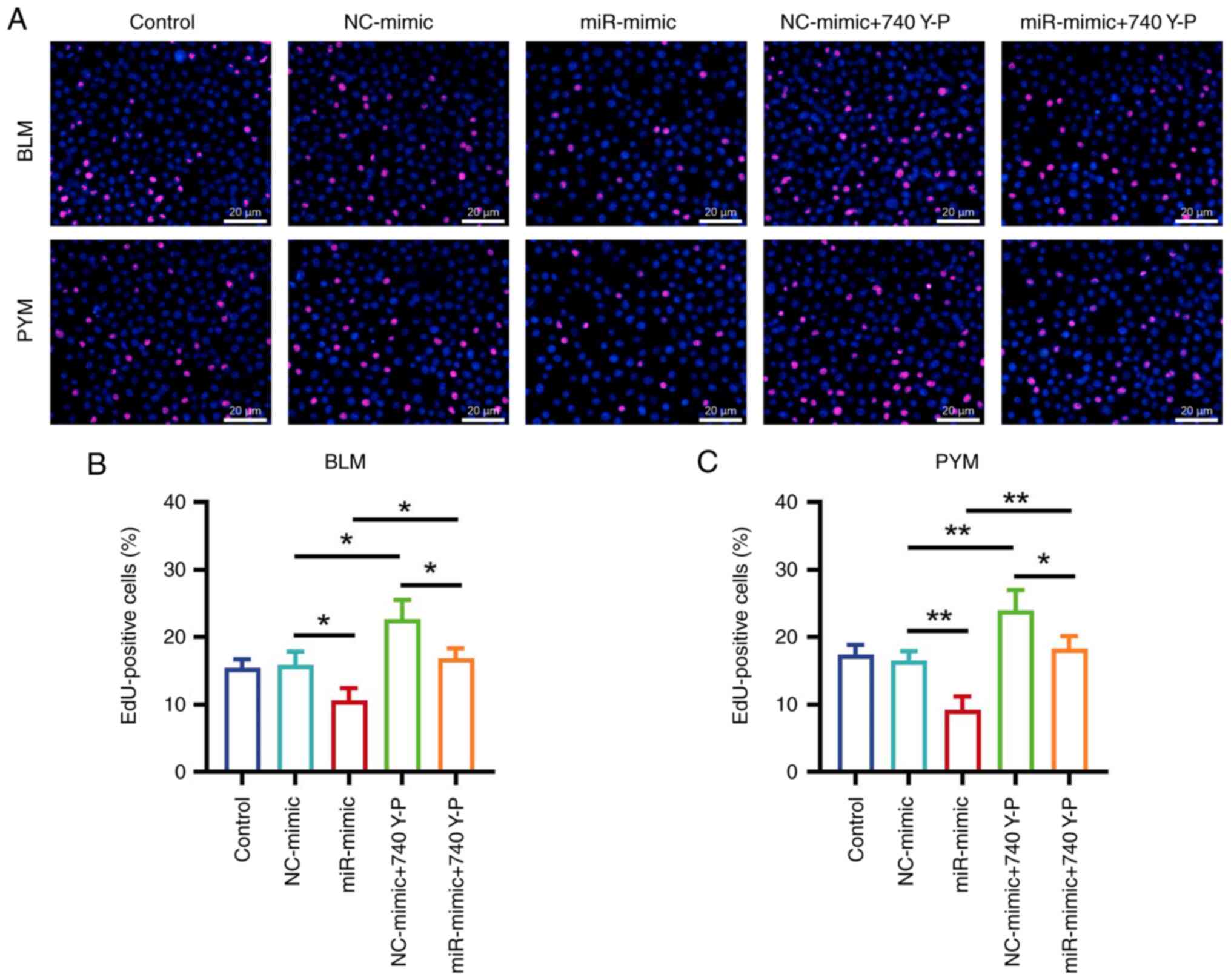
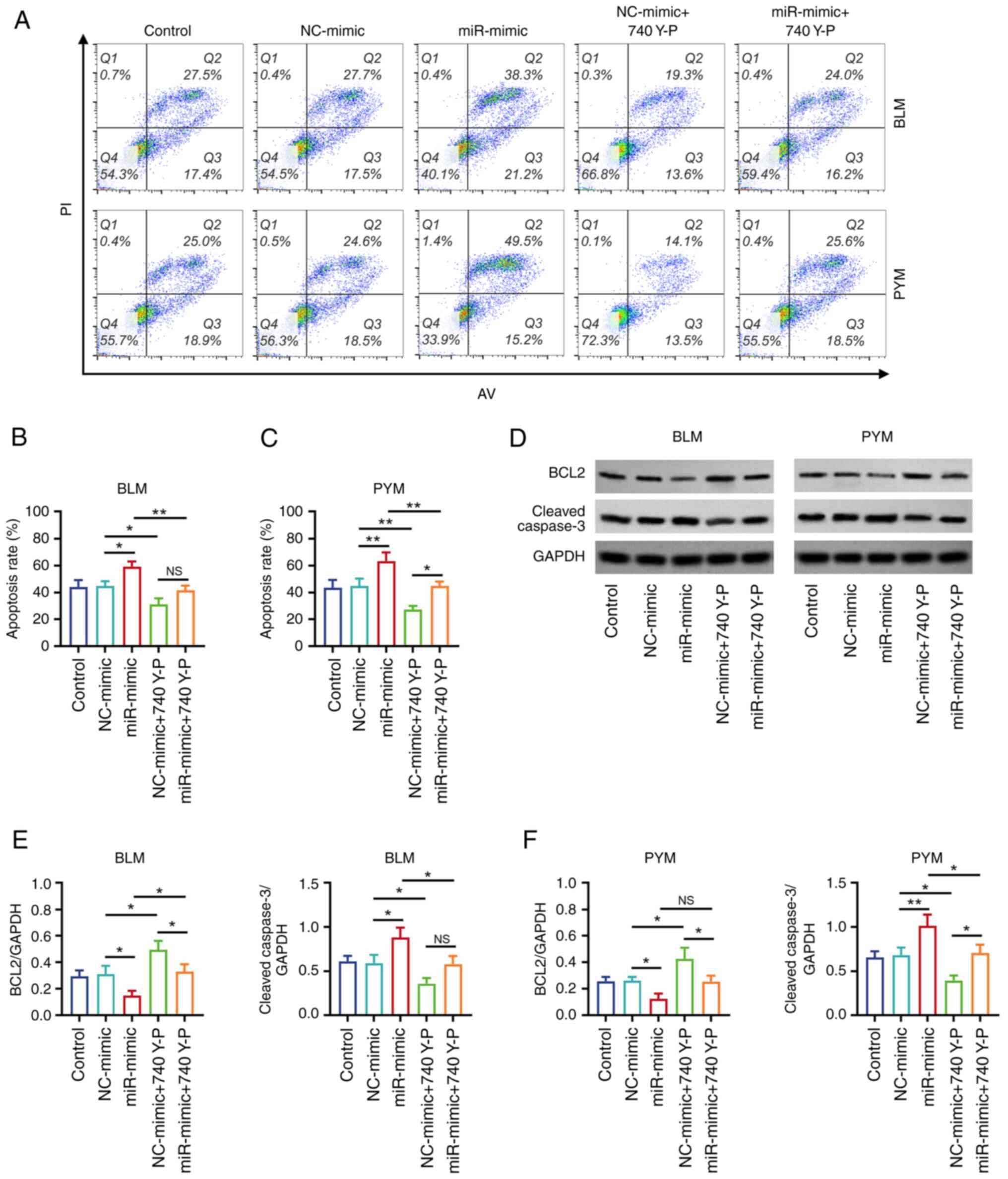
|
1
|
Rodriguez Bandera AI, Sebaratnam DF,
Wargon O and Wong LF: Infantile hemangioma. Part 1: Epidemiology,
pathogenesis, clinical presentation and assessment. J Am Acad
Dermatol. 85:1379–1392. 2021.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
2
|
Lin PF, Chen FC, Chen JY, Hu LH, Xie WJ,
Liu TY, Guo SB, Lin XM, Liu XW, Ye XH, et al: Incidence and
familial clustering of infantile haemangiomas: A multicentre study.
