|
1
|
Tang J and Zhuang S: Histone acetylation
and DNA methylation in ischemia/reperfusion injury. Clin Sci.
133:597–609. 2019.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
2
|
Wu M, Yiang G, Liao W, Tsai AP, Cheng YL,
Cheng PW, Li CY and Li CJ: Current mechanistic concepts in ischemia
and reperfusion injury. Cell Physiol Biochem. 46:1650–1667.
2018.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
3
|
Cadenas S: ROS and redox signaling in
myocardial ischemia-reperfusion injury and cardioprotection. Free
Radical Biol Med. 117:76–89. 2018.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
4
|
Ampofo E, Berg JJ, Menger MD and Laschke
MW: Maslinic acid alleviates ischemia/reperfusion-induced
inflammation by downregulation of NFkappaB-mediated adhesion
molecule expression. Sci Rep. 9(6119)2019.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
5
|
Tuo QZ, Lei P, Jackman KA, Li XL, Xiong H,
Li XL, Liuyang ZY, Roisman L, Zhang ST, Ayton S, et al:
Tau-mediated iron export prevents ferroptotic damage after ischemic
stroke. Mol Psychiatry. 22:1520–1530. 2017.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
6
|
Jiang GP, Liao YJ, Huang LL, Zeng XJ and
Liao XH: Effects and molecular mechanism of pachymic acid on
ferroptosis in renal ischemia reperfusion injury. Mol Med Rep.
23(63)2021.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
7
|
Liu XB and Liu WJ: The role of regulated
cell death in renal ischemia-reperfusion injury. Sheng Li Xue Bao.
74:320–332. 2022.PubMed/NCBI(In Chinese).
|
|
8
|
Cui X, Lin L, Sun X, Wang L and Shen R:
Curcumin protects against renal ischemia/reperfusion injury by
regulating oxidative stress and inflammatory response. Evid Based
Complement Alternat Med. 2021(8490772)2021.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
9
|
Latunde-Dada GO: Ferroptosis: Role of
lipid peroxidation, iron and ferritinophagy. Biochim Biophys Acta
Gen Subj. 1861:1893–1900. 2017.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
10
|
Dixon SJ, Lemberg KM, Lamprecht MR, Skouta
R, Zaitsev EM, Gleason CE, Patel DN, Bauer AJ, Cantley AM, Yang WS,
et al: Ferroptosis: An iron-dependent form of nonapoptotic cell
death. Cell. 149:1060–1072. 2012.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
11
|
Linkermann A, Skouta R, Himmerkus N, Mulay
SR, Dewitz C, De Zen F, Prokai A, Zuchtriegel G, Krombach F, Welz
PS, et al: Synchronized renal tubular cell death involves
ferroptosis. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA. 111:16836–16841.
2014.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
12
|
Tao W, Liu F, Zhang J, Fu S, Zhan H and
Qian K: miR-3587 inhibitor attenuates ferroptosis following renal
ischemia-reperfusion through HO-1. Front Mol Biosci.
8(789927)2021.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
13
|
Wang J, Chen JJ, Huang JH, Lv BD, Huang
XJ, Hu Q, Fu J, Huang WJ and Tao TT: Protective effects of total
flavonoids from Lysimachia christinae on calcium
oxalate-induced oxidative stress in a renal cell line and renal
tissue. Evid Based Complement Alternat Med.
2021(6667902)2021.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
14
|
Peluso MR, Miranda CL, Hobbs DJ, Proteau
RR and Stevens JF: Xanthohumol and related prenylated flavonoids
inhibit inflammatory cytokine production in LPS-activated THP-1
monocytes: structure-activity relationships and in silico binding
to myeloid differentiation protein-2 (MD-2). Planta Med.
76:1536–1543. 2010.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
15
|
Liu M, Hansen PE, Wang G, Qiu L, Dong J,
Yin H, Qian Z, Yang M and Miao J: Pharmacological profile of
xanthohumol, a prenylated flavonoid from hops (Humulus
lupulus). Molecules. 20:754–779. 2015.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
16
|
Yen TL, Hsu CK, Lu WJ, Hsieh CY, Hsiao G,
Chou DS, Wu GJ and Sheu JR: Neuroprotective effects of xanthohumol,
a prenylated flavonoid from hops (Humulus lupulus), in
ischemic stroke of rats. J Agric Food Chem. 60:1937–1944.
