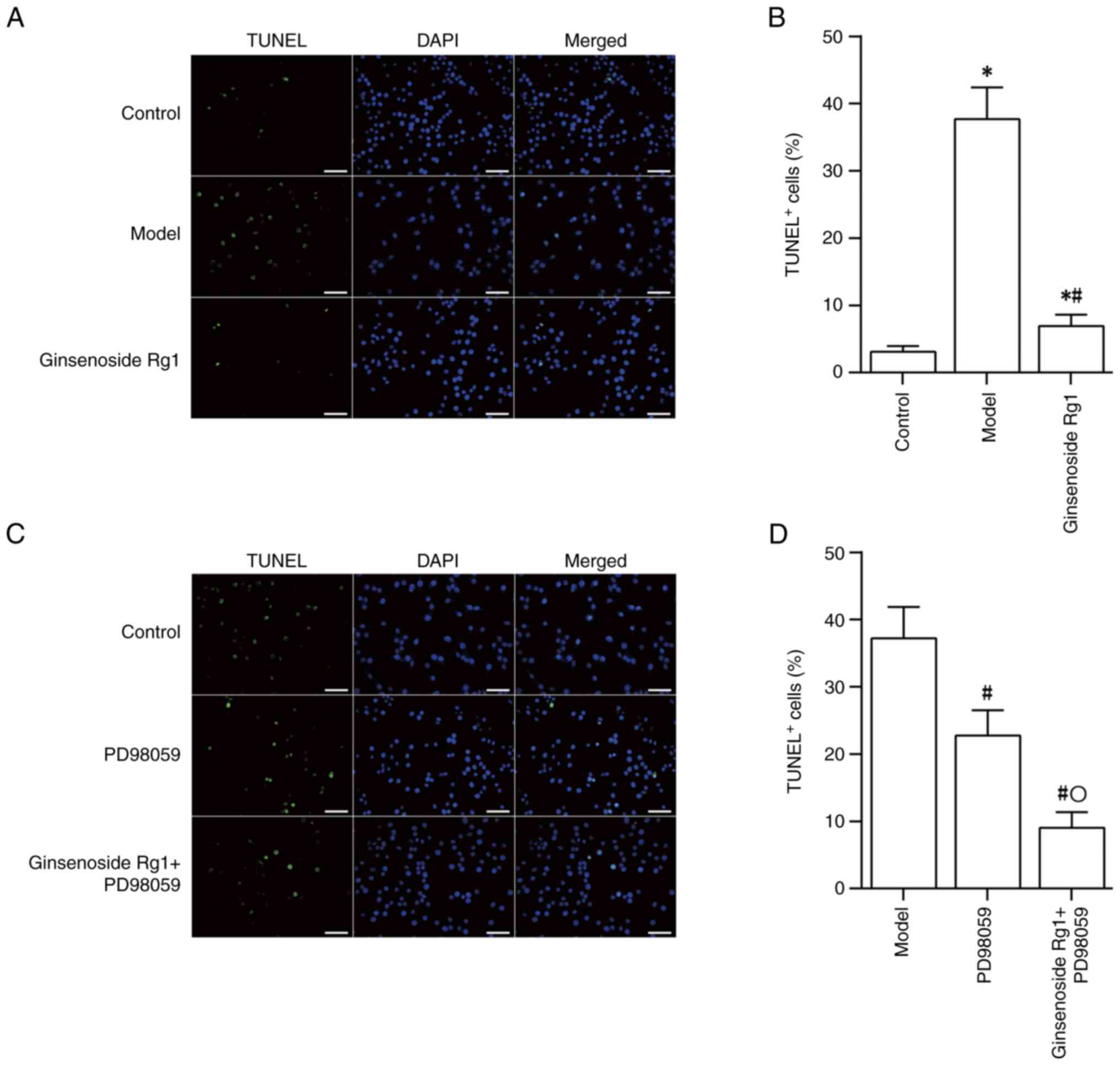
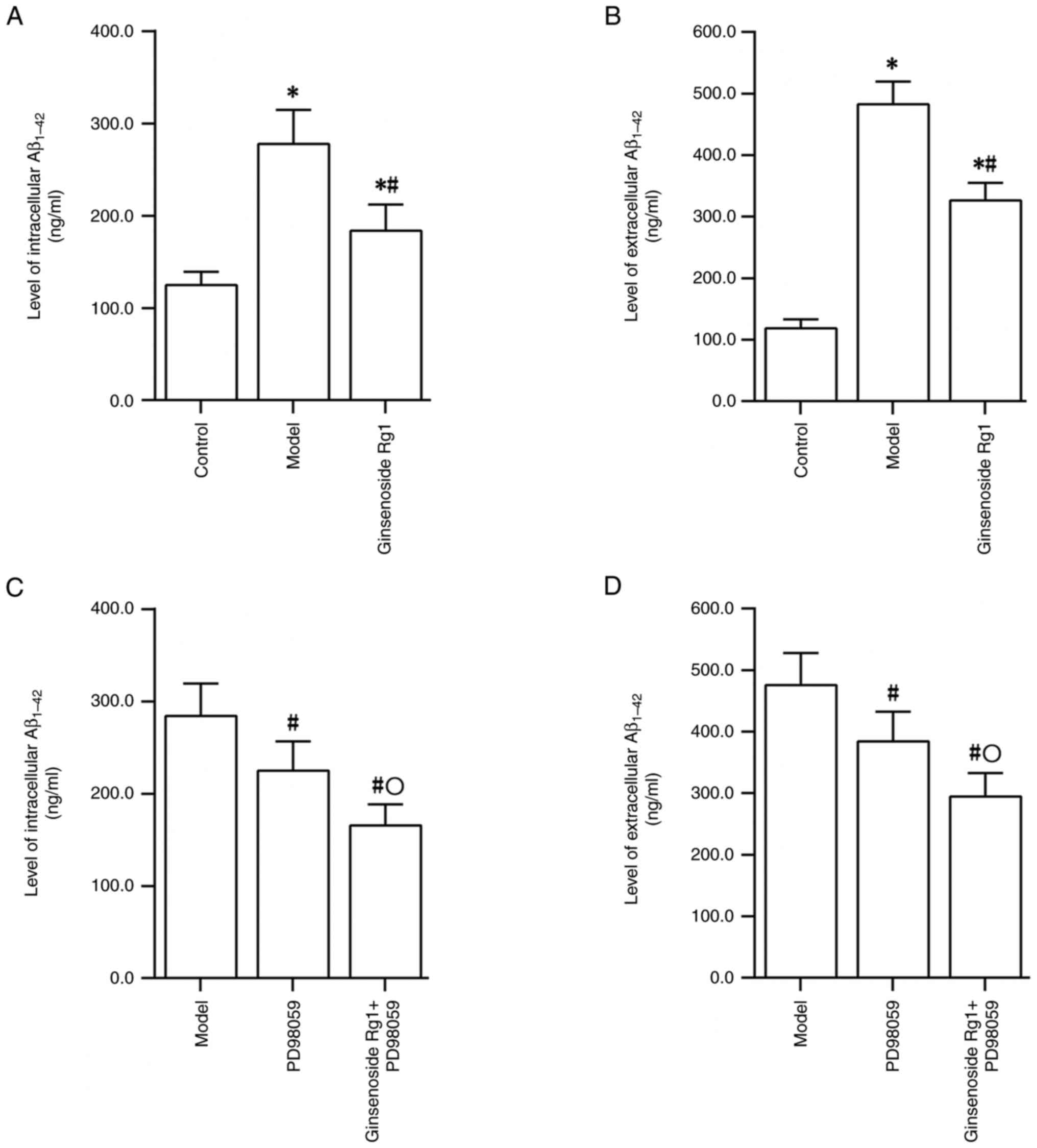
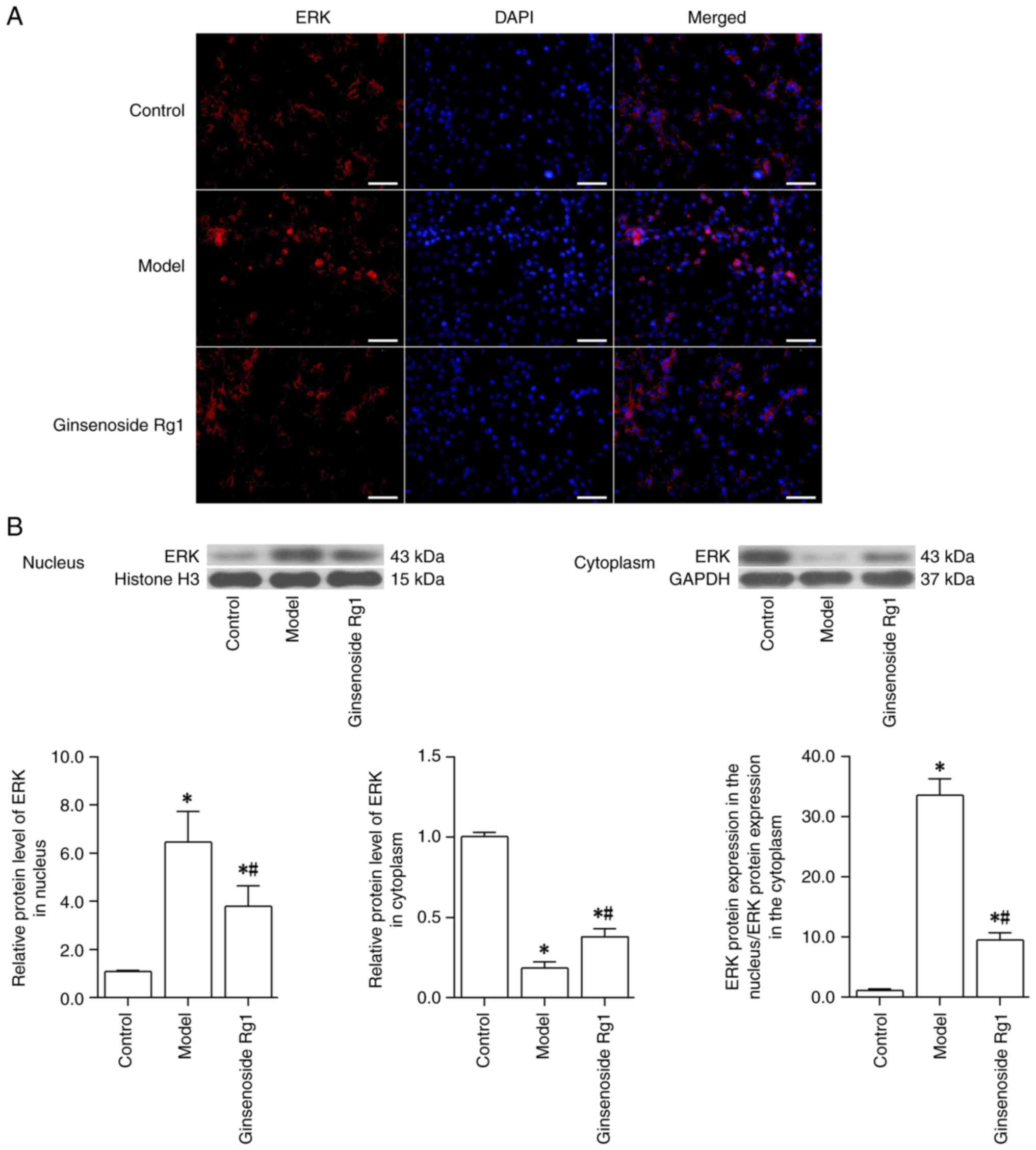
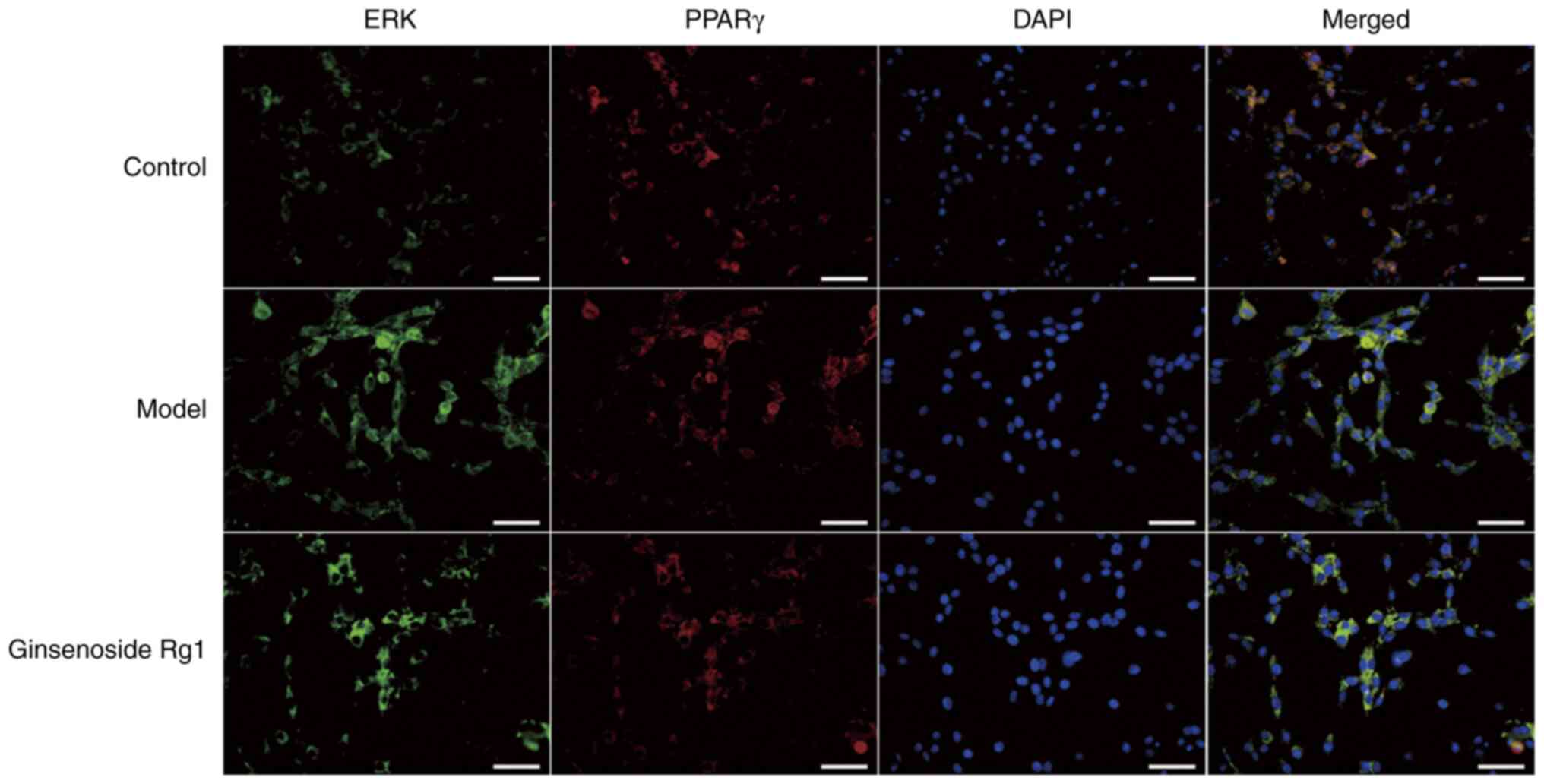
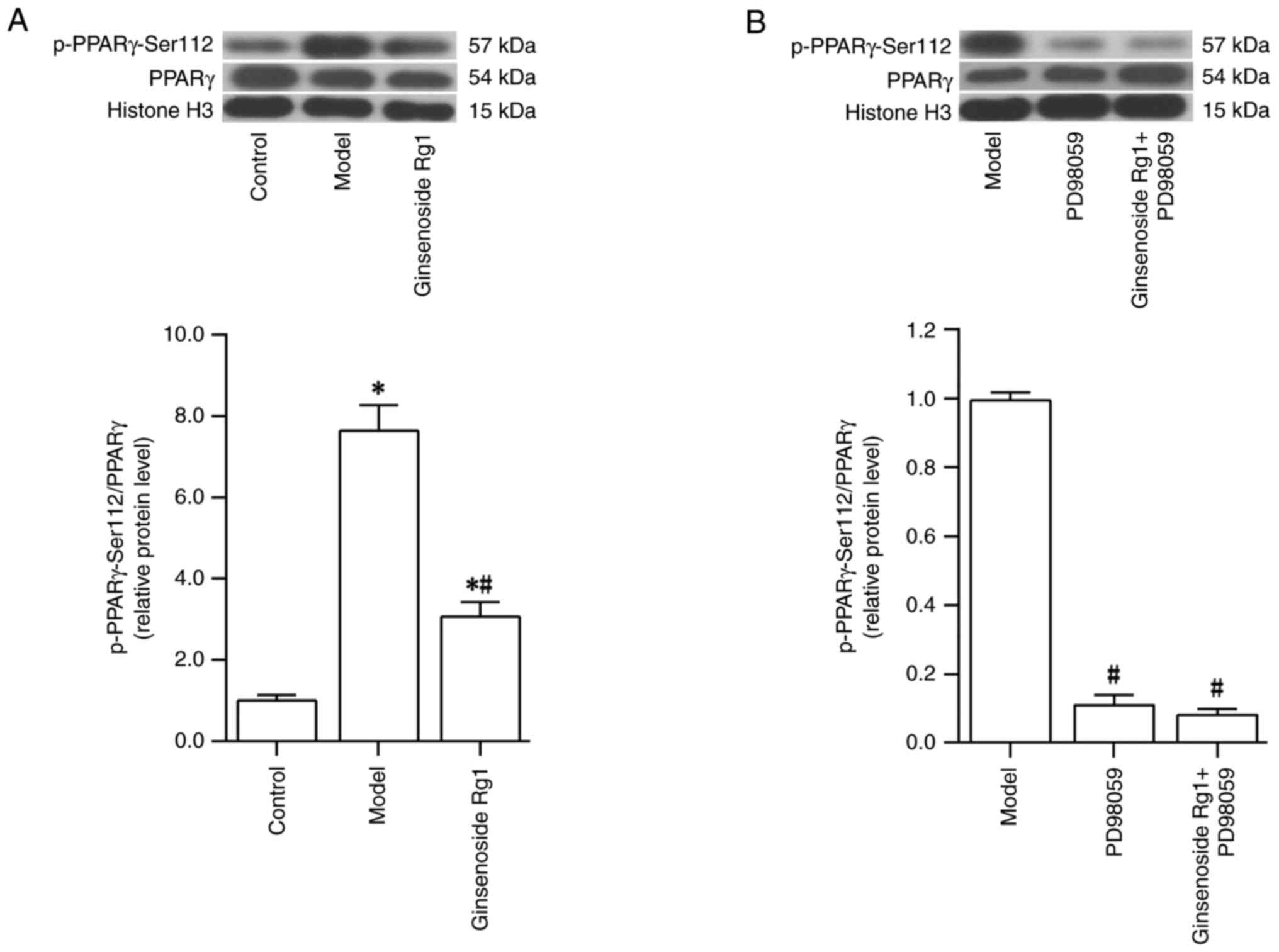
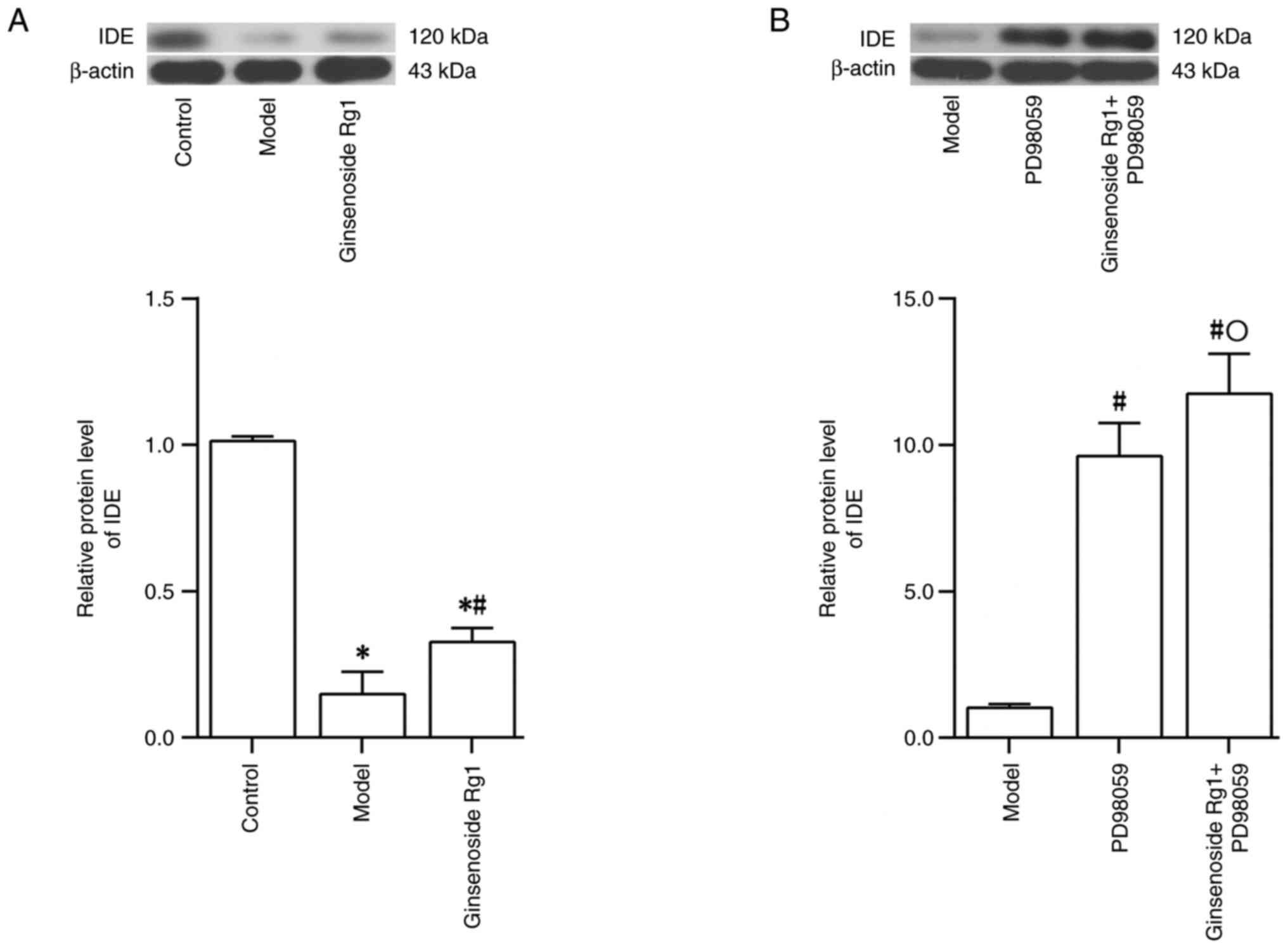
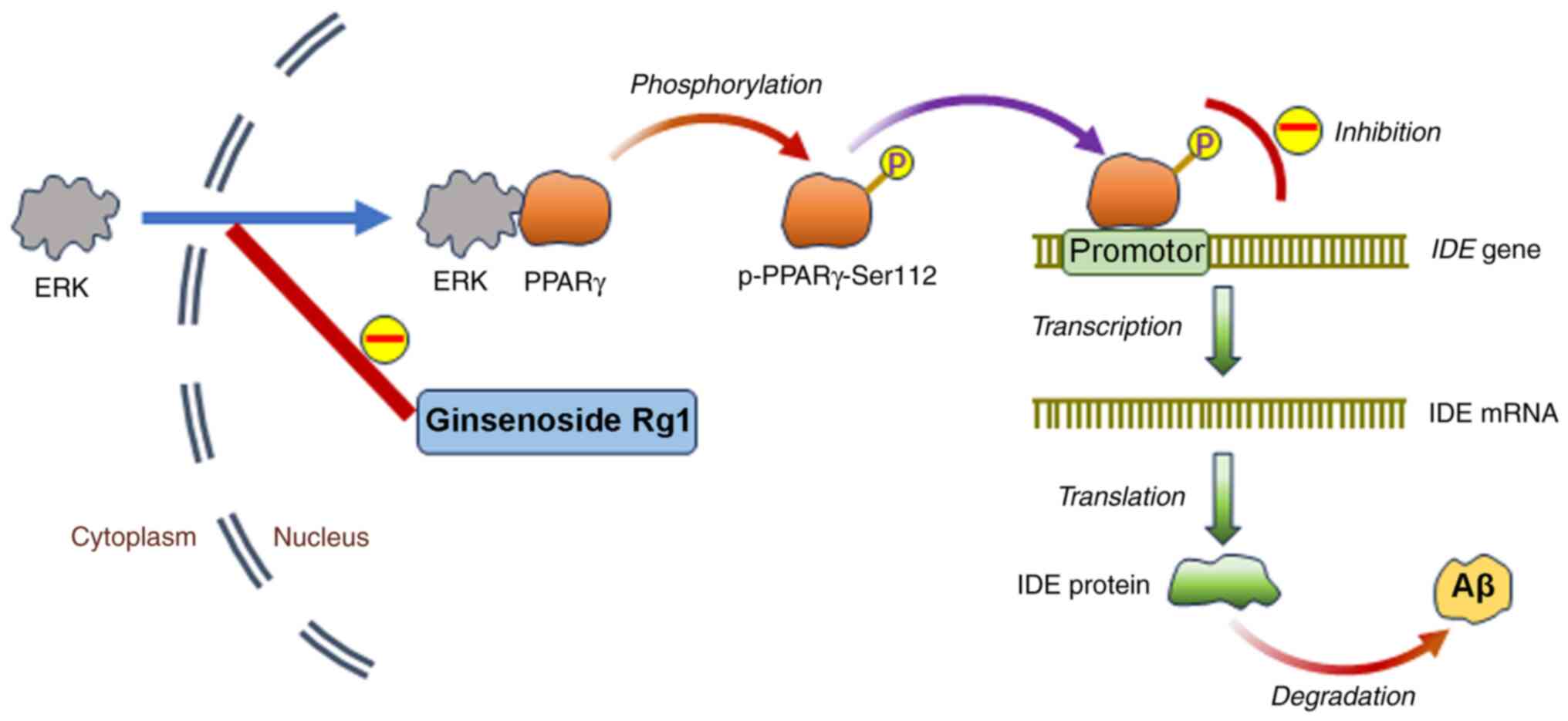
|
1
|
Murphy MP and LeVine H III: Alzheimer's
disease and the amyloid-beta peptide. J Alzheimers Dis. 19:311–323.
2010.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
2
|
Seino Y, Kawarabayashi T, Wakasaya Y,
Watanabe M, Takamura A, Yamamoto-Watanabe Y, Kurata T, Abe K, Ikeda
M, Westaway D, et al: Amyloid β accelerates phosphorylation of tau
and neurofibrillary tangle formation in an amyloid precursor
protein and tau double-transgenic mouse model. J Neurosci Res.
88:3547–3554. 2010.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
