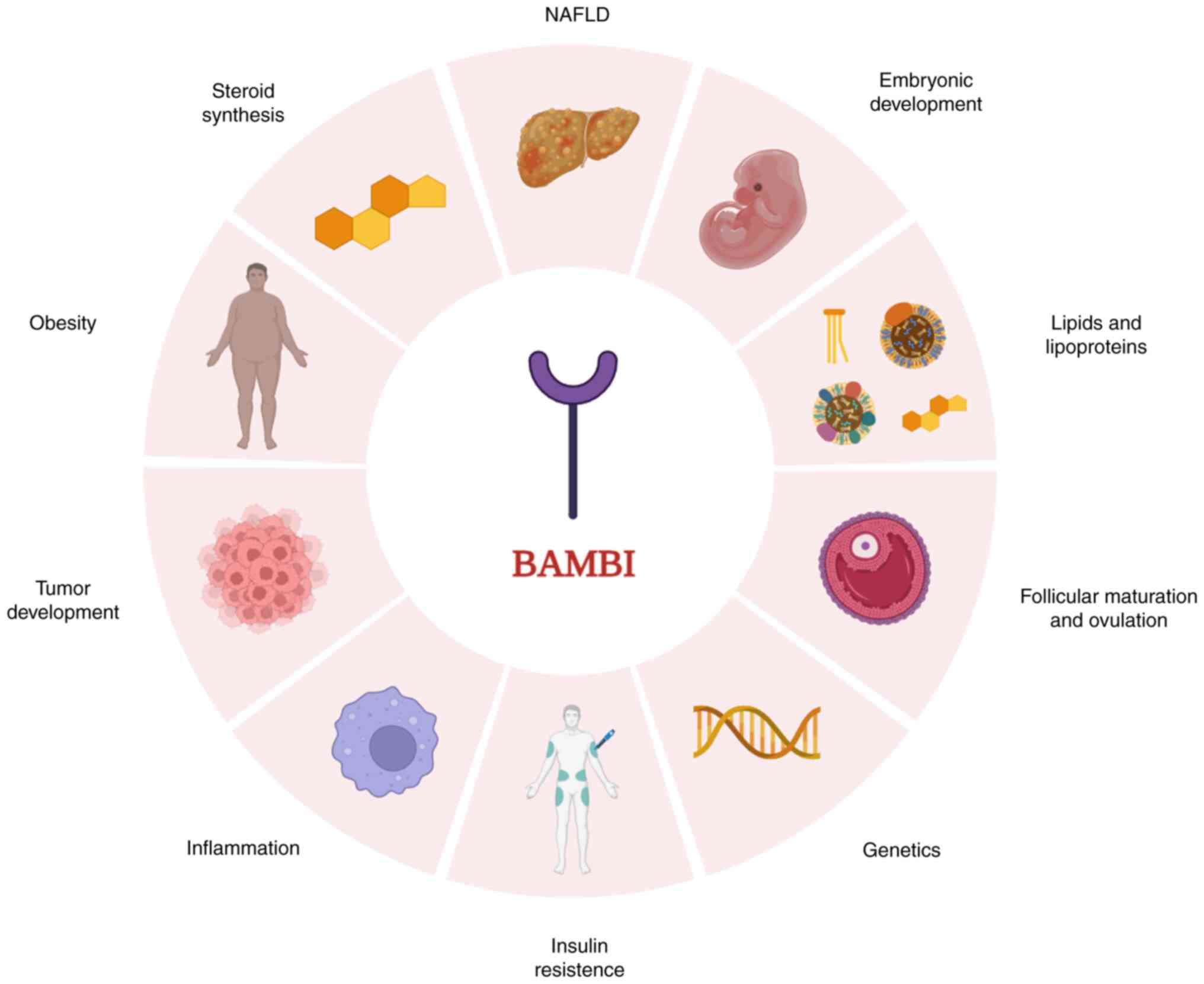
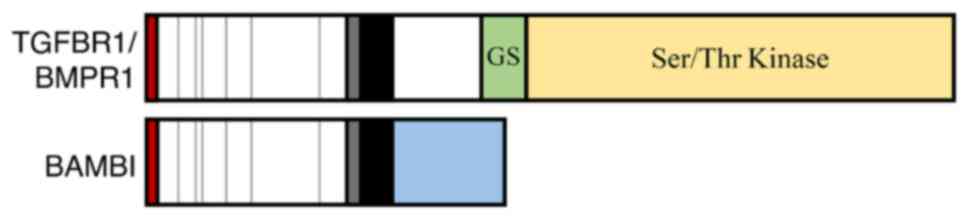
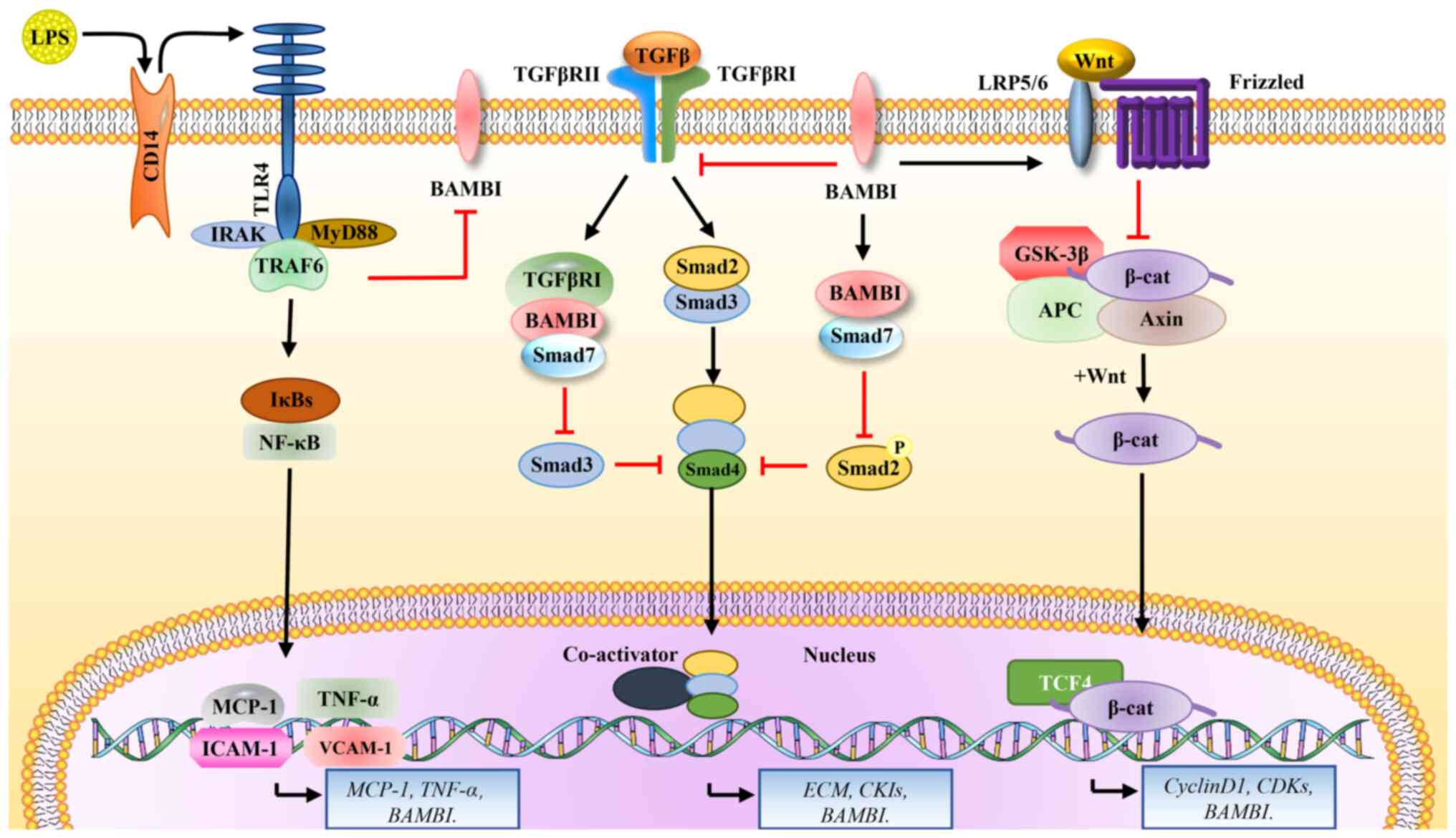
|
1
|
Onichtchouk D, Chen YG, Dosch R, Gawantka
V, Delius H, Massagué J and Niehrs C: Silencing of TGF-beta
signalling by the pseudoreceptor BAMBI. Nature. 401:480–485.
