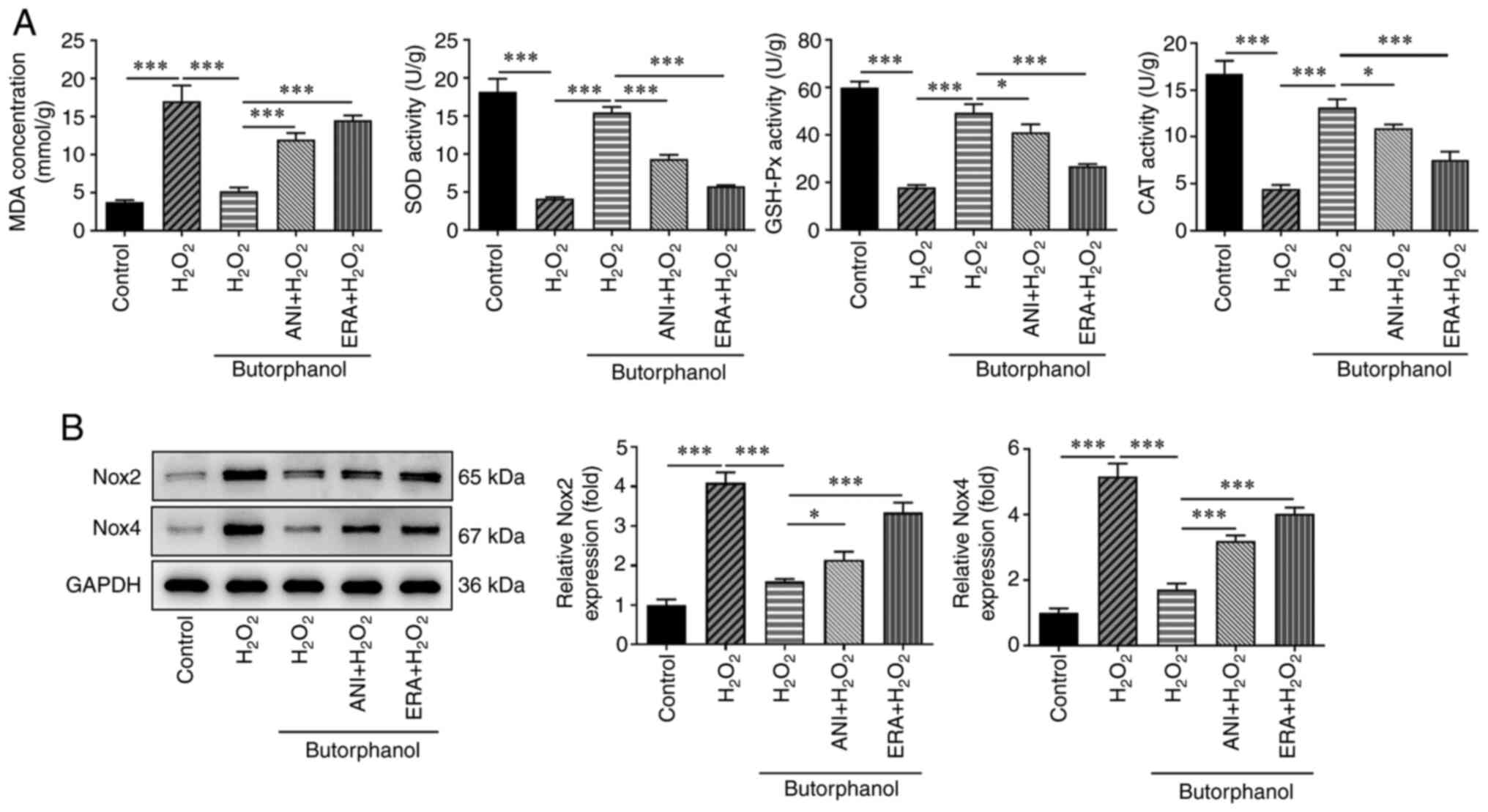
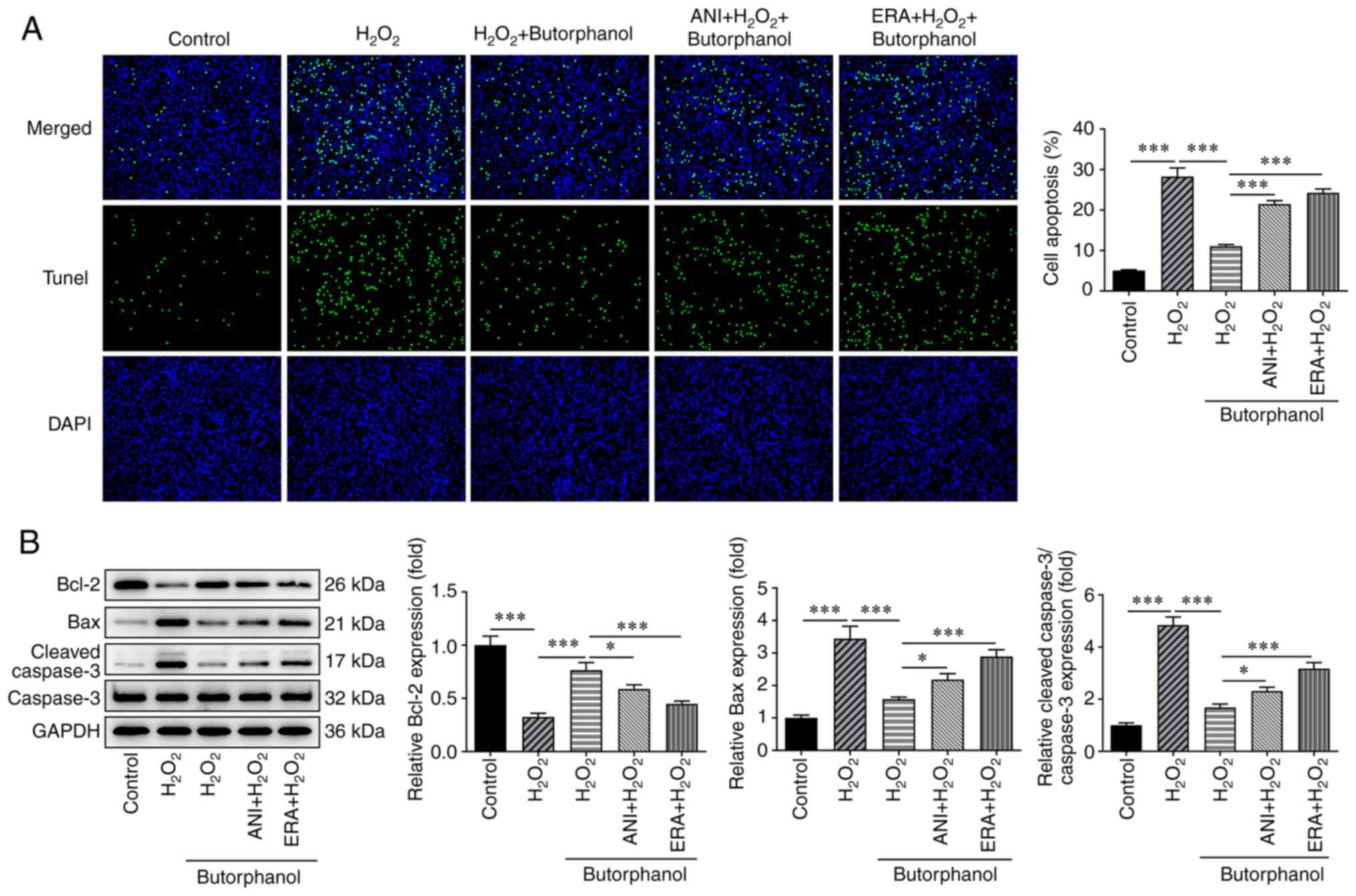
|
1
|
Luan G, Pan F, Bu L, Wu K, Wang A and Xu
X: Butorphanol promotes macrophage phenotypic transition to inhibit
inflammatory lung injury via κ receptors. Front Immunol.
12(692286)2021.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
2
|
Jose DE, Ganapathi P, Anish Sharma NG,
Shankaranarayana P, Aiyappa DS and Nazim M: Postoperative pain
relief with epidural buprenorphine versus epidural butorphanol in
laparoscopic hysterectomies: A comparative study. Anesth Essays
Res. 10:82–87. 2016.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
3
|
Yang Z, Wang L, Hu Y and Wang F:
Butorphanol protects PC12 cells against OGD/R-induced inflammation
and apoptosis. Mol Med Rep. 22:1969–1975. 2020.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
4
|
Wang B, Li Y, Shen Y, Xu Y and Zhang C:
Butorphanol inhibits the malignant biological behaviors of ovarian
cancer cells via down-regulating the expression of TMEFF1. Onco
Targets Ther. 13:10973–10981. 2020.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
5
|
Dugger BN and Dickson DW: Pathology of
neurodegenerative diseases. Cold Spring Harb Perspect Biol.
9(a028035)2017.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
6
|
Li J, Cao F, Yin HL, Huang ZJ, Lin ZT, Mao
N, Sun B and Wang G: Ferroptosis: Past, present and future. Cell
Death Dis. 11(88)2020.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
7
|
Reichert CO, de Freitas FA, Sampaio-Silva
J, Rokita-Rosa L, Barros PL, Levy D and Bydlowski SP: Ferroptosis
mechanisms involved in neurodegenerative diseases. Int J Mol Sci.
21(8765)2020.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
8
|
Wang X, Zhao J, Han Z and Tang F:
Protective effects of semen crotonis pulveratum on trinitrobenzene
sulphonic acid-induced colitis in rats and
H2O2-induced intestinal cell apoptosis in
vitro. Int J Mol Med. 35:1699–1707. 2015.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
9
|
Cai X, Zhu L, Chen X, Sheng Y, Guo Q, Bao
J and Xu J: X/XO or H2O2 induced IPEC-J2 cell as a new in vitro
model for studying apoptosis in post-weaning piglets.