2012.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
17
|
Oberbauer E, Urmann C, Steffenhagen C,
Bieler L, Brunner D, Furtner T, Humpel C, Bäumer B, Bandtlow C,
Couillard-Despres S, et al: Chroman-like cyclic prenylflavonoids
promote neuronal differentiation and neurite outgrowth and are
neuroprotective. J Nutr Biochem. 24:1953–1962. 2013.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
18
|
Huo H, Zhou Z, Qin J, Liu W, Wang B and Gu
Y: Erastin disrupts mitochondrial permeability transition pore
(mPTP) and induces apoptotic death of colorectal cancer cells. PLoS
One. 11(e0154605)2016.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
19
|
Lin JH, Yang KT, Lee WS, Ting PC, Luo YP,
Lin DJ, Wang YS and Chang JC: Xanthohumol protects the rat
myocardium against ischemia/reperfusion injury-induced ferroptosis.
Oxid Med Cell Longev. 2022(9523491)2022.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
20
|
Ma H, Wang X, Zhang W, Li H, Zhao W, Sun J
and Yang M: Melatonin suppresses ferroptosis induced by high
glucose via activation of the Nrf2/HO-1 signaling pathway in type 2
diabetic osteoporosis. Oxid Med Cell Longev.
2020(9067610)2020.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
21
|
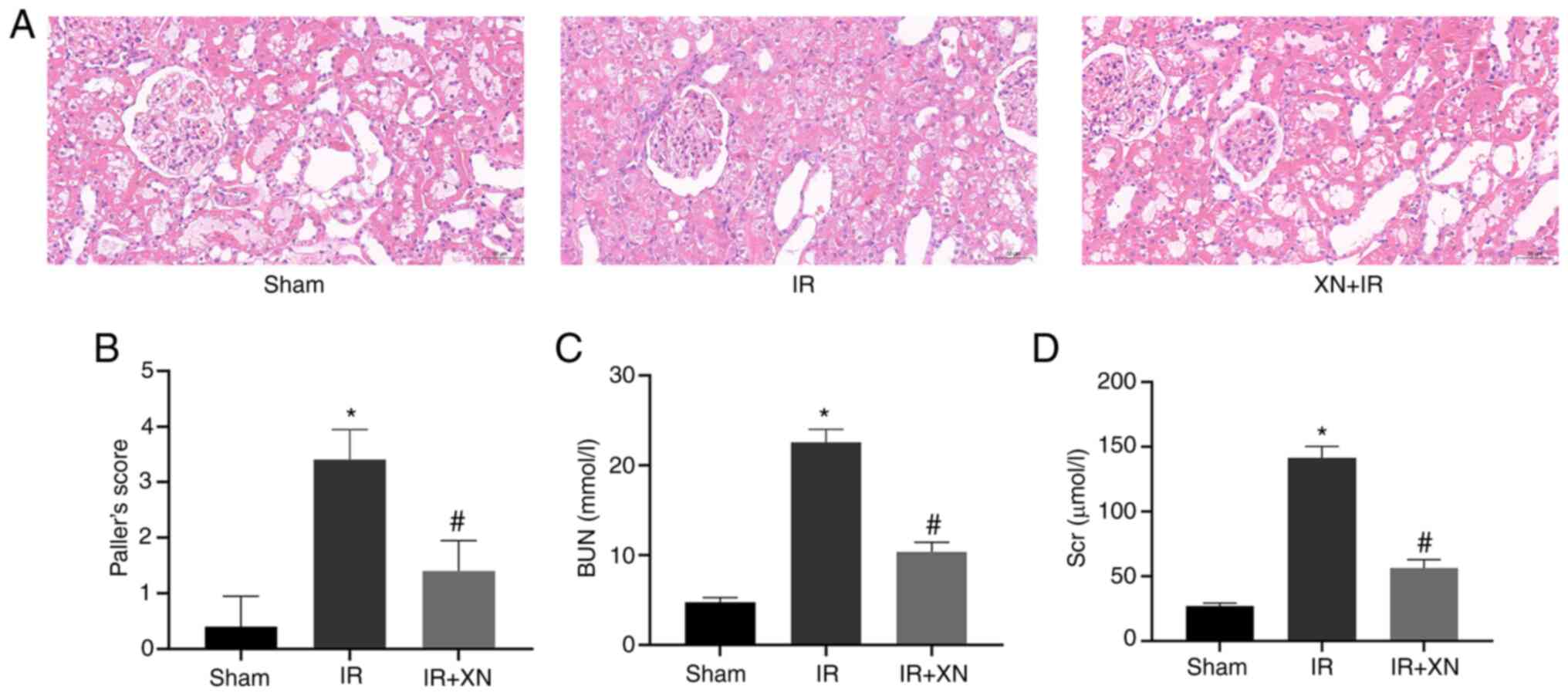
Paller MS: Free radical-mediated
postischemic injury in renal transplantation. Ren Fail. 14:257–260.