1999.PubMed/NCBI View
Article : Google Scholar
|
|
2
|
Degen WG, Weterman MA, van Groningen JJ,
Cornelissen IM, Lemmers JP, Agterbos MA, Geurts van Kessel A, Swart
GW and Bloemers HP: Expression of nma, a novel gene, inversely
correlates with the metastatic potential of human melanoma cell
lines and xenografts. Int J Cancer. 65:460–465. 1996.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
3
|
Knight C, Simmons D, Gu TT,
Gluhak-Heinrich J, Pavlin D, Zeichner-David M and MacDougall M:
Cloning, characterization, and tissue expression pattern of mouse
Nma/BAMBI during odontogenesis. J Dent Res. 80:1895–1902.
2001.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
4
|
Chen X, Zhao C, Xu Y, Huang K, Wang Y,
Wang X, Zhou X, Pang W, Yang G and Yu T: Adipose-specific BMP and
activin membrane-bound inhibitor (BAMBI) deletion promotes
adipogenesis by accelerating ROS production. J Biol Chem.
296(100037)2021.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
5
|
Yao X, Yu T, Xi F, Xu Y, Ma L, Pan X, Chen
S, Han M, Yin Y, Dai X, et al: BAMBI shuttling between cytosol and
membrane is required for skeletal muscle development and
regeneration. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 509:125–132.
2019.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
6
|
Zhang Y, Guo Z, Du Z, Yao Z, Guo T, Cheng
Y, Wang K, Ma X, Chen C, Kebreab E, et al: Effects of BAMBI on
luteinized follicular granulosa cell proliferation and steroid
hormone production in sheep. Mol Reprod Dev. 90:153–165.
2023.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
7
|
Yang Y, Guo C, Liao B, Cao J, Liang C and
He X: BAMBI inhibits inflammation through the activation of
autophagy in experimental spinal cord injury. Int J Mol Med.
39:423–429. 2017.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
8
|
Weber F, Treeck O, Mester P and Buechler
C: Expression and function of BMP and activin membrane-bound
inhibitor (BAMBI) in chronic liver diseases and hepatocellular
carcinoma. Int J Mol Sci. 24(3473)2023.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
9
|
Pawlak JB and Blobe GC: TGF-β superfamily
co-receptors in cancer. Dev Dyn. 251:137–163. 2022.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
10
|
Nickel J, Ten Dijke P and Mueller TD:
TGF-β family co-receptor function and signaling. Acta Bioch Bioph
Sin (Shanghai). 50:12–36. 2018.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
11
|
Kirsch T, Sebald W and Dreyer MK: Crystal
structure of the BMP-2-BRIA ectodomain complex. Nat Struct Biol.
7:492–496. 2000.PubMed/NCBI View
Article : Google Scholar
|
|
12
|
Luo W and Lin SC: Axin: A master scaffold
for multiple signaling pathways. Neurosignals. 13:99–113.
2004.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
13
|
Bai L, Chang HM, Cheng JC, Klausen C, Chu
G, Leung PCK and Yang G: SMAD1/5 mediates bone morphogenetic
protein 2-induced up-regulation of BAMBI expression in human
granulosa-lutein cells. Cell Signal. 37:52–61. 2017.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
14
|
Guillot N, Kollins D, Gilbert V, Xavier S,
Chen J, Gentle M, Reddy A, Bottinger E, Jiang R, Rastaldi MP, et
al: BAMBI regulates angiogenesis and endothelial homeostasis
through modulation of alternative TGFβ signaling. PLoS One.
