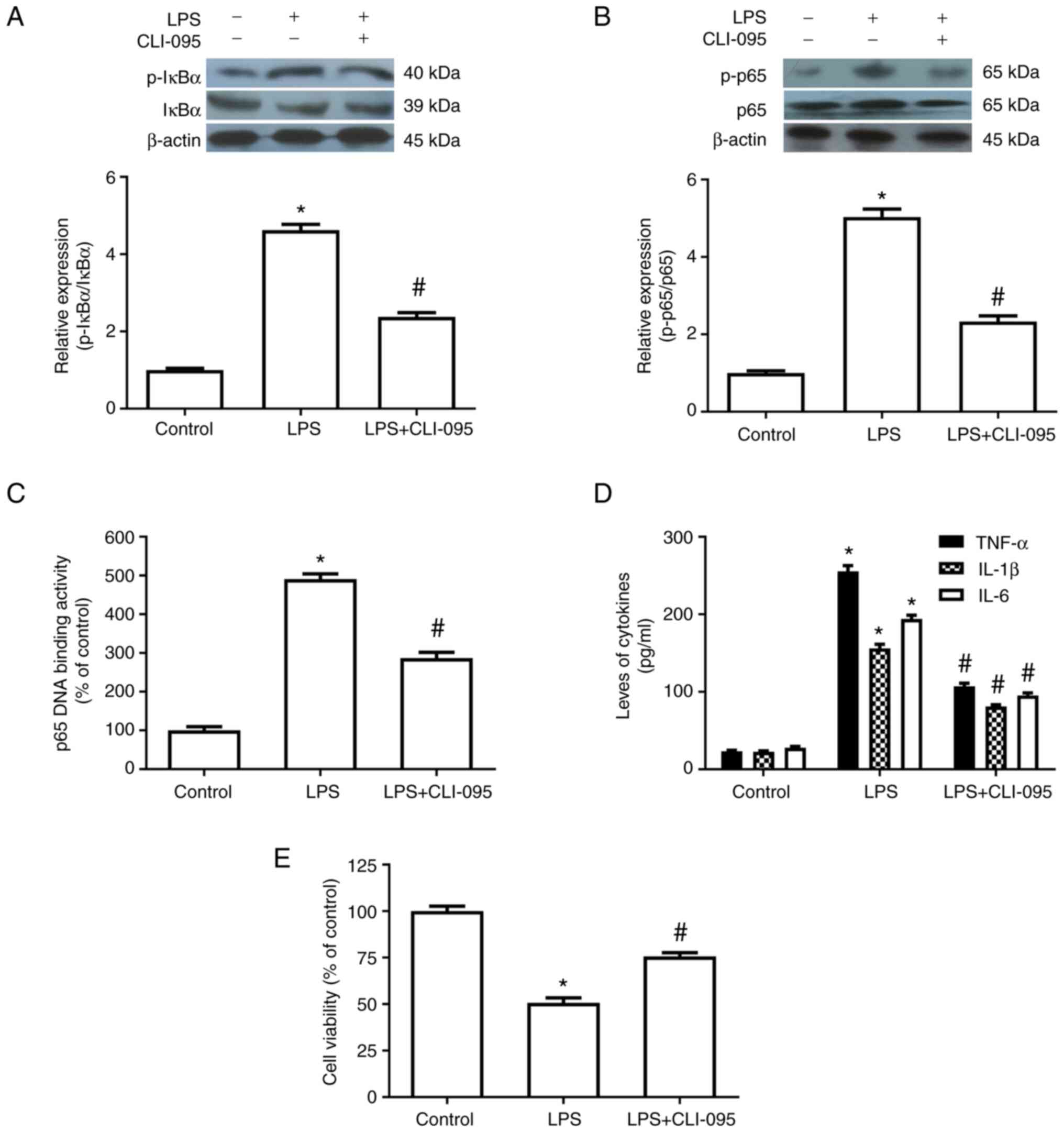
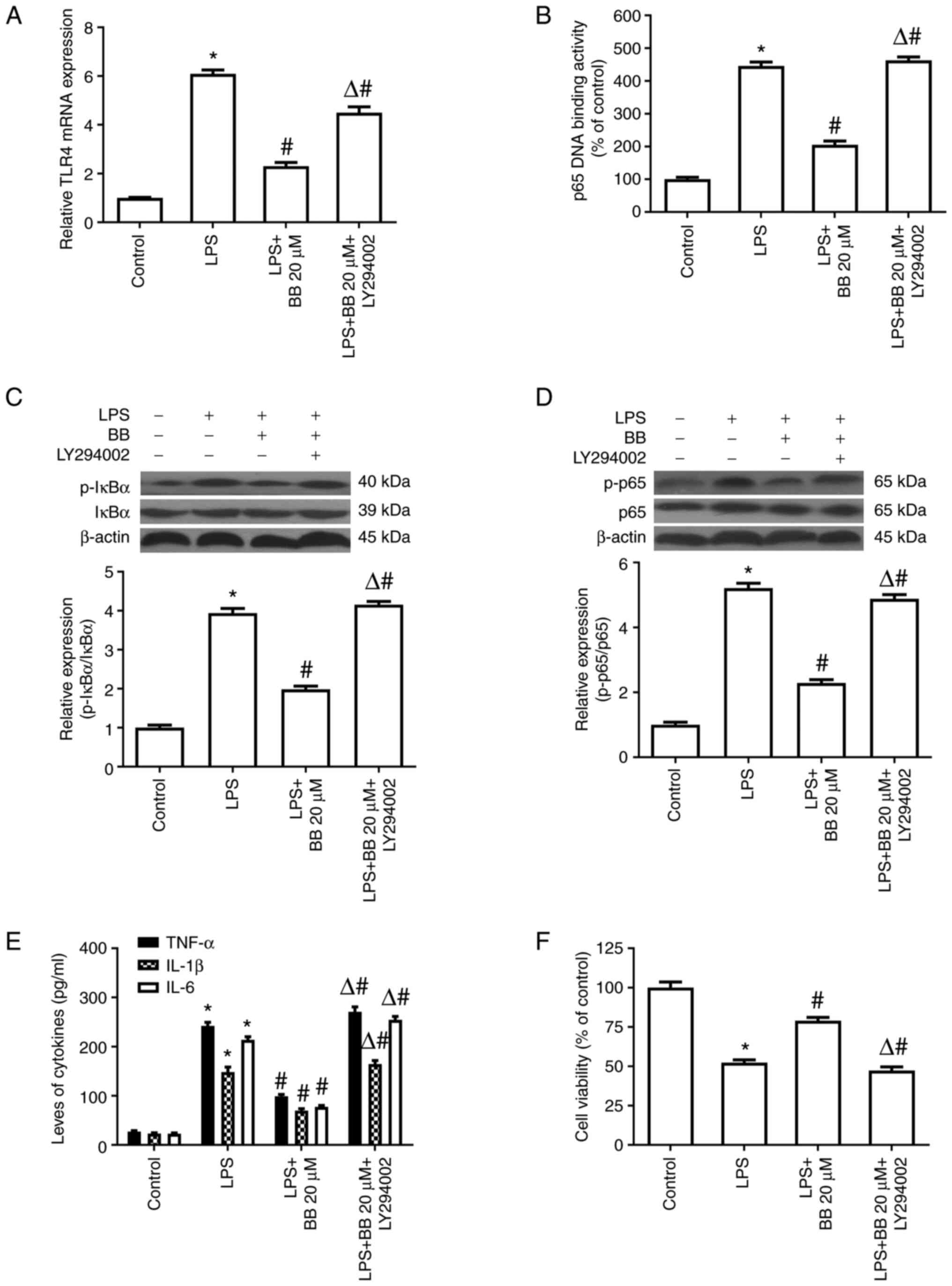
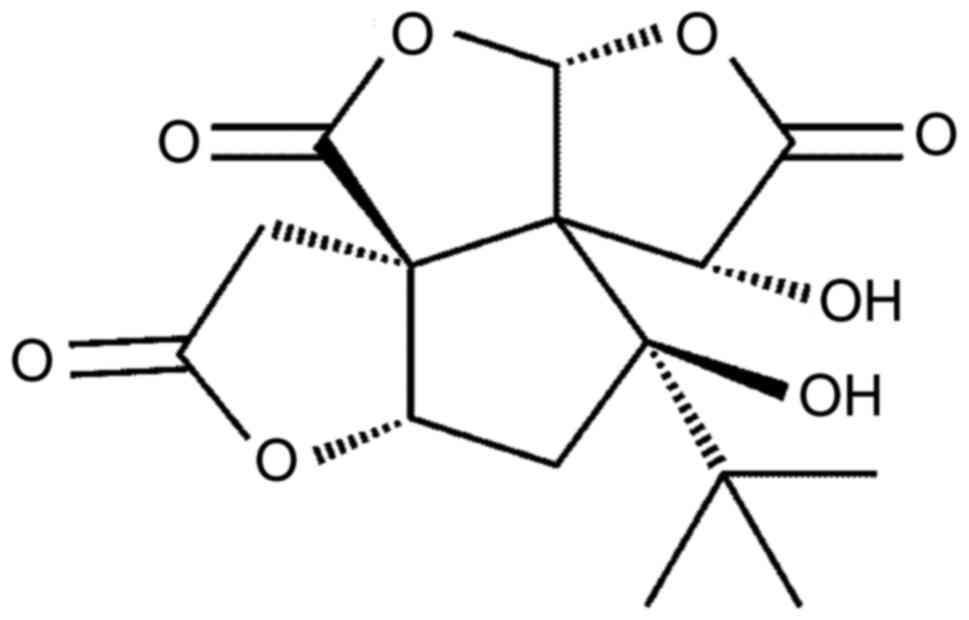
|
1
|
Szabo G and Csak T: Inflammasomes in liver
diseases. J Hepatol. 57:642–654. 2012.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
2
|
Yu S, Wang Y, Jing L, Claret FX, Li Q,
Tian T, Liang X, Ruan Z, Jiang L, Yao Y, et al: Autophagy in the
‘inflammation-carcinogenesis' pathway of liver and HCC
immunotherapy. Cancer Lett. 411:82–89. 2017.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
3
|
Lam P, Cheung F, Tan HY, Wang N, Yuen MF
and Feng Y: Hepatoprotective effects of Chinese medicinal herbs: A
focus on anti-inflammatory and anti-oxidative activities. Int J Mol
Sci. 17(465)2016.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
4
|
Li H, Huang MH, Jiang JD and Peng ZG:
Hepatitis C: From inflammatory pathogenesis to
anti-inflammatory/hepatoprotective therapy. World J Gastroenterol.
24:5297–5311. 2018.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
5
