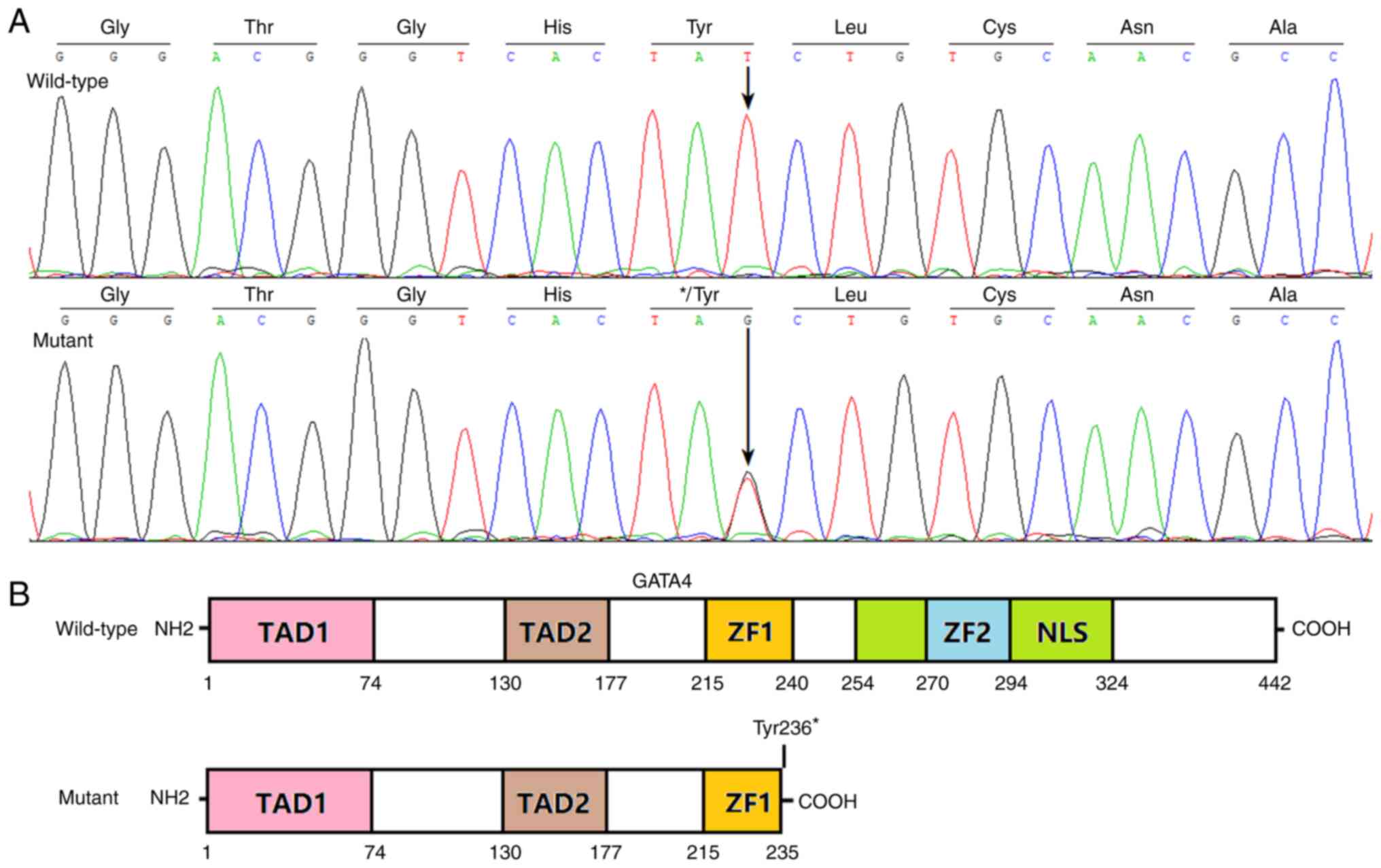
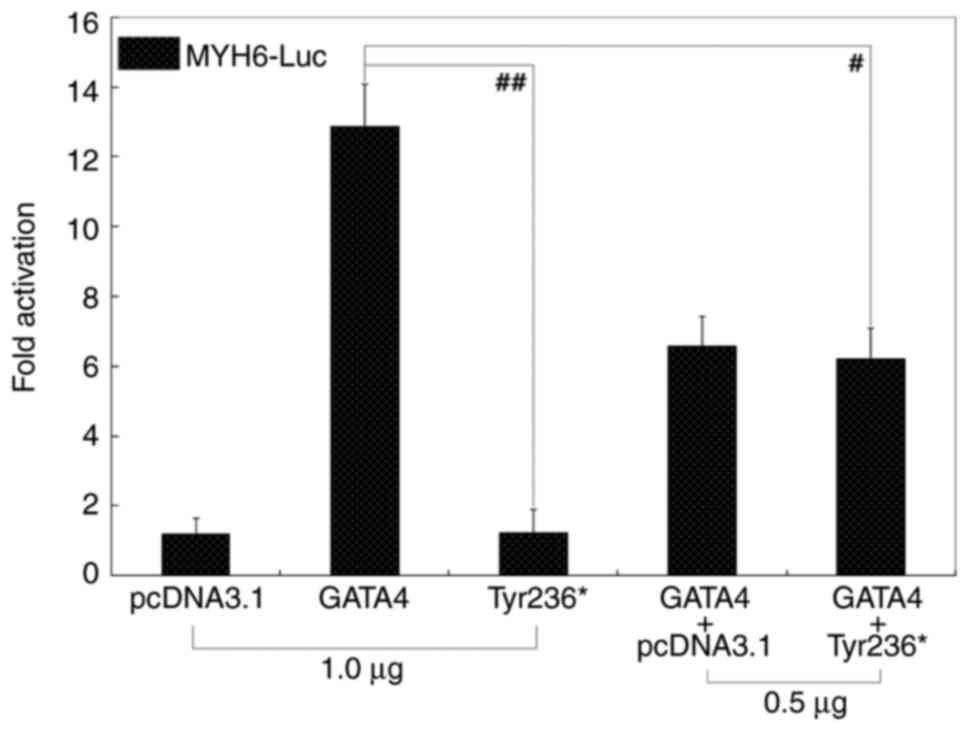
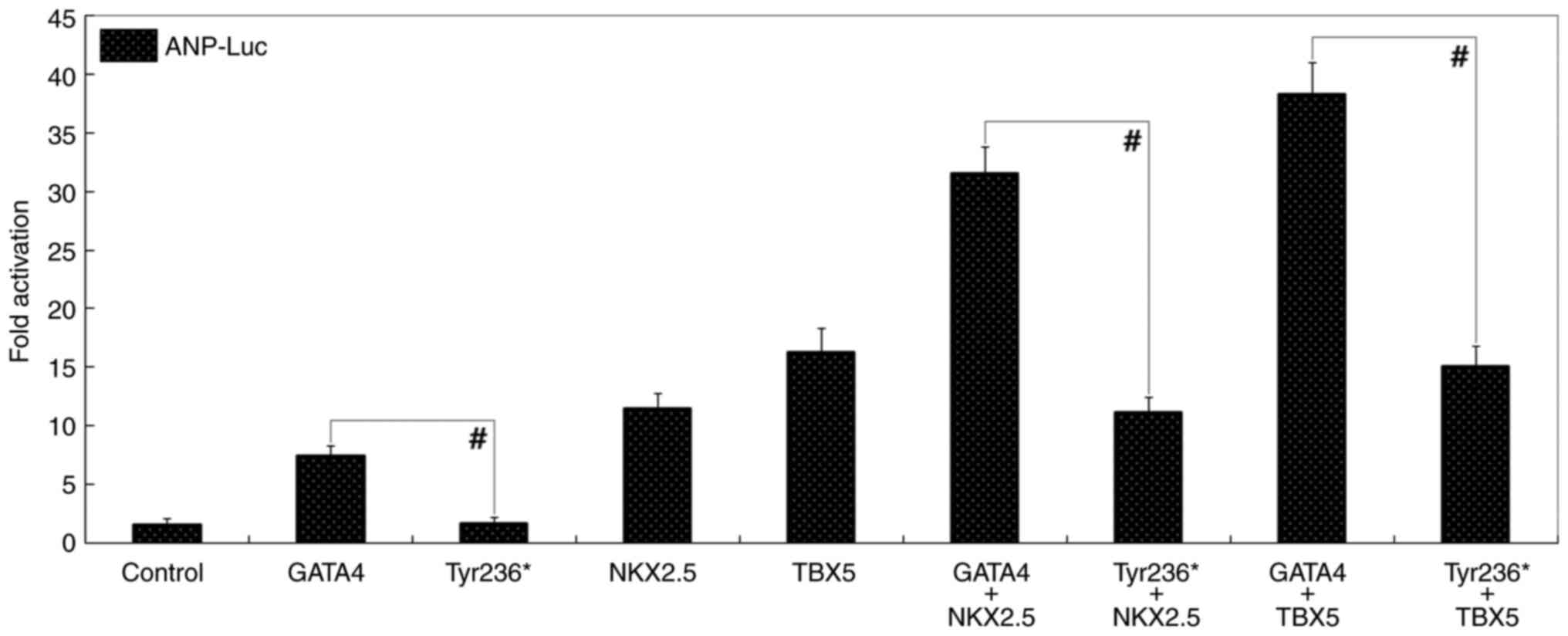
|
1
|
Tsao CW, Aday AW, Almarzooq ZI, Anderson
CAM, Arora P, Avery CL, Baker-Smith CM, Beaton AZ, Boehme AK,
Buxton AE, et al: Heart disease and stroke statistics-2023 update:
A report from the American Heart Association. Circulation.
147:e93–e621. 2023.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
2
|
Diab NS, Barish S, Dong W, Zhao S,
Allington G, Yu X, Kahle KT, Brueckner M and Jin SC: Molecular
genetics and complex inheritance of congenital heart disease. Genes
(Basel). 12(1020)2021.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
3
|
Spaziani G, Girolami F, Arcieri L, Calabri
GB, Porcedda G, Di Filippo C, Surace FC, Pozzi M and Favilli S:
Bicuspid aortic valve in children and adolescents: A comprehensive
review. Diagnostics (Basel). 12(1751)2022.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
4
|
Martin LJ and Benson DW: Focused
strategies for defining the genetic architecture of congenital
heart defects. Genes (Basel). 12(827)2021.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
5
|
Brudy L, Meyer M, Oberhoffer R, Ewert P
and Müller J: Move more-be happier? Physical activity and
health-related quality of life in children with congenital heart
disease. Am Heart J. 241:68–73. 2021.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
6
|
Moons P, Luyckx K, Thomet C, Budts W,
Enomoto J, Sluman MA, Lu CW, Jackson JL, Khairy P, Cook SC, et al:
Physical functioning, mental health, and quality of life in
different congenital heart defects: Comparative analysis in 3538
patients from 15 countries. Can J Cardiol. 37:215–223.
