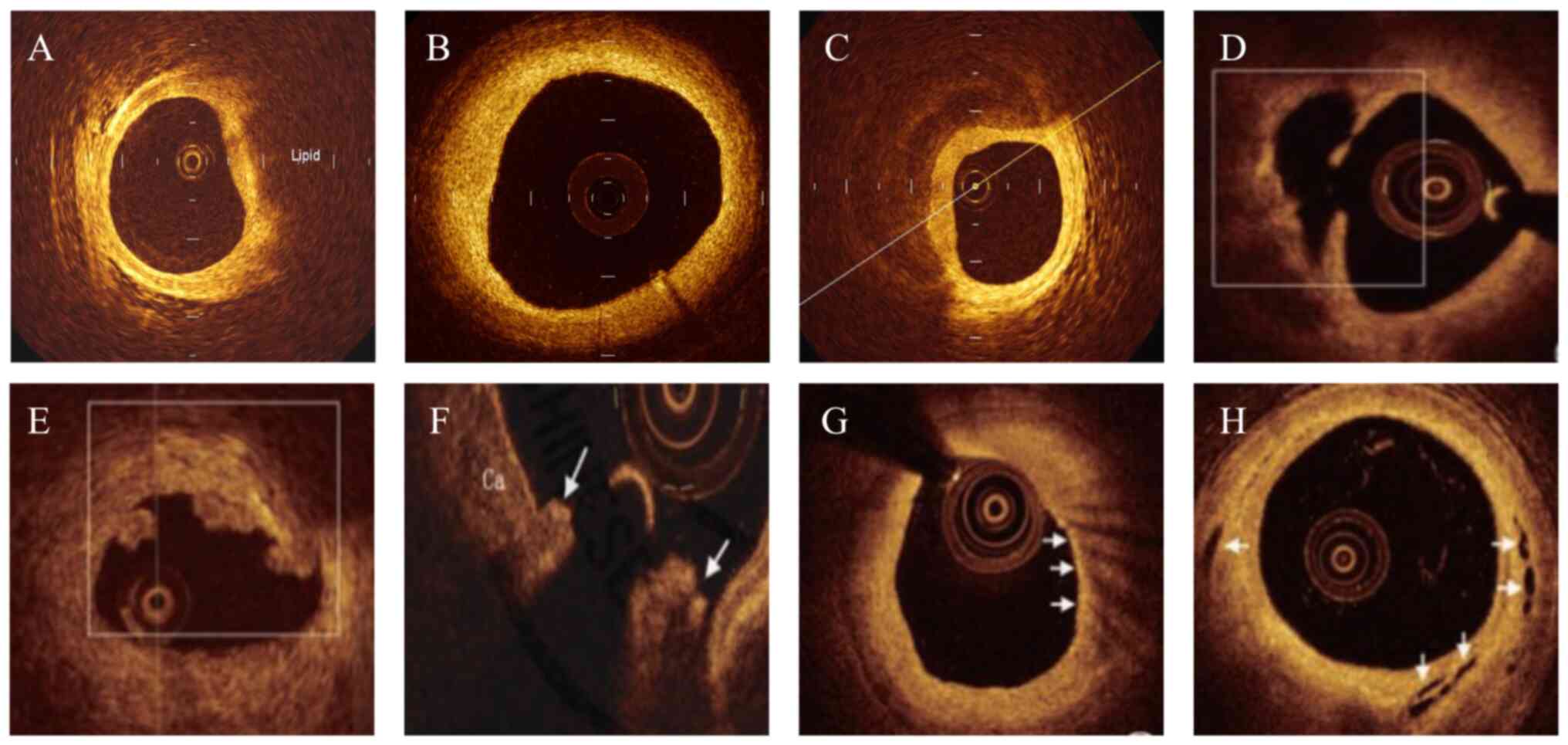
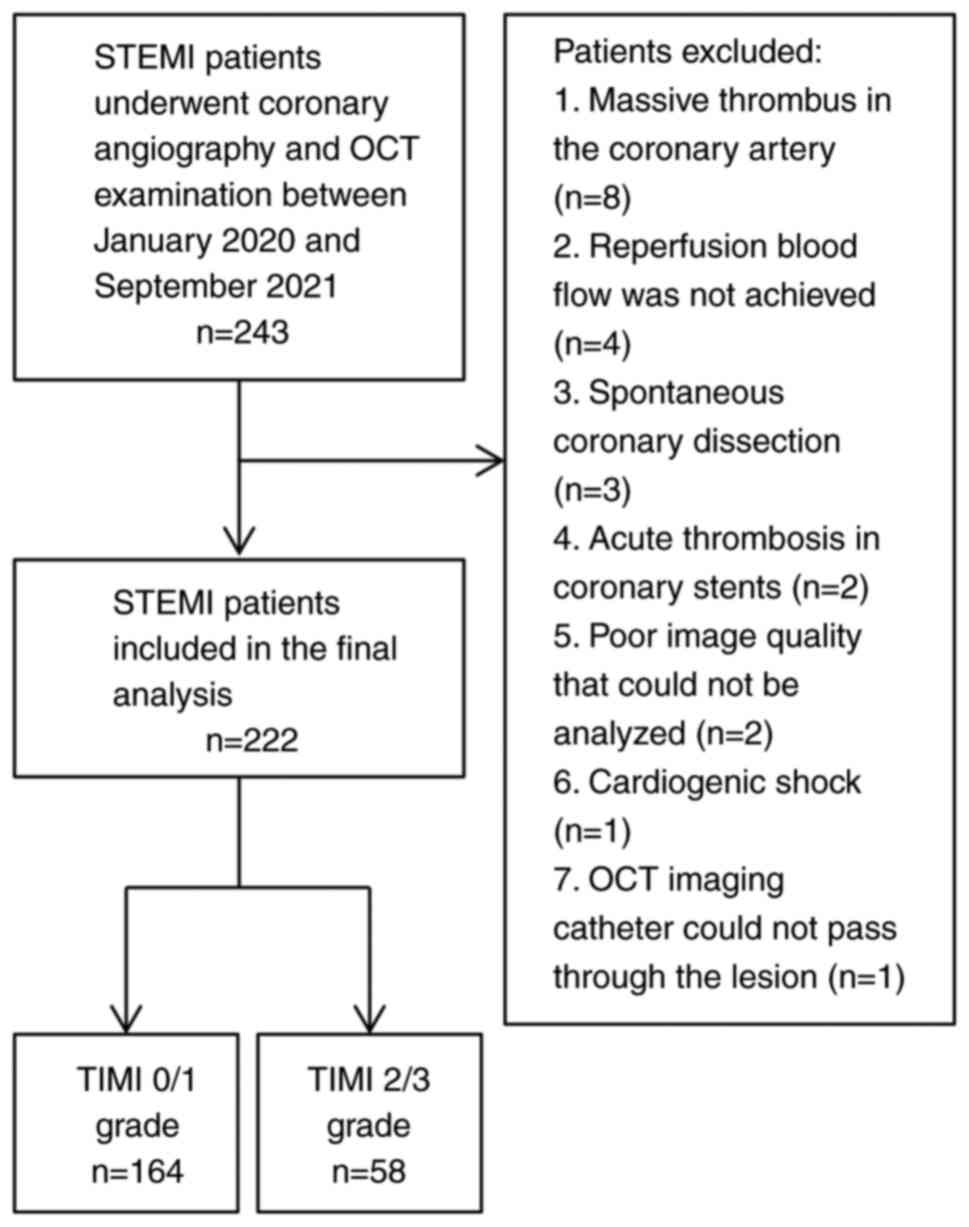
|
1
|
Kuhn J, Olié V, Grave C, Le Strat Y,
Bonaldi C and Joly P: Estimating the future burden of myocardial
infarction in france until 2035: An illness-death model-based
approach. Clin Epidemiol. 14:255–264. 2022.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
2
|
Fang C, Yin Y, Jiang S, Zhang S, Wang J,
Wang Y, Li L, Wang Y, Guo J, Yu H, et al: Increased vulnerability
and distinct layered phenotype at culprit and nonculprit lesions in
STEMI versus NSTEMI. JACC Cardiovasc Imaging. 15:672–681.