|
Seki E and Schwabe RF: Hepatic
inflammation and fibrosis: Functional links and key pathways.
Hepatology. 61:1066–1079. 2015.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
6
|
Liu J, Abate W, Xu J, Corry D, Kaul B and
Jackson SK: Three-dimensional spheroid cultures of A549 and HepG2
cells exhibit different lipopolysaccharide (LPS) receptor
expression and LPS-induced cytokine response compared with
monolayer cultures. Innate Immun. 17:245–255. 2011.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
7
|
Ju C and Mandrekar P: Macrophages and
alcohol-related liver inflammation. Alcohol Res. 37:251–262.
2015.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
8
|
Park BJ, Lee YJ and Lee HR: Chronic liver
inflammation: Clinical implications beyond alcoholic liver disease.
World J Gastroentero. 20:2168–2175. 2014.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
9
|
Wang Y, Zhou X, Zhao D, Wang X, Gurley EC,
Liu R, Li X, Hylemon PB, Chen W and Zhou H: Berberine inhibits free
fatty acid and LPS-induced inflammation via modulating ER stress
response in macrophages and hepatocytes. PLoS One.
15(e0232630)2020.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
10
|
Lu S, Duan M, Guo Z, Zhou Y, Wu D, Zhang
X, Wang Y, Ye C, Ju R, Li J, et al: Carboxyamidotriazole exerts
anti-inflammatory activity in lipopolysaccharide-induced RAW264.7
macrophages by inhibiting NF-κB and MAPKs pathways. Exp Ther Med.
20:1455–1466. 2020.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
11
|
Huang XY, Ansari AR, Huang HB, Zhao X, Li
NY, Sun ZJ, Peng KM, Zhong J and Liu HZ: Lipopolysaccharide
mediates immuno-pathological alterations in young chicken liver
through TLR4 signaling. BMC Immunol. 18(12)2017.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
12
|
Zhang J, Wieser A, Lin H, Li H, Hu M,
Behrens IK, Schiergens TS, Gerbes AL and Steib CJ: Kupffer cell
activation by different microbial lysates: Toll-like receptor-2
plays pivotal role on thromboxane A2 production in mice and humans.