3
|
Chen Y, Fu AKY and Ip NY: Synaptic
dysfunction in Alzheimer's disease: Mechanisms and therapeutic
strategies. Pharmacol Ther. 195:186–198. 2019.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
4
|
Jawhar S, Trawicka A, Jenneckens C, Bayer
TA and Wirths O: Motor deficits, neuron loss, and reduced anxiety
coinciding with axonal degeneration and intraneuronal Aβ
aggregation in the 5XFAD mouse model of Alzheimer's disease.
Neurobiol Aging. 33:196.e29–e40. 2012.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
5
|
Cai Z, Hussain MD and Yan LJ: Microglia,
neuroinflammation, and beta-amyloid protein in Alzheimer's disease.
Int J Neurosci. 124:307–321. 2014.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
6
|
Esteras N and Abramov AY: Mitochondrial
calcium deregulation in the mechanism of beta-amyloid and tau
pathology. Cells. 9(2135)2020.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
7
|
Caruso G, Spampinato SF, Cardaci V, Caraci
F, Sortino MA and Merlo S: β-amyloid and oxidative stress:
Perspectives in drug development. Curr Pharm Des. 25:4771–4781.
2019.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
8
|
Huang Z, Yan Q, Wang Y, Zou Q, Li J, Liu Z
and Cai Z: Role of mitochondrial dysfunction in the pathology of
amyloid-β. J Alzheimers Dis. 78:505–514. 2020.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
9
|
Tran MH, Yamada K and Nabeshima T: Amyloid
beta-peptide induces cholinergic dysfunction and cognitive
deficits: A minireview. Peptides. 23:1271–1283. 2002.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
10
|
Du J, Zhang L, Liu SB, Zhang C, Huang XQ,