1992.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
22
|
Livak KJ and Schmittgen TD: Analysis of
relative gene expression data using real-time quantitative PCR and
the 2(-Delta Delta C(T)) method. Methods. 25:402–408.
2001.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
23
|
Sundaresan M, Yu ZX, Ferrans VJ, Irani K
and Finkel T: Requirement for generation of H2O2 for
platelet-derived growth factor signal transduction. Science.
270:296–299. 1995.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
24
|
Kellum JA, Romagnani P, Ashuntantang G,
Ronco C, Zarbock A and Anders HJ: Acute kidney injury. Nat Rev Dis
Primers. 7(52)2021.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
25
|
Ronco C, Bellomo R and Kellum JA: Acute
kidney injury. Lancet. 394:1949–1964. 2019.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
26
|
Martin LC: Naringin, trimetazidine and
baroreflex in renal ischemia-reperfusion injury. Arq Bras Cardiol.
117:298–299. 2021.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
27
|
Kim K, Yang H, Yi J, Son HE, Ryu JY, Kim
YC, Jeong JC, Chin HJ, Na KY, Chae DW, et al: Real-time clinical
decision support based on recurrent neural networks for in-hospital
acute kidney injury: External validation and model interpretation.
J Med Internet Res. 23(e24120)2021.PubMed/NCBI View
Article : Google Scholar
|
|
28
|
Paragas N, Qiu A, Zhang Q, Samstein B,
Deng SX, Schmidt-Ott KM, Viltard M, Yu W, Forster CS, Gong G, et
al: The Ngal reporter mouse detects the response of the kidney to
injury in real time. Nat Med. 17:216–222. 2011.PubMed/NCBI View
Article : Google Scholar
|
|
29
|
Su X, Zhou M, Li Y, Zhang J, An N, Yang F,
Zhang G, Yuan C, Chen H, Wu H and Xing Y: Protective effects of
natural products against myocardial ischemia/reperfusion:
Mitochondria-targeted therapeutics. Biomed Pharmacother.
149(112893)2022.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
30
|
Li K, Xiao K, Zhu S, Wang Y and Wang W:
Chinese herbal medicine for primary liver cancer therapy:
Perspectives and challenges. Front Pharmacol.
13(889799)2022.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
31
|
Chen W, Becker T, Qian F and Ring J: Beer
and beer compounds: Physiological effects on skin health. J Eur
Acad Dermatol Venereol. 28:142–150. 2014.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
32
|
Krajnovic T, Kaluderovic GN, Wessjohann
LA, Mijatovic S and Maksimovic-Ivanic D: Versatile antitumor
potential of isoxanthohumol: Enhancement of paclitaxel activity in
vivo. Pharmacol Res. 105:62–73. 2016.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
33
|
Negrao R, Costa R, Duarte D, Taveira GT,
Mendanha M, Moura L, Vasques L, Azevedo I and Soares R:
Angiogenesis and inflammation signaling are targets of beer
polyphenols on vascular cells. J Cell Biochem. 111:1270–1279.
2010.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
34
|
Negrao R, Duarte D, Costa R and Soares R:
Isoxanthohumol modulates angiogenesis and inflammation via vascular
endothelial growth factor receptor, tumor necrosis factor alpha and
nuclear factor kappa B pathways. Biofactors. 39:608–622.
2013.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
35
|
Cho YC, You SK, Kim HJ, Cho CW, Lee IS and
Kang BY: Xanthohumol inhibits IL-12 production and reduces chronic
allergic contact dermatitis. Int Immunopharmacol. 10:556–561.
2010.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
36
|
Kiyofuji A, Yui K, Takahashi K and Osada
K: Effects of xanthohumol-rich hop extract on the differentiation
of preadipocytes. J Oleo Sci. 63:593–597. 2014.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
37
|
Izzo G, Soder O and Svechnikov K: The
prenylflavonoid phytoestrogens 8-prenylnaringenin and
isoxanthohumol diferentially suppress steroidogenesis in rat Leydig
cells in ontogenesis. J Appl Toxicol. 31:589–594. 2011.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
38
|
Dorn C, Kraus B, Motyl M, Weiss TS, Gehrig
M, Scholmerich J, Heilmann J and Hellerbrand C: Xanthohumol, a
chalcon derived from hops, inhibits hepatic inflammation and
fibrosis. Mol Nutr Food Res. 54 (Suppl 2):S205–S213.