Eur J Immunol. 50:1988–1997. 2020.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
13
|
Zhang X, Jiang W, Zhou AL, Zhao M and
Jiang DR: Inhibitory effect of oxymatrine on hepatocyte apoptosis
via TLR4/PI3K/Akt/GSK-3β signaling pathway. World J Gastroenterol.
23:3839–3849. 2017.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
14
|
Kim MS, Lee S, Jung N, Lee K, Choi J, Kim
SH, Jun J, Lee WM, Chang Y and Kim D: The vitamin D analogue
paricalcitol attenuates hepaticischemia/reperfusion injury through
down-regulation of Toll-like receptor 4 signaling in rats. Arch Med
Sci. 13:459–469. 2017.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
15
|
Cho HI, Hong JM, Choi JW, Choi HS, Kwak
JH, Lee DU, Kook Lee S and Lee SM: β-Caryophyllene alleviates
D-galactosamine and lipopolysaccharide-induced hepatic injury
through suppression of the TLR4 and RAGE signaling pathways. Eur J
Pharmacol. 764:613–621. 2015.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
16
|
Standiford LR, Standiford TJ, Newstead MJ,
Zeng X, Ballinger MN, Kovach MA, Reka AK and Bhan U: TLR4-dependent
GM-CSF protects against lung injury in Gram-negative bacterial
pneumonia. Am J Physiol Lung Cell Mol Physiol. 302:L447–L454.
2012.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
17
|
Li Y, Yin S, Chen Y, Zhang Q, Huang R, Jia
B, Jie W, Yao K, Wang J, Tong X, et al: Hepatitis B virus-induced
hyperactivation of B cells in chronic hepatitis B patients via
TLR4. J Cell Mol Med. 24:6096–6106. 2020.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
18
|
Tian J, Zhao Y, Wang L and Li L: Role of
TLR4/MyD88/NF-κB signaling in heart and liver-related complications
in a rat model of type 2 diabetes mellitus. J Int Med Res.
49(300060521997590)2021.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
19
|
Qu Y, Li X, Xu F, Zhao S, Wu X, Wang Y and
Xie J: Kaempferol alleviates murine experimental colitis by
restoring gut microbiota and inhibiting the LPS-TLR4-NF-κB axis.
Front Immunol. 12(679897)2021.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
20
|
Mitchell S, Vargas J and Hoffmann A:
Signaling via the NFκB system. Wiley Interdiscip Rev Syst Biol Med.
8:227–241. 2016.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
21
|
Sun X, Li P, Qu X and Liu W: Isovitexin
alleviates acute gouty arthritis in rats by inhibiting inflammation
via the TLR4/MyD88/NF-κB pathway. Pharm Biol. 59:1326–1333.
2021.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
22
|
Zhang S, Feng Z, Gao W, Duan Y, Fan G,
Geng X, Wu B, Li K, Liu K and Peng C: Aucubin attenuates liver
ischemia-reperfusion injury by inhibiting the HMGB1/TLR-4/NF-κB
signaling pathway, oxidative stress, and apoptosis. Front
Pharmacol. 11(544124)2020.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
23
|
Sherif IO and Al-Shaalan NH: Vildagliptin
attenuates hepatic ischemia/reperfusion injury via the TLR4/NF-κB
signaling pathway. Oxid Med Cell Longev.
2018(3509091)2018.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
24
|
Liu H, Zhang W, Dong S, Song L, Zhao S, Wu
C, Wang X, Liu F, Xie J, Wang J and Wang Y: Protective effects of
sea buckthorn polysaccharide extracts against LPS/d-GalN-induced
acute liver failure in mice via suppressing TLR4-NF-κB signaling. J
Ethnopharmacol. 176:69–78. 2015.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
25
|
Lai L, Chen Y, Tian X, Li X, Zhang X, Lei
J, Bi Y, Fang B and Song X: Artesunate alleviates hepatic fibrosis
induced by multiple pathogenic factors and inflammation through the
inhibition of LPS/TLR4/NF-κB signaling pathway in rats. Eur J
Pharmacol. 765:234–241. 2015.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
26
|
Zahid M, Arif M, Rahman MA and Mujahid M:
Hepatoprotective and antioxidant activities of Annona squamosa seed
extract against alcohol-induced liver injury in Sprague Dawley
rats. Drug Chem Toxicol. 43:588–594. 2020.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
27
|
Jiang M, Li J, Peng Q, Liu Y, Liu W, Luo
C, Peng J, Li J, Yung KK and Mo Z: Neuroprotective effects of
bilobalide on cerebral ischemia and reperfusion injury are
associated with inhibition of pro-inflammatory mediator production
and down-regulation of JNK1/2 and p38 MAPK activation. J
Neuroinflammation. 11(167)2014.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
28
|
Priyanka A, Nisha VM, Anusree SS and Raghu
KG: Bilobalide attenuates hypoxia induced oxidative stress,
inflammation, and mitochondrial dysfunctions in 3T3-L1 adipocytes
via its antioxidant potential. Free Radic Res. 48:1206–1217.