2021.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
7
|
Freiberger A, Busse A, Ewert P,
Huntgeburth M, Kaemmerer H, Kohls N, Nagdyman N, Richter C, Röhrich
C, von Scheidt F, et al: Quality of life in adults with congenital
heart disease with and without pulmonary hypertension: A
comparative study. Cardiovasc Diagn Ther. 12:758–766.
2022.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
8
|
Ly R, Karsenty C, Amedro P, Cohen S,
Domanski O, Godart F, Radojevic J, Vaksmann G, Naccache N, Boubrit
A, et al: Health-Related quality of life and its association with
outcomes in adults with congenital heart disease and heart failure:
Insight From FRESH-ACHD Registry. J Am Heart Assoc.
12(e027819)2023.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
9
|
Meyer M, Brudy L, Fuertes-Moure A, Hager
A, Oberhoffer-Fritz R, Ewert P and Müller J: E-Health exercise
intervention for pediatric patients with congenital heart disease:
A randomized controlled trial. J Pediatr. 233:163–168.
2021.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
10
|
Fritz C, Hock J, Oberhoffer R, Hager A,
Ewert P and Müller J: reduced parasympathetic activity in patients
with different types of congenital heart disease and associations
to exercise capacity. J Cardiopulm Rehabil Prev. 41:35–39.
2021.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
11
|
Sheng SP, Feinberg JL, Bostrom JA, Tang Y,
Sweeney G, Pierre A, Katz ES, Whiteson JH, Haas F, Dodson JA and
Halpern DG: Adherence and exercise capacity improvements of
patients with adult congenital heart disease participating in
cardiac rehabilitation. J Am Heart Assoc.
11(e023896)2022.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
12
|
Masood IR, Detterich J, Cerrone D,
Lewinter K, Shah P, Kato R and Sabati A: Reduced forced vital
capacity and the number of chest wall surgeries are associated with
decreased exercise capacity in children with congenital heart
disease. Pediatr Cardiol. 43:54–61. 2022.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
13
|
Willinger L, Hock J, Hager A,
Oberhoffer-Fritz R, Ewert P and Müller J: Heart-Focused anxiety is
prevalent in adults with congenital heart disease and associated
with reduced exercise capacity. J Cardiopulm Rehabil Prev.
43:277–281. 2023.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
14
|
Sadhwani A, Wypij D, Rofeberg V, Gholipour
A, Mittleman M, Rohde J, Velasco-Annis C, Calderon J, Friedman KG,
Tworetzky W, et al: Fetal brain volume predicts neurodevelopment in
congenital heart disease. Circulation. 145:1108–1119.
2022.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
15
|
Parekh SA, Cox SM, Barkovich AJ, Chau V,
Steurer MA, Xu D, Miller SP, McQuillen PS and Peyvandi S: The
effect of size and asymmetry at birth on brain injury and
neurodevelopmental outcomes in congenital heart disease. Pediatr
Cardiol. 43:868–877. 2022.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
16
|
Peyvandi S and Rollins C: Fetal brain
development in congenital heart disease. Can J Cardiol. 39:115–122.
2023.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
17
|
Brossard-Racine M and Panigrahy A:
Structural brain alterations and their associations with function
in children, adolescents, and young adults with congenital heart
disease. Can J Cardiol. 39:123–132. 2023.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
18
|
Cromb D, Bonthrone AF, Maggioni A, Cawley
P, Dimitrova R, Kelly CJ, Cordero-Grande L, Carney O, Egloff A,
Hughes E, et al: Individual assessment of perioperative brain
growth trajectories in infants with congenital heart disease:
Correlation with clinical and surgical risk factors. J Am Heart
Assoc. 12(e028565)2023.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
19
|
Karsenty C, Waldmann V, Mulder B, Hascoet
S and Ladouceur M: Thromboembolic complications in adult congenital
heart disease: the knowns and the unknowns. Clin Res Cardiol.
10:1380–1391. 2021.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
20
|
Giang KW, Fedchenko M, Dellborg M,
Eriksson P and Mandalenakis Z: Burden of ischemic stroke in
patients with congenital heart disease: A nationwide, case-control
study. J Am Heart Assoc. 10(e020939)2021.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
21
|
Yeh HR, Kim EH, Yu JJ, Yun TJ, Ko TS and
Yum MS: Arterial ischemic stroke in children with congenital heart
diseases. Pediatr Int. 64(e15200)2022.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
22
|
Kourelis G, Kanakis M, Samanidis G,
Tzannis K, Bobos D, Kousi T, Apostolopoulou S, Kakava F,
Kyriakoulis K, Bounta S, et al: Acute kidney injury predictors and
outcomes after cardiac surgery in children with congenital heart
disease: An observational cohort study. Diagnostics (Basel).