J Eur Acad Dermatol Venereol. 36:1641–1647. 2022.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
3
|
Anderson KR, Schoch JJ, Lohse CM, Hand JL,
Davis DM and Tollefson MM: Increasing incidence of infantile
hemangiomas (IH) over the past 35 years: Correlation with
decreasing gestational age at birth and birth weight. J Am Acad
Dermatol. 74:120–126. 2016.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
4
|
Seiffert A, Schneider M, Roessler J,
Larisch K and Pfeiffer D: Incidence, treatment patterns, and health
care costs of infantile hemangioma: Results of a retrospective
german database analysis. Pediatr Dermatol. 34:450–457.
2017.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
5
|
Leaute-Labreze C, Harper JI and Hoeger PH:
Infantile haemangioma. Lancet. 390:85–94. 2017.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
6
|
Sebaratnam DF, Rodriguez Bandera AL, Wong
LF and Wargon O: Infantile hemangioma. Part 2: Management. J Am
Acad Dermatol. 85:1395–1404. 2021.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
7
|
Lee JC, Modiri O, England RW, Shawber CJ
and Wu JK: Propranolol therapy in infantile hemangioma: It is not
just about the beta. Plast Reconstr Surg. 147:875–885.
2021.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
8
|
Colmant C and Powell J: Medical management
of infantile hemangiomas: An update. Paediatr Drugs. 24:29–43.
2022.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
9
|
Wang C, Sun J, Guo L, Song D, Zhang X, Liu
Z and Wang L: Low-dose sclerotherapy with lauromacrogol in the
treatment of infantile hemangiomas: A retrospective analysis of 368
cases. Front Oncol. 12(1014465)2022.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
10
|
Hassan Y, Osman AK and Altyeb A:
Noninvasive management of hemangioma and vascular malformation
using intralesional bleomycin injection. Ann Plast Surg. 70:70–73.
2013.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
11
|
Ji Y, Chen S, Yang K, Zhang X, Zhou J, Li
L, Xiang B, Qiu T, Dai S, Jiang X, et al: Efficacy and safety of
propranolol vs atenolol in infants with problematic infantile
hemangiomas: A randomized clinical trial. JAMA Otolaryngol Head
Neck Surg. 147:599–607. 2021.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
12
|
Kim KH, Choi TH, Choi Y, Park YW, Hong KY,
Kim DY, Choe YS, Lee H, Cheon JE, Park JB, et al: Comparison of
efficacy and safety between propranolol and steroid for infantile
hemangioma: A randomized clinical trial. JAMA Dermatol.
153:529–536. 2017.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
13
|
Chen T, Gudipudi R, Nguyen SA, Carroll W
and Clemmens C: Should propranolol remain the gold standard for
treatment of infantile hemangioma? A systematic review and
meta-analysis of propranolol versus atenolol. Ann Otol Rhinol
Laryngol. 132:332–340. 2023.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
14
|
Wu HW, Wang X, Zhang L, Zheng JW, Liu C
and Wang YA: Topical timolol vs. oral propranolol for the treatment
of superficial infantile hemangiomas. Front Oncol.
8(605)2018.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
15
|
McGahan JP and Goldman RE: Percutaneous
sclerotherapy with bleomycin and ethiodized oil: A welcomed
minimally invasive treatment for giant liver hemangiomas.
Radiology. 301:472–473. 2021.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
16
|
Chen ZY, Wang QN, Zhu YH, Zhou LY, Xu T,
He ZY and Yang Y: Progress in the treatment of infantile
hemangioma. Ann Transl Med. 7(692)2019.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
17
|
Ayoobi Yazdi N, Mehrabinejad MM, Dashti H,
Pourghorban R, Nassiri Toosi M and Rokni Yazdi H: Percutaneous
Sclerotherapy with bleomycin and ethiodized oil: A promising
treatment in symptomatic giant liver hemangioma. Radiology.
301:464–471. 2021.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
18
|
Tiwari P, Pandey V, Bera RN, Tiwary N,
Mishra A and Sharma SP: Sandwich therapy in the management of
propranolol resistant infantile hemangioma of the lip. J Stomatol
Oral Maxillofac Surg. 123:e499–e505. 2022.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
19
|
Hou J, Wang M, Tang H, Wang Y and Huang H:
Pingyangmycin sclerotherapy for infantile hemangiomas in oral and
maxillofacial regions: an evaluation of 66 consecutive patients.