2014.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
29
|
Priyanka A, Sindhu G, Shyni GL, Preetha
Rani MR, Nisha VM and Raghu KG: Bilobalide abates inflammation,
insulin resistance and secretion of angiogenic factors induced by
hypoxia in 3T3-L1 adipocytes by controlling NF-κB and JNK
activation. Int Immunopharmacol. 42:209–217. 2017.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
30
|
Zhou JM, Gu SS, Mei WH, Zhou J, Wang ZZ
and Xiao W: Ginkgolides and bilobalide protect BV2 microglia cells
against OGD/reoxygenation injury by inhibiting TLR2/4 signaling
pathways. Cell Stress Chaperones. 21:1037–1053. 2016.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
31
|
Norikura T, Mukai Y, Fujita S, Mikame K,
Funaoka M and Sato S: Lignophenols decrease oleate-induced
apolipoprotein-B secretion in HepG2 cells. Basic Clin Pharmacol
Toxicol. 107:813–817. 2010.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
32
|
Wollborn J, Wunder C, Stix J, Neuhaus W,
Bruno RR, Baar W, Flemming S, Roewer N, Schlegel N and Schick MA:
Phosphodiesterase-4 inhibition with rolipram attenuates
hepatocellular injury in hyperinflammation in vivo and in vitro
without influencing inflammation and HO-1 expression. J Pharmacol
Pharmacother. 6:13–23. 2015.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
33
|
Liu M, Fang G, Yin S, Zhao X, Zhang C, Li
J and Liu Z: Caffeic acid prevented LPS-induced injury of primary
bovine mammary epithelial cells through inhibiting NF-κB and MAPK
activation. Mediators Inflamm. 2019(1897820)2019.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
34
|
Xiong W, Ma H, Zhang Z, Jin M, Wang J, Xu
Y and Wang Z: The protective effect of icariin and phosphorylated
icariin against LPS-induced intestinal epithelial cells injury.
Biomed Pharmacother. 118(109246)2019.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
35
|
Livak KJ and Schmittgen TD: Analysis of
relative gene expression data using real-time quantitative PCR and
the 2(-Delta Delta C(T)) method. Methods. 25:402–408.
2001.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
36
|
Latruffe N: Natural products and
inflammation. Molecules. 22(120)2017.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
37
|
Amaral-Machado L, Oliveira WN, Rodrigues
VM, Albuquerque NA, Alencar ÉN and Egito EST: Could natural
products modulate early inflammatory responses, preventing acute
respiratory distress syndrome in COVID-19-confirmed patients?
Biomed Pharmacother. 134(111143)2021.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
38
|
Beutler JA: Natural products as a
foundation for drug discovery. Curr Protoc Pharmacol.
86(e67)2019.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
39
|
LeBlanc JF, Wiseman D, Lakatos PL and
Bessissow T: Elderly patients with inflammatory bowel disease:
Updated review of the therapeutic landscape. World J Gastroenterol.
25:4158–4171. 2019.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
40
|
Chale-Dzul J, Pérez-Cabeza de Vaca R,
Quintal-Novelo C, Olivera-Castillo L and Moo-Puc R:
Hepatoprotective effect of a fucoidan extract from Sargassum
fluitans Borgesen against CCl4-induced toxicity in rats.
Int J Biol Macromol. 145:500–509. 2020.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
41
|
Feng Z, Sun Q, Chen W, Bai Y, Hu D and Xie
X: The neuroprotective mechanisms of ginkgolides and bilobalide in
cerebral ischemic injury: A literature review. Mol Med.