7(e39406)2012.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
15
|
Yan X, Lin Z, Chen F, Zhao X, Chen H, Ning
Y and Chen YG: Human BAMBI cooperates with Smad7 to inhibit
transforming growth factor-beta signaling. J Biol Chem.
284:30097–30104. 2009.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
16
|
Paulsen M, Legewie S, Eils R, Karaulanov E
and Niehrs C: Negative feedback in the bone morphogenetic protein 4
(BMP4) synexpression group governs its dynamic signaling range and
canalizes development. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA. 108:10202–10207.
2011.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
17
|
Wu Y, Li Q, Zhou X, Yu J, Mu Y, Munker S,
Xu C, Shen Z, Müllenbach R, Liu Y, et al: Decreased levels of
active SMAD2 correlate with poor prognosis in gastric cancer. PLoS
One. 7(e35684)2012.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
18
|
Shehata MM, Sallam AM, Naguib MG and
El-Mesallamy HO: Overexpression of BAMBI and SMAD7 impacts
prognosis of acute myeloid leukemia patients: A potential TERT
non-canonical role. Cancer Biomark. 31:47–58. 2021.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
19
|
Sekiya T, Oda T, Matsuura K and Akiyama T:
Transcriptional regulation of the TGF-beta pseudoreceptor BAMBI by
TGF-beta signaling. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 320:680–684.
2004.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
20
|
Kashani B, Zandi Z, Pourbagheri-Sigaroodi
A, Bashash D and Ghaffari SH: The role of toll-like receptor 4
(TLR4) in cancer progression: A possible therapeutic target? J Cell
Physiol. 236:4121–4137. 2021.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
21
|
Medzhitov R, Preston-Hurlburt P and
Janeway CA Jr: A human homologue of the Drosophila Toll protein
signals activation of adaptive immunity. Nature. 388:394–397.
1997.PubMed/NCBI View
Article : Google Scholar
|
|
22
|
Federico S, Pozzetti L, Papa A, Carullo G,
Gemma S, Butini S, Campiani G and Relitti N: Modulation of the
innate immune response by targeting toll-like receptors: A
perspective on their agonists and antagonists. J Med Chem.
63:13466–13513. 2020.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
23
|
Koushki K, Shahbaz SK, Mashayekhi K,
Sadeghi M, Zayeri ZD, Taba MY, Banach M, Al-Rasadi K, Johnston TP
and Sahebkar A: Anti-inflammatory action of statins in
cardiovascular disease: The role of inflammasome and toll-like
receptor pathways. Clin Rev Allergy Immunol. 60:175–199.
2021.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
24
|
Seki E, De Minicis S, Osterreicher CH,
Kluwe J, Osawa Y, Brenner DA and Schwabe RF: TLR4 enhances TGF-beta
signaling and hepatic fibrosis. Nat Med. 13:1324–1332.
2007.PubMed/NCBI View
Article : Google Scholar
|
|
25
|
Liu C, Chen X, Yang L, Kisseleva T,
Brenner DA and Seki E: Transcriptional repression of the
transforming growth factor β (TGF-β) Pseudoreceptor BMP and activin
membrane-bound inhibitor (BAMBI) by Nuclear Factor κB (NF-κB) p50
enhances TGF-β signaling in hepatic stellate cells. J Biol Chem.
289:7082–7091. 2014.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
26
|
Tao L, Xue D, Shen D, Ma W, Zhang J, Wang
X, Zhang W, Wu L, Pan K, Yang Y, et al: MicroRNA-942 mediates
hepatic stellate cell activation by regulating BAMBI expression in
human liver fibrosis. Arch Toxicol. 92:2935–2946. 2018.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
27
|
He Y, Ou Z, Chen X, Zu X, Liu L, Li Y, Cao
Z, Chen M, Chen Z, Chen H, et al: LPS/TLR4 signaling enhances TGF-β
response through downregulating BAMBI during prostatic hyperplasia.