2022.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
3
|
Sun R, Hu S, Guagliumi G, Jia H, Tian J,
Li L, Zhang S, Wang Y, Zhang S, Hou J and Yu B: Pre-infarction
angina and culprit lesion morphologies in patients with a first
ST-segment elevation acute myocardial infarction: Insights from in
vivo optical coherence tomography. EuroIntervention. 14:1768–1775.
2019.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
4
|
Bauer T, Zeymer U, Diallo A, Vicaut E,
Bolognese L, Cequier A, Huber K, Montalescot G, Hamm CW and Van't
Hof AW: ATLANTIC Investigators. Impact of preprocedural TIMI flow
on clinical outcome in low-risk patients with ST-elevation
myocardial infarction: Results from the ATLANTIC study. Catheter
Cardiovasc Interv. 95:494–500. 2020.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
5
|
Bouisset F, Deney A, Ferrières J,
Panagides V, Becker M, Riviere N, Yvorel C, Commeau P, Adjedj J,
Benamer H, et al: Mechanical complications in ST-elevation
myocardial infarction: The impact of pre-hospital delay. Int J
Cardiol. 345:14–19. 2021.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
6
|
Kalinskaya A, Dukhin O, Lebedeva A,
Maryukhnich E, Rusakovich G, Vorobyeva D, Shpektor A, Margolis L
and Vasilieva E: Circulating cytokines in myocardial infarction are
associated with coronary blood flow. Front Immunol.
13(837642)2022.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
7
|
Somuncu MU, Akgun T, Cakır MO, Akgul F,
Serbest NG, Karakurt H, Can M and Demir AR: The elevated soluble
ST2 predicts no-reflow phenomenon in ST-elevation myocardial
infarction undergoing primary percutaneous coronary intervention. J
Atheroscler Thromb. 26:970–978. 2019.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
8
|
Mirbolouk F, Gholipour M, Salari A,
Shakiba M, Kheyrkhah J, Nikseresht V, Sotoudeh N, Moghadam N,
Mirbolouk MJ and Far MM: CHA2DS2-VASc score predict no-reflow
phenomenon in primary percutaneous coronary intervention in primary
percutaneous coronary intervention. J Cardiovasc Thorac Res.
10:46–52. 2018.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
9
|
Søndergaard FT, Beske RP, Frydland M,
Møller JE, Helgestad OKL, Jensen LO, Holmvang L, Goetze JP,
Engstrøm T and Hassager C: Soluble ST2 in plasma is associated with
post-procedural no-or-slow reflow after primary percutaneous
coronary intervention in ST-elevation myocardial infarction. Eur
Heart J Acute Cardiovasc Care. 12:48–52. 2023.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
10
|
Stalikas N, Papazoglou AS, Karagiannidis
E, Panteris E, Moysidis D, Daios S, Anastasiou V, Patsiou V,
Koletsa T, Sofidis G, et al: Association of stress induced
hyperglycemia with angiographic findings and clinical outcomes in
patients with ST-elevation myocardial infarction. Cardiovasc
Diabetol. 21(140)2022.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
11
|
Araki M, Park SJ, Dauerman HL, Uemura S,
Kim JS, Di Mario C, Johnson TW, Guagliumi G, Kastrati A, Joner M,
et al: Optical coherence tomography in coronary atherosclerosis
assessment and intervention. Nat Rev Cardiol. 19:684–703.
2022.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
12
|
Weng Z, Zhao C, Qin Y, Liu C, Pan W, Hu S,
He L, Xu Y, Zeng M, Feng X, et al: Peripheral atherosclerosis in
acute coronary syndrome patients with plaque rupture vs plaque
erosion: A prospective coronary optical coherence tomography and
peripheral ultrasound study. Am Heart J. 263:159–168.