12(2397)2022.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
23
|
Xie Y, Jiang W, Cao J and Xie H:
Dexmedetomidine attenuates acute kidney injury in children
undergoing congenital heart surgery with cardiopulmonary bypass by
inhibiting the TLR3/NF-κB signaling pathway. Am J Transl Res.
13:2763–2773. 2021.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
24
|
Gillesén M, Fedchenko M, Giang KW,
Dimopoulos K, Eriksson P, Dellborg M and Mandalenakis Z: Chronic
kidney disease in patients with congenital heart disease: A
nationwide, register-based cohort study. Eur Heart J Open.
2(oeac055)2022.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
25
|
Reiter FP, Hadjamu NJ, Nagdyman N,
Zachoval R, Mayerle J, De Toni EN, Kaemmerer H and Denk G:
Congenital heart disease-associated liver disease: A narrative
review. Cardiovasc Diagn Ther. 11:577–590. 2021.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
26
|
Rosenzweig EB and Krishnan U: Congenital
heart disease-associated pulmonary hypertension. Clin Chest Med.
42:9–18. 2021.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
27
|
Chiu SN, Lu CW, Lin MT, Chen CA, Wu MH and
Wang JK: Pulmonary hypertension in adult congenital heart disease
in Asia: A distinctive feature of complex congenital heart disease.
J Am Heart Assoc. 11(e022596)2022.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
28
|
Lindberg L: Long-Term follow-up of
pediatric patients with severe postoperative pulmonary hypertension
after correction of congenital heart defects. Pediatr Cardiol.
43:827–836. 2022.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
29
|
Snygg-Martin U, Giang KW, Dellborg M,
Robertson J and Mandalenakis Z: Cumulative incidence of infective
endocarditis in patients with congenital heart disease: A
nationwide, case-control study over nine decades. Clin Infect Dis.
73:1469–1475. 2021.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
30
|
van Melle JP, Roos-Hesselink JW, Bansal M,
Kamp O, Meshaal M, Pudich J, Luksic VR, Rodriguez-Alvarez R,
Sadeghpour A, Hanzevacki JS, et al: Infective endocarditis in adult
patients with congenital heart disease. Int J Cardiol. 370:178–185.
2023.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
31
|
Havers-Borgersen E, Butt JH, Østergaard L,
Petersen JK, Torp-Pedersen C, Køber L and Fosbøl EL: Long-term
incidence of infective endocarditis among patients with congenital
heart disease. Am Heart J. 259:9–20. 2023.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
32
|
Arnaert S, De Meester P, Troost E, Droogne
W, Van Aelst L, Van Cleemput J, Voros G, Gewillig M, Cools B, Moons
P, et al: Heart failure related to adult congenital heart disease:
prevalence, outcome and risk factors. ESC Heart Fail. 8:2940–2950.
2021.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
33
|
Egbe AC, Miranda WR, Jain CC, Bonnichsen
CR, Anderson JH, Dearani JA, Warnes CA, Crestanello J and Connolly
HM: Incidence and outcomes of advanced heart failure in adults with
congenital heart disease. Circ Heart Fail.
15(e009675)2022.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
34
|
Lu CW, Wang JK, Yang HL, Kovacs AH, Luyckx
K, Ruperti-Repilado FJ, Van De Bruaene A, Enomoto J, Sluman MA,
Jackson JL, et al: Heart failure and patient-reported outcomes in
adults with congenital heart disease from 15 countries. J Am Heart
Assoc. 11(e024993)2022.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
35
|
Fischer AJ, Enders D, Wasmer K, Marschall
U, Baumgartner H and Diller GP: Impact of specialized
electrophysiological care on the outcome of catheter ablation for
supraventricular tachycardias in adults with congenital heart
disease: Independent risk factors and gender aspects. Heart Rhythm.
18:1852–1859. 2021.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
36
|
Casteigt B, Samuel M, Laplante L, Shohoudi
A, Apers S, Kovacs AH, Luyckx K, Thomet C, Budts W, Enomoto J, et
al: Atrial arrhythmias and patient-reported outcomes in adults with
congenital heart disease: An international study. Heart Rhythm.
18:793–800. 2021.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
37
|
Wasmer K, Eckardt L, Baumgartner H and
Köbe J: Therapy of supraventricular and ventricular arrhythmias in
adults with congenital heart disease-narrative review. Cardiovasc
Diagn Ther. 11:550–562. 2021.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
38
|
Vehmeijer JT, Koyak Z, Leerink JM,
Zwinderman AH, Harris L, Peinado R, Oechslin EN, Robbers-Visser D,
Groenink M, Boekholdt SM, et al: Identification of patients at risk
of sudden cardiac death in congenital heart disease: The
PRospEctiVE study on implaNTable cardIOverter defibrillator therapy
and suddeN cardiac death in Adults with Congenital Heart Disease
(PREVENTION-ACHD). Heart Rhythm. 18:785–792. 2021.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
39
|
Diller GP, Orwat S, Lammers AE, Radke RM,
De-Torres-Alba F, Schmidt R, Marschall U, Bauer UM, Enders D,
Bronstein L, et al: Lack of specialist care is associated with
increased morbidity and mortality in adult congenital heart
disease: A population-based study. Eur Heart J. 42:4241–4248.