Li J, Zhao NM and Wang Z: PPARgamma transcriptionally regulates the
expression of insulin-degrading enzyme in primary neurons. Biochem
Biophys Res Commun. 383:485–490. 2009.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
11
|
Sahoo BR, Panda PK, Liang W, Tang WJ,
Ahuja R and Ramamoorthy A: Degradation of Alzheimer's amyloid-β by
a catalytically inactive insulin-degrading enzyme. J Mol Biol.
433(166993)2021.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
12
|
Kurochkin IV, Guarnera E and Berezovsky
IN: Insulin-degrading enzyme in the fight against Alzheimer's
disease. Trends Pharmacol Sci. 39:49–58. 2018.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
13
|
Hu BY, Liu XJ, Qiang R, Jiang ZL, Xu LH,
Wang GH, Li X and Peng B: Treatment with ginseng total saponins
improves the neurorestoration of rat after traumatic brain injury.
J Ethnopharmacol. 155:1243–1255. 2014.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
14
|
Bai L, Gao J, Wei F, Zhao J, Wang D and
Wei J: Therapeutic potential of ginsenosides as an adjuvant
treatment for diabetes. Front Pharmacol. 9(423)2018.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
15
|
Fang F, Chen X, Huang T, Lue LF, Luddy JS
and Yan SS: Multi-faced neuroprotective effects of ginsenoside Rg1
in an Alzheimer mouse model. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1822:286–292.
2012.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
16
|
Yang Y, Wang L, Zhang C, Guo Y, Li J, Wu
C, Jiao J and Zheng H: Ginsenoside Rg1 improves Alzheimer's disease
by regulating oxidative stress, apoptosis, and neuroinflammation
through Wnt/GSK-3β/β-catenin signaling pathway. Chem Biol Drug Des.