2023.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
13
|
Fracassi F, Crea F, Sugiyama T, Yamamoto
E, Uemura S, Vergallo R, Porto I, Lee H, Fujimoto J, Fuster V and
Jang IK: Healed culprit plaques in patients with acute coronary
syndromes. J Am Coll Cardiol. 73:2253–2263. 2019.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
14
|
Shimokado A, Matsuo Y, Kubo T, Nishiguchi
T, Taruya A, Teraguchi I, Shiono Y, Orii M, Tanimoto T, Yamano T,
et al: In vivo optical coherence tomography imaging and
histopathology of healed coronary plaques. Atherosclerosis.
275:35–42. 2018.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
15
|
Reindl M, Tiller C, Holzknecht M, Lechner
I, Henninger B, Mayr A, Brenner C, Klug G, Bauer A, Metzler B and
Reinstadler SJ: Association of myocardial injury with serum
procalcitonin levels in patients with ST-elevation myocardial
infarction. JAMA Netw Open. 3(e207030)2020.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
16
|
Gibson CM, Cannon CP, Daley WL, Dodge JT
Jr, Alexander B Jr, Marble SJ, McCabe CH, Raymond L, Fortin T,
Poole WK and Braunwald E: TIMI frame count: A quantitative method
of assessing coronary artery flow. Circulation. 93:879–888.
1996.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
17
|
Jiao Y, Su Y, Shen J, Hou X, Li Y, Wang J,
Liu B, Qiu D, Sun Z, Chen Y, et al: Evaluation of the long-term
prognostic ability of triglyceride-glucose index for elderly acute
coronary syndrome patients: A cohort study. Cardiovasc Diabetol.
21(3)2022.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
18
|
Li Z, Tang Z, Wang Y, Liu Z, Wang G, Zhang
L, Wu Y and Guo J: Assessment of radial artery atherosclerosis in
acute coronary syndrome patients: An in vivo study using optical
coherence tomography. BMC Cardiovasc Disord. 22(120)2022.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
19
|
Yamanaka Y, Shimada Y, Tonomura D,
Terashita K, Suzuki T, Yano K, Nishiura S, Yoshida M, Tsuchida T
and Fukumoto H: Laser vaporization of intracoronary thrombus and
identifying plaque morphology in ST-segment elevation myocardial
infarction as assessed by optical coherence tomography. J Interv
Cardiol. 2021(5590109)2021.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
20
|
Kanaya T, Noguchi T, Otsuka F, Asaumi Y,
Kataoka Y, Morita Y, Miura H, Nakao K, Fujino M, Kawasaki T, et al:
Optical coherence tomography-verified morphological correlates of
high-intensity coronary plaques on non-contrast T1-weighted
magnetic resonance imaging in patients with stable coronary artery
disease. Eur Heart J Cardiovasc Imaging. 20:75–83. 2019.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
21
|
Russo M, Fracassi F, Kurihara O, Kim HO,
Thondapu V, Araki M, Shinohara H, Sugiyama T, Yamamoto E, Lee H, et
al: Healed plaques in patients with stable angina pectoris.
Arterioscler Thromb Vasc Biol. 40:1587–1597. 2020.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
22
|
Higuma T, Soeda T, Yamada M, Yokota T,
Yokoyama H, Nishizaki F, Xing L, Yamamoto E, Bryniarski K, Dai J,
et al: Coronary plaque characteristics associated with reduced TIMI
(Thrombolysis in Myocardial Infarction) flow grade in patients with
st-segment-elevation myocardial infarction: A combined optical
coherence tomography and intravascular ultrasound study. Circ
Cardiovasc Interv. 9(e003913)2016.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
23
|
Wang J, Fang C, Zhang S, Li L, Lu J, Wang
Y, Wang Y, Yu H, Wei G, Yin Y, et al: Systemic and local factors
associated with reduced thrombolysis in myocardial infarction flow
in ST-segment elevation myocardial infarction patients with plaque
erosion detected by intravascular optical coherence tomography. Int
J Cardiovasc Imaging. 37:399–409. 2021.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
24
|
Yu H, Dai J, Fang C, Jiang S, Mintz GS and
Yu B: Prevalence, morphology, and predictors of intra-stent plaque
rupture in patients with acute coronary syndrome: An optical
coherence tomography study. Clin Appl Thromb Hemost.