Cytotechnology. 68:713–724. 2016.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
10
|
Rice ME: H2O2: A dynamic neuromodulator.
Neuroscientist. 17:389–406. 2011.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
11
|
Falcicchia C, Tozzi F, Arancio O,
Watterson DM and Origlia N: Involvement of p38 MAPK in synaptic
function and dysfunction. Int J Mol Sci. 21(5624)2020.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
12
|
Su AR, Qiu M, Li YL, Xu WT, Song SW, Wang
XH, Song HY, Zheng N and Wu ZW: BX-795 inhibits HSV-1 and HSV-2
replication by blocking the JNK/p38 pathways without interfering
with PDK1 activity in host cells. Acta Pharmacol Sin. 38:402–414.
2017.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
13
|
Lanna A, Gomes DC, Muller-Durovic B,
McDonnell T, Escors D, Gilroy DW, Lee JH, Karin M and Akbar AN: A
sestrin-dependent Erk-Jnk-p38 MAPK activation complex inhibits
immunity during aging. Nat Immunol. 18:354–363. 2017.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
14
|
Li J, Xu B, Chen Z, Zhou C, Liao L, Qin Y,
Yang C, Zhang X, Hu Z, Sun L, et al: PI3K/AKT/JNK/p38 signalling
pathway-mediated neural apoptosis in the prefrontal cortex of mice
is involved in the antidepressant-like effect of pioglitazone. Clin
Exp Pharmacol Physiol. 45:525–535. 2018.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
15
|
Wu K, Hu L and Hou J: Selective
suppression of Notch1 inhibits proliferation of renal cell
carcinoma cells through JNK/p38 pathway. Oncol Rep. 35:2795–2800.
2016.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
16
|
Ye F, Chai W, Xie M, Yang M, Yu Y, Cao L
and Yang L: HMGB1 regulates erastin-induced ferroptosis via
RAS-JNK/p38 signaling in HL-60/NRASQ61L cells. Am J
Cancer Res. 9:730–739. 2019.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
17
|
Zhang H, Jiao W, Cui H, Sun Q and Fan H:
Combined exposure of alumina nanoparticles and chronic stress
exacerbates hippocampal neuronal ferroptosis via activating
IFN-γ/ASK1/JNK signaling pathway in rats. J Hazard Mater.
411(125179)2021.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
18
|
Aminzadeh A, Dehpour AR, Safa M,
Mirzamohammadi S and Sharifi AM: Investigating the protective
effect of lithium against high glucose-induced neurotoxicity in
PC12 cells: Involvements of ROS, JNK and P38 MAPKs, and apoptotic
mitochondria pathway. Cell Mol Neurobiol. 34:1143–1150.
2014.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
19
|
Reith W: Neurodegenerative diseases.
Radiologe. 58:241–258. 2018.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar : (In German).
|
|
20
|
Radi E, Formichi P, Battisti C and
Federico A: Apoptosis and oxidative stress in neurodegenerative
diseases. J Alzheimers Dis. 42 (Suppl 3):S125–S152. 2014.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
21
|
Erekat NS: Apoptosis and its therapeutic
implications in neurodegenerative diseases. Clin Anat. 35:65–78.
2022.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
22
|
Singh A, Kukreti R, Saso L and Kukreti S:
Oxidative stress: A key modulator in neurodegenerative diseases.
Molecules. 24(1583)2019.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
23
|
Wu C, Zhao W, Yu J, Li S, Lin L and Chen
X: Induction of ferroptosis and mitochondrial dysfunction by
oxidative stress in PC12 cells. Sci Rep. 8(574)2018.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
24
|
Tsukamoto A, Iimuro M, Sato R, Yamazaki J
and Inomata T: Effect of midazolam and butorphanol premedication on
inhalant isoflurane anesthesia in mice. Exp Anim. 64:139–145.
2015.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
25
|
Bu X, Xia W, Wang X, Lu S and Gao Y:
Butylphthalide inhibits nerve cell apoptosis in cerebral infarction
rats via the JNK/p38 MAPK signaling pathway. Exp Ther Med.
21(565)2021.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
26
|
Lv WP, Li MX and Wang L: Peroxiredoxin 1
inhibits lipopolysaccharide-induced oxidative stress in lung tissue
by regulating P38/JNK signaling pathway. Eur Rev Med Pharmacol Sci.
21:1876–1883. 2017.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
27
|
Li WW, Gao XM, Wang XM, Guo H and Zhang
BL: Icariin inhibits hydrogen peroxide-induced toxicity through
inhibition of phosphorylation of JNK/p38 MAPK and p53 activity.
Mutat Res. 708:1–10. 2011.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
28
|
Huang LH, Li J, Gu JP, Qu MX, Yu J and
Wang ZY: Butorphanol attenuates myocardial ischemia reperfusion
injury through inhibiting mitochondria-mediated apoptosis in mice.
Eur Rev Med Pharmacol Sci. 22:1819–1824. 2018.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|