2021.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
40
|
Williams JL, Torok RD, D'Ottavio A, Spears
T, Chiswell K, Forestieri NE, Sang CJ, Paolillo JA, Walsh MJ,
Hoffman TM, et al: Causes of death in infants and children with
congenital heart disease. Pediatr Cardiol. 42:1308–1315.
2021.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
41
|
Triedman JK and Newburger JW: Trends in
congenital heart disease: The next decade. Circulation.
133:2716–2733. 2016.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
42
|
Bouma BJ and Mulder BJ: Changing landscape
of congenital heart disease. Circ Res. 120:908–922. 2017.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
43
|
Rao PS and Agarwal A: Advances in the
diagnosis and management of congenital heart disease in children.
Children (Basel). 9(1056)2022.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
44
|
Williams RG: Late causes of death after
congenital heart defects: A population-based study from finland. J
Am Coll Cardiol. 68:499–501. 2016.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
45
|
Niwa K, Kaemmerer H and von Kodolitsch Y:
Current diagnosis and management of late complications in adult
congenital heart disease. Cardiovasc Diagn Ther. 11:478–480.
2021.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
46
|
Huang RT, Xue S, Xu YJ, Zhou M and Yang
YQ: Somatic GATA5 mutations in sporadic tetralogy of Fallot. Int J
Mol Med. 33:1227–1235. 2014.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
47
|
Boyd R, McMullen H, Beqaj H and Kalfa D:
Environmental exposures and congenital heart disease. Pediatrics.
149(e2021052151)2022.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
48
|
García-Flores E, Rodríguez-Pérez JM,
Borgonio-Cuadra VM, Vargas-Alarcón G, Calderón-Colmenero J,
Sandoval JP, García-Montes JA, Espinoza-Gutiérrez VM, Reyes-García
JG, Cazarín-Santos BG, et al: DNA Methylation Levels of the TBX5
gene promoter are associated with congenital septal defects in
mexican paediatric patients. Biology (Basel). 11(96)2022.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
49
|
Zhou J, Xiong Y, Dong X, Wang H, Qian Y,
Ma D and Li X: Genome-wide methylation analysis reveals
differentially methylated CpG sites and altered expression of heart
development-associated genes in fetuses with cardiac defects. Exp
Ther Med. 22(1032)2021.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
50
|
Hu C, Huang S, Wu F and Ding H:
MicroRNA-219-5p participates in cyanotic congenital heart disease
progression by regulating cardiomyocyte apoptosis. Exp Ther Med.
21(36)2021.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
51
|
Choudhury TZ and Garg V: Molecular genetic
mechanisms of congenital heart disease. Curr Opin Genet Dev.
75(101949)2022.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
52
|
Sharma V, Goessling LS, Brar AK, Joshi CS,
Mysorekar IU and Eghtesady P: Coxsackievirus B3 infection early in
pregnancy induces congenital heart defects through suppression of
fetal cardiomyocyte proliferation. J Am Heart Assoc.
10(e017995)2021.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
53
|
Han X, Wang B, Jin D, Liu K, Wang H, Chen
L and Zu Y: Precise dose of folic acid supplementation is essential
for embryonic heart development in zebrafish. Biology (Basel).
11(28)2021.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
54
|
Wang C, Lv H, Ling X, Li H, Diao F, Dai J,
Du J, Chen T, Xi Q, Zhao Y, et al: Association of assisted
reproductive technology, germline de novo mutations and congenital
heart defects in a prospective birth cohort study. Cell Res.
31:919–928. 2021.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
55
|
Lahrouchi N, Postma AV, Salazar CM, De
Laughter DM, Tjong F, Piherová L, Bowling FZ, Zimmerman D, Lodder
EM, Ta-Shma A, et al: Biallelic loss-of-function variants in PLD1
cause congenital right-sided cardiac valve defects and neonatal
cardiomyopathy. J Clin Invest. 131(e142148)2021.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
56
|
Roifman M, Chung BHY, Reid DM, Teitelbaum
R, Martin N, Nield LE, Thompson M, Shannon P and Chitayat D:
Heterozygous NOTCH1 deletion associated with variable congenital
heart defects. Clin Genet. 99:836–841. 2021.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
57
|
Ekure EN, Adeyemo A, Liu H, Sokunbi O,
Kalu N, Martinez AF, Owosela B, Tekendo-Ngongang C, Addissie YA,
Olusegun-Joseph A, et al: Exome sequencing and congenital heart
disease in sub-saharan Africa. Circ Genom Precis Med.
14(e003108)2021.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
58
|
van Walree ES, Dombrowsky G, Jansen IE,
Mirkov MU, Zwart R, Ilgun A, Guo D, Clur SB, Amin AS, Savage JE, et
al: Germline variants in HEY2 functional domains lead to congenital
heart defects and thoracic aortic aneurysms. Gene Med. 23:103–110.
2021.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
59
|
Fu F, Li R, Lei TY, Wang D, Yang X, Han J,
Pan M, Zhen L, Li J, Li FT, et al: Compound heterozygous mutation
of the ASXL3 gene causes autosomal recessive congenital heart
disease. Hum Genet. 140:333–348. 2021.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
60
|
Zhao L, Jiang WF, Yang CX, Qiao Q, Xu YJ,
Shi HY, Qiu XB, Wu SH and Yang YQ: SOX17 loss-of-function variation
underlying familial congenital heart disease. Eur J Med Genet.