25(57)2019.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
42
|
Bu S, Yuan CY, Xue Q, Chen Y and Cao F:
Bilobalide suppresses adipogenesis in 3T3-L1 adipocytes via the
AMPK signaling pathway. Molecules. 24(3503)2019.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
43
|
Li Y, Jiang J, Tong L, Gao T, Bai L, Xue
Q, Xing J, Wang Q, Lyu H, Cai M and Sun Z: Bilobalide protects
against ischemia/reperfusion-induced oxidative stress and
inflammatory responses via the MAPK/NF-κB pathways in rats. BMC
Musculoskelet Disord. 21(449)2020.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
44
|
Maerz S, Liu CH, Guo W and Zhu YZ:
Anti-ischaemic effects of bilobalide on neonatal rat cardiomyocytes
and the involvement of the platelet-activating factor receptor.
Biosci Rep. 31:439–447. 2011.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
45
|
Zhang Y and Zhai H: Bilobalide assuages
morphine-induced addiction in hippocampal neuron cells through
upregulation of microRNA-101. J Biochem Mol Toxicol.
34(e22493)2020.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
46
|
Hui S and Fangyu W: Protective effects of
bilobalide against ethanol-induced gastric ulcer in vivo/vitro.
Biomed Pharmacother. 85:592–600. 2017.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
47
|
Sui RX, Miao Q, Wang J, Wang Q, Song LJ,
Yu JW, Cao L, Xiao W, Xiao BG and Ma CG: Protective and therapeutic
role of Bilobalide in cuprizone-induced demyelination. Int
Immunopharmacol. 66:69–81. 2019.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
48
|
Al-Oqail MM, Farshori NN, Al-Sheddi ES,
Al-Massarani SM, Siddiqui MA and Al-Khedhairy AA: Petroselinum
sativum protects HepG2 cells from cytotoxicity and oxidative stress
induced by hydrogen peroxide. Mol Biol Rep. 47:2771–2780.
2020.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
49
|
Dey D, Chaskar S, Bhatt N and Chitre D:
Hepatoprotective activity of BV-7310, a proprietary herbal
formulation of phyllanthus niruri, tephrosia purpurea, boerhavia
diffusa, and andrographis paniculata, in alcohol-induced HepG2
cells and alcohol plus a haloalkane, CCl4, induced liver
damage in rats. Evid Based Complement Alternat Med.
2020(6428906)2020.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
50
|
Ou TT, Kuo CY, Chyau CC, Lee HJ, Peng JS
and Wang CJ: Improvement of lipopolysaccharide-induced hepatic
injuries and inflammation with mulberry extracts. J Sci Food Agric.
93:1880–1886. 2013.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
51
|
Hua J, Yin N, Yang B, Zhang J, Ding J, Fan
Y and Hu G: Ginkgolide B and bilobalide ameliorate neural cell
apoptosis in α-synuclein aggregates. Biomed Pharmacother.
96:792–797. 2017.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
52
|
Cao A and Li X: Bilobalide protects H9c2
cell from oxygen-glucose-deprivation-caused damage through
upregulation of miR-27a. Artif Cells Nanomed Biotechnol.
47:2980–2988. 2019.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
53
|
Mao D, Li H, Zhang L, Xu J, Yu C and Zhang
Q: Bilobalide alleviates IL-17-induced inflammatory injury in ATDC5
cells by downregulation of microRNA-125a. J Biochem Mol Toxicol.
33(e22405)2019.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
54
|
Zhan X, Zhang J, Chen H, Liu L, Zhou Y,
Zheng T, Li S, Zhang Y, Zheng B and Gong Q: . Capsaicin alleviates
acetaminophen-induced acute liver injury in mice. Clin Immunol.
220(108578)2020.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
55
|
Du YC, Lai L, Zhang H, Zhong FR, Cheng HL,
Qian BL, Tan P, Xia XM and Fu WG: Kaempferol from Penthorum
chinense Pursh suppresses HMGB1/TLR4/NF-κB signaling and NLRP3
inflammasome activation in acetaminophen-induced hepatotoxicity.
Food Funct. 11:7925–7934. 2020.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
56
|
Del Campo JA, Gallego P and Grande L: Role
of inflammatory response in liver diseases: Therapeutic strategies.
World J Hepatol. 10:1–7. 2018.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
57
|
Xu R, Zhang Z and Wang FS: Liver fibrosis:
Mechanisms of immune-mediated liver injury. Cell Mol Immunol.
9:296–301. 2012.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
58
|
Liu M, Xu Y, Han X, Yin L, Xu L, Qi Y,
Zhao Y, Liu K and Peng J: Dioscin alleviates alcoholic liver
fibrosis by attenuating hepatic stellate cell activation via the
TLR4/MyD88/NF-κB signaling pathway. Sci Rep.