99:884–896. 2022.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
17
|
Kwan KKL, Yun H, Dong TTX and Tsim KWK:
Ginsenosides attenuate bioenergetics and morphology of mitochondria
in cultured PC12 cells under the insult of amyloid beta-peptide. J
Ginseng Res. 45:473–481. 2021.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
18
|
Wang L, Lu J, Zeng Y, Guo Y, Wu C, Zhao H,
Zheng H and Jiao J: Improving Alzheimer's disease by altering gut
microbiota in tree shrews with ginsenoside Rg1. FEMS Microbiol
Lett. 367(fnaa011)2020.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
19
|
Quan Q, Li X, Feng J, Hou J, Li M and
Zhang B: Ginsenoside Rg1 reduces β-amyloid levels by inhibiting
CDΚ5-induced PPARγ phosphorylation in a neuron model of Alzheimer's
disease. Mol Med Rep. 22:3277–3288. 2020.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
20
|
Urushibara N, Mitsuhashi S, Sasaki T,
Kasai H, Yoshimizu M, Fujita H and Oda A: JNK and p38 MAPK are
independently involved in tributyltin-mediated cell death in
rainbow trout (Oncorhynchus mykiss) RTG-2 cells. Comp Biochem
Physiol C Toxicol Pharmacol. 149:468–475. 2009.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
21
|
Guo YJ, Pan WW, Liu SB, Shen ZF, Xu Y and
Hu LL: ERK/MAPK signalling pathway and tumorigenesis. Exp Ther Med.
19:1997–2007. 2020.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
22
|
Turjanski AG, Vaqué JP and Gutkind JS: MAP
kinases and the control of nuclear events. Oncogene. 26:3240–3253.
2007.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
23
|
Ge C, Cawthorn WP, Li Y, Zhao G,
Macdougald OA and Franceschi RT: Reciprocal control of osteogenic
and adipogenic differentiation by ERK/MAP kinase phosphorylation of
Runx2 and PPARγ transcription factors. J Cell Physiol. 231:587–596.
2016.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
24
|
Yang EJ, Ahn S, Ryu J, Choi MS, Choi S,
Chong YH, Hyun JW, Chang MJ and Kim HS: Phloroglucinol attenuates
the cognitive deficits of the 5XFAD mouse model of Alzheimer's
disease. PLoS One. 10(e0135686)2015.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
25
|
Li Y, Guan Y, Wang Y, Yu CL, Zhai FG and
Guan LX: Neuroprotective effect of the ginsenoside Rg1 on cerebral
ischemic injury in vivo and in vitro is mediated by PPARγ regulated
antioxidative and anti-inflammatory pathways. Evid Based Complement
Alternat Med. 2017(7842082)2017.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
26
|
Kiwanuka E, Junker JP and Eriksson E:
Transforming growth factor β1 regulates the expression of CCN2 in
human keratinocytes via Smad-ERK signalling. Int Wound J.
14:1006–1018. 2017.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
27
|
El Ouarrat D, Isaac R, Lee YS, Oh DY,
Wollam J, Lackey D, Riopel M, Bandyopadhyay G, Seo JB,
Sampath-Kumar R and Olefsky JM: TAZ is a negative regulator of
PPARγ activity in adipocytes and TAZ deletion improves insulin
sensitivity and glucose tolerance. Cell Metab. 31:162–173.e5.
2020.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
28
|
Jiang B, Xu S, Hou X, Pimentel DR, Brecher
P and Cohen RA: Temporal control of NF-kappaB activation by ERK
differentially regulates interleukin-1beta-induced gene expression.
J Biol Chem. 279:1323–1329. 2004.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
29
|
Mut M, Lule S, Demir O, Kurnaz IA and
Vural I: Both mitogen-activated protein kinase
(MAPK)/extracellular-signal-regulated kinases (ERK) 1/2 and
phosphatidylinositide-3-OH kinase (PI3K)/Akt pathways regulate
activation of E-twenty-six (ETS)-like transcription factor 1
(Elk-1) in U138 glioblastoma cells. Int J Biochem Cell Biol.
44:302–310. 2012.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
30
|
Zuo Z, Liu J, Sun Z, Cheng YW, Ewing M,
Bugge TH, Finkel T, Leppla SH and Liu S: ERK and c-Myc signaling in
host-derived tumor endothelial cells is essential for solid tumor
growth. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA. 120(e2211927120)2023.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
31
|
Monje P, Hernández-Losa J, Lyons RJ,
Castellone MD and Gutkind JS: Regulation of the transcriptional
activity of c-Fos by ERK. A novel role for the prolyl isomerase
PIN1. J Biol Chem. 280:35081–35084. 2005.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
32
|
Lin N, Chen LM, Pan XD, Zhu YG, Zhang J,
Shi YQ and Chen XC: Tripchlorolide attenuates β-amyloid generation
via suppressing PPARγ-regulated BACE1 activity in N2a/APP695 cells.
Mol Neurobiol. 53:6397–6406. 2016.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
33
|
Sadleir KR, Eimer WA, Cole SL and Vassar
R: Aβ reduction in BACE1 heterozygous null 5XFAD mice is associated
with transgenic APP level. Mol Neurodegener. 10(1)2015.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
34
|
Wagner N and Wagner KD: The role of PPARs
in disease. Cells. 9(2367)2020.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
35
|
Szanto A, Balint BL, Nagy ZS, Barta E,
Dezso B, Pap A, Szeles L, Poliska S, Oros M, Evans RM, et al: STAT6
transcription factor is a facilitator of the nuclear receptor
PPARγ-regulated gene expression in macrophages and dendritic cells.
Immunity. 33:699–712. 2010.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
36
|
Vallée A, Lecarpentier Y, Guillevin R and
Vallée JN: Effects of cannabidiol interactions with Wnt/β-catenin
pathway and PPARγ on oxidative stress and neuroinflammation in
Alzheimer's disease. Acta Biochim Biophys Sin (Shanghai).
49:853–866. 2017.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
37
|
Janani C and Ranjitha Kumari BD: PPAR
gamma gene-a review. Diabetes Metab Syndr. 9:46–50. 2015.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
38
|
Prashantha Kumar BR, Kumar AP, Jose JA,
Prabitha P, Yuvaraj S, Chipurupalli S, Jeyarani V, Manisha C,
Banerjee S, Jeyabalan JB, et al: Minutes of PPAR-γ agonism and
neuroprotection. Neurochem Int. 140(104814)2020.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
39
|
Rodriguez-Rivera J, Denner L and Dineley
KT: Rosiglitazone reversal of Tg2576 cognitive deficits is
independent of peripheral gluco-regulatory status. Behav Brain Res.