Sci Rep. 6(27051)2016.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
28
|
Wanninger J, Neumeier M, Bauer S, Weiss
TS, Eisinger K, Walter R, Dorn C, Hellerbrand C, Schäffler A and
Buechler C: Adiponectin induces the transforming growth factor
decoy receptor BAMBI in human hepatocytes. FEBS Lett.
585:1338–1344. 2011.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
29
|
Dediulia T: Expression analysis and
functional studies of Bone Morphogenetic Protein and Activin
Membrane-Bound Inhibitor (BAMBI) in hepatocellular carcinoma
(unpublished PhD thesis). Ruperto Carola University Heidelberg,
Heidelberg, 2019.
|
|
30
|
Tomita K, Teratani T, Suzuki T, Shimizu M,
Sato H, Narimatsu K, Okada Y, Kurihara C, Irie R, Yokoyama H, et
al: Free cholesterol accumulation in hepatic stellate cells:
Mechanism of liver fibrosis aggravation in nonalcoholic
steatohepatitis in mice. Hepatology. 59:154–169. 2014.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
31
|
Tomita K, Teratani T, Suzuki T, Shimizu M,
Sato H, Narimatsu K, Usui S, Furuhashi H, Kimura A, Nishiyama K, et
al: Acyl-CoA: Cholesterol acyltransferase 1 mediates liver fibrosis
by regulating free cholesterol accumulation in hepatic stellate
cells. J Hepatol. 61:98–106. 2014.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
32
|
Chen M, Liu J, Yang W and Ling W:
Lipopolysaccharide mediates hepatic stellate cell activation by
regulating autophagy and retinoic acid signaling. Autophagy.
13:1813–1827. 2017.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
33
|
MacDonald BT, Tamai K and He X:
Wnt/beta-catenin signaling: Components, mechanisms, and diseases.
Dev Cell. 17:9–26. 2009.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
34
|
Perugorria MJ, Olaizola P, Labiano I,
Esparza-Baquer A, Marzioni M, Marin JJG, Bujanda L and Banales JM:
Wnt-beta-catenin signalling in liver development, health and
disease. Nat Rev Gastroenterol Hepatol. 16:121–136. 2019.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
35
|
Cong F, Schweizer L and Varmus H: Wnt
signals across the plasma membrane to activate the beta-catenin
pathway by forming oligomers containing its receptors, Frizzled and
LRP. Development. 131:5103–5115. 2004.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
36
|
Zeng X, Tamai K, Doble B, Li S, Huang H,
Habas R, Okamura H, Woodgett J and He X: A dual-kinase mechanism
for Wnt co-receptor phosphorylation and activation. Nature.
438:873–877. 2005.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
37
|
Davidson G, Wu W, Shen J, Bilic J, Fenger
U, Stannek P, Glinka A and Niehrs C: Casein kinase 1 gamma couples
Wnt receptor activation to cytoplasmic signal transduction. Nature.
438:867–872. 2005.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
38
|
Schwarz-Romond T, Fiedler M, Shibata N,
Butler PJ, Kikuchi A, Higuchi Y and Bienz M: The DIX domain of
Dishevelled confers Wnt signaling by dynamic polymerization. Nat
Struct Mol Biol. 14:484–492. 2007.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
39
|
Gao C and Chen YG: Dishevelled: The hub of
Wnt signaling. Cell Signal. 22:717–727. 2010.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
40
|
Vlad A, Rohrs S, Klein-Hitpass L and
Muller O: The first five years of the Wnt targetome. Cell Signal.
20:795–802. 2008.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
41
|
Lu HJ, Yan J, Jin PY, Zheng GH, Zhang HL,
Bai M, Wu DM, Lu J and Zheng YL: Mechanism of MicroRNA-708
Targeting BAMBI in cell proliferation, migration, and apoptosis in
mice with melanoma via the Wnt and TGF-β signaling pathways.
Technol Cancer Res Treat. 17(1533034618756784)2018.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
42
|
Liu K, Song X, Ma H, Liu L, Wen X, Yu J,
Wang L and Hu S: Knockdown of BAMBI inhibits β-catenin and
transforming growth factor β to suppress metastasis of gastric
cancer cells. Mol Med Rep. 10:874–880. 2014.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
43
|
Yuan H, Liu H, Liu Z, Zhu D, Amos CI, Fang
S, Lee JE and Wei Q: Genetic variants in Hippo pathway genes YAP 1,
TEAD 1 and TEAD 4 are associated with melanoma-specific survival.