5(18038)2015.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
59
|
Chen Y, Zeng Z, Shen X, Wu Z, Dong Y and
Cheng JC: MicroRNA-146a-5p negatively regulates pro-inflammatory
cytokine secretion and cell activation in lipopolysaccharide
stimulated human hepatic stellate cells through inhibition of
toll-Like receptor 4 signaling pathways. Int J Mol Sci.
17(1076)2016.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
60
|
Wu G, Yang Q, Yu Y, Lin S, Feng Y, Lv Q,
Yang J and Hu J: Taurine inhibits Kupffer cells activation induced
by lipopolysaccharide in alcoholic liver damaged rats. Adv Exp Med
Biol 975 Pt. 2:789–800. 2017.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
61
|
Song S, Chu L, Liang H, Chen J, Liang J,
Huang Z, Zhang B and Chen X: Protective effects of dioscin against
doxorubicin-induced hepatotoxicity via regulation of
Sirt1/FOXO1/NF-κb signal. Front Pharmacol. 10(1030)2019.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
62
|
Fu T, Wang S, Liu J, Cai E, Li H, Li P and
Zhao Y: Protective effects of alpha-mangostin against
acetaminophen-induced acute liver injury in mice. Eur J Pharmacol.
827:173–180. 2018.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
63
|
Lu L, Wu C, Lu BJ, Xie D, Wang Z, Bahaji
Azami NL, An YT, Wang HJ, Ye G and Sun MY: BabaoDan cures hepatic
encephalopathy by decreasing ammonia levels and alleviating
inflammation in rats. J Ethnopharmacol. 249(112301)2020.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
64
|
Liu Q, Jin Z, Xu Z, Yang H, Li L, Li G, Li
F, Gu S, Zong S, Zhou J, et al: Antioxidant effects of ginkgolides
and bilobalide against cerebral ischemia injury by activating the
Akt/Nrf2 pathway in vitro and in vivo. Cell Stress Chaperones.
24:441–452. 2019.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
65
|
Qin YR, Ma CQ, Wang DP, Zhang QQ, Liu MR,
Zhao HR, Jiang JH and Fang Q: Bilobalide alleviates
neuroinflammation and promotes autophagy in Alzheimer's disease by
upregulating lincRNA-p21. Am J Transl Res. 13:2021–2040.
2021.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
66
|
Zheng Y, Wu Z, Yi F, Orange M, Yao M, Yang
B, Liu J and Zhu H: By Activating Akt/eNOS Bilobalide B inhibits
autophagy and promotes angiogenesis following focal cerebral
ischemia reperfusion. Cell Physiol Biochem. 47:604–616.
2018.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
67
|
Adcock IM: Transcription factors as
activators of gene transcription: AP-1 and NF-kappa B. Monaldi Arch
Chest Dis. 52:178–186. 1997.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
68
|
Mitchell JP and Carmody RJ: NF-κB and the
transcriptional control of inflammation. Int Rev Cell Mol Biol.
335:41–84. 2018.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
69
|
Li Q and Verma IM: NF-kappaB regulation in
the immune system. Nat Rev Immunol. 2:725–734. 2002.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
70
|
Pahl HL: Activators and target genes of
Rel/NF-kappaB transcription factors. Oncogene. 18:6853–6866.
1999.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
71
|
Freitas RHCN and Fraga CAM: NF-κB-IKKβ
pathway as a target for drug development: Realities, challenges and
perspectives. Curr Drug Targets. 19:1933–1942. 2018.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
72
|
Lin TH, Pajarinen J, Lu L, Nabeshima A,
Cordova LA, Yao Z and Goodman SB: NF-κB as a therapeutic target in
inflammatory-associated bone diseases. Adv Protein Chem Struct
Biol. 107:117–154. 2017.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
73
|
Fouad D, Badr A and Attia HA:
Hepatoprotective activity of raspberry ketone is mediated via
inhibition of the NF-κB/TNF-α/caspase axis and mitochondrial
apoptosis in chemically induced acute liver injury. Toxicol Res
(Camb). 8:663–676. 2019.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
74
|
Amen Y, Sherif AE, Shawky NM, Abdelrahman
RS, Wink M and Sobeh M: Grape-leaf extract attenuates
alcohol-induced liver injury via interference with NF-κB signaling
pathway. Biomolecules. 10(558)2020.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
75
|
Wu B, Wang R, Li S, Wang Y, Song F, Gu Y
and Yuan Y: Antifibrotic effects of Fraxetin on carbon
tetrachloride-induced liver fibrosis by targeting NF-κB/IκBα, MAPKs
and Bcl-2/Bax pathways. Pharmacol Rep. 71:409–416. 2019.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
76
|
Zhang H, Cao N, Yang Z, Fang X, Yang X, Li
H, Hong Z and Ji Z: Bilobalide alleviated dextran sulfate
sodium-induced experimental colitis by inhibiting M1 macrophage
polarization through the NF-κB signaling pathway. Front Pharmacol.