64(104211)2021.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
61
|
Shi HY, Xie MS, Yang CX, Huang RT, Xue S,
Liu XY, Xu YJ and Yang YQ: Identification of SOX18 as a new gene
predisposing to congenital heart disease. Diagnostics (Basel).
12(1917)2022.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
62
|
Huang RT, Guo YH, Yang CX, Gu JN, Qiu XB,
Shi HY, Xu YJ, Xue S and Yang YQ: SOX7 loss-of-function variation
as a cause of familial congenital heart disease. Am J Transl Res.
14:1672–1684. 2022.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
63
|
Abhinav P, Zhang GF, Zhao CM, Xu YJ, Wang
J and Yang YQ: A novel KLF13 mutation underlying congenital patent
ductus arteriosus and ventricular septal defect, as well as
bicuspid aortic valve. Exp Ther Med. 23(311)2022.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
64
|
Paszkowska A, Piekutowska-Abramczuk D,
Ciara E, Mirecka-Rola A, Brzezinska M, Wicher D, Kostrzewa G,
Sarnecki J and Ziółkowska L: Clinical presentation of left
ventricular noncompaction cardiomyopathy and bradycardia in three
families carrying HCN4 pathogenic variants. Genes (Basel).
13(477)2022.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
65
|
Ke ZP, Zhang GF, Guo YH, Sun YM, Wang J,
Li N, Qiu XB, Xu YJ and Yang YQ: A novel PRRX1 loss-of-function
variation contributing to familial atrial fibrillation and
congenital patent ductus arteriosus. Genet Mol Biol.
45(e20210378)2022.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
66
|
Debiec RM, Hamby SE, Jones PD, Safwan K,
Sosin M, Hetherington SL, Sprigings D, Sharman D, Lee K,
Salahshouri P, et al: Contribution of NOTCH1 genetic variants to
bicuspid aortic valve and other congenital lesions. Heart.
108:1114–1120. 2022.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
67
|
Wang Z, Qiao XH, Xu YJ, Liu XY, Huang RT,
Xue S, Qiu HY and Yang YQ: SMAD1 Loss-of-Function variant
responsible for congenital heart disease. Biomed Res Int.
2022(9916325)2022.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
68
|
Meerschaut I, Steyaert W, Bové T, François
K, Martens T, De Groote K, De Wilde H, Muiño Mosquera L, Panzer J,
Vandekerckhove K, et al: Exploring the mutational landscape of
isolated congenital heart defects: An exome sequencing study using
cardiac DNA. Genes (Basel). 13(1214)2022.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
69
|
De Ita M, Gaytán-Cervantes J, Cisneros B,
Araujo MA, Huicochea-Montiel JC, Cárdenas-Conejo A, Lazo-Cárdenas
CC, Ramírez-Portillo CI, Feria-Kaiser C, Peregrino-Bejarano L, et
al: Clustering of genetic anomalies of cilia outer dynein arm and
central apparatus in patients with transposition of the great
arteries. Genes (Basel). 13(1662)2022.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
70
|
Okashah S, Vasudeva D, El Jerbi A,
Khodjet-El-Khil H, Al-Shafai M, Syed N, Kambouris M, Udassi S,
Saraiva LR, Al-Saloos H, et al: Investigation of genetic causes in
patients with congenital heart disease in qatar: Findings from the
Sidra Cardiac Registry. Genes (Basel). 13(1369)2022.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
71
|
Azab B, Aburizeg D, Ji W, Jeffries L,
Isbeih NJ, Al-Akily AS, Mohammad H, Osba YA, Shahin MA, Dardas Z,
et al: TBX5 variant with the novel phenotype of mixed-type total
anomalous pulmonary venous return in Holt-Oram Syndrome and
variable intrafamilial heart defects. Mol Med Rep.
25(210)2022.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
72
|
Li YJ, Wang J, Ye WG, Liu XY, Li L, Qiu
XB, Chen H, Xu YJ, Yang YQ, Bai D and Huang RT: Discovery of GJC1
(Cx45) as a new gene underlying congenital heart disease and
arrhythmias. Biology (Basel). 12(346)2023.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
73
|
Wang H, Xiao F, Qian Y, Wu B, Dong X, Lu
Y, Cheng G, Wang L, Yan K, Yang L, et al: Genetic architecture in
neonatal intensive care unit patients with congenital heart
defects: a retrospective study from the China Neonatal Genomes
Project. J Med Genet. 60:247–253. 2023.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
74
|
Wang Y, Xu YJ, Yang CX, Huang RT, Xue S,
Yuan F and Yang YQ: SMAD4 loss-of-function mutation predisposes to
congenital heart disease. Eur J Med Genet.
66(104677)2023.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
75
|
Deng Q, Wang X, Gao J, Xia X, Wang Y,
Zhang Y and Chen Y: Growth restriction and congenital heart disease
caused by a novel TAB2 mutation: A case report. Exp Ther Med.