216:255–261. 2011.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
40
|
Heneka MT, Sastre M, Dumitrescu-Ozimek L,
Hanke A, Dewachter I, Kuiperi C, O'Banion K, Klockgether T, Van
Leuven F and Landreth GE: Acute treatment with the PPARgamma
agonist pioglitazone and ibuprofen reduces glial inflammation and
Abeta1-42 levels in APPV717I transgenic mice. Brain. 128:1442–1453.
2005.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
41
|
Yamanaka M, Ishikawa T, Griep A, Axt D,
Kummer MP and Heneka MT: PPARγ/RXRα-induced and CD36-mediated
microglial amyloid-β phagocytosis results in cognitive improvement
in amyloid precursor protein/presenilin 1 mice. J Neurosci.
32:17321–17331. 2012.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
42
|
Zolezzi JM, Silva-Alvarez C, Ordenes D,
Godoy JA, Carvajal FJ, Santos MJ and Inestrosa NC: Peroxisome
proliferator-activated receptor (PPAR) γ and PPARα agonists
modulate mitochondrial fusion-fission dynamics: Relevance to
reactive oxygen species (ROS)-related neurodegenerative disorders?
PLoS One. 8(e64019)2013.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
43
|
Nicolakakis N, Aboulkassim T, Ongali B,
Lecrux C, Fernandes P, Rosa-Neto P, Tong XK and Hamel E: Complete
rescue of cerebrovascular function in aged Alzheimer's disease
transgenic mice by antioxidants and pioglitazone, a peroxisome
proliferator-activated receptor gamma agonist. J Neurosci.
28:9287–9296. 2008.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
44
|
Xu S, Liu G, Bao X, Wu J, Li S, Zheng B,
Anwyl R and Wang Q: Rosiglitazone prevents amyloid-β
oligomer-induced impairment of synapse formation and plasticity via
increasing dendrite and spine mitochondrial number. J Alzheimers
Dis. 39:239–251. 2014.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
45
|
Brunmeir R and Xu F: Functional regulation
of PPARs through post-translational modifications. Int J Mol Sci.
19(1738)2018.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
46
|
Ye P, Zhang XJ, Wang ZJ and Zhang C:
Effect of aging on the expression of peroxisome
proliferator-activated receptor gamma and the possible relation to
insulin resistance. Gerontology. 52:69–75. 2006.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
47
|
Bartl J, Monoranu CM, Wagner AK, Kolter J,
Riederer P and Grünblatt E: Alzheimer's disease and type 2
diabetes: Two diseases, one common link? World J Biol Psychiatry.
14:233–240. 2013.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
48
|
Hu E, Kim JB, Sarraf P and Spiegelman BM:
Inhibition of adipogenesis through MAP kinase-mediated
phosphorylation of PPARgamma. Science. 274:2100–2103.
1996.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
49
|
Camp HS and Tafuri SR: Regulation of
peroxisome proliferator-activated receptor gamma activity by
mitogen-activated protein kinase. J Biol Chem. 272:10811–10816.
1997.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
50
|
Irnaten M, Duff A, Clark A and O'Brien C:
Intra-cellular calcium signaling pathways (PKC, RAS/RAF/MAPK, PI3K)
in lamina cribrosa cells in glaucoma. J Clin Med.
10(62)2020.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
51
|
Stechschulte LA, Hinds TD Jr, Khuder SS,
Shou W, Najjar SM and Sanchez ER: FKBP51 controls cellular
adipogenesis through p38 kinase-mediated phosphorylation of GRα and
PPARγ. Mol Endocrinol. 28:1265–1275. 2014.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
52
|
Camp HS, Tafuri SR and Leff T: c-Jun
N-terminal kinase phosphorylates peroxisome proliferator-activated
receptor-gamma1 and negatively regulates its transcriptional
activity. Endocrinology. 140:392–397. 1999.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
53
|
Vingtdeux V, Chandakkar P, Zhao H, Blanc
L, Ruiz S and Marambaud P: CALHM1 ion channel elicits amyloid-β
clearance by insulin-degrading enzyme in cell lines and in vivo in
the mouse brain. J Cell Sci. 128:2330–2338. 2015.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
54
|
Quan Q, Qian Y, Li X and Li M: CDK5
participates in amyloid-β production by regulating PPARγ
phosphorylation in primary rat hippocampal neurons. J Alzheimers
Dis. 71:443–460. 2019.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
55
|
Burgermeister E and Seger R: MAPK kinases
as nucleo-cytoplasmic shuttles for PPARgamma. Cell Cycle.
6:1539–1548. 2007.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
56
|
Wójtowicz S, Strosznajder AK, Jeżyna M and
Strosznajder JB: The novel role of PPAR alpha in the brain:
Promising target in therapy of Alzheimer's disease and other
neurodegenerative disorders. Neurochem Res. 45:972–988.
2020.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
57
|
Strosznajder AK, Wójtowicz S, Jeżyna MJ,
Sun GY and Strosznajder JB: Recent insights on the role of PPAR-β/δ
in neuroinflammation and neurodegeneration, and tts potential
target for therapy. Neuromolecular Med. 23:86–98. 2021.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
58
|
Malm T, Mariani M, Donovan LJ, Neilson L
and Landreth GE: Activation of the nuclear receptor PPARδ is
neuroprotective in a transgenic mouse model of Alzheimer's disease
through inhibition of inflammation. J Neuroinflammation.
12(7)2015.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
59
|
An YQ, Zhang CT, Du Y, Zhang M, Tang SS,
Hu M, Long Y, Sun HB and Hong H: PPARδ agonist GW0742 ameliorates
Aβ1-42-induced hippocampal neurotoxicity in mice. Metab Brain Dis.
31:663–671. 2016.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
60
|
Lee WJ, Ham SA, Lee GH, Choi MJ, Yoo H,
Paek KS, Lim DS, Hong K, Hwang JS and Seo HG: Activation of
peroxisome proliferator-activated receptor delta suppresses BACE1
expression by up-regulating SOCS1 in a JAK2/STAT1-dependent manner.