Int J Oral Maxillofac Surg. 40:1246–1251. 2011.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
20
|
Zhang C, Liu P, Huang J, Liao Y, Pan C,
Liu J, Du Q, Liu T, Shang C, Ooi S, et al: Circular RNA
hsa_circ_0043280 inhibits cervical cancer tumor growth and
metastasis via miR-203a-3p/PAQR3 axis. Cell Death Dis.
12(888)2021.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
21
|
Chen L, Gao H, Liang J, Qiao J, Duan J,
Shi H, Zhen T, Li H, Zhang F, Zhu Z and Han A: miR-203a-3p promotes
colorectal cancer proliferation and migration by targeting PDE4D.
Am J Cancer Res. 8:2387–2401. 2018.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
22
|
Dai L, Zhang W, Wu X and Zhou S:
MicroRNA-203a-3p may prevent the development of thyroid papillary
carcinoma via repressing MAP3K1 and activating autophagy. J Clin
Lab Anal. 36(e24470)2022.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
23
|
Hu Z, Liu X, Guo J, Zhuo L, Chen Y and
Yuan H: Knockdown of lncRNA MEG8 inhibits cell proliferation and
invasion, but promotes cell apoptosis in hemangioma, via
miR-203-induced mediation of the Notch signaling pathway. Mol Med
Rep. 24(872)2021.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
24
|
Hu Z, Zhuo L, Li Y, Duan D and Guo J:
MicroRNA-203a-3p suppresses endothelial cell proliferation and
invasion, and promotes apoptosis in hemangioma by inactivating the
VEGF-mediated PI3K/AKT pathway. Exp Ther Med.
24(644)2022.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
25
|
Mabeta P and Pepper MS: Inhibition of
hemangioma development in a syngeneic mouse model correlates with
bcl-2 suppression and the inhibition of Akt kinase activity.
Angiogenesis. 15:131–139. 2012.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
26
|
Peng LX, Zhao P, Zhao HS, Pan E, Yang BB
and Li Q: Phosphoinositide 3-kinase/Akt pathway is involved in
pingyangmycin-induced growth inhibition, apoptosis and reduction of
invasive potential in EOMA mouse hemangioendothelioma cells. Mol
Med Rep. 12:8275–8281. 2015.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
27
|
Zhou B, Li L, Qiu X, Wu J, Xu L and Shao
W: Long non-coding RNA ANRIL knockdown suppresses apoptosis and
pro-inflammatory cytokines while enhancing neurite outgrowth via
binding microRNA-125a in a cellular model of Alzheimer's disease.
Mol Med Rep. 22:1489–1497. 2020.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
28
|
Zhao N, Du L, Ma Y, Wang Y, Ma J and Fang
Z: LncRNA NEAT1/microRNA-124 regulates cell viability, inflammation
and fibrosis in high-glucose-treated mesangial cells. Exp Ther Med.
24(507)2022.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
29
|
Livak KJ and Schmittgen TD: Analysis of
relative gene expression data using real-time quantitative PCR and
the 2(-Delta Delta C(T)) method. Methods. 25:402–408.
2001.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
30
|
Tian S, Lou L, Tian M, Lu G, Tian J and
Chen X: MAPK4 deletion enhances radiation effects and triggers
synergistic lethality with simultaneous PARP1 inhibition in
cervical cancer. J Exp Clin Cancer Res. 39(143)2020.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
31
|
Lin F, Yang Y, Wei S, Huang X, Peng Z, Ke
X, Zeng Z and Song Y: Hydrogen sulfide protects against high
glucose-induced human umbilical vein endothelial cell injury
through activating PI3K/Akt/eNOS pathway. Drug Des Devel Ther.