2010.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
39
|
Albini A, Dell'Eva R, Vene R, Ferrari N,
Buhler DR, Noonan DM and Fassina G: Mechanisms of the
antiangiogenic activity by the hop flavonoid xanthohumol: NF-kappaB
and Akt as targets. FASEB J. 20:527–529. 2006.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
40
|
Saito K, Matsuo Y, Imafuji H, Okubo T,
Maeda Y, Sato T, Shamoto T, Tsuboi K, Morimoto M, Takahashi H, et
al: Xanthohumol inhibits angiogenesis by suppressing nuclear
factor-κB activation in pancreatic cancer. Cancer Sci. 109:132–140.
2018.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
41
|
Dorn C, Massinger S, Wuzik A, Heilmann J
and Hellerbrand C: Xanthohumol suppresses inflammatory response to
warm ischemia-reperfusion induced liver injury. Exp Mol Pathol.
94:10–16. 2013.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
42
|
Jiao Y, Cao Y, Lu X, Wang J, Saitgareeva
A, Kong X, Song C, Li J, Tian K, Zhang S, et al: Xanthohumol
protects neuron from cerebral ischemia injury in experimental
stroke. Mol Biol Rep. 47:2417–2425. 2020.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
43
|
Friedmann AJP, Schneider M, Proneth B,
Tyurina YY, Tyurin VA, Hammond VJ, Herbach N, Aichler M, Walch A,
Eggenhofer E, et al: Inactivation of the ferroptosis regulator Gpx4
triggers acute renal failure in mice. Nat Cell Biol. 16:1180–1191.
2014.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
44
|
Gao M, Monian P, Quadri N, Ramasamy R and
Jiang X: Glutaminolysis and transferrin regulate ferroptosis. Mol
Cell. 59:298–308. 2015.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
45
|
Gascon S, Murenu E, Masserdotti G, Ortega
F, Russo GL, Petrik D, Deshpande A, Heinrich C, Karow M, Robertson
SP, et al: Identification and successful negotiation of a metabolic
checkpoint in direct neuronal reprogramming. Cell Stem Cell.
18:396–409. 2016.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
46
|
Pan J, Zhao J, Feng L, Xu X, He Z and
Liang W: Inhibition of USP14 suppresses ROS-dependent ferroptosis
and alleviates renal ischemia/reperfusion injury. Cell Biochem
Biophys. 81:87–96. 2023.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
47
|
Qi Y, Hu M, Qiu Y, Zhang L, Yan Y, Feng Y,
Feng C, Hou X, Wang Z, Zhang D and Zhao J: Mitoglitazone
ameliorates renal ischemia/reperfusion injury by inhibiting
ferroptosis via targeting mitoNEET. Toxicol Appl Pharmacol.
465(116440)2023.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
48
|
Dong B, Ding C, Xiang H, Zheng J, Li X,
Xue W and Li Y: USP7 accelerates FMR1-mediated ferroptosis by
facilitating TBK1 ubiquitination and DNMT1 deubiquitination after
renal ischemia-reperfusion injury. Inflamm Res. 71:1519–1533.
2022.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
49
|
Shen B, Zhao C, Wang Y, Peng Y, Cheng J,
Li Z, Wu L, Jin M and Feng H: Aucubin inhibited lipid accumulation
and oxidative stress via Nrf2/HO-1 and AMPK signalling pathways. J
Cell Mol Med. 23:4063–4075. 2019.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
50
|
Di Tu Q, Jin J, Hu X, Ren Y, Zhao L and He
Q: Curcumin improves the renal autophagy in rat experimental
membranous nephropathy via regulating the PI3K/AKT/mTOR and
Nrf2/HO-1 signaling pathways. Biomed Res Int.