25(258)2023.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
76
|
Afouda BA: Towards understanding the
gene-specific roles of GATA factors in heart development: Does
GATA4 lead the way? Int J Mol Sci. 23(5255)2022.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
77
|
Yang YQ, Gharibeh L, Li RG, Xin YF, Wang
J, Liu ZM, Qiu XB, Xu YJ, Xu L, Qu XK, et al: GATA4
loss-of-function mutations underlie familial tetralogy of fallot.
Hum Mutat. 34:1662–1671. 2013.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
78
|
Dixit R, Narasimhan C, Balekundri VI,
Agrawal D, Kumar A and Mohapatra B: Functionally significant, novel
GATA4 variants are frequently associated with Tetralogy of Fallot.
Hum Mutat. 39:1957–1972. 2018.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
79
|
Wei D, Bao H, Liu XY, Zhou N, Wang Q, Li
RG, Xu YJ and Yang YQ: GATA5 loss-of-function mutations underlie
tetralogy of fallot. Int J Med Sci. 10:34–42. 2013.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
80
|
Lin X, Huo Z, Liu X, Zhang Y, Li L, Zhao
H, Yan B, Liu Y, Yang Y and Chen YH: A novel GATA6 mutation in
patients with tetralogy of Fallot or atrial septal defect. J Hum
Genet. 55:662–667. 2010.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
81
|
Wang J, Luo XJ, Xin YF, Liu Y, Liu ZM,
Wang Q, Li RG, Fang WY, Wang XZ and Yang YQ: Novel GATA6 mutations
associated with congenital ventricular septal defect or tetralogy
of fallot. DNA Cell Biol. 31:1610–1617. 2012.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
82
|
Huang RT, Xue S, Xu YJ and Yang YQ:
Somatic mutations in the GATA6 gene underlie sporadic tetralogy of
Fallot. Int J Mol Med. 31:51–58. 2013.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
83
|
Liu XY, Wang J, Zheng JH, Bai K, Liu ZM,
Wang XZ, Liu X, Fang WY and Yang YQ: Involvement of a novel GATA4
mutation in atrial septal defects. Int J Mol Med. 28:17–23.
2011.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
84
|
Jiang WF, Xu YJ, Zhao CM, Wang XH, Qiu XB,
Liu X, Wu SH and Yang YQ: A novel TBX5 mutation predisposes to
familial cardiac septal defects and atrial fibrillation as well as
bicuspid aortic valve. Genet Mol Biol. 43(e20200142)2020.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
85
|
Benson DW, Silberbach GM, Kavanaugh-McHugh
A, Cottrill C, Zhang Y, Riggs S, Smalls O, Johnson MC, Watson MS,
Seidman JG, et al: Mutations in the cardiac transcription factor
NKX2.5 affect diverse cardiac developmental pathways. J Clin
Invest. 104:1567–1573. 1999.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
86
|
Goldmuntz E, Geiger E and Benson DW:
NKX2.5 mutations in patients with tetralogy of fallot. Circulation.
104:2565–2568. 2001.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
87
|
McElhinney DB, Geiger E, Blinder J, Benson
DW and Goldmuntz E: NKX2.5 mutations in patients with congenital
heart disease. J Am Coll Cardiol. 42:1650–1655. 2003.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
88
|
Baban A, Postma AV, Marini M, Trocchio G,
Santilli A, Pelegrini M, Sirleto P, Lerone M, Albanese SB, Barnett
P, et al: Identification of TBX5 mutations in a series of 94
patients with Tetralogy of Fallot. Am J Med Genet A.
164A:3100–3107. 2014.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
89
|
Amodio V, Tevy MF, Traina C, Ghosh TK and
Capovilla M: Transactivation in Drosophila of human enhancers by
human transcription factors involved in congenital heart diseases.
Dev Dyn. 241:190–199. 2012.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
90
|
Charron F, Paradis P, Bronchain O, Nemer G
and Nemer M: Cooperative interaction between GATA-4 and GATA-6
regulates myocardial gene expression. Mol Cell Biol. 19:4355–4365.
1999.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
91
|
Jiang Y and Evans T: The Xenopus
GATA-4/5/6 genes are associated with cardiac specification and can
regulate cardiac-specific transcription during embryogenesis. Dev
Biol. 174:258–270. 1996.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
92
|
Garg V, Kathiriya IS, Barnes R,
Schluterman MK, King IN, Butler CA, Rothrock CR, Eapen RS,
Hirayama-Yamada K, Joo K, et al: GATA4 mutations cause human
congenital heart defects and reveal an interaction with TBX5.
Nature. 424:443–447. 2003.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
93
|
Durocher D, Charron F, Warren R, Schwartz
RJ and Nemer M: The cardiac transcription factors Nkx2-5 and GATA-4
are mutual cofactors. EMBO J. 16:5687–5696. 1997.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
94
|
Nemer G, Fadlalah F, Usta J, Nemer M,
Dbaibo G, Obeid M and Bitar F: A novel mutation in the GATA4 gene
in patients with Tetralogy of Fallot. Hum Mutat. 27:293–294.
2006.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
95
|
Martincorena I and Campbell PJ: Somatic
mutation in cancer and normal cells. Science. 349:1483–1489.
2015.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
96
|
Maslov AY and Vijg J: Somatic mutation
burden in relation to aging and functional life span: Implications
for cellular reprogramming and rejuvenation. Curr Opin Genet Dev.