14:621–633. 2020.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
32
|
Jin W, Chen L, Gao F, Yang M, Liu Y and
Wang B: Down-regulation of miR-556-3p inhibits hemangioma cell
proliferation and promotes apoptosis by targeting VEGFC. Cell Mol
Biol (Noisy-le-grand). 66:204–207. 2020.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
33
|
Wu Y, Li H, Xie J, Wang F, Cao D and Lou
Y: miR-139-5p affects cell proliferation, migration and
adipogenesis by targeting insulin-like growth factor 1 receptor in
hemangioma stem cells. Int J Mol Med. 45:569–577. 2020.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
34
|
Yuan X, Xu Y, Wei Z and Ding Q: CircAP2A2
acts as a ceRNA to participate in infantile hemangiomas progression
by sponging miR-382-5p via regulating the expression of VEGFA. J
Clin Lab Anal. 34(e23258)2020.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
35
|
Hu X, Bai S, Li L, Tian P, Wang S, Zhang
N, Shen B, Du J and Liu S: MiR-200c-3p increased HDMEC
proliferation through the notch signaling pathway. Exp Biol Med
(Maywood). 246:897–905. 2021.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
36
|
Wu M, Chen Y, Feng L, Dai H, Fang S and Xu
J: MiR-206 promotes extracellular matrix accumulation and relieves
infantile hemangioma through targeted inhibition of DNMT3A. Cell
Cycle. 20:978–992. 2021.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
37
|
Ma Q, Dai X, Lu W, Qu X, Liu N and Zhu C:
Silencing long non-coding RNA MEG8 inhibits the proliferation and
induces the ferroptosis of hemangioma endothelial cells by
regulating miR-497-5p/NOTCH2 axis. Biochem Biophys Res Commun.
556:72–78. 2021.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
38
|
An N and Zheng B: MiR-203a-3p inhibits
pancreatic cancer cell proliferation, EMT, and apoptosis by
regulating SLUG. Technol Cancer Res Treat.
19(1533033819898729)2020.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
39
|
Martin M, Zhang J, Miao Y, He M, Kang J,
Huang HY, Chou CH, Huang TS, Hong HC, Su SH, et al: Role of
endothelial cells in pulmonary fibrosis via SREBP2 activation. JCI
Insight. 6(e125635)2021.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
40
|
Udalov S, Dumitrascu R, Pullamsetti SS,
Al-tamari HM, Weissmann N, Ghofrani HA, Guenther A, Voswinckel R,
Seeger W, Grimminger F and Schermuly RT: Effects of
phosphodiesterase 4 inhibition on bleomycin-induced pulmonary
fibrosis in mice. BMC Pulm Med. 10(26)2010.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
41
|
Xiao Z, Qu Z, Chen Z, Fang Z, Zhou K,
Huang Z, Guo X and Zhang Y: LncRNA HOTAIR is a prognostic biomarker
for the proliferation and chemoresistance of colorectal cancer via
MiR-203a-3p-mediated Wnt/ss-catenin signaling pathway. Cell Physiol
Biochem. 46:1275–1285. 2018.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
42
|
Shen M, Dong C, Ruan X, Yan W, Cao M,
Pizzo D, Wu X, Yang L, Liu L, Ren X and Wang SE:
Chemotherapy-induced extracellular vesicle miRNAs promote breast
cancer stemness by targeting ONECUT2. Cancer Res. 79:3608–3621.
2019.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
43
|
Santangelo A, Rossato M, Lombardi G,
Benfatto S, Lavezzari D, De Salvo GL, Indraccolo S, Dechecchi MC,
Prandini P, Gambari R, et al: A molecular signature associated with
prolonged survival in glioblastoma patients treated with
regorafenib. Neuro Oncol. 23:264–276. 2021.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
44
|
Yang K, Qiu T, Zhou J, Gong X, Zhang X,
Lan Y, Zhang Z and Ji Y: Blockage of glycolysis by targeting PFKFB3
suppresses the development of infantile hemangioma. J Transl Med.
21(85)2023.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
45
|
Zhao Y, Li D, Han Y, Wang H, Du R and Yan
Z: The ester derivatives obtained by C-ring modification of
podophyllotoxin-induced apoptosis and inhibited proliferation in
hemangioma endothelial cells via downregulation of PI3K/Akt
signaling pathway. Chem Biol Drug Des. 99:828–838. 2022.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
46
|
Zhang Y, Zheng Y and Zhu G: MiR-203a-3p
targets PTEN to promote hepatocyte proliferation by regulating
PI3K/Akt pathway in BRL-3A cells. Biosci Biotechnol Biochem.
84:725–733. 2020.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|