2020(7069052)2020.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
51
|
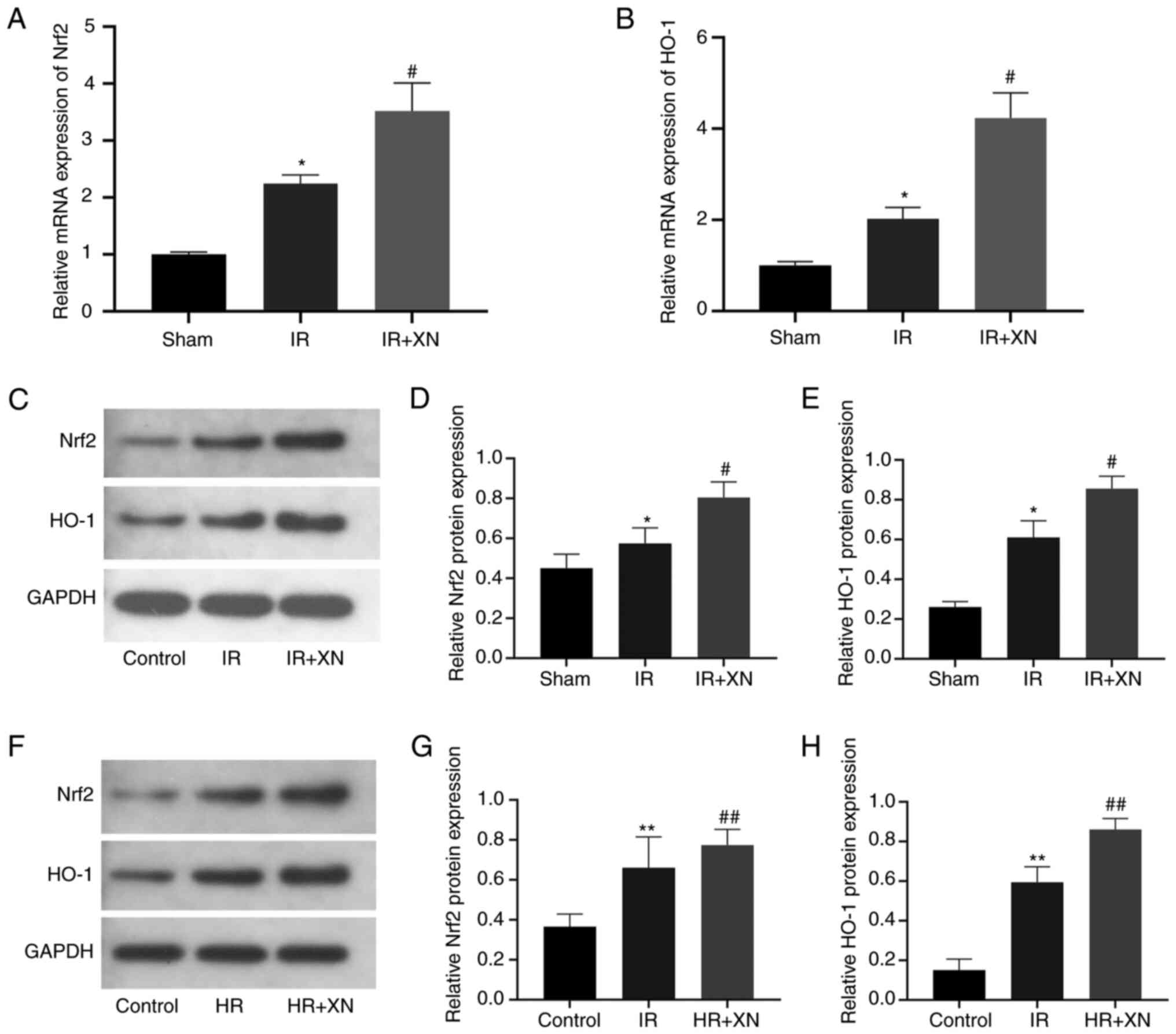
Loboda A, Damulewicz M, Pyza E, Jozkowicz
A and Dulak J: Role of Nrf2/HO-1 system in development, oxidative
stress response and diseases: An evolutionarily conserved
mechanism. Cell Mol Life Sci. 73:3221–3247. 2016.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
52
|
Qiao J, Ma H, Chen M and Bai J: Vitamin D
alleviates neuronal injury in cerebral ischemia-reperfusion via
enhancing the Nrf2/HO-1 antioxidant pathway to counteract
NLRP3-mediated pyroptosis. J Neuropathol Exp Neurol. 82:722–733.
2023.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
53
|
Li X, Yi L, Liu X, Chen X, Chen S and Cai
S: Isoquercitrin played a neuroprotective role in rats after
cerebral ischemia/reperfusion through Up-regulating neuroglobin and
anti-oxidative stress. Transplant Proc. 55:1751–1761.
2023.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|