83(102132)2023.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
97
|
Vijg J and Dong X: Pathogenic mechanisms
of somatic mutation and genome mosaicism in aging. Cell. 182:12–23.
2020.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
98
|
Erickson RP: Somatic gene mutation and
human disease other than cancer: An update. Mutat Res. 705:96–106.
2010.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
99
|
Walsh C, Choudhury S and Chen MH:
Landscape of somatic mutations in aging human heart muscle cells.
Nat Aging. 2:686–687. 2022.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
100
|
Choudhury S, Huang AY, Kim J, Zhou Z,
Morillo K, Maury EA, Tsai JW, Miller MB, Lodato MA, Araten S, et
al: Somatic mutations in single human cardiomyocytes reveal
age-associated DNA damage and widespread oxidative genotoxicity.
Nat Aging. 2:714–725. 2022.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
101
|
Salazar M, Consoli F, Villegas V, Caicedo
V, Maddaloni V, Daniele P, Caianiello G, Pachón S, Nuñez F,
Limongelli G, et al: Search of somatic GATA4 and NKX2.5 gene
mutations in sporadic septal heart defects. Eur J Med Genet.
54:306–309. 2011.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
102
|
Wang J, Lu Y, Chen H, Yin M, Yu T and Fu
Q: Investigation of somatic NKX2-5, GATA4 and HAND1 mutations in
patients with tetralogy of Fallot. Pathology. 43:322–326.
2011.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
103
|
Cheng C, Lin Y, Yang F, Wang W, Wu C, Qin
J, Shao X and Zhou L: Mutational screening of affected cardiac
tissues and peripheral blood cells identified novel somatic
mutations in GATA4 in patients with ventricular septal defect. J
Biomed Res. 25:425–430. 2011.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
104
|
Esposito G, Butler TL, Blue GM, Cole AD,
Sholler GF, Kirk EP, Grossfeld P, Perryman BM, Harvey RP and Winlaw
DS: Somatic mutations in NKX2–5, GATA4, and HAND1 are not a common
cause of tetralogy of Fallot or hypoplastic left heart. Am J Med
Genet A. 155A:2416–2421. 2011.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
105
|
Yin J, Qian J, Dai G, Wang C, Qin Y, Xu T,
Li Z, Zhang H and Yang S: Search of Somatic Mutations of NKX2-5 and
GATA4 Genes in Chinese patients with sporadic congenital heart
disease. Pediatr Cardiol. 40:17–22. 2019.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
106
|
Heineke J, Auger-Messier M, Xu J, Oka T,
Sargent MA, York A, Klevitsky R, Vaikunth S, Duncan SA, Aronow BJ,
et al: Cardiomyocyte GATA4 functions as a stress-responsive
regulator of angiogenesis in the murine heart. J Clin Invest.
117:3198–3210. 2007.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
107
|
Pikkarainen S, Tokola H, Kerkelä R and
Ruskoaho H: GATA transcription factors in the developing and adult
heart. Cardiovasc Res. 63:196–207. 2004.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
108
|
Zhang H, Toyofuku T, Kamei J and Hori M:
GATA-4 regulates cardiac morphogenesis through transactivation of
the N-cadherin gene. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 312:1033–1038.
2003.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
109
|
Kuo CT, Morrisey EE, Anandappa R, Sigrist
K, Lu MM, Parmacek MS, Soudais C and Leiden JM: GATA4 transcription
factor is required for ventral morphogenesis and heart tube
formation. Genes Dev. 11:1048–1060. 1997.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
110
|
Molkentin JD, Lin Q, Duncan SA and Olson
EN: Requirement of the transcription factor GATA4 for heart tube
formation and ventral morphogenesis. Genes Dev. 11:1061–1072.
1997.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
111
|
Watt AJ, Battle MA, Li J and Duncan SA:
GATA4 is essential for formation of the proepicardium and regulates
cardiogenesis. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA. 101:12573–12578.
2004.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
112
|
Crispino JD, Lodish MB, Thurberg BL,
Litovsky SH, Collins T, Molkentin JD and Orkin SH: Proper coronary
vascular development and heart morphogenesis depend on interaction
of GATA-4 with FOG cofactors. Genes Dev. 15:839–844.
2001.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
113
|
Misra C, Sachan N, McNally CR, Koenig SN,
Nichols HA, Guggilam A, Lucchesi PA, Pu WT, Srivastava D and Garg
V: Congenital heart disease-causing Gata4 mutation displays
functional deficits in vivo. PLoS Genet. 8(e1002690)2012.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
114
|
Epstein JA and Parmacek MS: Recent
advances in cardiac development with therapeutic implications for
adult cardiovascular disease. Circulation. 112:592–597.
2005.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
115
|
Jiang JQ, Shen FF, Fang WY, Liu X and Yang
YQ: Novel GATA4 mutations in lone atrial fibrillation. Int J Mol
Med. 28:1025–1032. 2011.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
116
|
Zhao L, Xu JH, Xu WJ, Yu H, Wang Q, Zheng
HZ, Jiang WF, Jiang JF and Yang YQ: A novel GATA4 loss-of-function
mutation responsible for familial dilated cardiomyopathy. Int J Mol
Med. 33:654–660. 2014.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|