J Neurochem. 151:370–385. 2019.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
61
|
Zhang DX, Ma DY, Yao ZQ, Fu CY, Shi YX,
Wang QL and Tang QQ: ERK1/2/p53 and NF-κB dependent-PUMA activation
involves in doxorubicin-induced cardiomyocyte apoptosis. Eur Rev
Med Pharmacol Sci. 20:2435–2442. 2016.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
62
|
Song XP, Zhang YM, Sui SA, Li XY and Huang
Y: Activation of the ERK1/2 signaling pathway enhances
proliferation and apoptosis of trophoblast in preeclampsia rats.
Eur Rev Med Pharmacol Sci. 25:598–604. 2021.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
63
|
Ansari MY, Novak K and Haqqi TM:
ERK1/2-mediated activation of DRP1 regulates mitochondrial dynamics
and apoptosis in chondrocytes. Osteoarthritis Cartilage.
30:315–328. 2022.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
64
|
Mebratu Y and Tesfaigzi Y: How ERK1/2
activation controls cell proliferation and cell death: Is
subcellular localization the answer? Cell Cycle. 8:1168–1175.
2009.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
65
|
Yan Z, Ohuchida K, Fei S, Zheng B, Guan W,
Feng H, Kibe S, Ando Y, Koikawa K, Abe T, et al: Inhibition of
ERK1/2 in cancer-associated pancreatic stellate cells suppresses
cancer-stromal interaction and metastasis. J Exp Clin Cancer Res.
38(221)2019.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
66
|
Wang H, Du S, Cai J, Wang J and Shen X:
Apolipoprotein E2 promotes the migration and invasion of pancreatic
cancer cells via activation of the ERK1/2 signaling pathway. Cancer
Manag Res. 12:13161–13171. 2020.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
67
|
Chen S, Li Z, Wang Y and Fan S: BTN3A3
inhibits the proliferation, migration and invasion of ovarian
cancer cells by regulating ERK1/2 phosphorylation. Front Oncol.
12(952425)2022.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
68
|
Xu H, Zhao H and Yu J: HOXB5 promotes
retinoblastoma cell migration and invasion via ERK1/2
pathway-mediated MMPs production. Am J Transl Res. 10:1703–1712.
2018.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
69
|
Wang G, Yin L, Peng Y, Gao Y, Gao H, Zhang
J, Lv N, Miao Y and Lu Z: Insulin promotes invasion and migration
of KRASG12D mutant HPNE cells by upregulating MMP-2
gelatinolytic activity via ERK- and PI3K-dependent signalling. Cell
Prolif. 52(e12575)2019.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
70
|
Xu Y, Gao F, Zhang J, Cai P and Xu D:
Fibroblast growth factor receptor 2 promotes the proliferation,
migration, and invasion of ectopic stromal cells via activation of
extracellular-signal-regulated kinase signaling pathway in
endometriosis. Bioengineered. 13:8360–8371. 2022.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
71
|
Cheng XD, Gu JF, Yuan JR, Feng L and Jia
XB: Suppression of A549 cell proliferation and metastasis by
calycosin via inhibition of the PKC-α/ERK1/2 pathway: An in
vitro investigation. Mol Med Rep. 12:7992–8002. 2015.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
72
|
Li Y and Yang Q: Effect of PD98059 on
chemotherapy in patients with colorectal cancer through ERK1/2
pathway. J BUON. 24:1837–1844. 2019.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
73
|
Fang J, Zhao X, Li S, Xing X, Wang H,
Lazarovici P and Zheng W: Protective mechanism of artemisinin on
rat bone marrow-derived mesenchymal stem cells against apoptosis
induced by hydrogen peroxide via activation of
c-Raf-Erk1/2-p90rsk-CREB pathway. Stem Cell Res Ther.
10(312)2019.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
74
|
González-Casimiro CM, Cámara-Torres P,
Merino B, Diez-Hermano S, Postigo-Casado T, Leissring MA,
Cózar-Castellano I and Perdomo G: Effects of fasting and feeding on
transcriptional and posttranscriptional regulation of
insulin-degrading enzyme in mice. Cells. 10(2466)2021.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
75
|
Camberos MC, Pérez AA, Udrisar DP,
Wanderley MI and Cresto JC: ATP inhibits insulin-degrading enzyme
activity. Exp Biol Med (Maywood). 226:334–341. 2001.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
76
|
George S, Petit GH, Gouras GK, Brundin P
and Olsson R: Nonsteroidal selective androgen receptor modulators
and selective estrogen receptor β agonists moderate cognitive
deficits and amyloid-β levels in a mouse model of Alzheimer's
disease. ACS Chem Neurosci. 4:1537–1548. 2013.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
77
|
Zhao L, Teter B, Morihara T, Lim GP,
Ambegaokar SS, Ubeda OJ, Frautschy SA and Cole GM:
Insulin-degrading enzyme as a downstream target of insulin receptor
signaling cascade: Implications for Alzheimer's disease
intervention. J Neurosci. 24:11120–11126. 2004.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
78
|
Humpel C: Organotypic vibrosections from
whole brain adult Alzheimer mice (overexpressing
amyloid-precursor-protein with the Swedish-Dutch-Iowa mutations) as
a model to study clearance of beta-amyloid plaques. Front Aging
Neurosci. 7(47)2015.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
79
|
He Y, Zhao H and Su G: Ginsenoside Rg1
decreases neurofibrillary tangles accumulation in retina by
regulating activities of neprilysin and PKA in retinal cells of AD
mice model. J Mol Neurosci. 52:101–106. 2014.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
80
|
Li L, Wang Y, Qi B, Yuan D, Dong S, Guo D,
Zhang C and Yu M: Suppression of PMA-induced tumor cell invasion
and migration by ginsenoside Rg1 via the inhibition of
NF-κB-dependent MMP-9 expression. Oncol Rep. 32:1779–1786.
2014.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
81
|
Li CY, Deng W, Liao XQ, Deng J, Zhang YK
and Wang DX: The effects and mechanism of ginsenoside Rg1 on
myocardial remodeling in an animal model of chronic thromboembolic
pulmonary hypertension. Eur J Med Res. 18(16)2013.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|