Int J Cancer. 137:638–645. 2015.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
44
|
Zhao HJ, Chang HM, Klausen C, Zhu H, Li Y
and Leung PCK: Bone morphogenetic protein 2 induces the activation
of WNT/β-catenin signaling and human trophoblast invasion through
up-regulating BAMBI. Cell Signal. 67(109489)2020.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
45
|
Fritzmann J, Morkel M, Besser D, Budczies
J, Kosel F, Brembeck FH, Stein U, Fichtner I, Schlag PM and
Birchmeier W: A colorectal cancer expression profile that includes
transforming growth factor beta inhibitor BAMBI predicts metastatic
potential. Gastroenterology. 137:165–175. 2009.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
46
|
Sekiya T, Adachi S, Kohu K, Yamada T,
Higuchi O, Furukawa Y, Nakamura Y, Nakamura T, Tashiro K, Kuhara S,
et al: Identification of BMP and activin membrane-bound inhibitor
(BAMBI), an inhibitor of transforming growth factor-beta signaling,
as a target of the beta-catenin pathway in colorectal tumor cells.
J Biol Chem. 279:6840–6846. 2004.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
47
|
Subramaniam N, Sherman MH, Rao R, Wilson
C, Coulter S, Atkins AR, Evans RM, Liddle C and Downes M:
Metformin-mediated Bambi expression in hepatic stellate cells
induces prosurvival Wnt/beta-catenin signaling. Cancer Prev Res
(Phila). 5:553–561. 2012.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
48
|
Zhou L, Park J, Jang KY, Park HS, Wagle S,
Yang KH, Lee KB, Park BH and Kim JR: The overexpression of BAMBI
and its involvement in the growth and invasion of human
osteosarcoma cells. Oncol Rep. 30:1315–1322. 2013.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
49
|
Piché ME, Tchernof A and Després JP:
Obesity phenotypes, diabetes, and cardiovascular diseases. Circ
Res. 126:1477–1500. 2020.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
50
|
Van Camp JK, De Freitas F, Zegers D,
Beckers S, Verhulst SL, Van Hoorenbeeck K, Massa G, Verrijken A,
Desager KN, Van Gaal LF and Van Hul W: Investigation of common and
rare genetic variation in the BAMBI genomic region in light of
human obesity. Endocrine. 52:277–286. 2016.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
51
|
Luo X, Hutley LJ, Webster JA, Kim YH, Liu
DF, Newell FS, Widberg CH, Bachmann A, Turner N, Schmitz-Peiffer C,
et al: Identification of BMP and activin membrane-bound inhibitor
(BAMBI) as a potent negative regulator of adipogenesis and
modulator of autocrine/paracrine adipogenic factors. Diabetes.
61:124–136. 2012.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
52
|
Mai Y, Zhang Z, Yang H, Dong P, Chu G,
Yang G and Sun S: BMP and activin membrane-bound inhibitor (BAMBI)
inhibits the adipogenesis of porcine preadipocytes through
Wnt/β-catenin signaling pathway. Biochem Cell Biol. 92:172–182.
2014.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
53
|
Huang K, Shi X, Wang J, Yao Y, Peng Y,
Chen X, Li X and Yang G: Upregulated microRNA-106a promotes porcine
preadipocyte proliferation and differentiation by targeting
different genes. Genes (Basel). 10(805)2019.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
54
|
Yang X, Ning Y, Mei C, Zhang W, Sun J,
Wang S and Zan L: The role of BAMBI in regulating adipogenesis and
myogenesis and the association between its polymorphisms and growth
traits in cattle. Mol Biol Rep. 47:5963–5974. 2020.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
55
|
Polyzos SA, Kountouras J and Mantzoros CS:
Obesity and nonalcoholic fatty liver disease: From pathophysiology
to therapeutics. Metabolism. 92:82–97. 2019.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
56
|
Ferguson D and Finck BN: Emerging
therapeutic approaches for the treatment of NAFLD and type 2
diabetes mellitus. Nat Rev Endocrinol. 17:484–495. 2021.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
57
|
Pouwels S, Sakran N, Graham Y, Leal A,
Pintar T, Yang W, Kassir R, Singhal R, Mahawar K and Ramnarain D:
Non-alcoholic fatty liver disease (NAFLD): A review of
pathophysiology, clinical management and effects of weight loss.