11(718)2020.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
77
|
Takeuchi O and Akira S: Pattern
recognition receptors and inflammation. Cell. 140:805–820.
2010.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
78
|
Guven-Maiorov E, Keskin O, Gursoy A and
Nussinov R: A structural view of negative regulation of the
toll-like receptor-mediated inflammatory pathway: Biophys. J.
109:1214–1226. 2015.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
79
|
Chen Y, Lu Y, Pei C, Liang J, Ding P, Chen
S and Hou SZ: Monotropein alleviates secondary liver injury in
chronic colitis by regulating TLR4/NF-κB signaling and NLRP3
inflammasome. Eur J Pharmacol. 883(173358)2020.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
80
|
Zhang M, Xue Y, Chen H, Meng L, Chen B,
Gong H, Zhao Y and Qi R: Resveratrol inhibits MMP3 and MMP9
expression and secretion by suppressing TLR4/NF-κB/STAT3 activation
in Ox-LDL-greated HUVECs. Oxid Med Cell Longev.
2019(9013169)2019.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
81
|
Tao Y, Wang Y, Wang X, Wang C, Bao K, Ji
L, Jiang G and Hong M: Calycosin suppresses epithelial derived
initiative key factors and maintains epithelial barrier in allergic
inflammation via TLR4 mediated NF-κB pathway. Cell Physiol Biochem.
44:1106–1119. 2017.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
82
|
Ke B, Shen XD, Ji H, Kamo N, Gao F,
Freitas MC, Busuttil RW and Kupiec-Weglinski JW: HO-1-STAT3 axis in
mouse liver ischemia/reperfusion injury: Regulation of TLR4 innate
responses through PI3K/PTEN signaling. J Hepatol. 56:359–366.
2012.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
83
|
Kim SY, Jeong E, Joung SM and Lee JY:
PI3K/Akt contributes to increased expression of Toll-like receptor
4 in macrophages exposed to hypoxic stress. Biochem Biophys Res
Commun. 419:466–471. 2012.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
84
|
Tsukamoto K, Hazeki K, Hoshi M, Nigorikawa
K, Inoue N, Sasaki T and Hazeki O: Critical roles of the p110 beta
subtype of phosphoinositide 3-kinasein lipopolysaccharide-induced
Akt activation and negative regulation of nitrite production in RAW
264.7 cells. J Immunol. 180:2054–2061. 2008.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
85
|
Dong H, Zhang X, Dai X, Lu S, Gui B, Jin
W, Zhang S, Zhang S and Qian Y: Lithium ameliorates
lipopolysaccharide-induced microglial activation via inhibition of
toll-like receptor 4 expression by activating the PI3K/Akt/FoxO1
pathway. J Neuroinflammation. 11(140)2014.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
86
|
Shi C, Wu F, Yew DT, Xu J and Zhu Y:
Bilobalide prevents apoptosis through activation of the PI3K/Akt
pathway in SH-SY5Y cells. Apoptosis. 15:715–727. 2010.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
87
|
Sun H, Zhu X, Cai W and Qiu L: Hypaphorine
attenuates lipopolysaccharide-induced endothelial inflammation via
regulation of TLR4 and PPAR-γ dependent on PI3K/Akt/mTOR signal
pathway. Int J Mol Sci. 18(844)2017.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
88
|
Zhaocheng J, Jinfeng L, Luchang Y, Yequan
S, Feng L and Kai W: Ginkgolide A inhibits
lipopolysaccharide-induced inflammatory response in human coronary
artery endothelial cells via downregulation of TLR4-NF-κB signaling
through PI3K/Akt pathway. Pharmazie. 71:588–591. 2016.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|