28(10760296221146742)2022.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
25
|
Majeed K, Hartman E, Mori TA, Alcock R,
Spiro J, Ligthart J, Witberg K, Hillis G, van Soest G and Schultz
C: The effect of stent artefact on quantification of plaque
features using optical coherence tomography (OCT): A feasibility
and clinical utility study. Heart Lung Circ. 29:874–882.
2020.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
26
|
Ando H, Amano T, Matsubara T, Uetani T,
Nanki M, Marui N, Kato M, Yoshida T, Yokoi K, Kumagai S, et al:
Comparison of tissue characteristics between acute coronary
syndrome and stable angina pectoris. An integrated backscatter
intravascular ultrasound analysis of culprit and non-culprit
lesions. Circ J. 75:383–390. 2011.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
27
|
Soeda T, Higuma T, Abe N, Yamada M,
Yokoyama H, Shibutani S, Ong DS, Vergallo R, Minami Y, Lee H, et
al: Morphological predictors for no reflow phenomenon after primary
percutaneous coronary intervention in patients with ST-segment
elevation myocardial infarction caused by plaque rupture. Eur Heart
J Cardiovasc Imaging. 18:103–110. 2017.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
28
|
Falk E, Nakano M, Bentzon JF, Finn AV and
Virmani R: Update on acute coronary syndromes: The pathologists'
view. Eur Heart J. 34:719–728. 2013.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
29
|
Grover SP and Mackman N: Tissue factor in
atherosclerosis and atherothrombosis. Atherosclerosis. 307:80–86.
2020.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
30
|
Feng X, Xu Y, Zeng M, Qin Y, Weng Z, Sun
Y, Gao Z, He L, Zhao C, Wang N, et al: Optical coherence tomography
assessment of coronary lesions associated with microvascular
dysfunction in ST-segment elevation myocardial infarction. Circ J.
4(CJ-23-0200)2023.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
31
|
Tomaniak M, Katagiri Y, Modolo R, de Silva
R, Khamis RY, Bourantas CV, Torii R, Wentzel JJ, Gijsen FJH, van
Soest G, et al: Vulnerable plaques and patients: State-of-the-art.
Eur Heart J. 41:2997–3004. 2020.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
32
|
Dobrolińska MM, Gąsior P, Wańha W,
Pietraszewski P, Pociask E, Smolka G, Wojakowski W and Roleder T:
The influence of high-density lipoprotein cholesterol on maximal
lipid core burden indexing thin cap fibrous atheroma lesions as
assessed by near infrared spectroscopy. Cardiol J. 28:887–895.
2021.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
33
|
Araki M, Yonetsu T, Kurihara O, Nakajima
A, Lee H, Soeda T, Minami Y, McNulty I, Uemura S, Kakuta T and Jang
IK: Predictors of rapid plaque progression: An optical coherence
tomography study. JACC Cardiovasc Imaging. 14:1628–1638.
2021.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
34
|
Li J, Sheng Z, Tan Y, Zhou P, Liu C, Zhao
H, Song L, Zhou J, Chen R, Chen Y and Yan H: Association of plasma
trimethylamine N-Oxide level with healed culprit plaques examined
by optical coherence tomography in patients with ST-Segment
elevation myocardial infarction. Nutr Metab Cardiovasc Dis.
31:145–152. 2021.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
35
|
Yin WJ, Jing J, Zhang YQ, Tian F, Zhang T,
Zhou SS and Chen YD: Association between non-culprit healed plaque
and plaque progression in acute coronary syndrome patients: An
optical coherence tomography study. J Geriatr Cardiol. 18:631–644.
2021.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
36
|
Cao Y, Mintz GS, Matsumura M, Zhang W, Lin
Y, Wang X, Fujino A, Lee T, Murai T, Hoshino M, et al: The relation
between optical coherence tomography-detected layered pattern and
acute side branch occlusion after provisional stenting of coronary
bifurcation lesions. Cardiovasc Revasc Med. 20:1007–1013.
2019.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|