BMC Endocr Disord. 22(63)2022.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
58
|
Younossi Z, Anstee QM, Marietti M, Hardy
T, Henry L, Eslam M, George J and Bugianesi E: Global burden of
NAFLD and NASH: Trends, predictions, risk factors and prevention.
Nat Rev Gastroenterol Hepatol. 15:11–20. 2018.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
59
|
Dattaroy D, Seth RK, Sarkar S, Kimono D,
Albadrani M, Chandrashekaran V, Hasson FA, Singh UP, Fan D,
Nagarkatti M, et al: Sparstolonin B (SsnB) attenuates liver
fibrosis via a parallel conjugate pathway involving P53-P21 axis,
TGF-beta signaling and focal adhesion that is TLR4 dependent. Eur J
Pharmacol. 841:33–48. 2018.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
60
|
Zhang Q, Shi XE, Song C, Sun S, Yang G and
Li X: BAMBI Promotes C2C12 myogenic differentiation by enhancing
Wnt/β-Catenin Signaling. Int J Mol Sci. 16:17734–17745.
2015.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
61
|
Loveland KL, Bakker M, Meehan T, Christy
E, von Schönfeldt V, Drummond A and de Kretser D: Expression of
Bambi is widespread in juvenile and adult rat tissues and is
regulated in male germ cells. Endocrinology. 144:4180–4186.
2003.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
62
|
Bai L, Chu G, Wang W, Xiang A and Yang G:
BAMBI promotes porcine granulosa cell steroidogenesis involving
TGF-β signaling. Theriogenology. 100:24–31. 2017.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
63
|
Bai L, Chu G, Mai Y, Zheng J, Wang W,
Zhang Q and Yang G: Identification and expression analyses of BAMBI
mediated by FSH in swine luteinizing granulosa cells.
Theriogenology. 82:1094–1101. 2014.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
64
|
Baufeld A and Vanselow J: Increasing cell
plating density mimics an early post-LH stage in cultured bovine
granulosa cells. Cell Tissue Res. 354:869–880. 2013.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
65
|
Matsuda F, Inoue N, Manabe N and Ohkura S:
Follicular growth and atresia in mammalian ovaries: Regulation by
survival and death of granulosa cells. J Reprod Dev. 58:44–50.
2012.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
66
|
Ouellette Y, Price CA and Carriere PD:
Follicular fluid concentration of transforming growth factor-beta1
is negatively correlated with estradiol and follicle size at the
early stage of development of the first-wave cohort of bovine
ovarian follicles. Domest Anim Endocrinol. 29:623–633.
2005.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
67
|
Prather RS, Lorson M, Ross JW, Whyte JJ
and Walters E: Genetically engineered pig models for human
diseases. Annu Rev Anim Biosci. 1:203–219. 2013.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
68
|
Perleberg C, Kind A and Schnieke A:
Genetically engineered pigs as models for human disease. Dis Model
Mech. 11(dmm030783)2018.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
69
|
Lunney JK, Van Goor A, Walker KE,
Hailstock T, Franklin J and Dai C: Importance of the pig as a human
biomedical model. Sci Transl Med. 13(eabd5758)2021.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
70
|
Hou N, Du X and Wu S: Advances in pig
models of human diseases. Animal Model Exp Med. 5:141–152.
2022.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
71
|
Du Q, Fu YX, Shu AM, Lv X, Chen YP, Gao
YY, Chen J, Wang W, Lv GH, Lu JF and Xu HQ: Loganin alleviates
macrophage infiltration and activation by inhibiting the MCP-1/CCR2
axis in diabetic nephropathy. Life Sci. 272(118808)2021.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
72
|
Tesch GH: MCP-1/CCL2: A new diagnostic
marker and therapeutic target for progressive renal injury in
diabetic nephropathy. Am J Physiol Renal Physiol. 294:F697–F701.
2008.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
73
|
Liang D, Song Z, Liang W, Li Y and Liu S:
Metformin inhibits TGF-beta 1-induced MCP-1 expression through
BAMBI-mediated suppression of MEK/ERK1/2 signalling. Nephrology
(Carlton). 24:481–488. 2019.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
74
|
Li J, Gui Y, Ren J, Liu X, Feng Y, Zeng Z,
He W, Yang J and Dai C: Metformin protects against
cisplatin-induced tubular cell apoptosis and acute kidney injury
via AMPKα-regulated autophagy induction. Sci Rep.
6(23975)2016.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
75
|
Wang D, Chen X and Zhang R: BAMBI promotes
macrophage proliferation and differentiation in gliomas. Mol Med
Rep. 17:3960–3966. 2018.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
76
|
Sun SW, Chen L, Zhou M, Wu JH, Meng ZJ,
Han HL, Miao SY, Zhu CC and Xiong XZ: BAMBI regulates macrophages
inducing the differentiation of Treg through the TGF-β pathway in
chronic obstructive pulmonary disease. Respir Res.
20(26)2019.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
77
|
Pils D, Wittinger M, Petz M, Gugerell A,
Gregor W, Alfanz A, Horvat R, Braicu EI, Sehouli J, Zeillinger R,
et al: BAMBI is overexpressed in ovarian cancer and co-translocates
with Smads into the nucleus upon TGF-beta treatment. Gynecol Oncol.
117:189–197. 2010.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
78
|
Khin SS, Kitazawa R, Win N, Aye TT, Mori
K, Kondo T and Kitazawa S: BAMBI gene is epigenetically silenced in
subset of high-grade bladder cancer. Int J Cancer. 125:328–338.
2009.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
79
|
Sasaki T, Sasahira T, Shimura H, Ikeda S
and Kuniyasu H: Effect of Nma on growth inhibition by TGF-betaa in
human gastric carcinoma cell lines. Oncol Rep. 11:1219–1223.
2004.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
80
|
Yuan CL, Liang R, Liu ZH, Li YQ, Luo XL,
Ye JZ and Lin Y: Bone morphogenetic protein and activin
membrane-bound inhibitor overexpression inhibits gastric tumor cell
invasion via the transforming growth
factor-β/epithelial-mesenchymal transition signaling pathway. Exp
Ther Med. 15:5422–5430. 2018.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
81
|
Wang Z, Zhang Q, Sun Y and Shao F: Long
Non-Coding RNA PVT1 Regulates BAMBI to promote tumor progression in
non-small cell lung cancer by sponging miR-17-5p. Onco Targets
Ther. 13:131–142. 2020.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
82
|
Grotewold L, Plum M, Dildrop R, Peters T
and Rüther U: Bambi is coexpressed with Bmp-4 during mouse
embryogenesis. Mech Dev. 100:327–330. 2001.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
83
|
Chen J, Bush JO, Ovitt CE, Lan Y and Jiang
R: The TGF-beta pseudoreceptor gene Bambi is dispensable for mouse
embryonic development and postnatal survival. Genesis. 45:482–486.
2007.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
84
|
Higashihori N, Song Y and Richman JM:
Expression and regulation of the decoy bone morphogenetic protein
receptor BAMBI in the developing avian face. Dev Dyn.
237:1500–1508. 2008.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
85
|
Gonzales CB, Simmons D and MacDougall M:
Competing roles of TGFbeta and Nma/BAMBI in odontoblasts. J Dent
Res. 89:597–602. 2010.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
86
|
Xavier S, Gilbert V, Rastaldi MP, Krick S,
Kollins D, Reddy A, Bottinger E, Cohen CD and Schlondorff D: BAMBI
is expressed in endothelial cells and is regulated by
lysosomal/autolysosomal degradation. PLoS One.
5(e12995)2010.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|